Endo/Repro Exam 1: Calcium/Phosphate Regulation (Dr. Leavis)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what are some passive roles of calcium in the body?
- A cofactor for many enzymes (e.g. Lipase) and proteins
- A component in the blood clotting cascade

what are some active roles of calcium in the body (as an intracellular signal)?
- In the relaxation and constriction of blood vessels
- In cell aggregation and movement
- In muscle protein degradation
- In secretion of hormones as insulin
- In cell division
- In nerve impulse transmission

what are the three organ systems involved in calcium homeostasis?
- GI tract
- Kidneys
- Bone
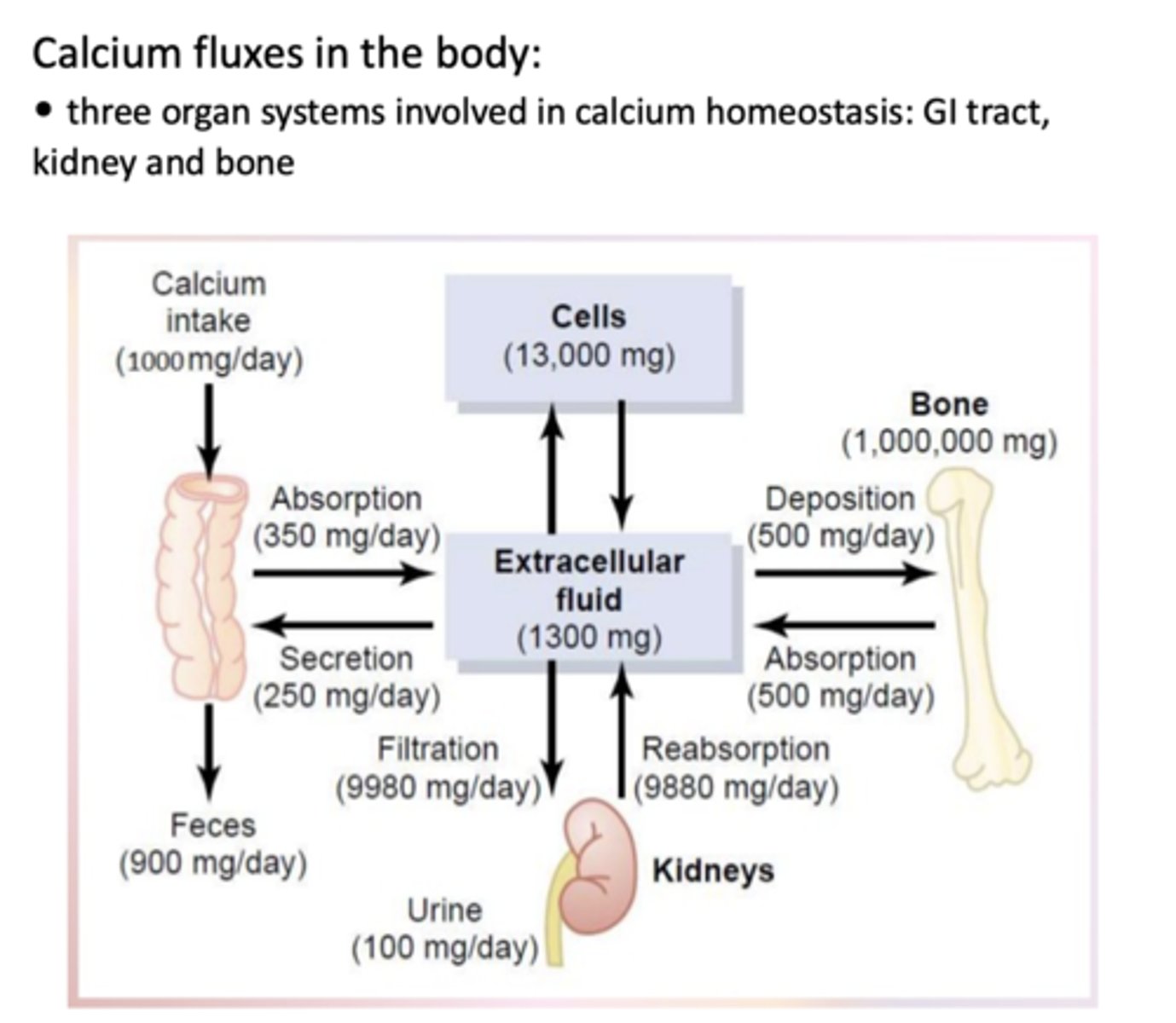
Dietary calcium intake averages about ______ gram per day- only about ______ mg of this is taken up into the blood stream and about ______ mg is secreted leaving a net intake of ~______ mg/day
1 gm (per day)
350 mg (into blood stream)
250 mg (secreted)
~100 mg/day (intake)

Most ingested calcium remains in the ___________ bound to the calcium-binding protein ___________. It is eliminated in the feces when the ___________ are shed from the GI lining.
Enterocytes, calbindin, enterocytes

What contains 99% of all the calcium in the body in the form of insoluble salt - acts as a reservoir?
Bone

bone resorption releases _____________ into bloodstream, raising Ca2+ levels
calcium

bone deposition _____ blood calcium
reduces

Almost a gram of calcium is filtered at the glomerulus and all but ~______mg/ day is reabsorbed
100mg

What has the following roles in the body?
- High energy molecules of the body
- Key factor in glycolysis
- Regulation of many cellular proteins
- Cell membrane component
phosphate

