AP GOPO - Waples Textbook's Unit 1 (Chapters 1 - 3)
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Pluralism
The theory that power shared between many groups produces the best outcomes in society & government.
Federal Rights VS State Rights
Federal laws apply to everyone in the United States. State and local laws apply to people who live or work in a particular state, commonwealth, territory, county, city, municipality, town, township or village.

Federalism
Federalism is a system of government in which the same territory is controlled by two levels of government.

The Fight for Student Rights
Students have used political tools available to them to secure their rights.

Bridget Mergens
Christian Bible study club-aided by National Legal Foundation

Boyd County students
Supported Gay-Straight Alliance.

Enlightenment Principles
When Americans assert their rights they are doing so based on revolutionary ideas.

Democracy
Power is held by the people.

Natural rights
The right to life, liberty, and property, which government cannot take away.

Social contract
People allow their governments to rule over them to ensure an orderly and functioning society.

The Declaration of Independence
Jefferson's arguments: British government no longer legitimate, inalienable rights were denied to citizens.

Popular sovereignty
The idea that the government's right to rule comes from the people.

Republicanism
The authority of the government comes from the people.
Representative government
Americans use free, fair, and frequent elections to hold officials accountable.

Jean-Jacque-Rousseau Opinion
Supports Social Contract.

Thomas Hobbes Opinion
Believed that humanity requires a government power to keep order.

Baron de Montesquieu Opinion
Gave ideas about separation of powers.

John Locke
Life, liberty, and freedom.

Two Visions of Liberty
Social, political and economic freedoms.

Participatory Democratic Theory
A theory that widespread political participation is essential for democratic government.

Pluralist Theory
A theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of groups in the policymaking process.
Elitist Theory
A theory of democracy that the elites have a disproportionate amount of influence in the policymaking process.

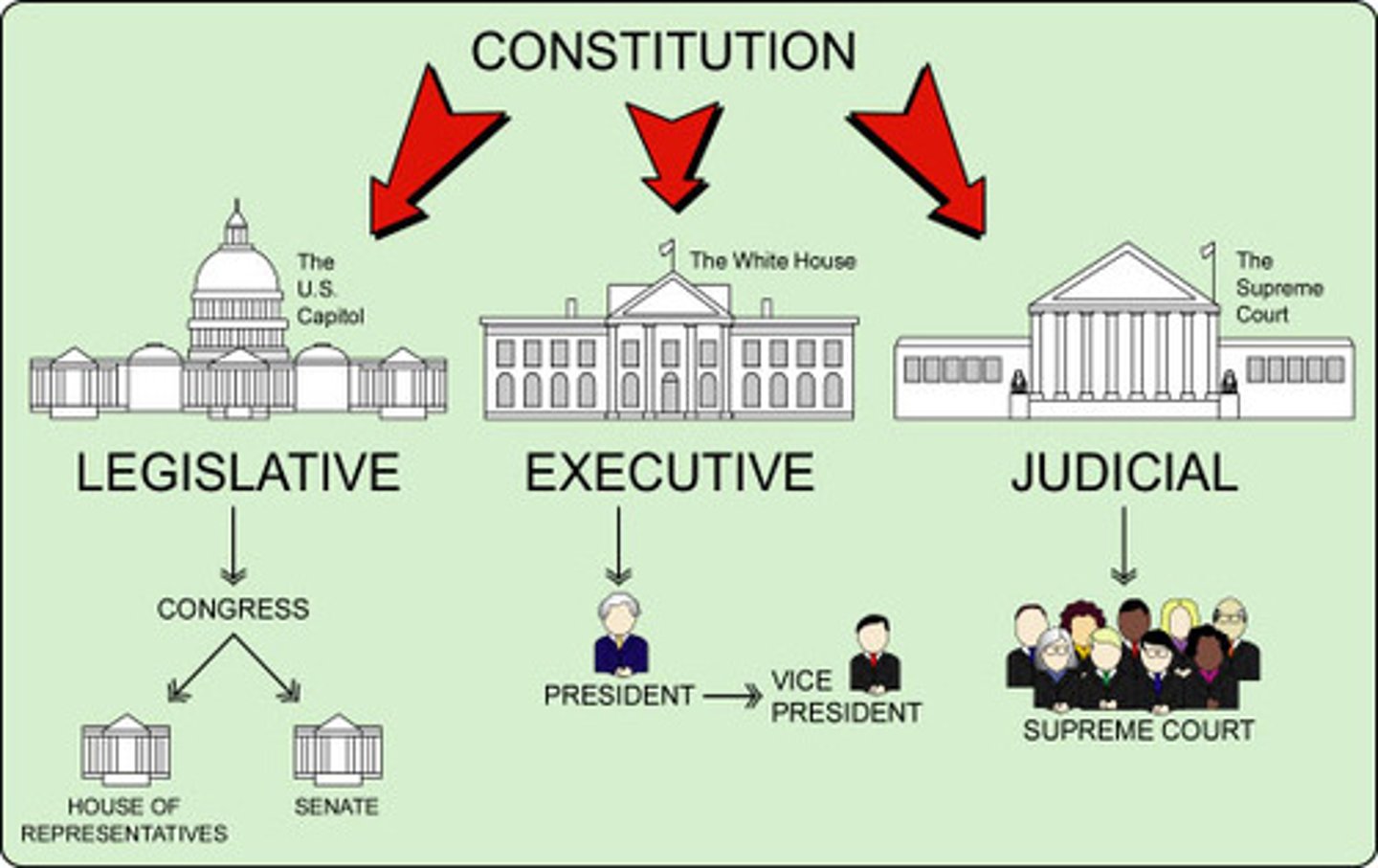
Political institutions
The structure of government, including the executive, legislature, and judiciary.

