AP Biology- missed
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
261 Terms
how does cohesion help with water moving up trees
stick together= makes a column
how does adhesion help with water moving up trees
adhere to the plant vessels
how does capillary action help water in plants
rise against gravitu through narrow channels
biochemical processes that sustain life, all chemical reactions that occur on a organism
metabolism
macromolecules of a carb
CHOS
macromolecules of a protein
CHON / S
macromolecules of a lipid
CHO / P
macromolecules of a nucleic acid
CHONP
monomers to polymers
dehydration synthesis
polymer to monomer
hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis is anabolic or catabolic
anabolic
hydrolysis is anabolic or catabolic
catabolic
parts of an amino acid
amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, and R group (side chain)
four levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
primary structure
linear sequence of acids
secondary structure
local folding of beta and alpha sheets
tertiary
3d folding from r group interactions
quaternary structure
many proteins come together
five functions of proteins
transport, recongize, movement, communication, enzyemes
two carbs for energy
glucose, fructose
two carbs for structure
cellulose and chitlin
why cant animals digest cellulose
no cellulase, which cant break beta bonds
which are soild room temp
sat fats
how many bonds do sat fats have
no double bonds
parts of a nucelotide
phosphate, pentose, nitrogenous base
phosphate - ___ side
hydroxyl - _____ side
5,3
which are purine
adenine and guanine
which are pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, and uracil
which pentose sugar lacks an oxygen at the 2’ carbon
dna
what is involved in translation of the ribosome?
RNA
when dna is breaking, what breaks
sugar and phosphate
what buds off the trans face of the golgi complex
secretory vesicles
5 evidence for endoymbiosis theory
they have double membranes, their own dna, they can independently replicate, and they are a similar size to prokaryotes
what are ribosomes made out of
protein and rRNA
where are ribosomes
rough er and cytoplasm
what is the only organelle eukaryotes and prokaryotes share
ribosomes
what to ribosomes do for DNA
they read the gene instructions from mrna and make amino acids to polypeptide chains
rough er function
make proteins and modify them for secretion or use within the cell.
smooth er
makes fats, detoxes and calcium levels
what does the golgi apparatus ship and with what
lipids and proteins with secretory vesicles
lysosomes have _______ enzyemes
digestive / hydrolytic
which organelle helps with tugor pressure
vacole
where is the krebs cycle and what organelle
matrix, mitochondria
where is the etc and atp and what organelle
cristae, mitochondria
where is photosynthesis organelle
choloroplast
what are cell walls made of
polysaccrides
are carrier/channel and aquaporins active or passive
passive
two types of transport proteins
carrier and channel
why are transport proteins solute specfic
binding sites
prokaryote and eukaryote in common
dna, ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane
what would happen if the rough er malfunctioned
cant asemble proteins and send to golgi
vacuoles help osmoregulation how
water balance by pumping ions and causing molecules to move
what do the hydrophobic and hydrophillic r groups dictate
interactions
proteins 3d structure
function
what do the chemical properties r groups dictate
interactions and bonding of protein structure
folding patterns
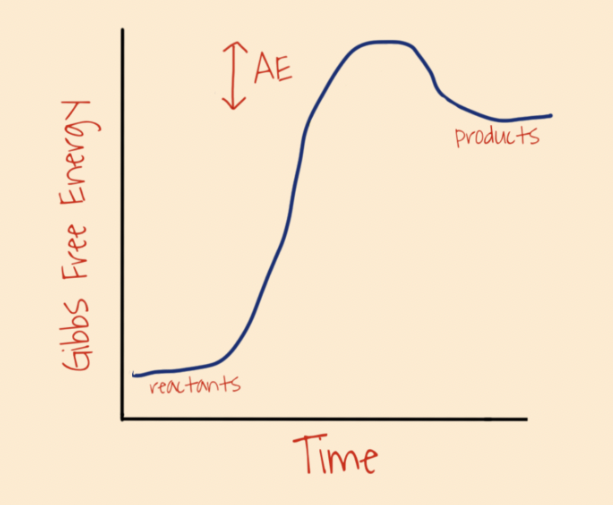
what is this reaction
uncatalyzed endergonic
reaction that absorbs energy
endergonic
chemical reaction that releases energy.