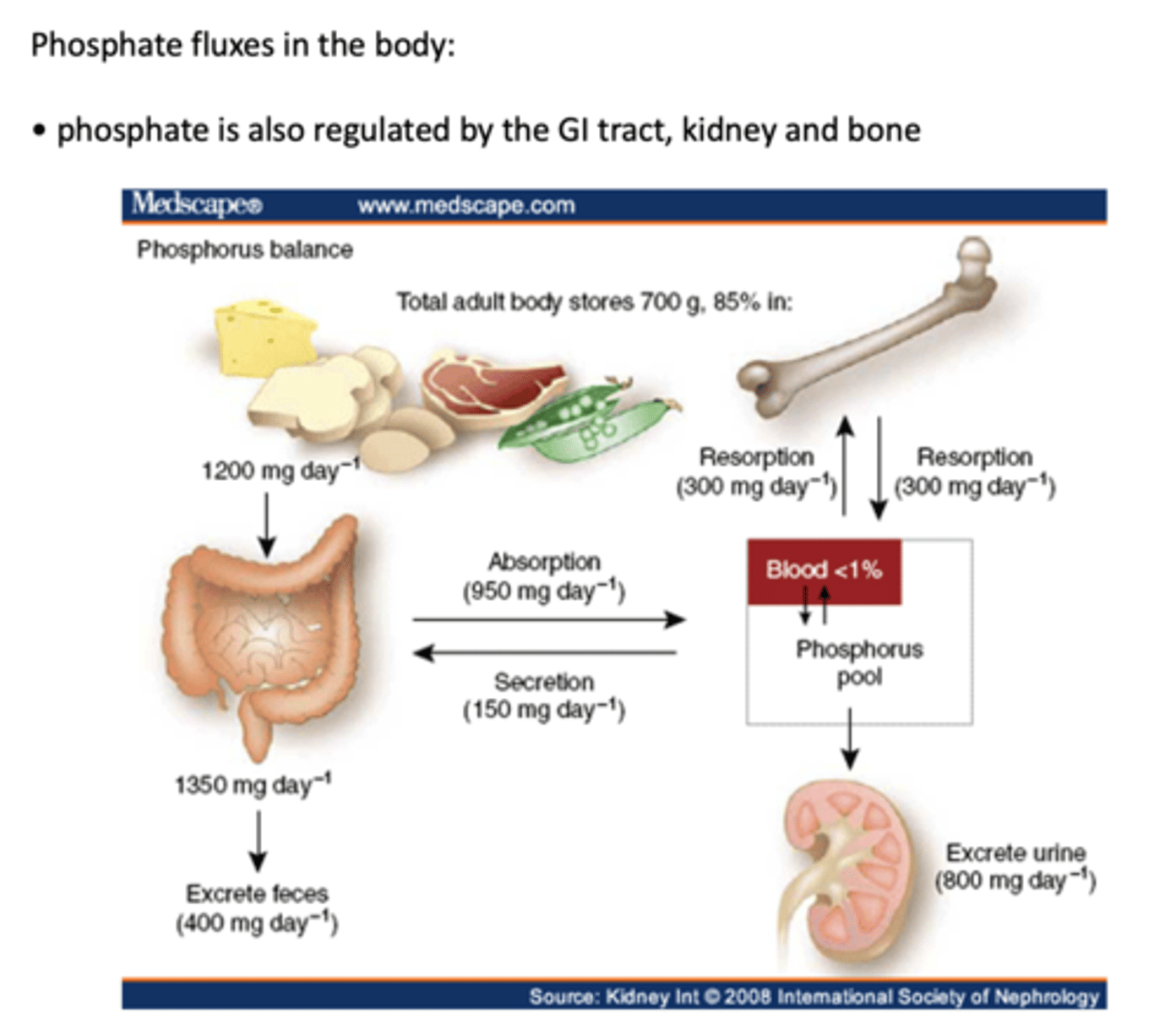
phosphate is regulated by what organ systems?
- GI tract
- Kidneys
- Bone
Bone is a dynamic organ system with continuous ______ formation, and remodeling
de novo
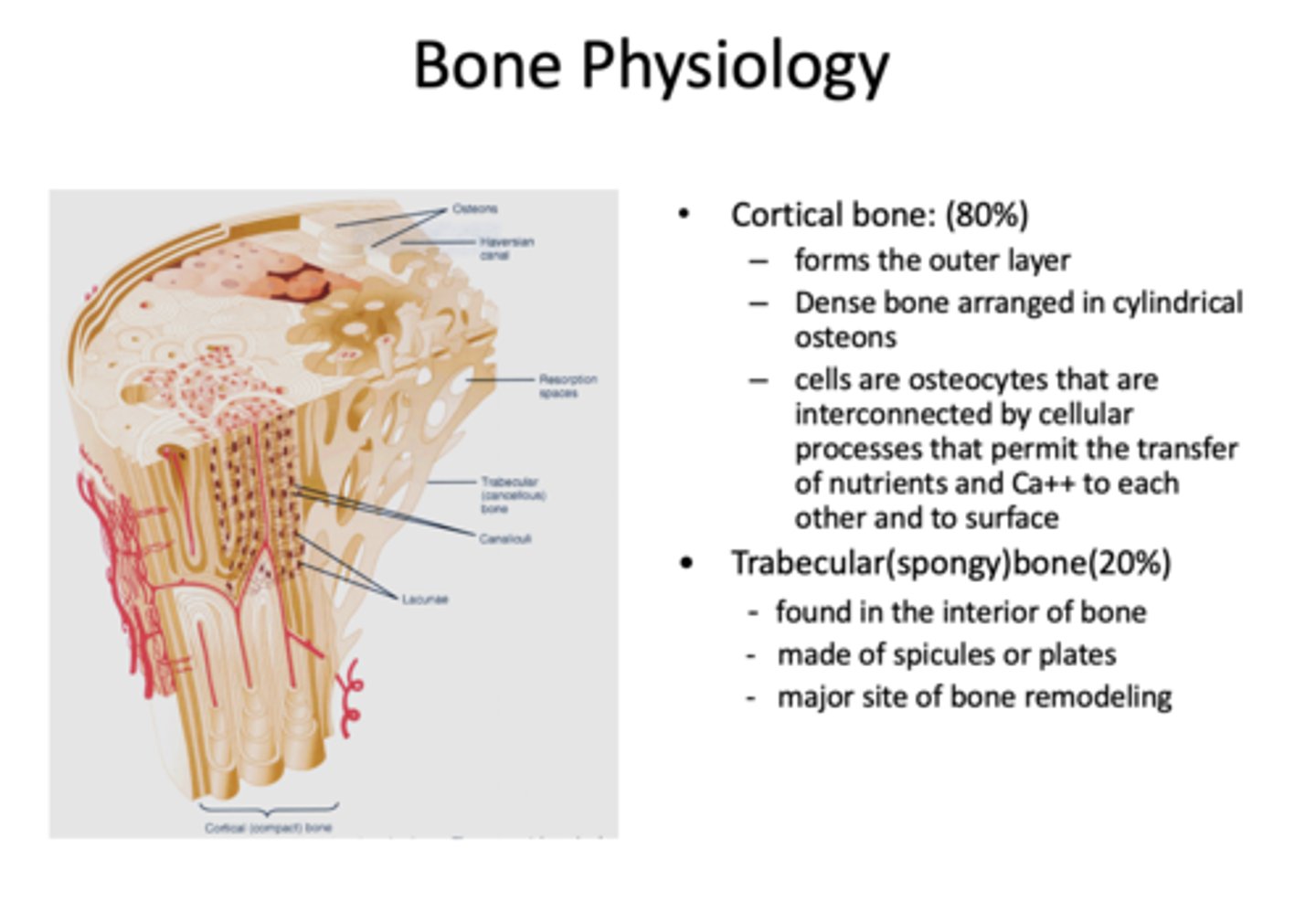
What has the following characteristics?
- Comprises 80% of bone
- Forms the outer layer
- Dense bone arranges in cylindrical osteons
Cortical bone (compact bone)
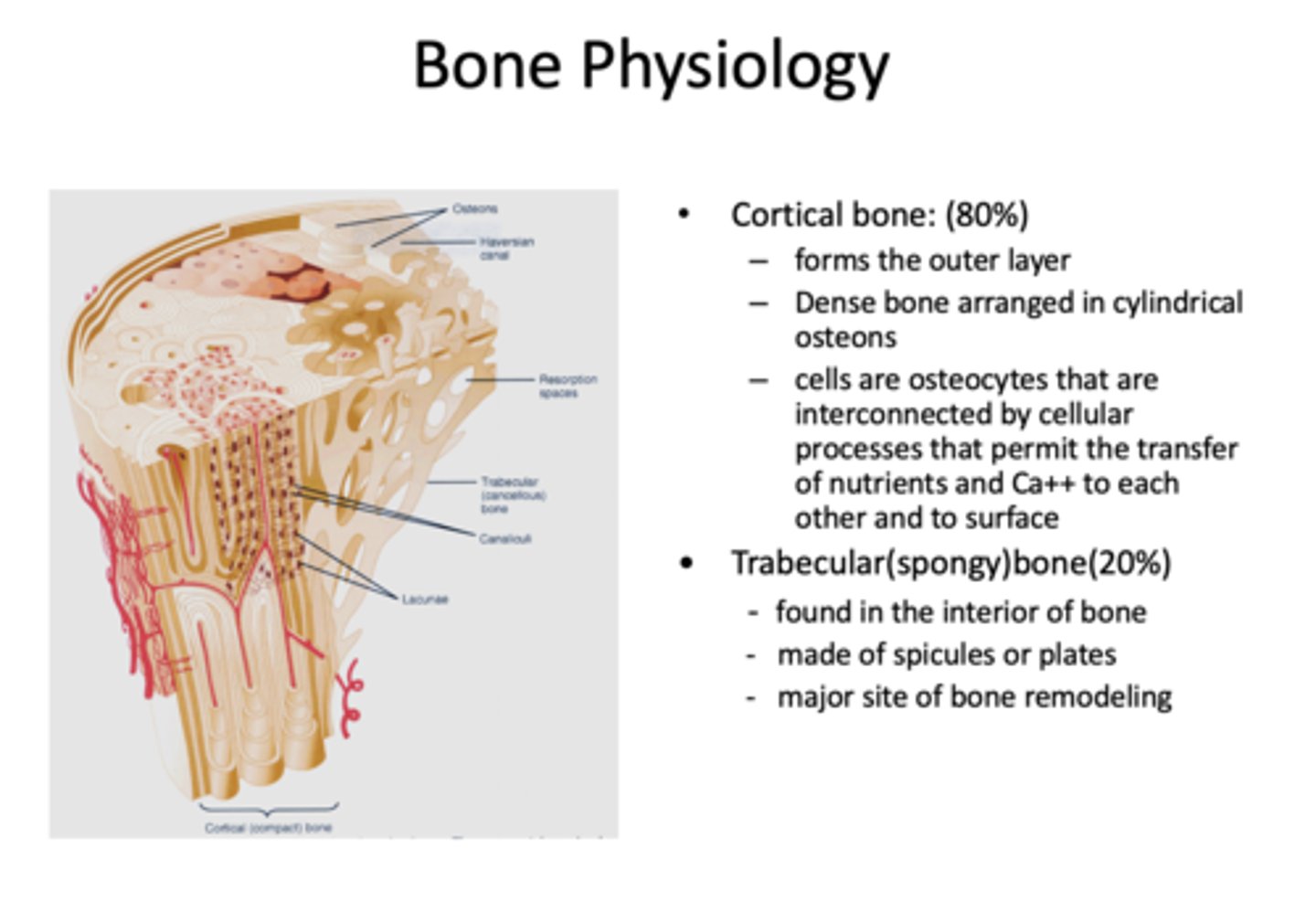
What has the following characteristics?
- Comprises 20% of bone