Constitutional Republic
A democratic system with elected representatives in which the Constitution is supreme law.

Constitution
A document that sets out the fundamental principles of governance and establishes the institutions of the government.

Republic
A government ruled by representatives of the people.

Confederation
Adopted by the Second Continental Congress in 1777, created a loose 'league of friendship' among the states.

Union of sovereign states
Supreme to national government.
Unicameral legislature
A one house legislature.

National government
Intentionally weak to avoid tyranny.
Shays's Rebellion
An internal rebellion that could not be stopped because the Confederal Congress could not raise an army.

Constitutional Convention
May 1787, 55 delegates from 12 of the 13 states met in Philadelphia to amend the Articles of Confederation.

James Madison
Father of the Constitution.

George Washington
President of the Constitutional Convention.

Alexander Hamilton
Leading proponent of a strong national government.

Civil liberties
Found in the Articles of the Confederation.

Writ of habeas corpus
The right of the people detained by the government to know the charges against them.

Bills of attainder
When the legislature declares someone guilty without a trial.

Ex post facto laws
Laws punishing people for acts that were not crimes at the time they were committed.

Virginia Plan
Proposed a three branch government with a bicameral legislature where larger states had more representation.

New Jersey Plan
Proposed a unicameral legislature with each state given one vote.

Three-Fifths Compromise
An agreement to count slaves as three-fifths of a person in calculating a state's representation.

Compromise on Importation
Slave trade not restricted until 1808.