exergonic
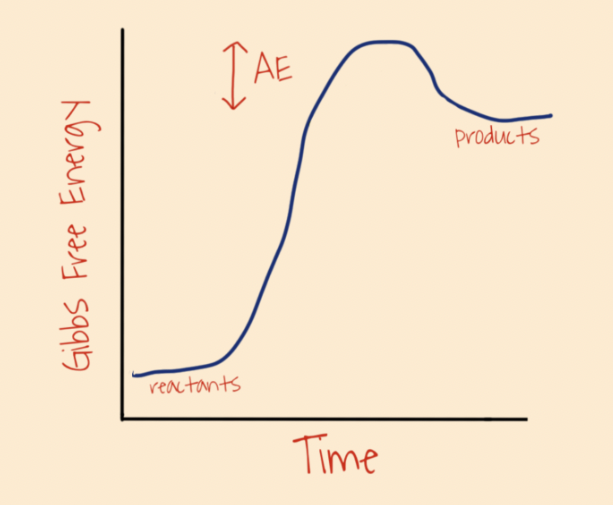
what is this
catalyzed exergonic
enzyemes are ____ and _____ specfic
substrate,condition
what must be compatible with an enzyemes active site? (of a substrate)
charge and shape
what will increase the rate of a reaction
substrate concentration and temperature
protein denaturation disrupts what structures?
2,3,4
what does denaturation do to an active site
destroys it so it cant bind
difference in energy from r to p in catalyzed vs uncatalyzed
the same
examples of exergonic reactions
atp hydroloysis and cellular respiration
how is energy from reactants than products in exergonic
higher
examples of endogonic reactions
atp formation, photosynthesis
how is energy from reactants than products in endergonic
lower
reactants for calvin cycle
carbon dioxide, ATP, NADPH
products for calvin cycle
glucose, ADP, NADP+
reactant for light reaction
water, light energy, NADP+, ADP
product for light reaction
oxygen, ATP, NADPH
where does light reaction occur?
thylakoid membrane
where does calvin cycle occur
stroma of chloroplasts
electrochem gradient of hydrogen ions for atp
protons build up in tylakoid membrane
gradient is created
atp synthase makes energy to move
phosporlytes adp and pi
photophosphorlyation
photophosphorlyation
the process of using light energy to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP during photosynthesis.
coenzyeme nadph
where
role
what does it carry and to where
what does it help convert
photosynthesis
reducing agent
high energy electrons to calvin cycle
co2 to glucose
three phases of calvin
fixation
reduction
regeneration
calvin cycle turns to make glucose
6
etc reactants
oxygen, NADH, FADH2
etc products
water, ATP, NADH
glycolysis reactants
glucose, ATP, NAD+
glycolysis products
pyruvate, ATP, NADH
krebs cycle reactants
acetyl-CoA, NAD+, FAD, ADP
krebs cycle products
CO2, ATP, NADH, FADH2
where does glycolysis occur
cytoplasm
where does krebs occur
mitochondrial matrix
where does etc take place, organelle
cristae of the mitochondria
cell respiration steps
glycolysis,
the Krebs cycle,
the electron transport chain
fermentation and cell resp. similar
glycolysis
in glycolysis, how is atp produced
substrate-level phosphorylation.
in etc, how is atp produced
oxidative phosphorylation
two sources of electrons for etc
nadh and fadh2
final electron acceptor to form what
oxygen to form water
what type of phosphorylation is photosynthesis
photophosphylation
what type of phosphorylation is cellular respiration
oxidative phosphorylation
Where is photosynthesis embedded
thylakoid in the choloroplasts
Where is cellular respiration embedded
cristae
electron donor molecules in photosynthesis
h2o