Comprehensive Genetics, Evolution, and Speciation Concepts for Biology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is the difference between somatic cell editing and germline editing?
Somatic cell editing affects only the individual and is not inherited, while germline editing alters the DNA in sperm or eggs, affecting future generations.
What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy involves altering the genes inside an individual's cells to treat or prevent disease.
What ethical concerns arose from He Jiankui's CRISPR-Cas9 experiment?
Concerns included lack of medical or ethical approval, unknown long-term effects of CCR5 deletion, and the procedure not being medically necessary.
What is the CCR5 co-receptor's role in HIV infection?
CCR5 is a chemokine receptor that HIV uses to enter immune cells.
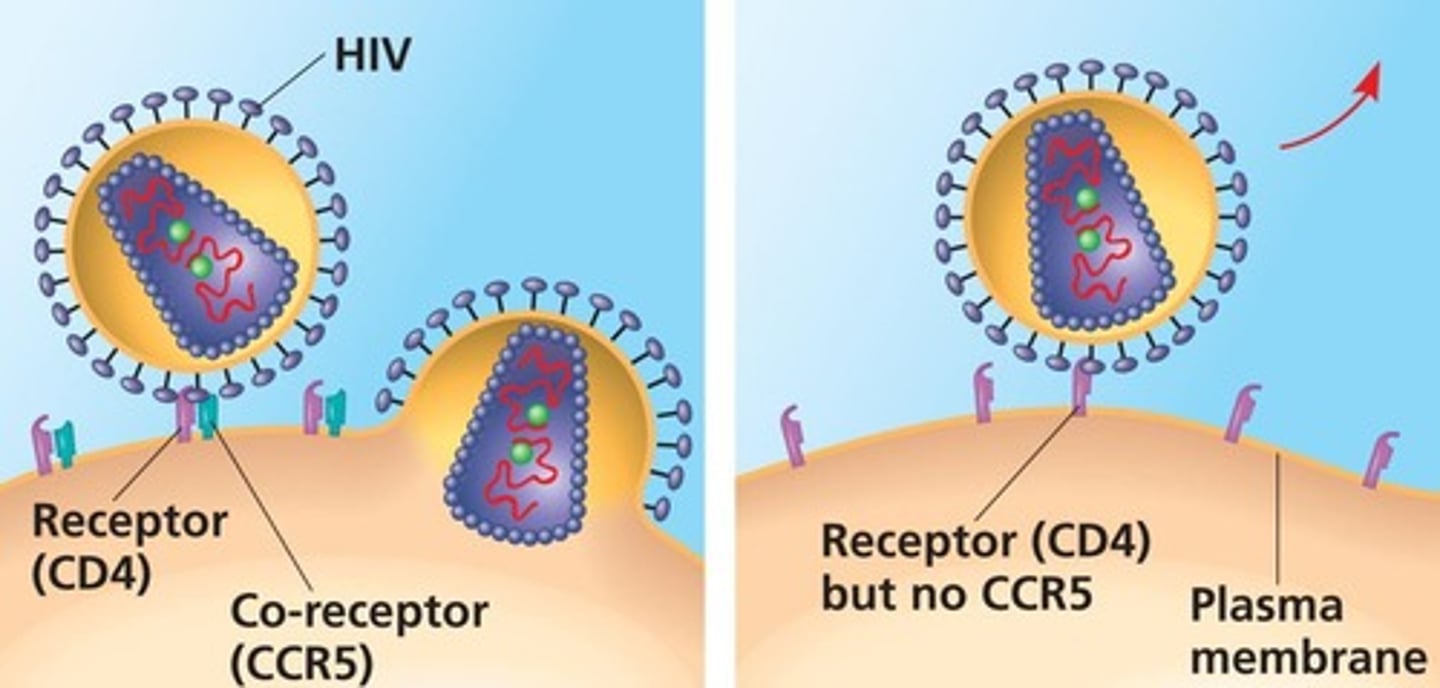
What was the outcome of He Jiankui's experiment on embryos?
Twin girls, known as Lulu and Nana, were born as the first reported gene-edited humans.
What are the five key mechanisms of evolutionary change?
1) Mutation, 2) Gene flow, 3) Sexual reproduction, 4) Genetic drift, 5) Natural selection.