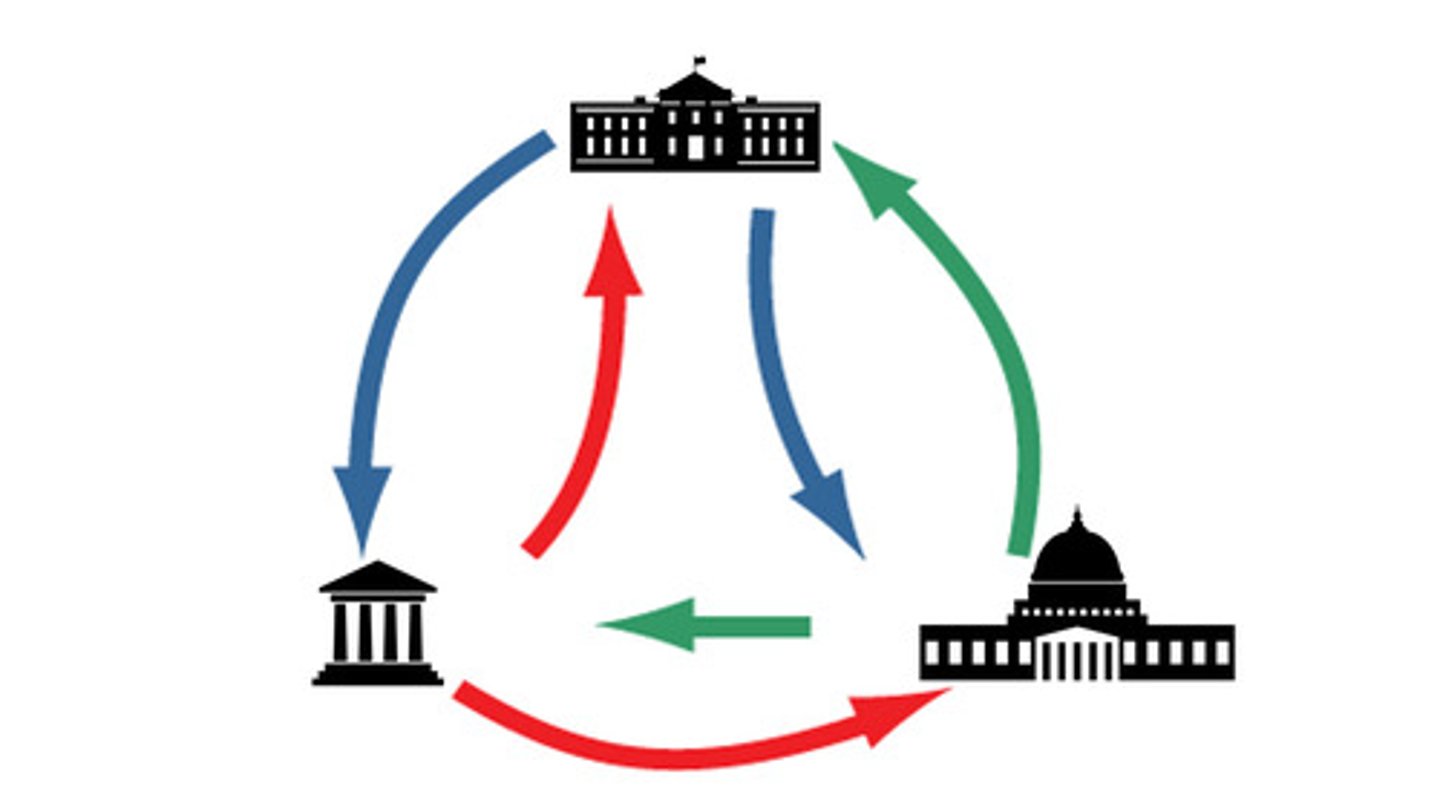
Separation of Powers
A design of government that distributes powers