- Found interiorly
- Made of spicules or plates
- Major site of bone remodeling
trabecular (spongy) bone
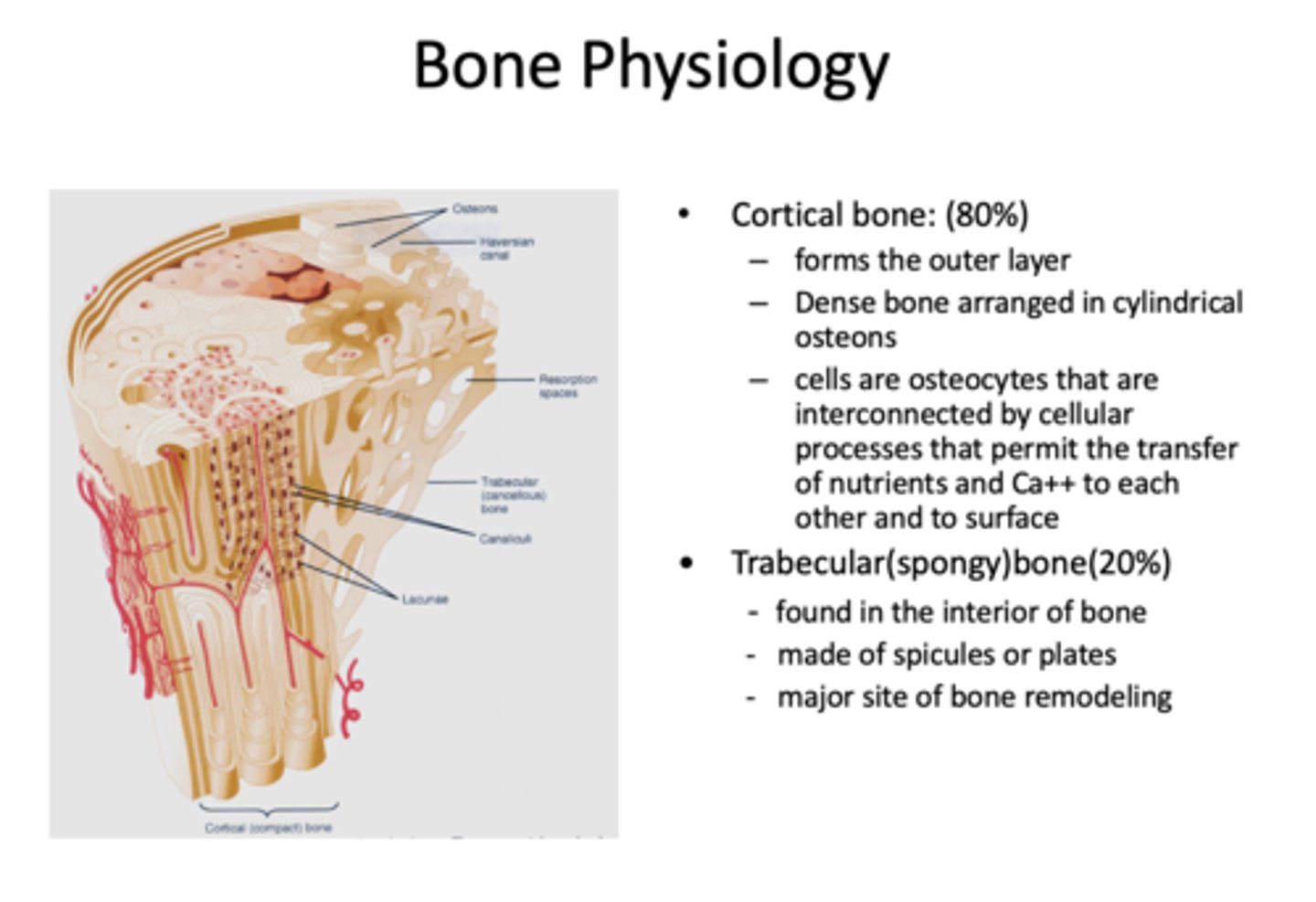
cells that maintain bone:
osteocytes
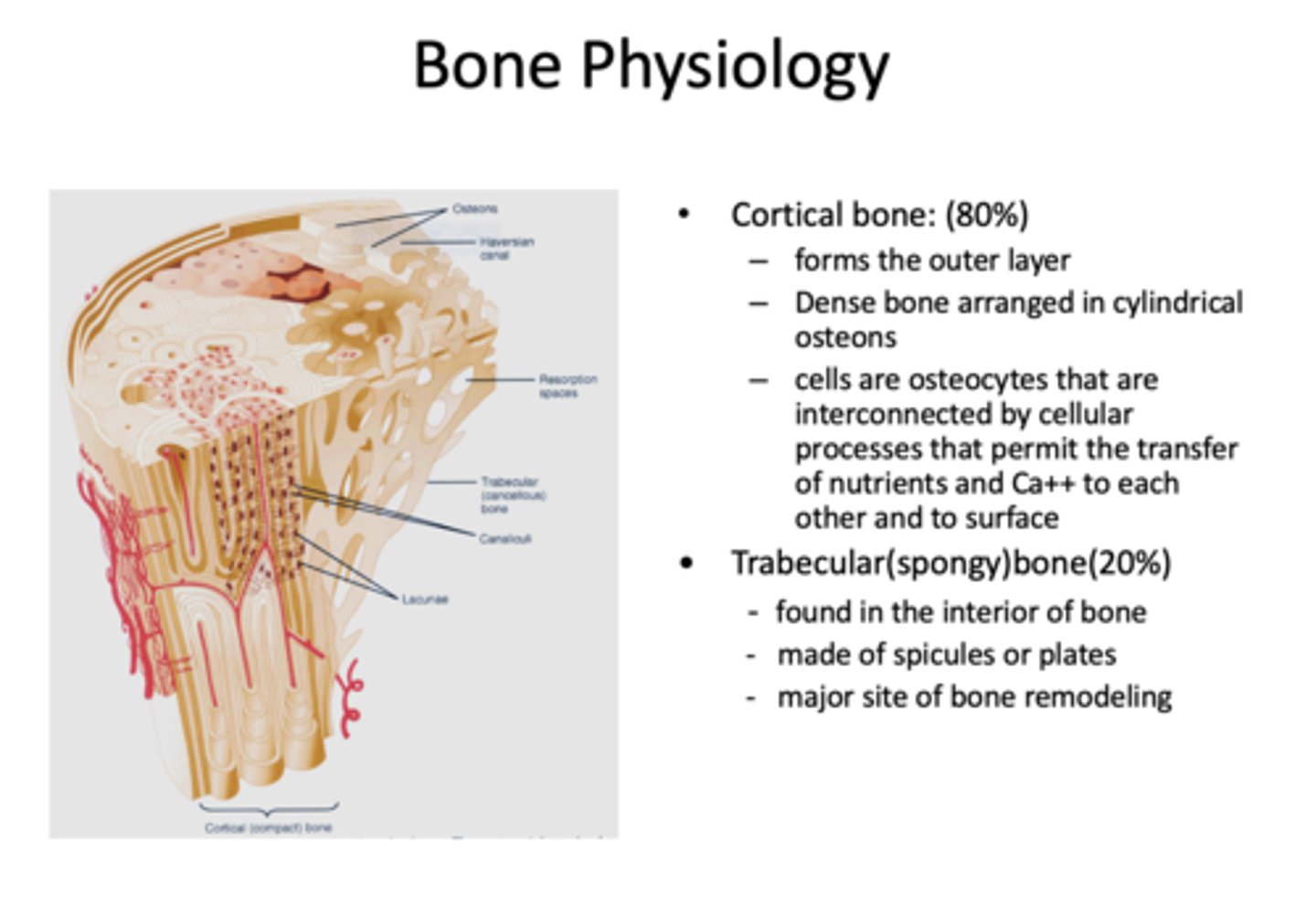
What cells are interconnected by cellular processes that permit the transfer of nutrients and Ca++ to each other and to surface?
osteocytes
osteoblasts promote bone formation by secreting osteoid, a complex matrix of proteins that includes
type I collagen, osteocalcin, and osteonectin