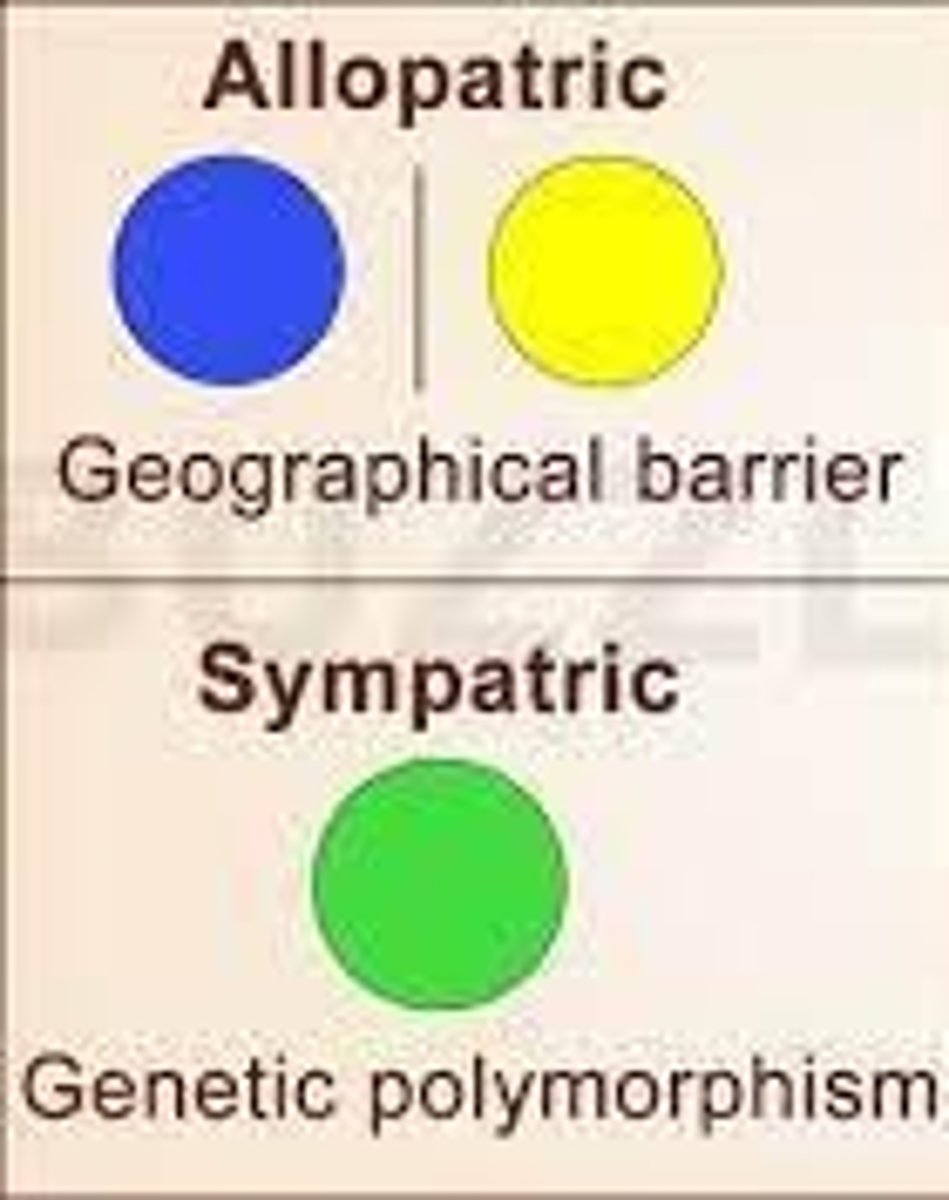
What is allopatric speciation?
Allopatric speciation occurs when a population is geographically isolated, leading to reduced gene flow and evolutionary divergence.
What is sympatric speciation?
Sympatric speciation occurs without geographic isolation, often through mechanisms like polyploidy or behavioral differences.
How does genetic drift affect allele frequencies?
Genetic drift causes random changes in allele frequencies due to chance events, especially in small populations.
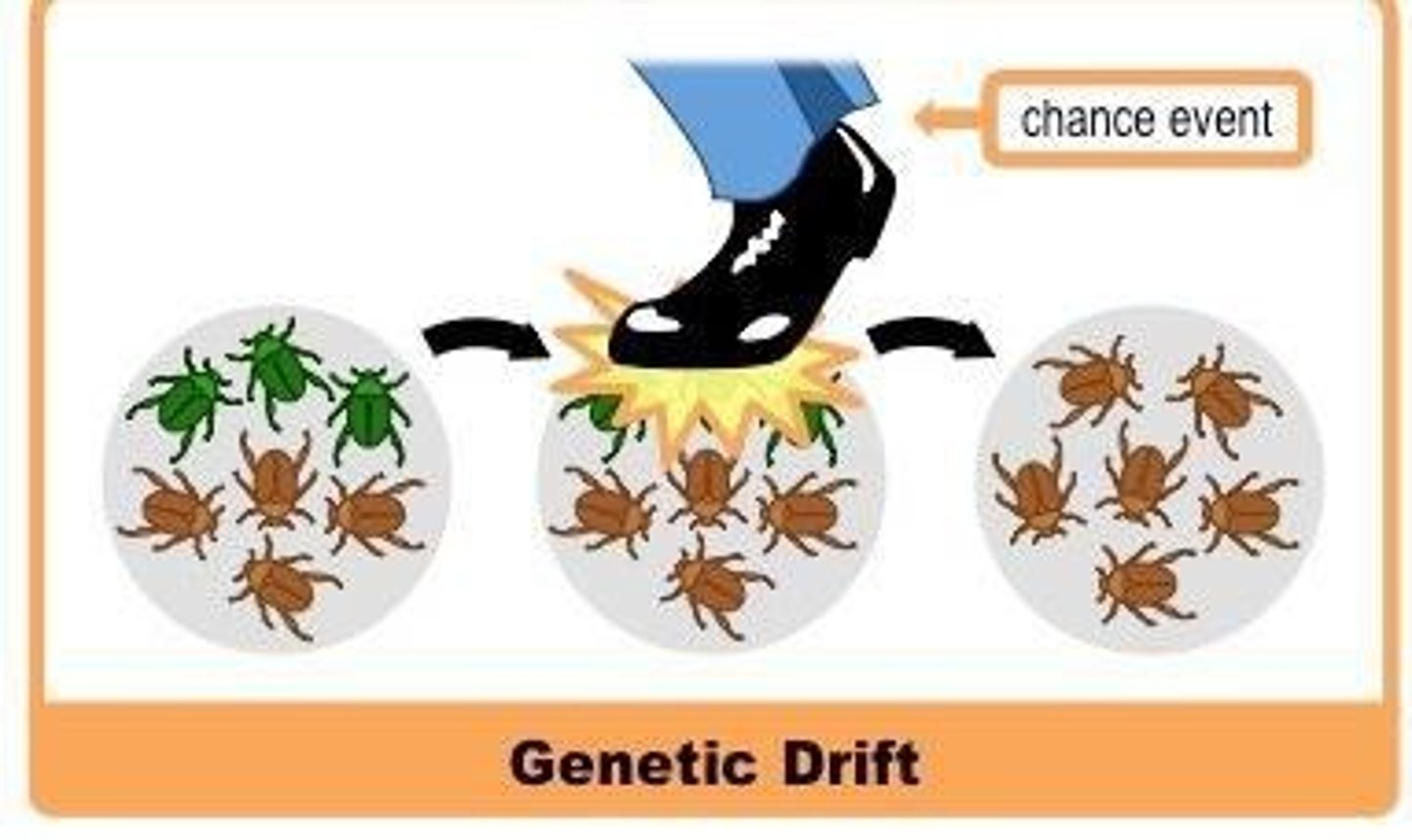
What is the impact of natural selection on a gene pool?