across institutions to avoid making one branch too powerful.
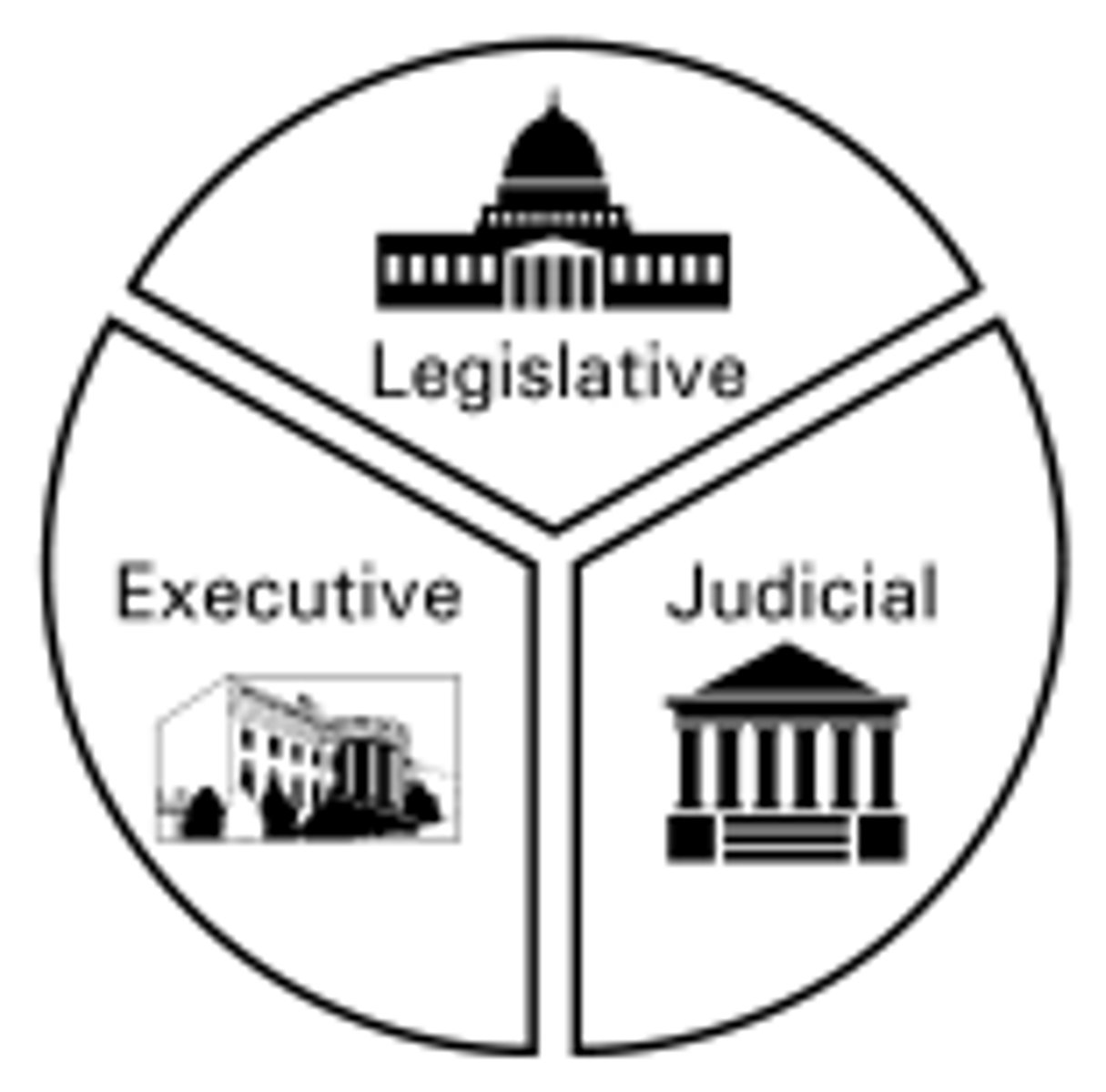

