Group 16
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Common oxidation states of Group 16
-2,+4 (not Oxygen),+6 (not Oxygen)
Describe the elemental forms of group 16
O forms a diatomic molecule with two LP and a double bond
S has the most naturally occurring allotropes and polymorphs than any other element
Selenium is similar to sulphur but also contains a metallic form
Te is a metalloid
Po is a radioactive metal
State and draw the Sulfur halides that can form
S2F2
SF2
SF4
SF6
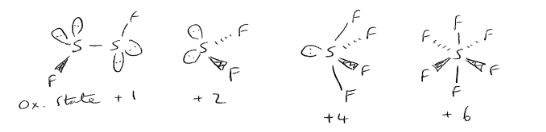
What is notable of SF4
Highly reactive and very toxic releasing HF in the lungs
Describe the notable features of SF6
Extremely inert being stale up to 500 degrees
Colourless,Odourless,Tasteless,Non-flammable,Non-toxic
Very dense at 6.4kg/m³
Used as an insulating gas in high voltage generators
No corresponding properties to other Sulphur Hexahalides
Hypervalence
Describe the hypervalency in SF6 and its formation
S8 + 24 F2 → 8 SF6
6 electrons from sulphur, each fluoride donates 1 electron to S-F bonding, giving it a total 12 valence electrons breaking the octet rules value of 8
Sulphur contains 4 orbitals for use (3S,3Py,3Px,3Pz) and the 6 Fluorines bonds to sulphur each using a single p orbital, A total of 10 atomic orbitals used in bonding meaning it forms 10 molecular orbitals
F-Based orbitals combine with Sulphur 3s to give 1 MO, Three more bonding MOs form with 3px, 3py, 3pz. Giving 4 bonding MO.
Due to sulphur have an opposite phase to its atomic orbitals, we form 4 antibonding MO. So we have 8 total MO
The final 2 MO come from non-bonding orbitals based entirely on fluorine
Describe bonding in SF6
Of the 12 electrons 8 occupy bonding MO and 4 occupy non-bonding orbitals.
Only 8 of the electrons are involved in S-F bonding. Remaining 4 are situated only on fluorine atoms
SF6 is stable as it has the 4 “extra” electrons placed entirely on the electronegative fluorine atoms.