Natural selection alters the composition of a gene pool by favoring individuals with advantageous traits, leading to evolutionary change.
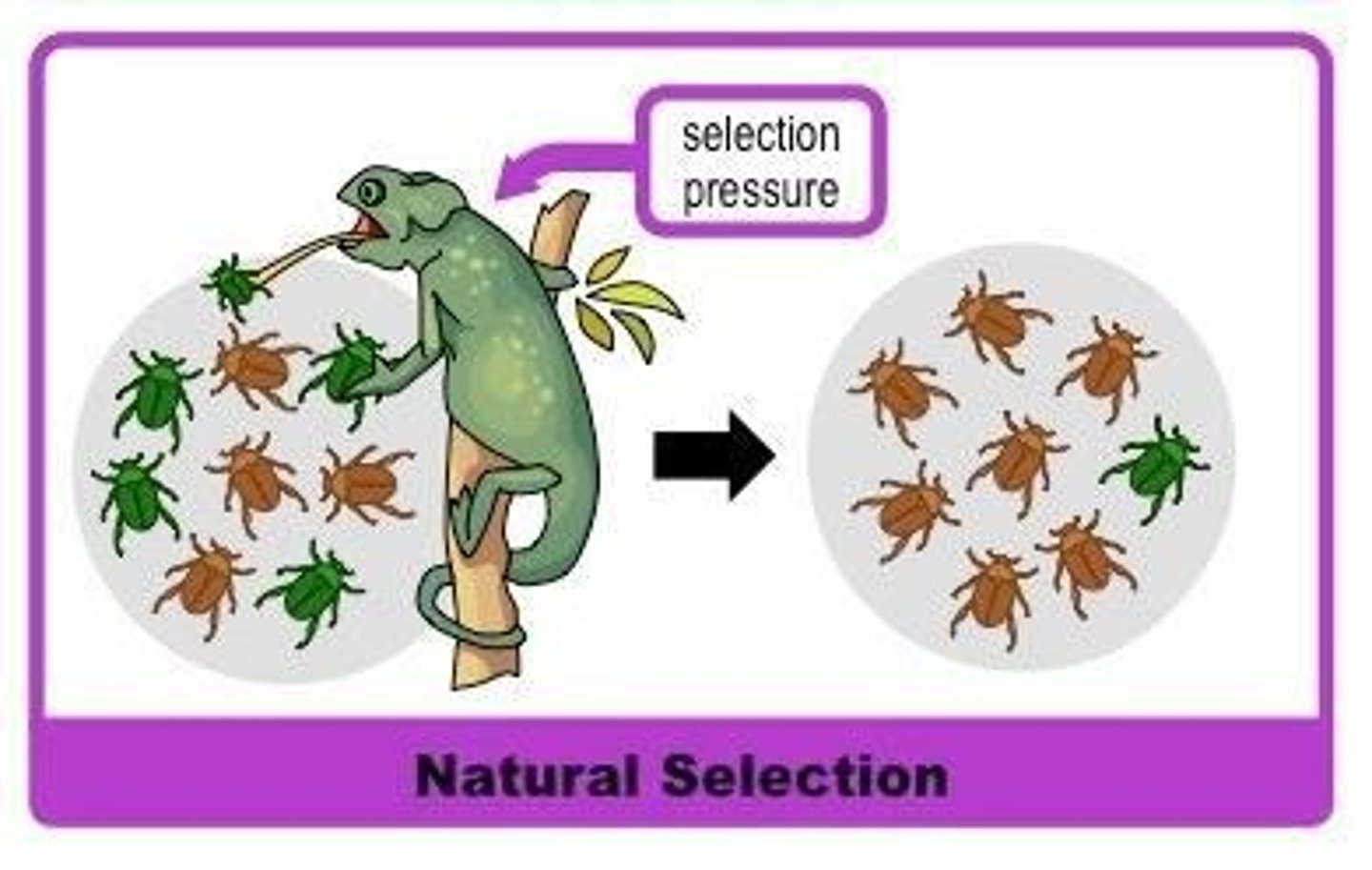
What is the role of gene flow in evolution?
Gene flow is the movement of alleles between populations, which can introduce new genetic material and reduce differences between populations.
