Biology - Unit 7: Transport in Flowering Plants
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
relate the structure of the root hair cells to their function of water and ion uptake
root hair increases the surface area of the cells significantly which will increase the rate of absorption
water enters root hair cells by osmosis
mineral ions enter root hair cells by active transport
outline the pathway taken by water through the root, stem and leaf
water enters roots via root hair cells, by the process of osmosis
water then moves across the root, through the cells of the root cortex
water travels from the roots to the leaves of plants in the xylem, where it moves into the cells of the leaf mesophyll
the pathway of water through a plant can be summarised as follows:
root hair cell → root cortex cells → xylem → leaf mesophyll cells
what is transpiration?
loss of water vapour from leaves
how does transpiration occur?
water travels from the roots to the leaves of plants in the xylem vessels
when water reaches the leaves it enters leaf mesophyll cells
water evaporates from the surface of leaf mesophyll cells into the air spaces in the leaf, from where it diffuses out of the leaf via the stomata in transpiration
what is the effect of temperature on transpiration rate?
as temperature increases, transpiration rate increases as the kinetic energy of water molecules increases.
thus, they evaporate and diffuse faster from the mesophyll cells.
what is the effect of wind speed on transpiration rate?
as wind speed increases, transpiration increases
the wind removes away the water vapour surrounding the leaf faster.
what is the effect of humidity on transpiration rate?
as humidity increases, transpiration rate decreases.
if the air surrounding the leaf has more water vapour, there’ll be a weak concentration gradient for diffusion.
what is the function of transpiration in plants?
transporting mineral ions
providing water to keep cells turgid in order to support the structure of the plant
providing water to leaf cells for photosynthesis
keeping the leaves cool
what is the effect of light intensity on transpiration rate?
as light intensity increases, transpiration rate increases.
increased light speeds up photosynthesis, causing the stomata to open for gas exchange.
while open, water vapour escapes through the stomata.
how does wilting occur?
if water loss from transpiration is faster than replacement, wilting occurs.
plant cells lose water and turgidity, causing tissues to become floppy and stems to fall.
prolonged wilting leads to leaf death, stopping photosynthesis and eventually killing the plan
what is the benefit of wilting?
wilted leaves may become folded, reducing the exposure of stomata to the outside air and slowing further water loss.
describe the transpiration stream?
transpiration stream is upward movement of water through xylem vessels
water moves from the roots to the leaves and is then lost from leaves by transpiration
water loss by transpiration drives transpiration pull which draws water upwards in the transpiration stream
each water molecule pulls on the molecule below it due to forces of attraction between water molecules
what is translocation?
the movement of sucrose and amino acids in the phloem from parts that produce or release them (sources) to parts of the plants that use or store them (sinks)
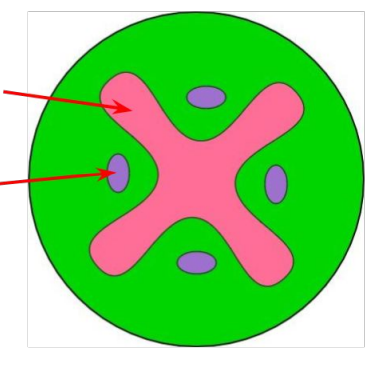
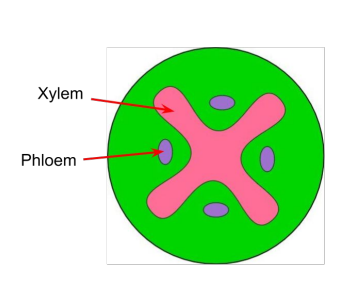
identify the positions of the xylem and phloem in this image of a transverse section of a stem.
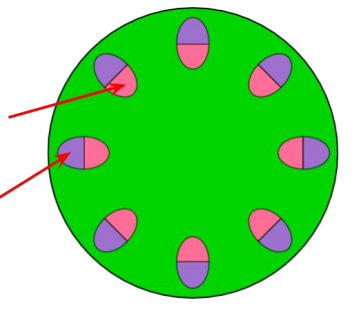
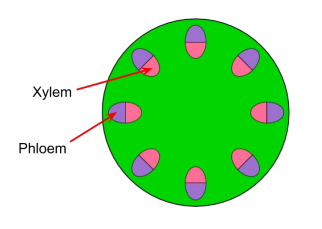
identify the positions of the xylem and phloem in this image of a transverse section of the roots.
state the function of the xylem.
transport of water and mineral ions
support
relate the structure of xylem vessels to their function
cells are joined end-to-end, thus forming a long continuous tube
there are no cell contents which allows free passage of water
outer walls are thickened with lignin which strengthens the tube
how can we investigate transpiration rate?
a single air bubble is introduced into the capillary tubing
the tap on the reservoir is opened to add water to push the air bubble back to zero on the scale
a timer is started and a set time is measured
the distance the air bubble travels along the scale is recorded
the experiment can be repeated with different environmental conditions
the faster the bubble moves, the greater the rate of water uptake — and so the greater the rate of transpiration
to test how temperature affects transpiration rate: change the room temperature with a heater
to test how wind speed affects transpiration rate: use a fan at different speeds
to test how light intensity affects transpiration rate: place a lamp at different distances from the plant