Gas exchange and blood proteins
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
where does gas exchange occur?
lungs - in tiny sacs aka alveoli
what are alveoli surrounded by?
a network of capillaries to help with gas exchange
gas exchange at the lungs process
move via diffusion (high concentration to low concentration)
oxygen diffuses from air in the alveoli into the blood
co2 diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli
how are alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
thin
large surface area
gas exchange at the lungs diagram
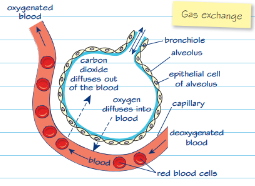
erythrocytes
red blood cells
role of haemoglobin in red blood cells
loads o2 at the lungs and unloads it at respiring tissues
loads co2 at respiring tissues and unloads it at the lungs
percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in inhaled air
21% oxygen
0.04% carbon dioxide
percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in exhaled air
16% oxygen
4% carbon dioxide
types of blood proteins
haemoglobin, myoglobin, foetal haemoglobin
where is haemoglobin found?
in red blood cells
function of haemoglobin
carries 4 oxygen molecules
transports oxygen around the body
removes co2 as a waste product
oxyhaemoglobin
oxygenated form of haemoglobin
where is myoglobin found?
in muscle cells
myoglobin function
an oxygen and iron binding protein which releases oxygen to muscle cells when oxygen conc. is low
carries one oxygen molecules
acts as an oxygen store
oxymyoglobin
oxygenated form of myoglobin
foetal haemoglobin
foetus cannot use its lungs, so relies on exchanging oxygen and co2 via diffusion from its mother’s blood
has a higher affinity for oxygen, so is more efficient at extracting oxygen from maternal circulation
what causes an increase in co2 in the blood?
increased rates of respiration
what happens to co2 in the blood?
it dissolves and forms carbonic acid
how does carbonic acid affect blood pH?
lowers it (makes it more acidic)
how does low pH affect haemoglobin?
causes haemoglobin to release more oxygen
why is the Bohr effect important during exercise?
ensures muscles receive more oxygen so they can continue working at a high rate
what is the Bohr effect?
the concept that a decrease in blood pH (due to increased CO2) reduces haemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen, causing more oxygen to be released to tissues