Checks & Balances
A design of government in which each branch has powers that can prevent the other branches from making policy.
Federalism
The sharing of power between the national government and the states.

Congress
Purpose is to make laws.

Enumerated / Expressed Powers
Authority specifically granted to a branch of the government in the Constitution.

Necessary and Proper Clause
Article I, Section 8, granting Congress necessary powers to carry out enumerated powers.

Implied Powers
Authority of the federal government that goes beyond its expressed powers.

The Executive Branch
Single executive (although debated) with a four-year term (no limit on terms) whose job is to carry out the laws that have been passed by Congress.

Executive Powers
Most powers shared with Congress to prevent tyranny, including veto, commander-in-chief, overseeing execution of law by bureaucracy, and treaty making.

Electoral College
Selected by the Electoral College - indirectly elected by the people.

The Judicial Branch
System of federal courts - responsible for hearing and deciding cases through the federal courts.

Supreme Court
Highest court in the land.

Lower Court Structure
Determined by Congress.

Jurisdiction
The authority to handle disputes between states and national government, between two or more states, and between citizens of different states.

Supremacy Clause
Constitution and all national treaties and laws shall be the supreme law of the land.
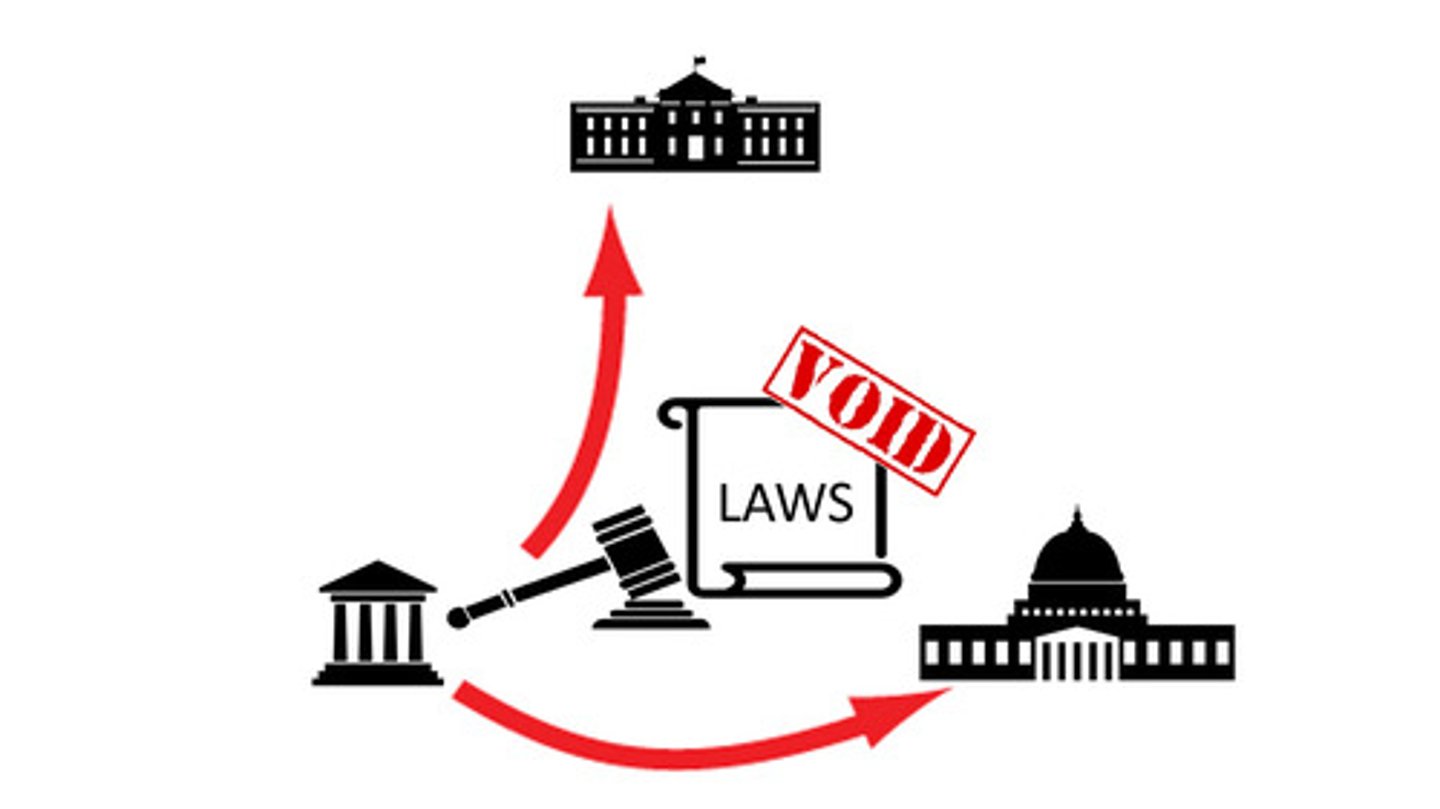
Judicial Review
The ability of the courts to overturn a law or executive action, not explicitly stated in the Constitution.
Amendment
Process by which changes may be made to the Constitution.

Two-Stage Process for Amendment
1. Passage by two-thirds vote in both House and Senate, or passage in a national convention called at the request of two-thirds of the states. 2. A majority vote in three-fourths of the state legislatures, or acceptance by ratifying conventions in three-fourths of the states.
Federalists
Supporters of the proposed Constitution, who called for a strong national government and pointed to the problems under the Articles of Confederation.

Federalist Papers
Published to sell the Constitution to the public and push delegates to ratify, authored by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the name 'Publius'.

Antifederalists
Opposed to the proposed Constitution, who called for stronger state governments and played on fears that a change in government would bring.

Federalist No. 10
Written by Madison, advocated for a large constitutional republic and feared the danger of factions.

Natural Check
A large and diverse republic that controls the effect of factions with more people and more opinions.

Federalist No. 51
Written by Madison, argued that separation of powers and checks and balances are keys to preventing tyranny.

Antifederalist Papers - Brutus No. 1
Expressed suspicion of power, arguing the country is too large to be governed as a republic and that the Constitution gave too much power to the national government.

The Bill of Rights
A list of rights and liberties that governments cannot take away, considered necessary to check the tendency of government to infringe on liberties of citizens.

1791 Amendments
Ten amendments added to the Constitution.

The primary goal of the government structure chosen by the Framers.
To reduce the ability of tyranny at a national level by dividing authority between multiple levels of government.

Conflict that arises from the division of power between state and national governments.
Continuous conflict over state versus national authority.
The method used by the Supreme Court to resolve disputes between the national government and the states.
By defining the ambiguous implied powers of Congress, either expanding national power or weakening it.

The central issue in Gonzales v. Raich (2012)
The legality of medical marijuana use, which was legal in California but illegal under federal law.