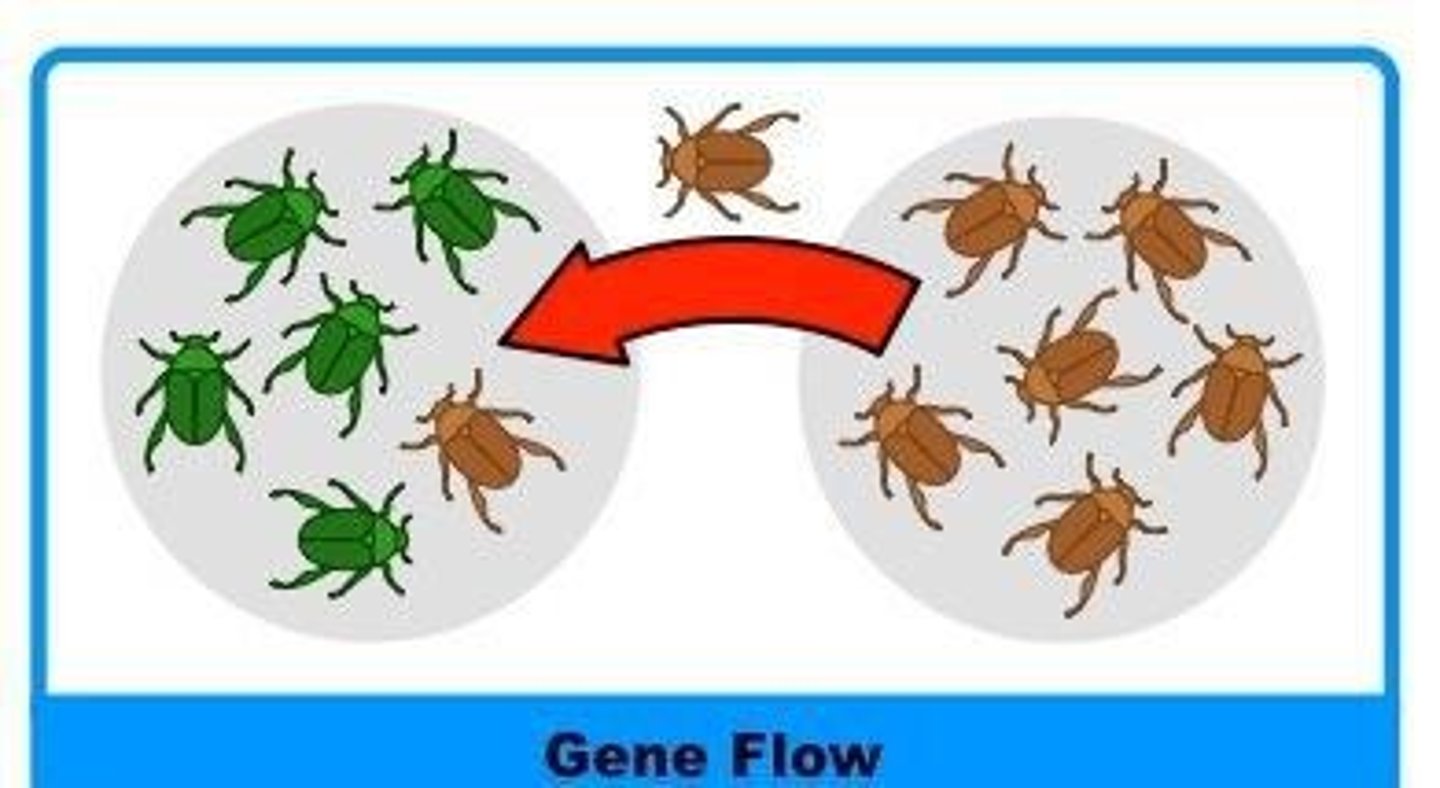
What is the significance of reproductive barriers in speciation?
Reproductive barriers prevent interbreeding between populations, allowing them to evolve independently.
What can cause changes in allele frequency within a gene pool?
Changes can result from mutation, gene flow, sexual reproduction, genetic drift, and natural selection.
How can environmental changes lead to allopatric speciation?
Environmental changes can create barriers that divide populations, leading to isolation and divergent evolution.
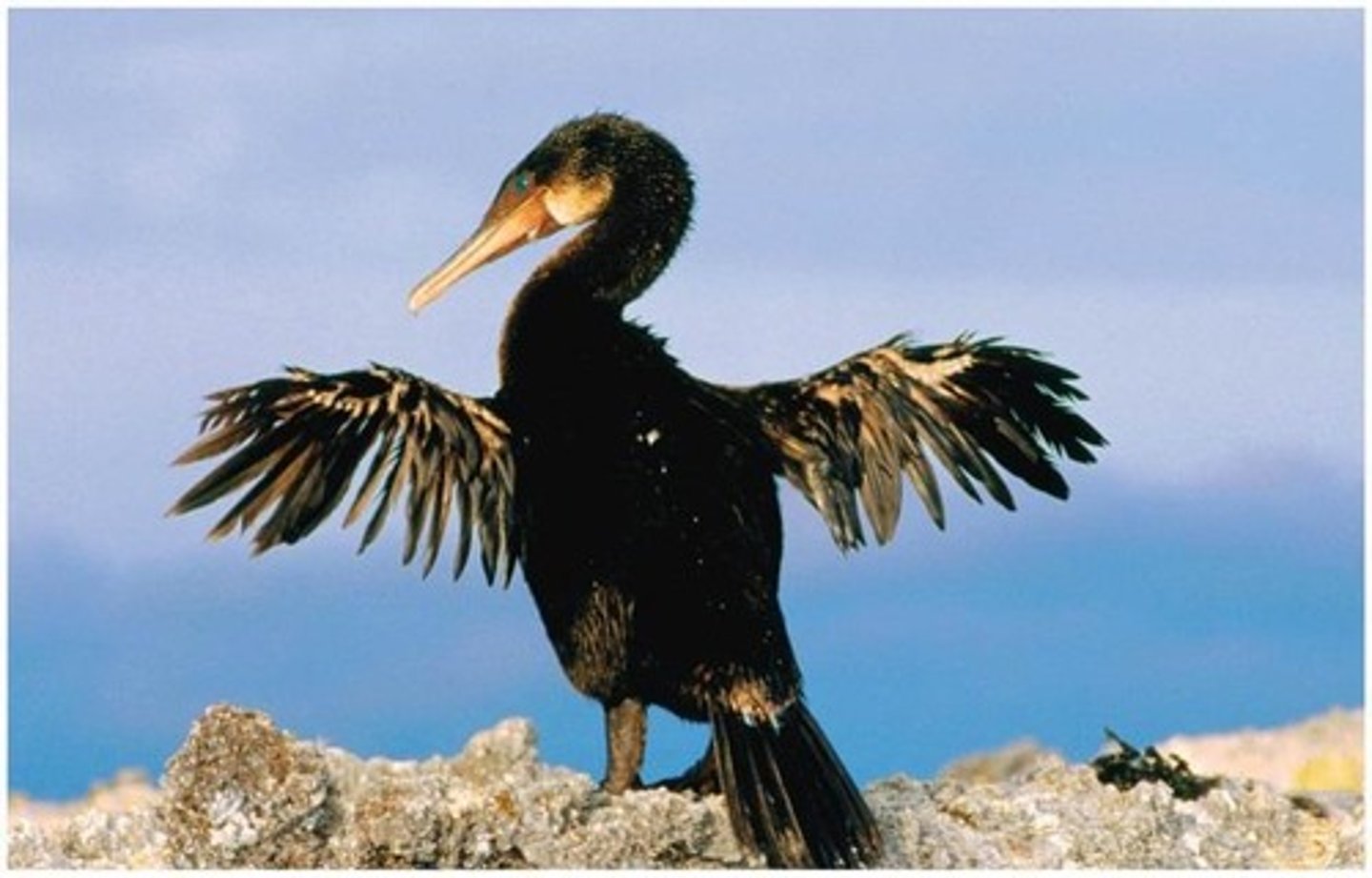
What is an example of allopatric speciation through colonization?