_____________ assembles into fibers that are highly ordered in the osteoid and provide a scaffolding for the nucleation of bone minerals
type I collagen

_____________ binds Ca++ and hydroxylapatite, the crystalline mineral of bone [Ca10(PO4)6OH2]
osteocalcin

_____________ binds to hydroxylapatite and collagen fibers
osteonectin

_____________ exocytose Ca++ and phosphate into the osteoid to promote crystal nucleation and growth
osteoblasts

What has the following characteristics?
- Derived from osteoblasts that have encased themselves within bone
- Play a role in transfer of minerals from the bone interior to the growth surfaces via canaliculi
osteocytes

What cells promote bone resorption on bone surfaces?
osteoclasts
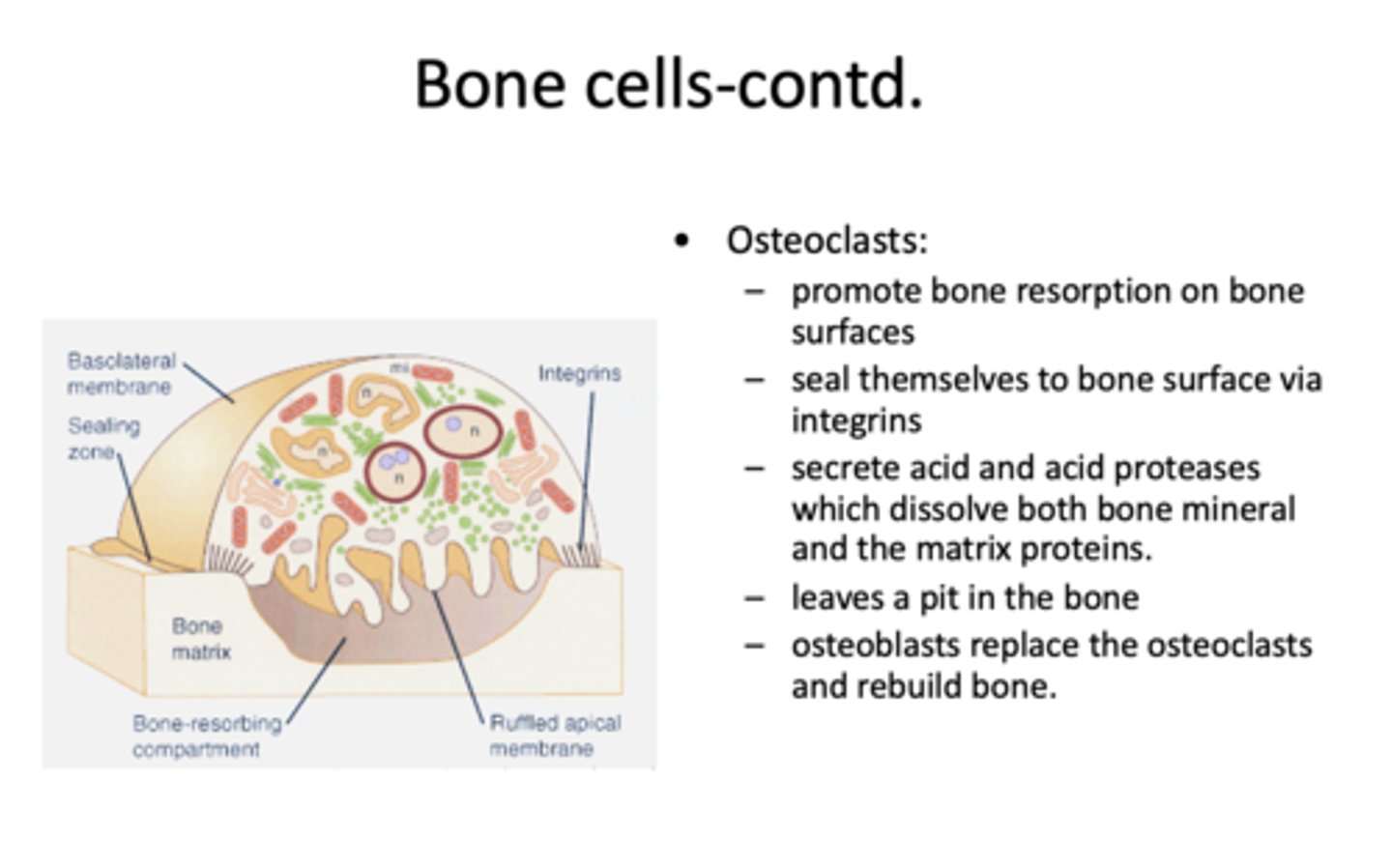
function of this cell:
- Seal themselves to bone surface via integrins
- Secrete acid and acid proteases which dissolve both bone mineral and the matrix protein
