Membranes & Membrane Proteins
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
drug-resistant pathogenic fungi
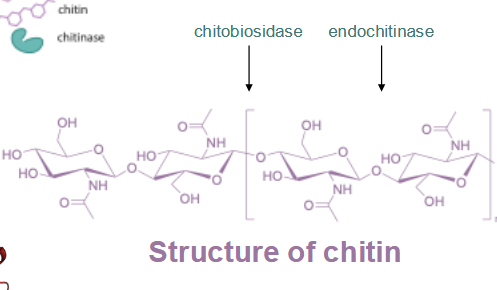
enzyme target for antifungals: chitin → chitobiosidase, endochitinase
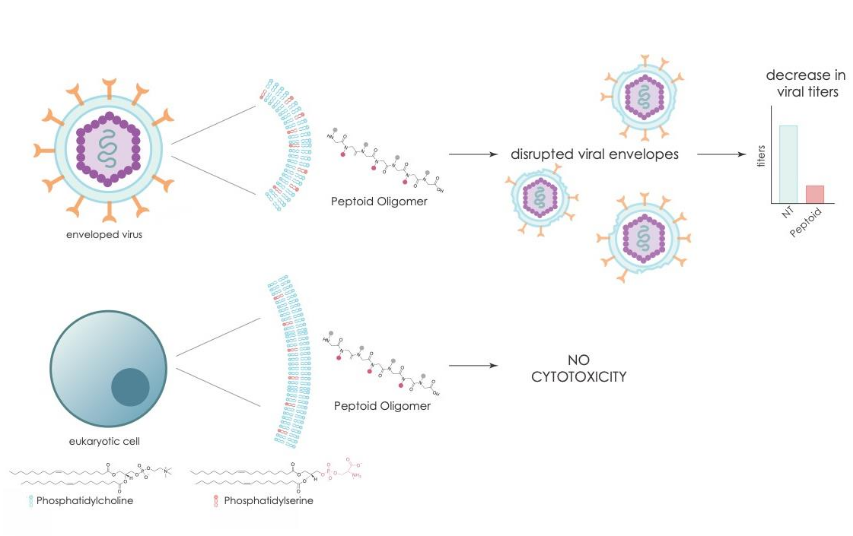
Selective disruption of viral membranes
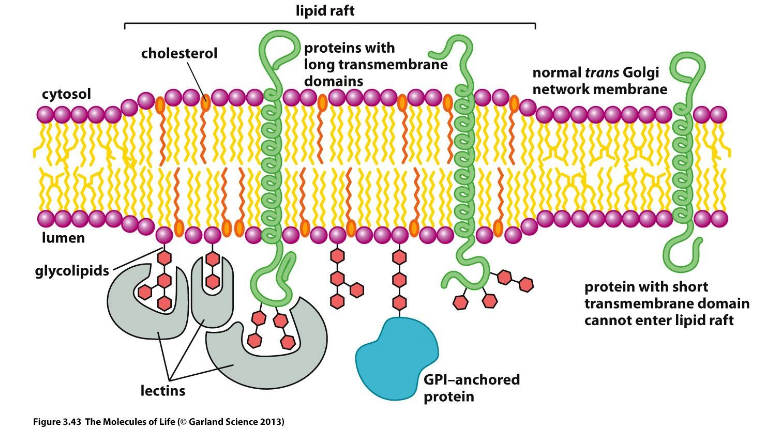
Structured Regions
Freely diffusing proteins in membranes probably would not give efficient communication or biological processes
Lipid rafts: thicker membranes, cholesterol rich, glycolipid rich, GPI-anchored proteins
Enriched in signaling proteins
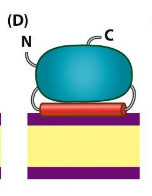
Peripheral membrane proteins
not strongly bound to the membrane; dissociated with mild detergent treatment or with high salt concentrations
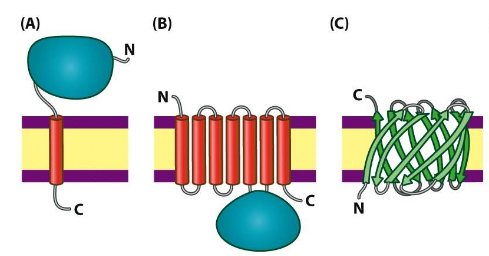
Integral membrane proteins
strongly imbedded in the bilayer; can only be removed from the membrane by denaturing the membrane (organic solvents, or strong detergents); Often transmembrane but not necessarily; Polar side chains are usually not found in membrane-spanning regions
ex. Glycophorin, bacteriorhodopsin
Lipid-anchored membrane proteins
covalently bonded to lipid
Amide-linked myristoyl anchors
Thioester-linked fatty acyl anchors
Thioether-linked prenyl anchors
Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchors
Hydropathy Plots
graphical means of describing the hydrophobicity of amino acid sequence segments is used to assess the likelihood of membranelocalization and topology.