The flightless cormorant of the Galápagos likely originated from a flying species that colonized the islands.

What is the effect of a geographic barrier on different organisms?
The impact of a geographic barrier varies; it may restrict movement for some species (like snails) while allowing others (like birds) to cross.
What evidence supports allopatric speciation?
Laboratory populations subjected to different environmental conditions develop reproductive barriers, indicating speciation.
What is the role of sexual reproduction in evolution?
Sexual reproduction introduces new gene combinations, potentially altering allele frequencies and contributing to evolutionary change.
What are the mechanisms of change in speciation?
The mechanisms include genetic drift, mutation, natural selection, sexual selection, and gene flow.
What factors can reduce gene flow in sympatric speciation?
Factors include polyploidy, sexual selection, and habitat differentiation.
What is polyploidy?
Polyploidy is the presence of extra sets of chromosomes, often resulting in the formation of new species without geographic separation.
What are the two types of polyploids?
The two types are autopolyploids (derived from a single species) and allopolyploids (derived from different species).
How do autopolyploids form?
Autopolyploids form through mitotic errors that lead to cells with more than two sets of chromosomes.
What is the outcome of mating between tetraploids and diploids?
Mating produces triploid offspring with reduced fertility.
What characterizes allopolyploids?
Allopolyploids have chromosomes from different species and often result in hybrid sterility.
How can allopolyploids reproduce?
Sterile hybrids can reproduce asexually, and allopolyploids can interbreed with each other but not with parent species.
Give an example of sympatric speciation through habitat differentiation.
Apple maggot flies evolved after switching hosts from hawthorn to apple, leading to habitat isolation.
What is sexual selection in the context of sympatric speciation?
Sexual selection can drive speciation, as seen in cichlids in Lake Victoria, where female mate choice is based on male coloration.
What evidence supports natural selection?
Morphological changes, such as beak length in soapberry bugs, provide evidence of natural selection.
How does artificial selection relate to morphological changes?
Artificial selection can be used to study morphological changes, as seen in the evolution of sex combs in fruit flies.
What is the difference between macroevolution and microevolution?
Macroevolution refers to large-scale changes, while microevolution involves small-scale changes in allele frequencies.
What is the role of natural selection in evolution?
Natural selection increases an organism's chance of survival by favoring specific traits.
What is the significance of Tragopogon mirus?
Tragopogon mirus is a new polyploid species formed from the hybridization of two previous species.
What happens to alleles that benefit one host plant in maggot flies?
Alleles that benefit flies using one host plant can harm those using another, leading to post-zygotic isolation.
What is the diploid number in allopolyploid species?
The diploid number equals the sum of the diploid numbers of both parent species.
What is an example of artificial selection in fruit flies?
Artificial selection has been used to mimic the evolution of sex combs in Drosophila melanogaster.
What is the primary cause of diversity of life on Earth?
Macroevolution, microevolution, natural selection, and changes in allele frequencies over time.
What are the two main types of speciation?
Allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation.
What drives allopatric speciation?
Changes in the environment and colonization of new environments.
What are the mechanisms of sympatric speciation?
Polyploidy, habitat differentiation, and sexual selection.
Who wrote the Principles of Geology?
Charles Lyell.
What is the definition of fitness in biology?
Individuals are considered more fit if they leave more viable offspring relative to other individuals.