- Leaves a pit in the bone
osteoclasts
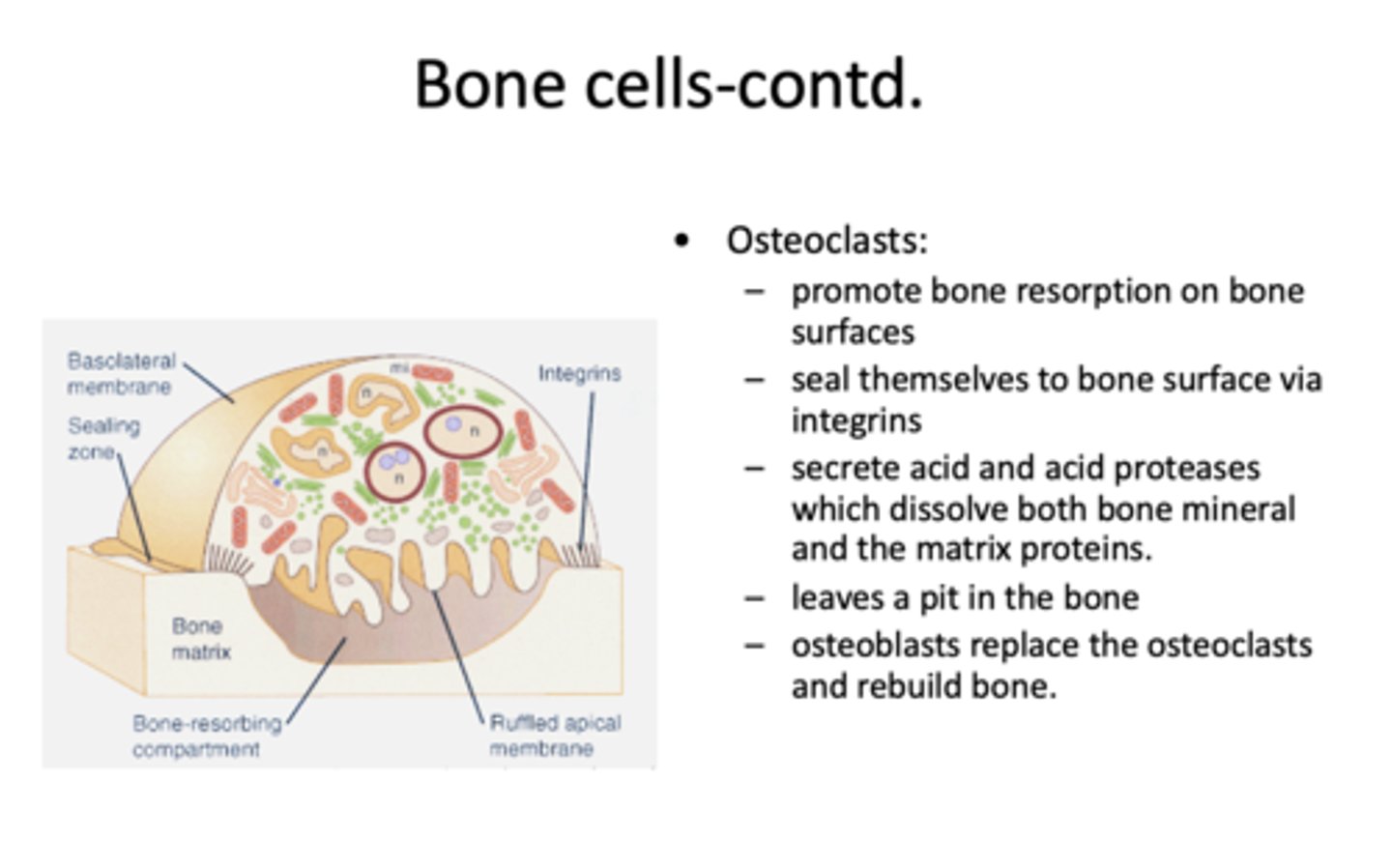
What cells replace the osteoclasts?
Osteoblasts (to rebuild bone!)
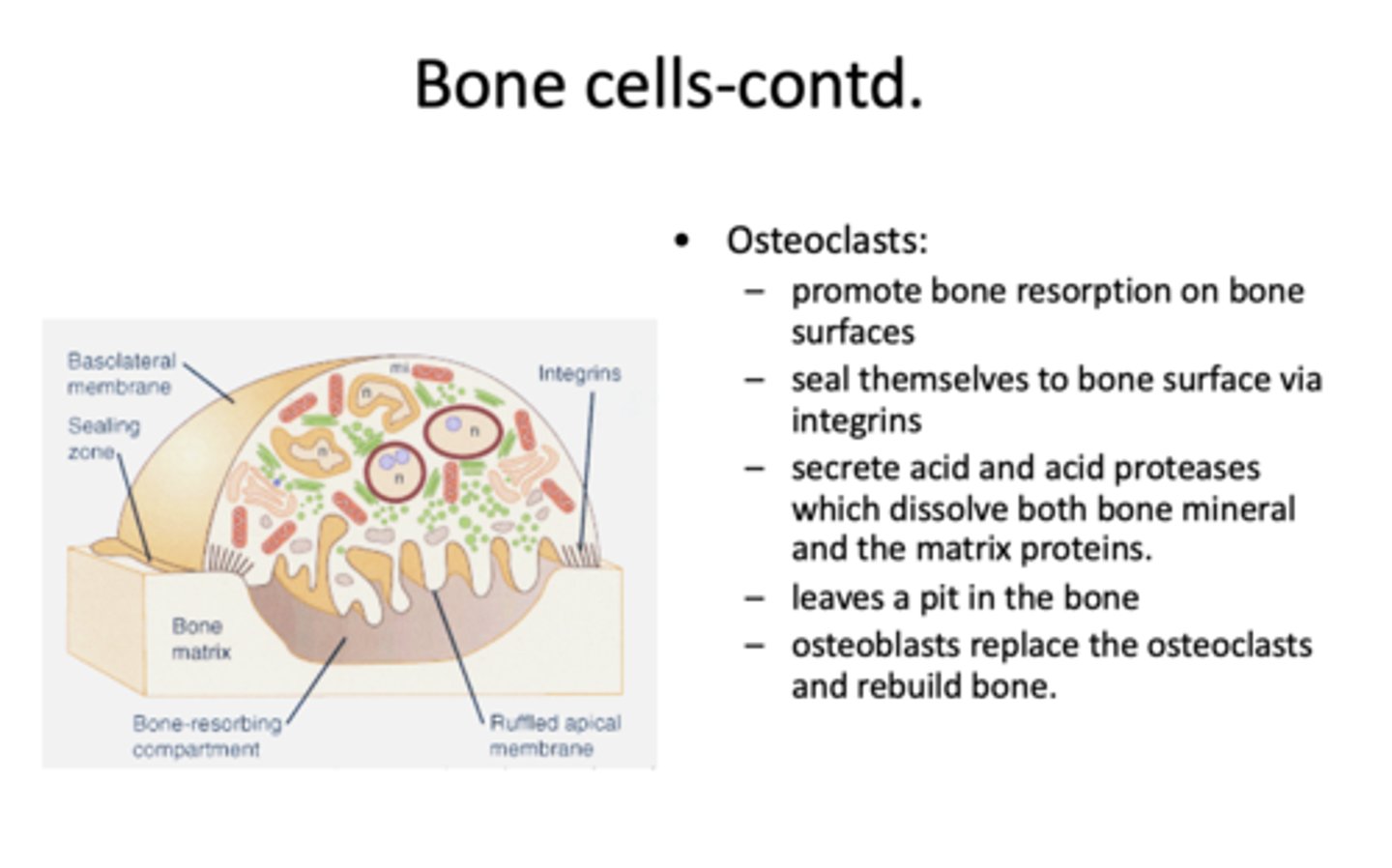
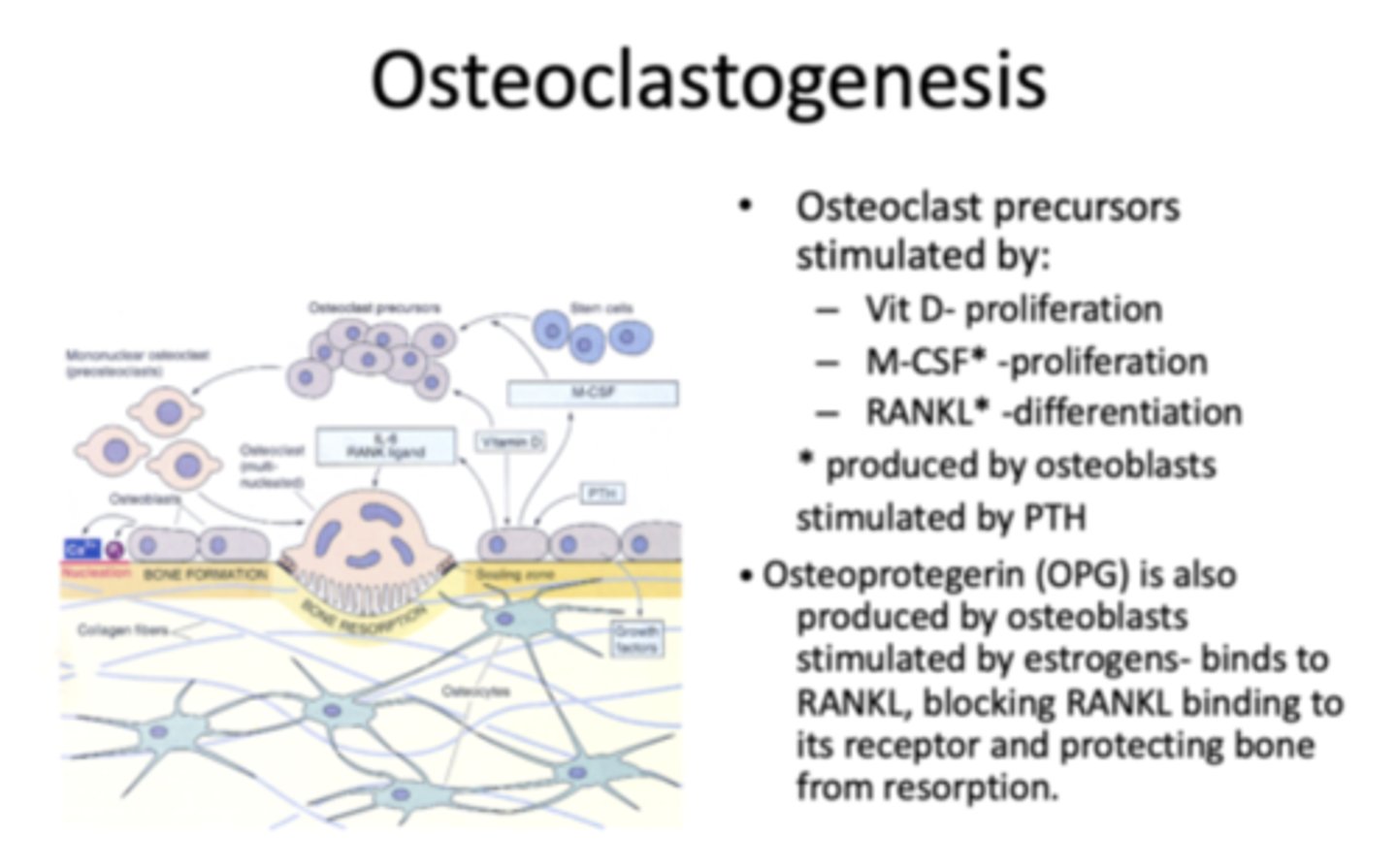
Osteoclast precursors are stimulated by what three things?
- VitD proliferation
- M-CSF proliferation
- RANKL differentiation
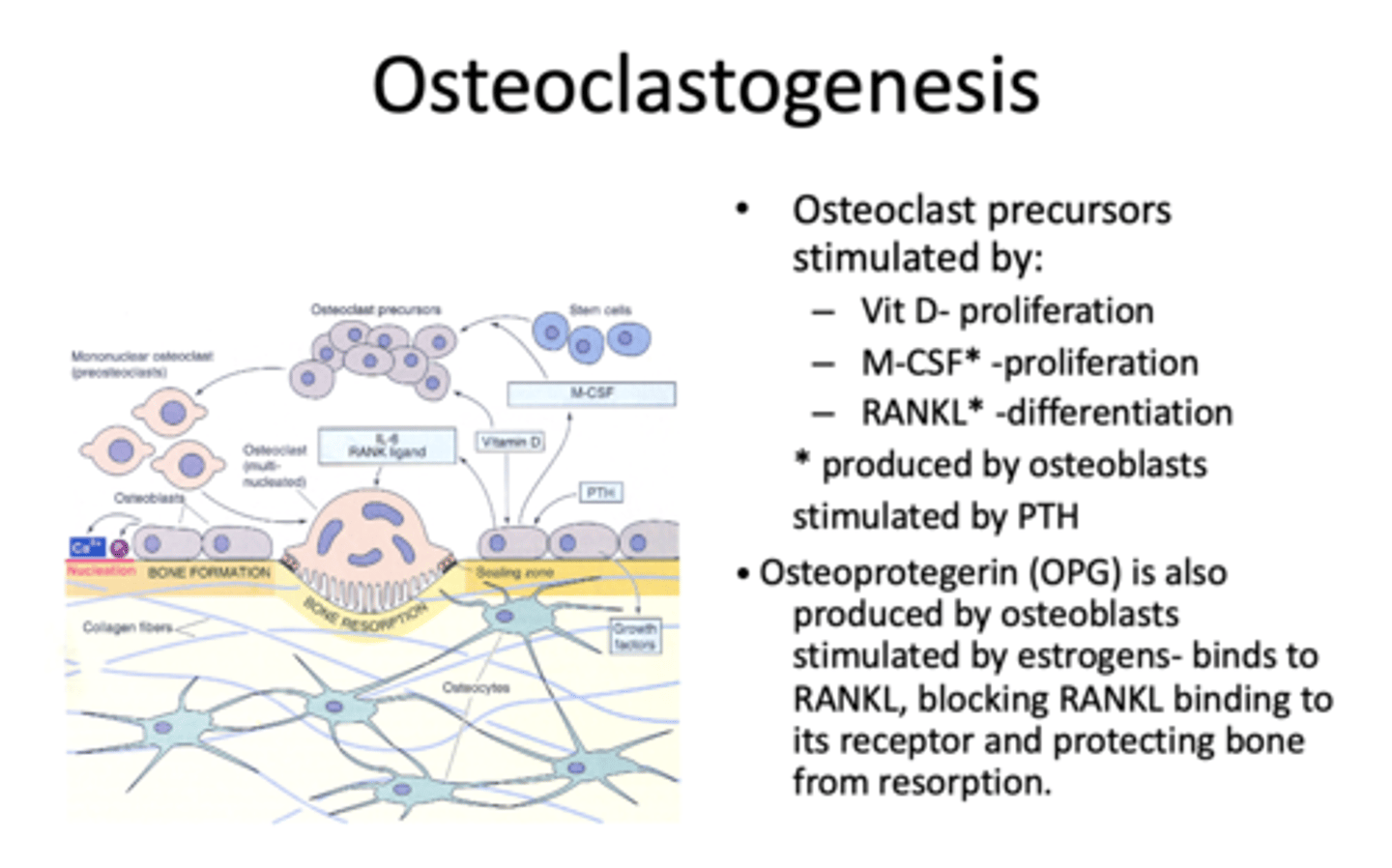
What are M-CSF and RANKL produced by?
osteoblasts stimulated by PTH