What does a unitary system of government imply about power at subnational levels?
Power delegated to subnational units is not constitutionally protected.

The significance of the Ninth and Tenth Amendments in the context of federalism.
The Ninth Amendment reserves powers not mentioned in the Constitution to the people, while the Tenth Amendment reserves powers to the states.
Enumerated or expressed powers
Powers granted specifically to the national government in the Constitution, especially to Congress.

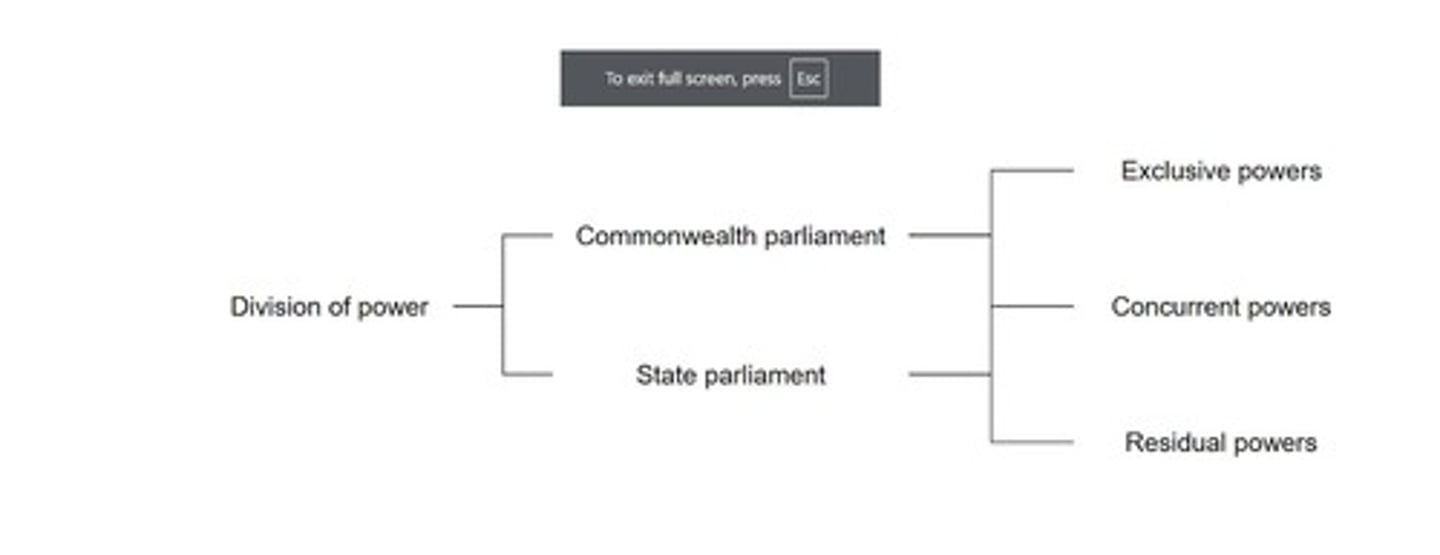
Exclusive powers
Powers that only the national government may exercise.
Implied powers
Powers not specifically granted to the federal government, allowing Congress to make laws to carry out its enumerated powers under the necessary and proper clause.

What does the Commerce Clause allow Congress to do?
Regulate commerce with foreign nations, among the states, and with Indian tribes.

What is the Necessary and Proper Clause also known as?
The elastic clause, which grants Congress the authority to legislate as needed to carry out its powers.

The Supremacy Clause states...
The Constitution and federal laws are the supreme law of the land, overriding state laws.

How does the Tenth Amendment protect state powers?
It reserves powers not given to the national government to the states and the people.

Concurrent powers
Powers granted in the Constitution that allow national and state authority to overlap in public policy areas.

The full faith and credit clause requires...
States to recognize the public acts, records, and civil court proceedings of other states.

Extradition in the context of state law
The requirement that officials in one state return a defendant to another state where a crime was allegedly committed.

The privileges and immunities clause prevents...
States from discriminating against people from out of state.

The issue in McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
Whether Congress could charter a national bank and if a state could tax that bank.

Outcome of McCulloch v. Maryland
The Necessary and Proper Clause allows Congress to exercise implied powers, and a state cannot tax a federal institution.
The Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth Amendments are known as.
The Civil War amendments that shifted power from states to the national government.