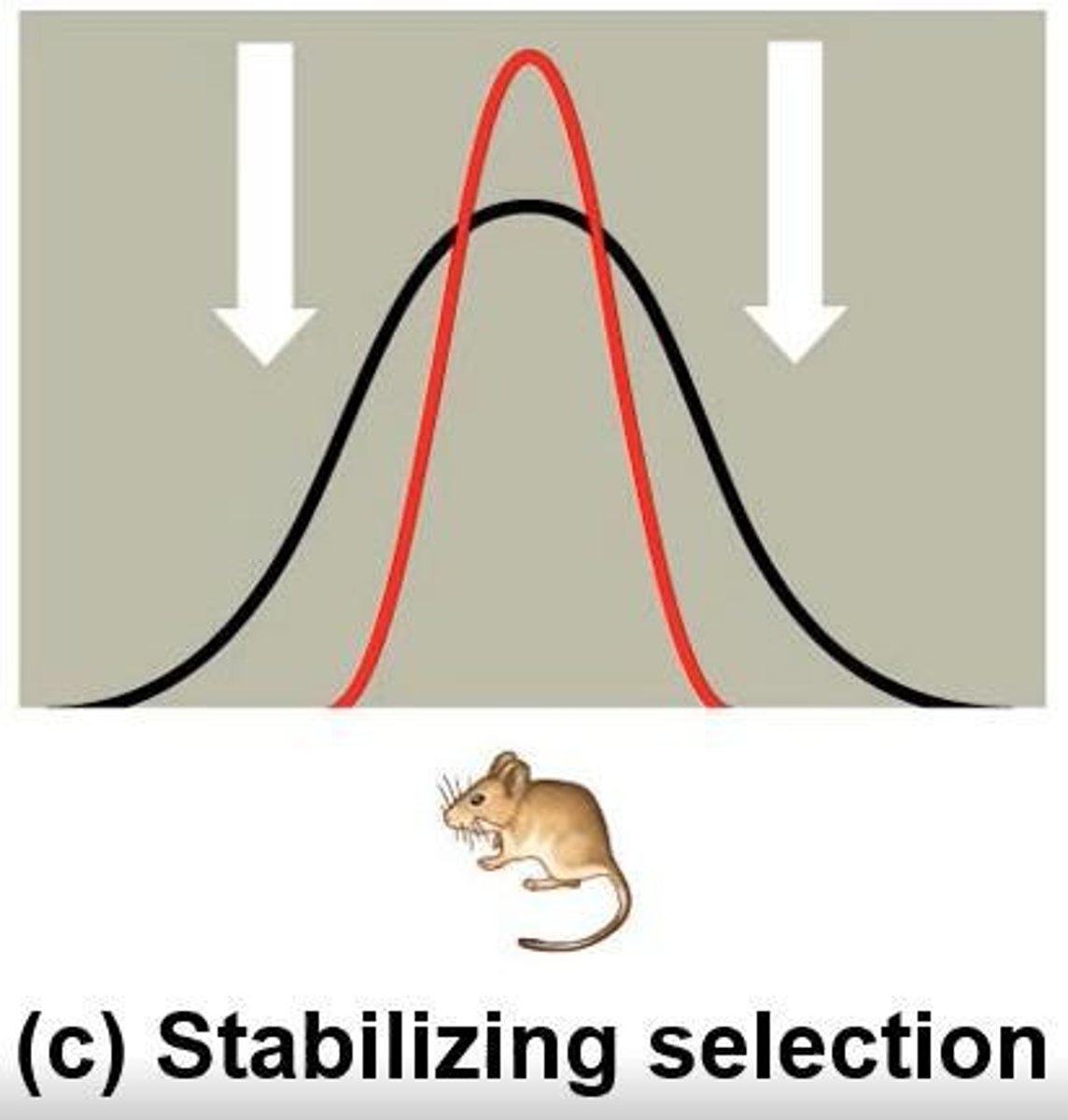
What type of natural selection favors individuals with an average phenotype?
Stabilizing selection.
What are alternative forms of genes called?
Alleles.
What is speciation?
The process of species formation, leading to the splitting of one population into two or more reproductively isolated populations.
What is the significance of Darwin's study of speciation?
It explains the tremendous diversity of life and the unity of life.
What is the reproductive barrier exemplified by coral spawning related to?
Temporal isolation, as some coral species time their spawning to correspond with specific phases of the moon.
What are the four options for how new species can originate?
Allopatric speciation, sympatric speciation, rapid evolutionary changes, and all of these options.
What is the process by which one species splits into two species called?
Speciation.
What is the relationship between genes and alleles?
Genes are sections of DNA that code for specific traits, while alleles are different forms of the same gene.
What is the significance of E.O. Wilson in the study of evolution?
He contributed significantly to the understanding of biodiversity and the processes of speciation.
How does colonization of new environments contribute to speciation?
It can lead to the development of new species as populations adapt to different environmental conditions.
What is the definition of parapatric speciation?
Speciation that occurs when populations are separated by a gradient of environmental conditions.
What is the relationship between allele frequency and evolution?
Changes in allele frequency in a population over time are a key indicator of evolution.
What is an example of a reproductive barrier in corals?
Temporal isolation, where spawning is timed with specific lunar phases.
What is the relationship between microevolution and macroevolution?
Speciation forms a conceptual bridge between microevolution (changes in allele frequency in a population over time) and macroevolution (broad patterns of evolutionary change above the species level).
What is microevolution?
Microevolution consists of changes in allele frequency in a population over time.
What does macroevolution refer to?
Macroevolution refers to broad patterns of evolutionary change above the species level.
What is geographic speciation also known as?
Geographic speciation is also called allopatric speciation.
What occurs during geographic speciation?
Geographic speciation occurs when a species is split into different populations due to a geographical obstruction, such as an advancing glacier or a deepening river valley.
Give an example of geographic speciation.
Small populations making their way to remote islands, such as Rakata after the destruction of the island of Krakatau.
Which statement is NOT true of natural selection?
The strongest individual will always be selected for.
What is one of the 'rules' of natural selection?
Natural selection only works with existing characteristics and cannot make new characteristics appear.
What is meant by 'trade-offs' in natural selection?
A characteristic may benefit an organism in one way but can be a disadvantage in another area of survival.
How does natural selection lead to gradual change?
Natural selection compounds over many years and can result in drastic changes.
What is a key characteristic of natural selection regarding existing traits?
Only existing characters can be selected for.
What can result from selection for very slight advantages over time?
It can lead to dramatic changes in form and function.
What is the significance of trade-offs in evolution?
All organisms are subject to the laws of physics, leading to trade-offs in forms that cannot be overcome by natural selection.
What is the outcome of natural selection over time?
It results in the survival of the best-suited individuals who can best utilize their surroundings.
What are the three definitions of species?