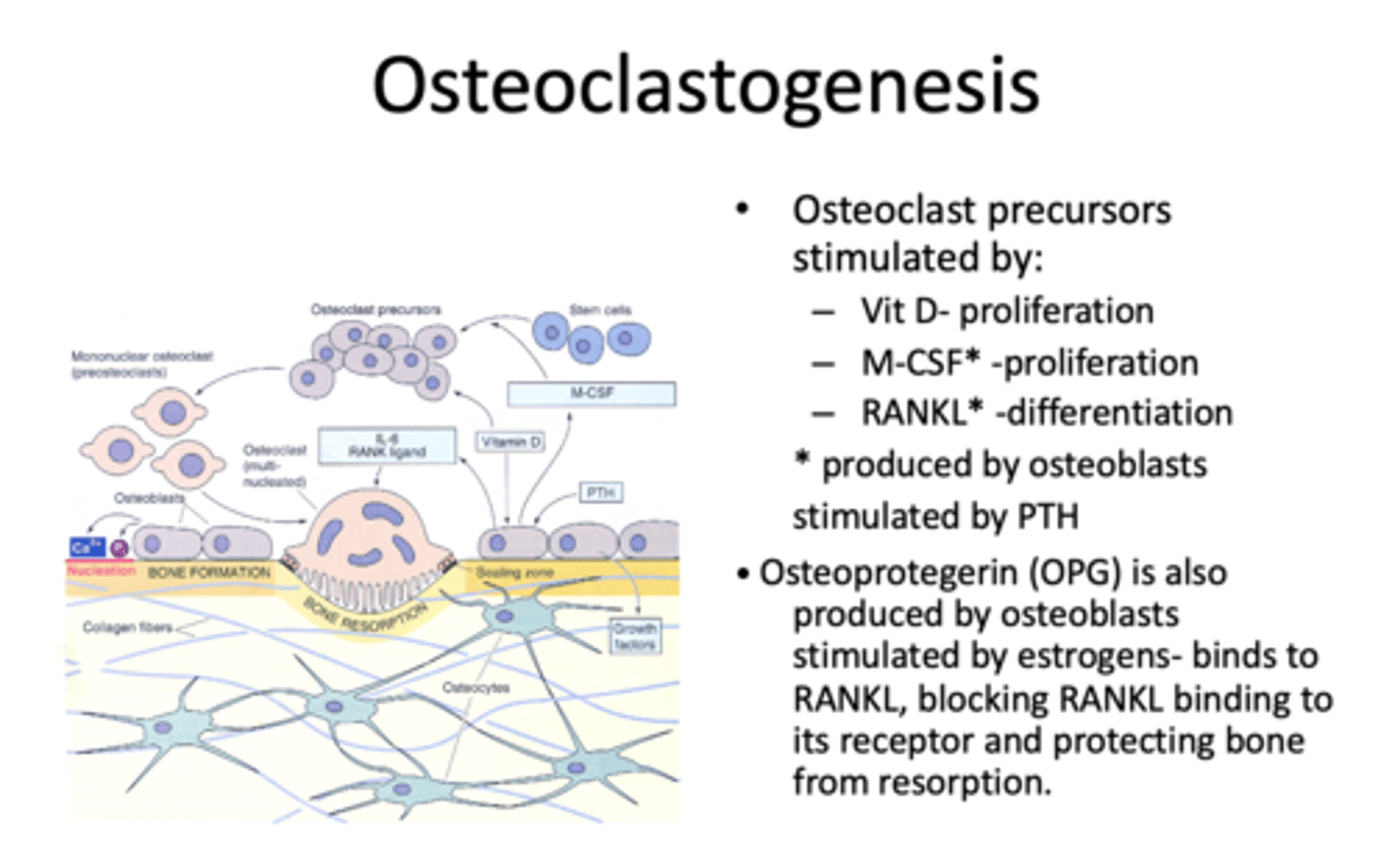
_______________ is produced by osteoblast, stimulated by estrogens- binds to RANKL, blocking RANKL binding to its receptor and protecting bone from resorption
Osteoprotegerin (OPG)
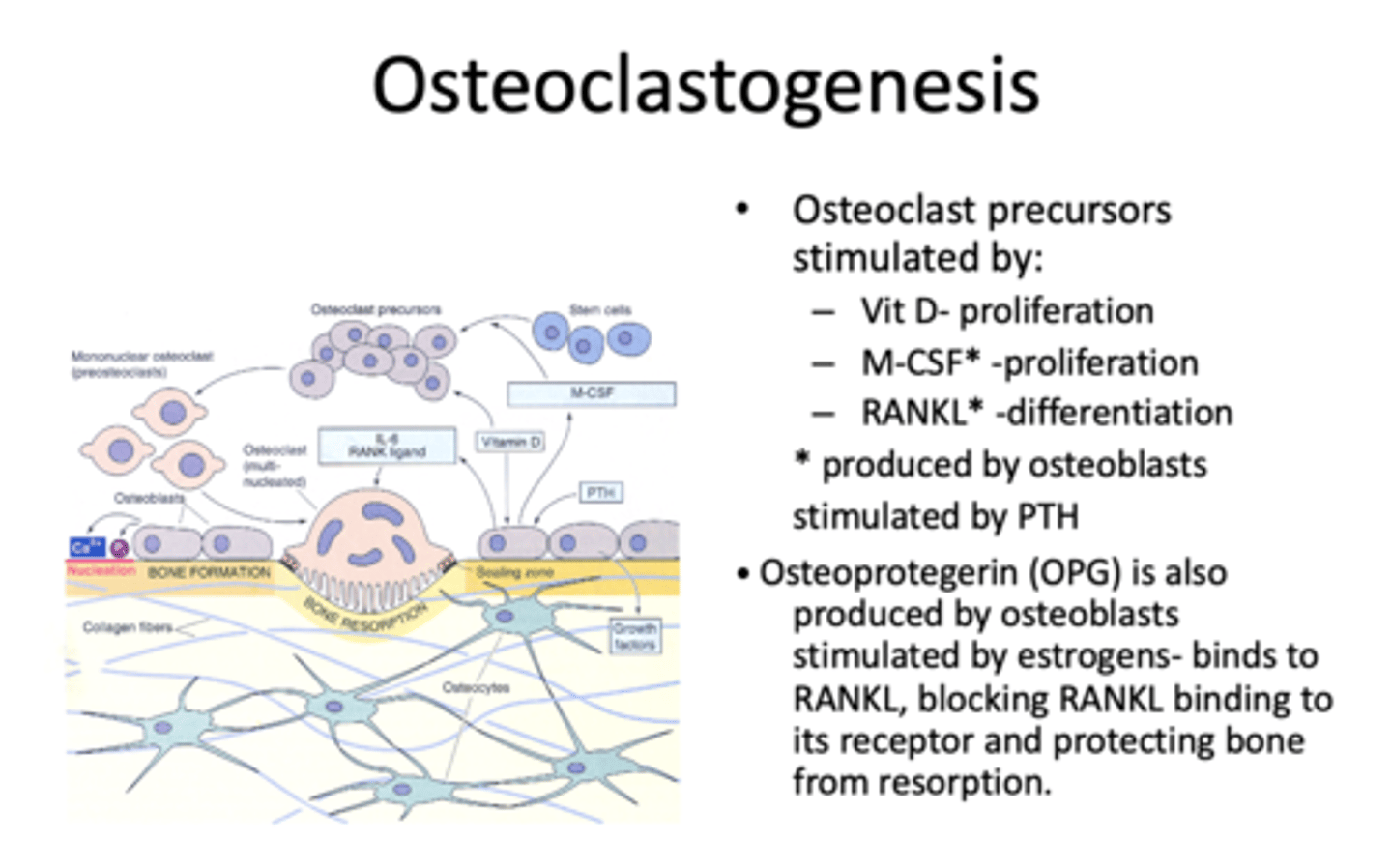
What is Osteoprotegerin (OPG) stimulated by?
Estrogens
Ca++ in bones turns over at a rate of ______% per year in infants and ______% per year in adults
100%, 18%