The Fourteenth Amendment guarantees...
Citizenship to persons born in the U.S. and prohibits states from denying due process or equal protection.

The significance of Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
It established the 'separate but equal' doctrine, strengthening state governments' ability to impose Jim Crow laws.

Dual Federalism
A form of American federalism where states and the national government operate independently in their own areas of public policy, with little overlap.
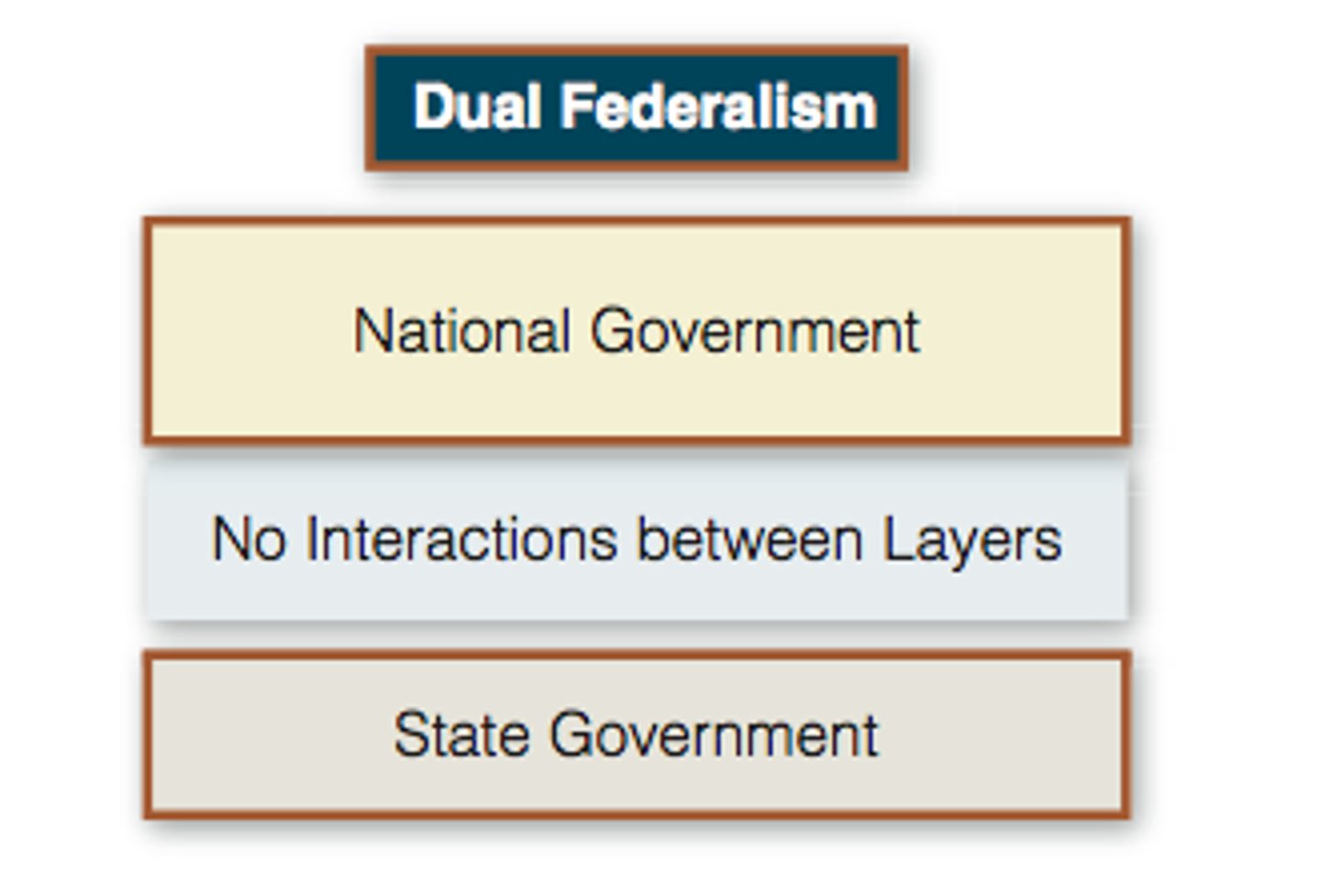
The metaphor used to describe dual federalism.
Dual Federalism is a layer cake.

What process weakened state power and blurred the distinction between state and national policies?
Selective incorporation, where the Supreme Court applies fundamental rights in the Bill of Rights to the states on a case-by-case basis.