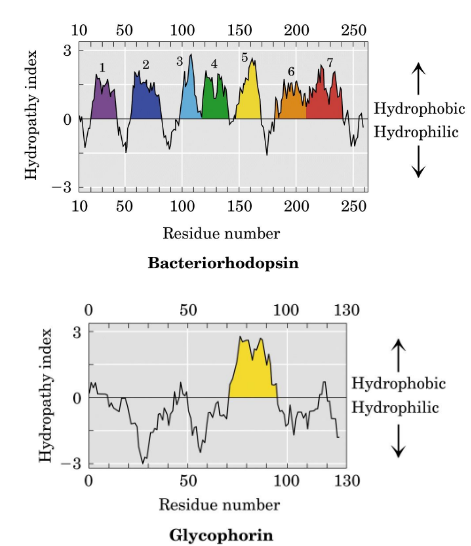
Why don’t we see loops, or disordered regions within the membrane?
nonpolar environment; No H-bond donors or acceptors provided by lipids in the hydrophobic interior of membrane; H-bond pairing of peptide backbone is satisfied by alpha-helix structure; An isolated helix is stable in membrane context (unlike a helix in aqueous environment)
Transporters” or “permeases”
Membrane proteins assist the transport of polar compounds; lower the energy barrier to transmembrane passage by providing a hydrophilic passage, allowing for facilitated diffusion.
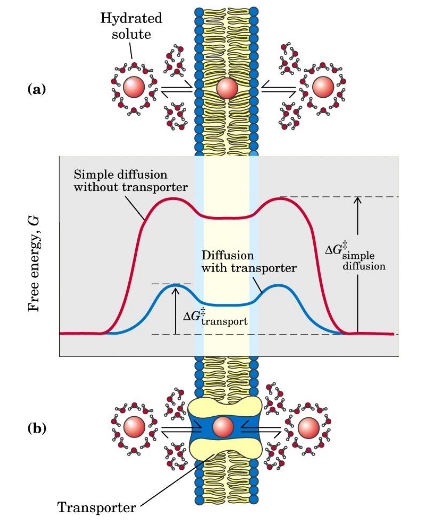
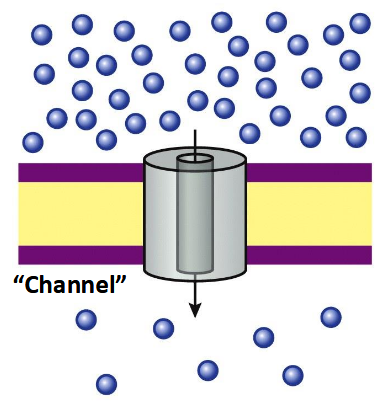
Passive transport
no energy required
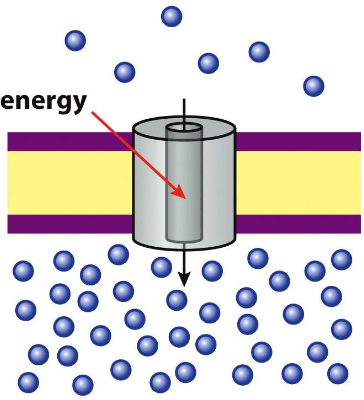
Active transport
energy required, can “pump” against concentration gradient
Membrane channels common architecture
-strands surrounding a large channel (d ~ 3 nm)
Porins are passive membrane transport channels (-barrels).