1) Morphological: based on shape/structure/anatomy; 2) Phylogenetic: based on phylogenetic tree; 3) Ecological: based on a species' ecological niche.
What is biological fitness?
Biological fitness refers to an individual's ability to produce more viable, fertile offspring relative to others in the same environment.
What is the significance of relative fitness?
Relative fitness depends on context and affects how well individuals adapt to their environment, influencing their reproductive success.
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is the mechanism of speciation that leads to adaptive change, favoring individuals that are better adapted to their environment.
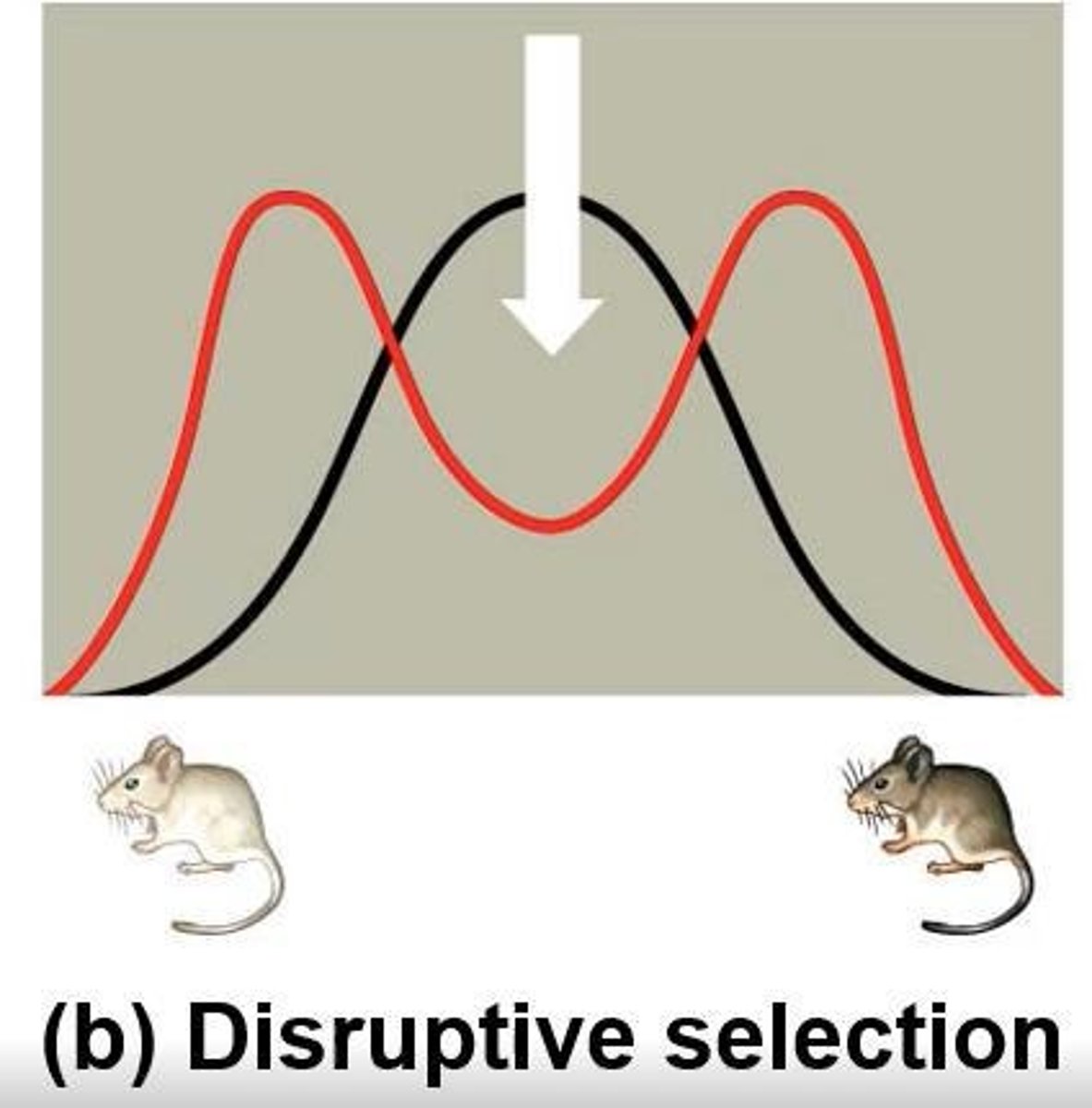
What are the three modes of selection?
1) Directional selection: favors one extreme phenotype; 2) Disruptive selection: favors both extremes; 3) Stabilizing selection: favors intermediate phenotypes.