Cooperative Federalism
A system where both state and national governments work together in the same areas of public policy.
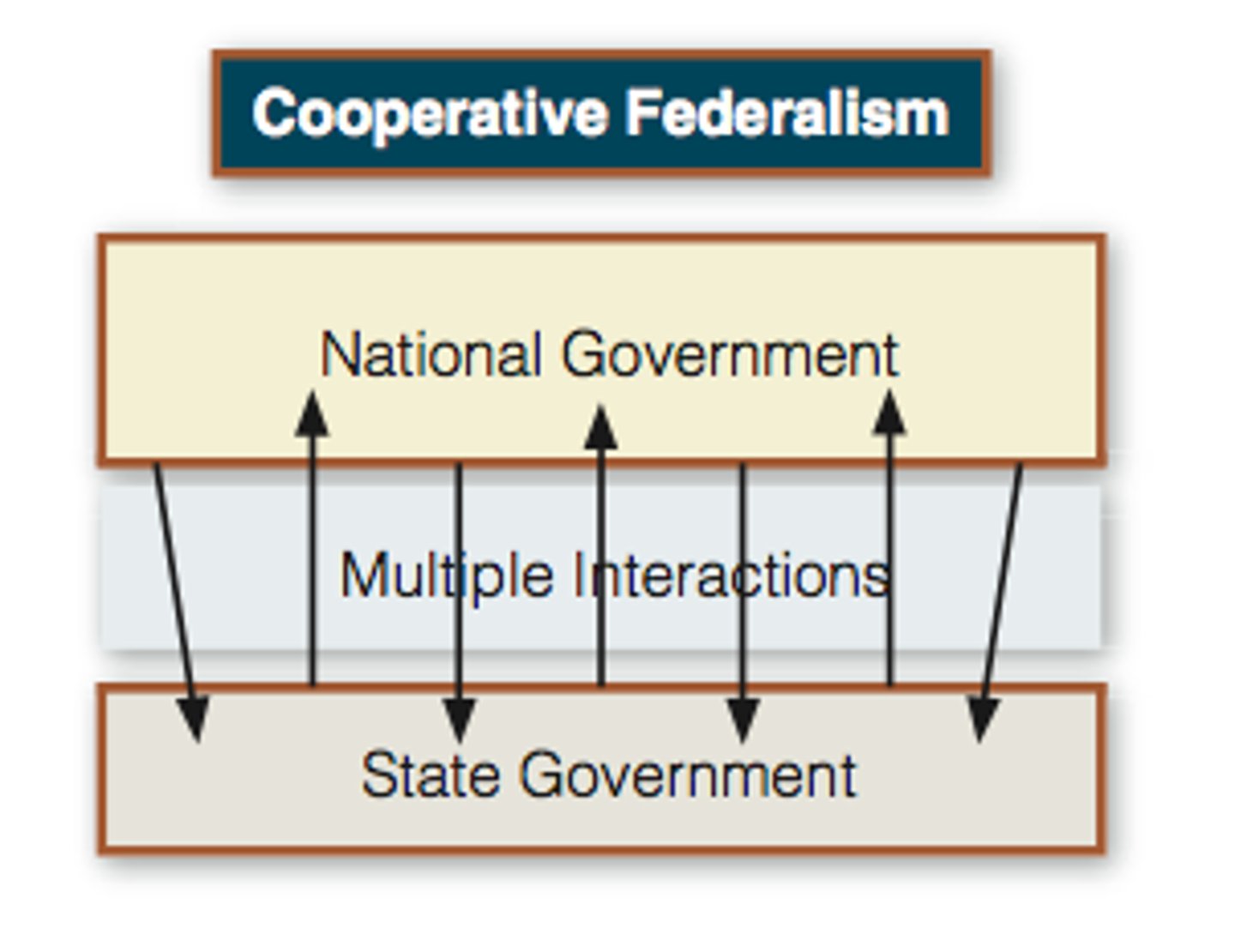
Metaphor used to describe cooperative federalism.
Cooperative federalism is a marble cake federalism.

A major event that led to a shift towards national policy and standards in the U.S.
The Great Depression, as states could not cope with economic inequities and turned to national policy for help.

Fiscal Federalism
The federal government's use of grants-in-aid to influence policies in the states.

Categorical Grants
Grants provided to states with specific provisions on their use, limiting how states can spend the funding.