Nonpolar residues face membrane polar residues face channel
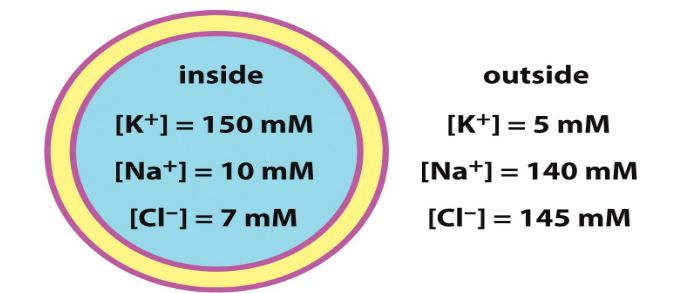
Electrochemical/concentration gradients of ions
These gradients are maintained by ATP-dependent pumps and channels - very specific
K+/Na+ gradient that is established can provide free energy to export other ions such as Cl-
Membrane Potential (ΔΨ or ΔV )
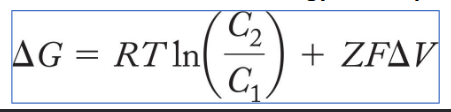
primary active transporters
one molecule up gradient; phosphorylated or ATp hydrolysis
secondary active transporters
one up, one down = use down transport to energize up
Antiporter
opposite directions of secondary active transport
Symporter
same directions of secondary active transport
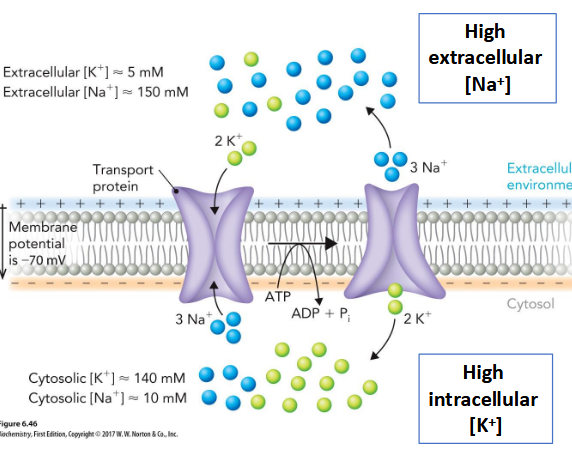
Na+–K+ ATPase
P-type Primary Transporter; Responsible for maintaining an electrochemical gradient across animal cell membranes
Binding of ATP to the N domain leads to phosphorylation of the P domain and subsequent conformational changes in the A domain
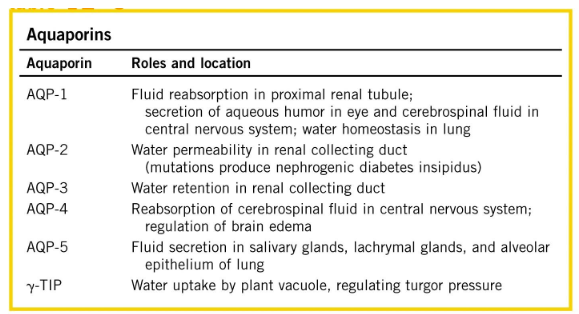
Aquaporins