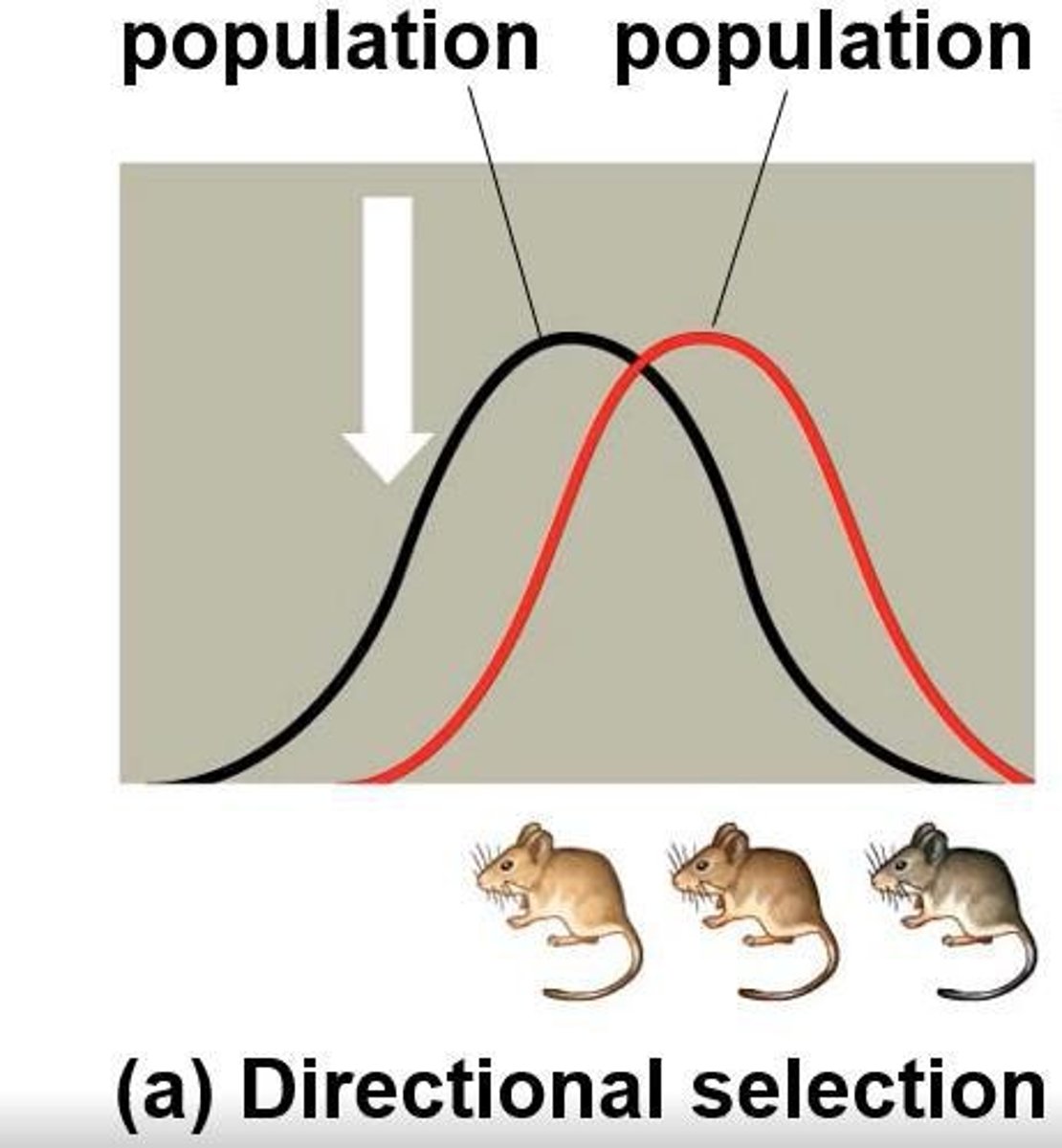
What is directional selection?
A type of selection that favors one extreme of a phenotype, leading to a shift in the population's traits.
What is disruptive selection?
A type of selection that favors both extremes of a phenotype, potentially leading to speciation.
What is stabilizing selection?
A type of selection that favors intermediate or average phenotypes, reducing variation in a trait.
What is an example of evidence for natural selection involving DNA?
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria, where the presence of antibiotics changes the environment and selects for resistant strains.
How does beak length in soapberry bugs illustrate natural selection?
Soapberry bugs have longer beaks in regions with larger fruit and shorter beaks in areas with smaller fruit, showing adaptation to food source.
What are homologous characteristics?
Similar traits in different organisms that indicate common ancestry, interpreted as homologies due to descent with modification.
What is the 'struggle for existence' in the context of natural selection?
The competition among individuals for limited resources, which influences survival and reproductive success.
What is the relationship between variation and evolution?
Variation is a prerequisite for evolution, as it provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
What is the role of environmental context in determining fitness?
The environment affects which traits are advantageous, thus influencing the relative fitness of individuals.
What is the difference between microevolution and macroevolution?
Microevolution refers to small-scale changes within a species, while macroevolution involves larger-scale changes that can lead to the emergence of new species.
What is allopatric evolution?
Speciation that occurs when populations are geographically isolated, leading to reproductive isolation and divergence.
What is sympatric evolution?
Speciation that occurs without geographic isolation, often through mechanisms like polyploidy or behavioral changes.
What is the significance of the phrase 'surviving offspring' in biological fitness?
It highlights that fitness is not about physical strength but about reproductive success and the ability to leave viable offspring.
What does the term 'adaptive change' refer to?
Changes in a species that enhance its ability to survive and reproduce in its environment, often driven by natural selection.
What is the importance of lines of evidence for natural selection?
They provide support for the theory of evolution, demonstrating how species adapt over time through various mechanisms.

What do evolutionary trees represent?
Hypotheses about the relationships among different groups of organisms.
What is an example of a homologous characteristic in tetrapods?
Digit-bearing limbs.
What are analogous structures?
Similar structures that have arisen independently in different species, such as the wings of bats and birds.
What is a vestigial organ?
A functionless or reduced remnant of an organ that was once functional in an ancestor, like the pelvic bone in whales.
What does embryology provide evidence for in evolutionary biology?
It shows that closely related species go through similar stages of development, indicating common ancestry.
What are pharyngeal arches?
Structures in vertebrate embryos that develop into various features, such as gills in fish.
What does biogeography study?
The distribution of life forms over geographical areas, both in the past and present.
What is the difference between allopatric and sympatric speciation?
Allopatric speciation occurs when populations are geographically separated, while sympatric speciation occurs within the same geographic area due to ecological differences.
What is macroevolution?
Large-scale evolutionary changes that occur above the species level, contributing to the evolution of new species.
How does Darwin describe the mystery of speciation?
As the process that leads to the splitting of one population into two or more reproductively isolated populations.
What is an example of disruptive selection in sympatric speciation?
The differentiation of three-spine sticklebacks into forms that occupy different habitats.