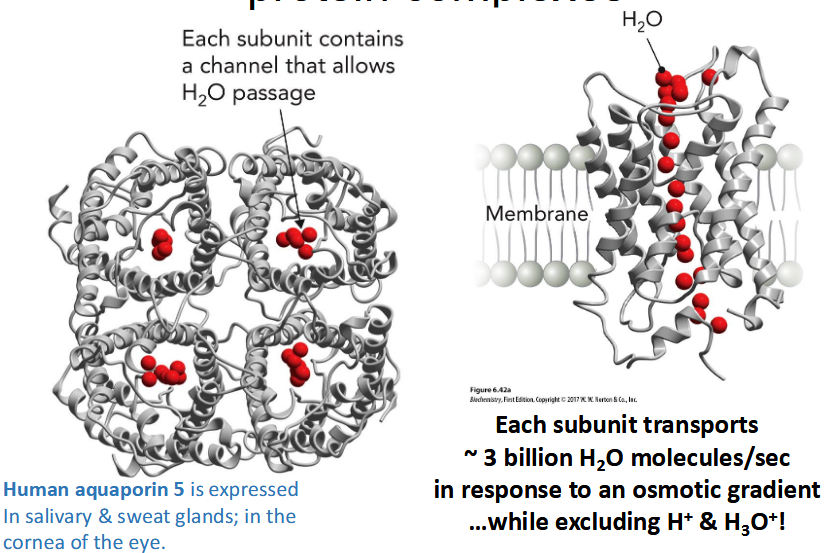
protein family of passive transport channels; Transmembrane channels that facilitate passage of water (and glycerol or urea), Particularly important in erythrocytes, renal ducts, and plant vacuoles, Associated with multiple disease states
tetrameric protein complexes; Selectivity of aquaporins is
mediated by a “constriction point”
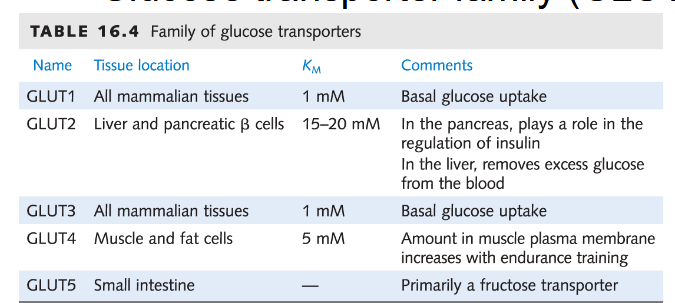
Glucose transporter family (GLUT)
Enhances diffusion of glucose by 50,000 fold; Highly specific for D-glucose over L-glucose, mannose, galactose
Kinetics of glucose transport are enzyme-like; Rate as a function of solute concentration can be saturated. Suggests a distinct binding site and mechanism of transport.
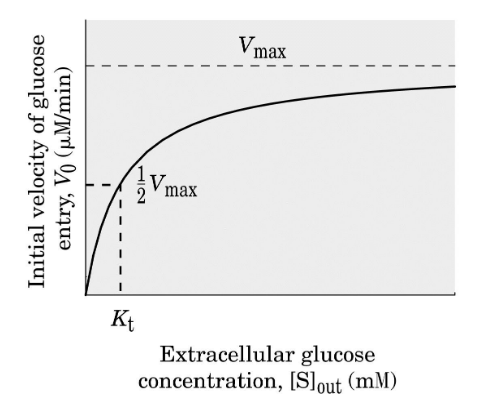
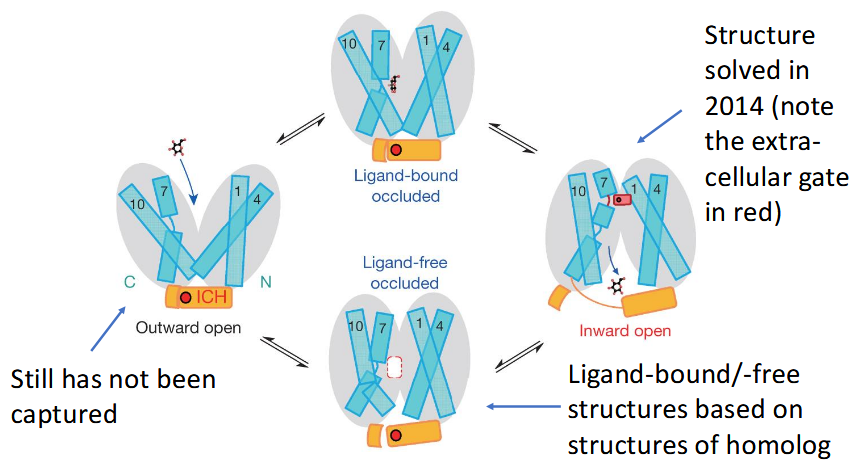
alternating access model (GLUT1)
Receptor Proteins
Information Gatekeepers of the Cell; generation of second messengers by an upstream signaling protein results in signal amplification through the activation of one or more downstream target proteins