A local cycle of bone resorption followed by osteoblastic replacement of bone takes about ______ days
100
parathyroid hormone (PTH) and VitD3 ___________ blood Ca2+ levels
increase
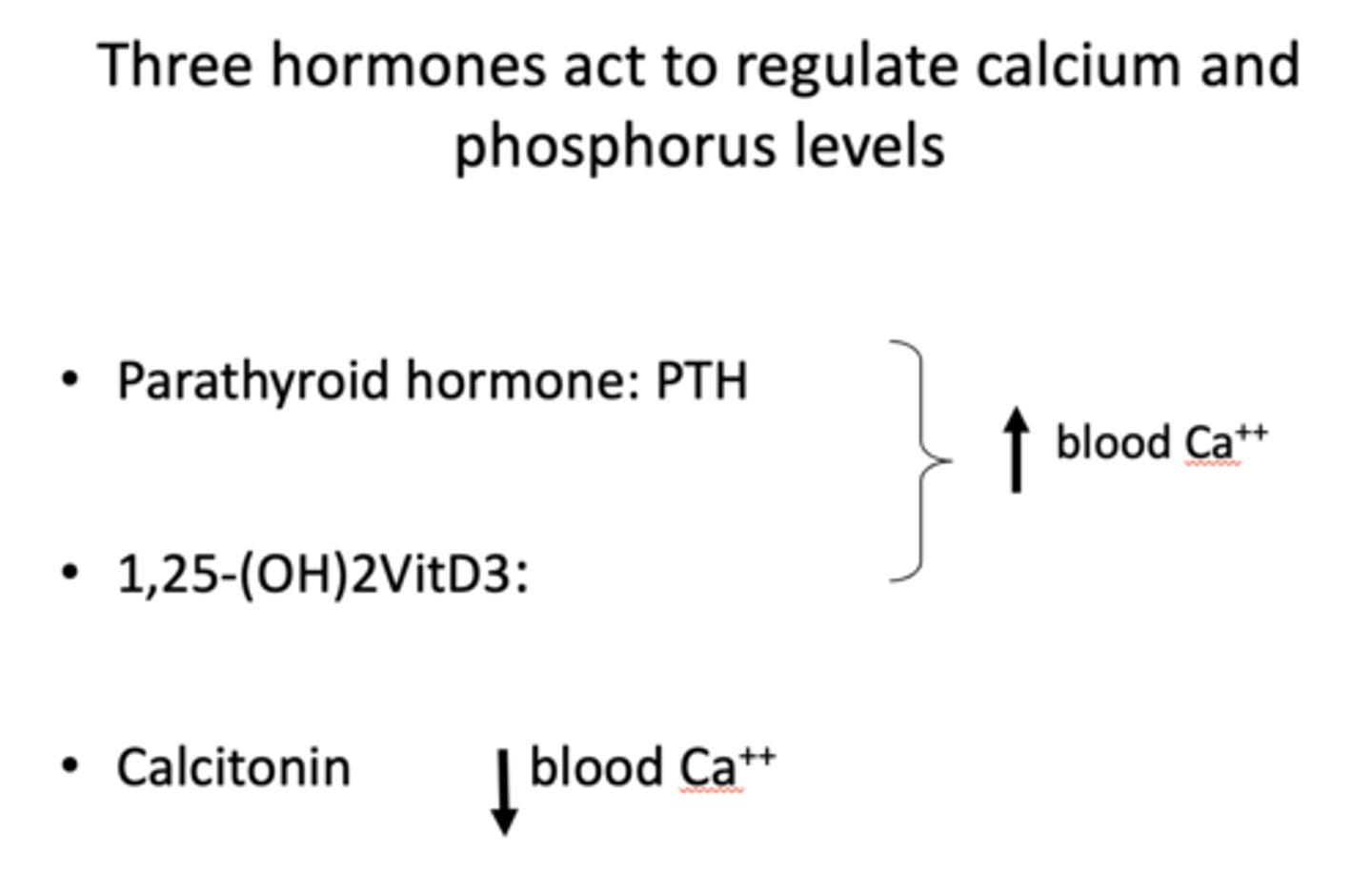
Calcitonin ___________ blood Ca2+ levels
Decreases
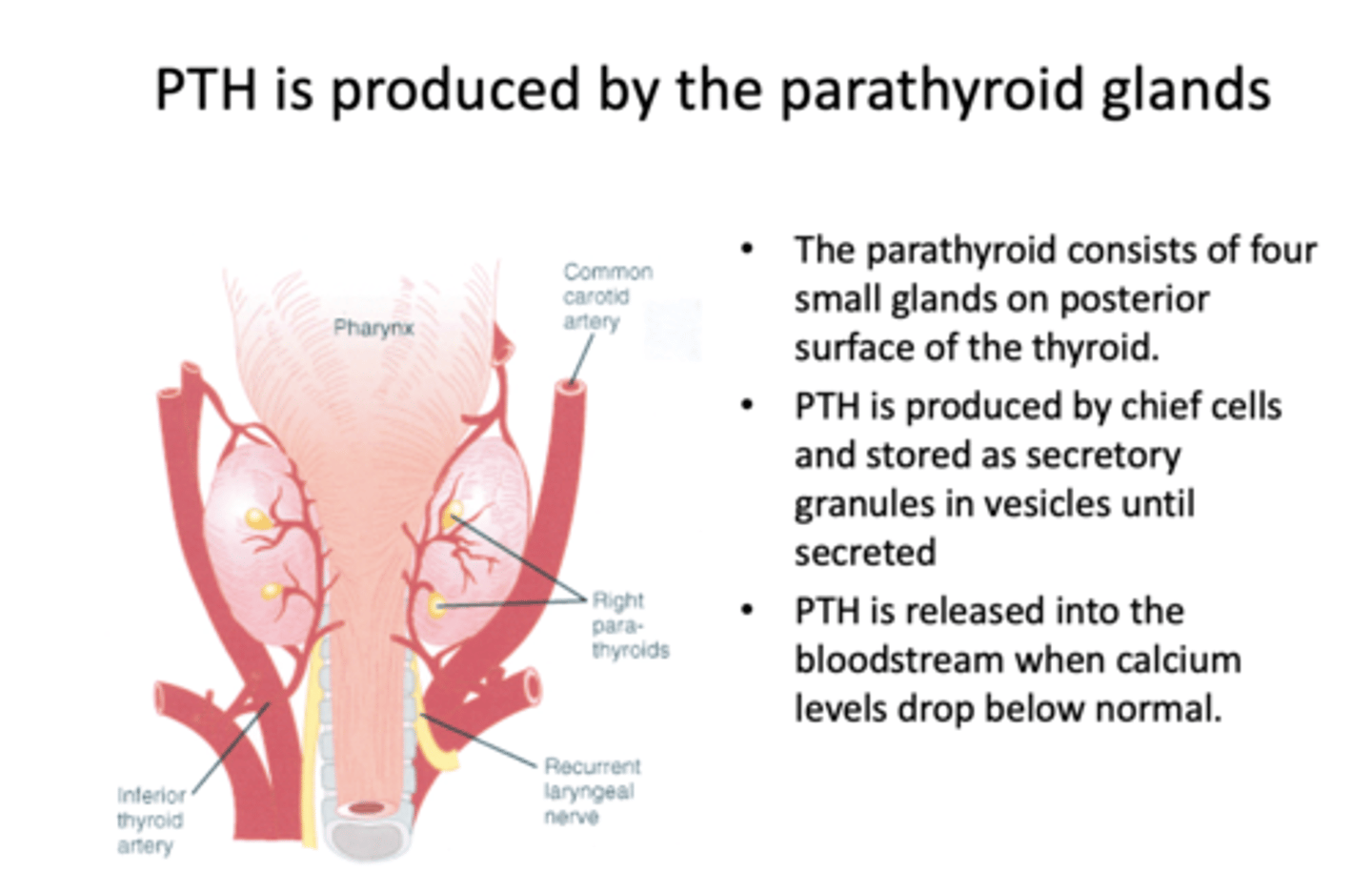
PTH is produced by what?
chief cells in parathyroid glands
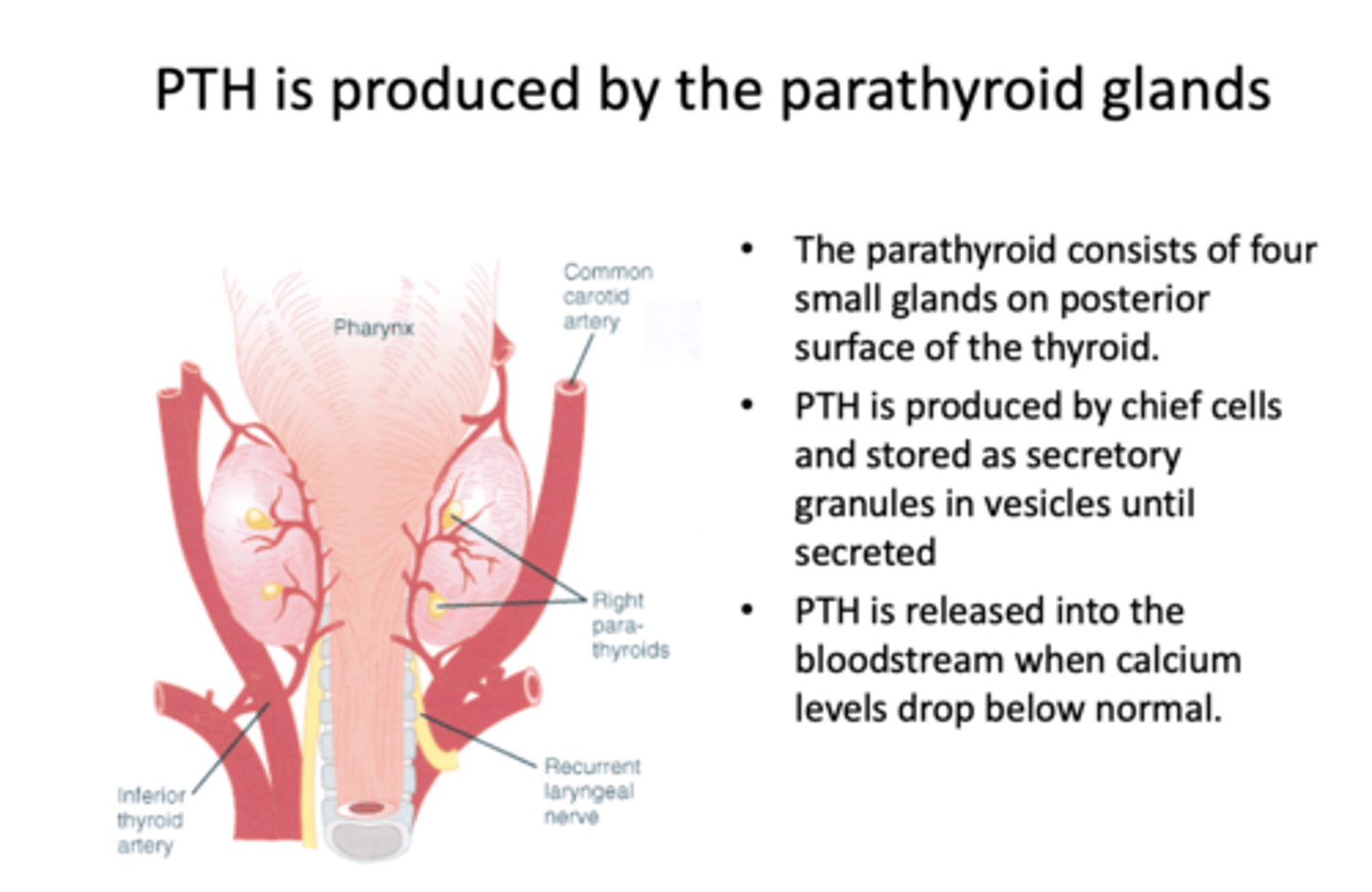
When is PTH released into the bloodstream?
When calcium levels drop below normal
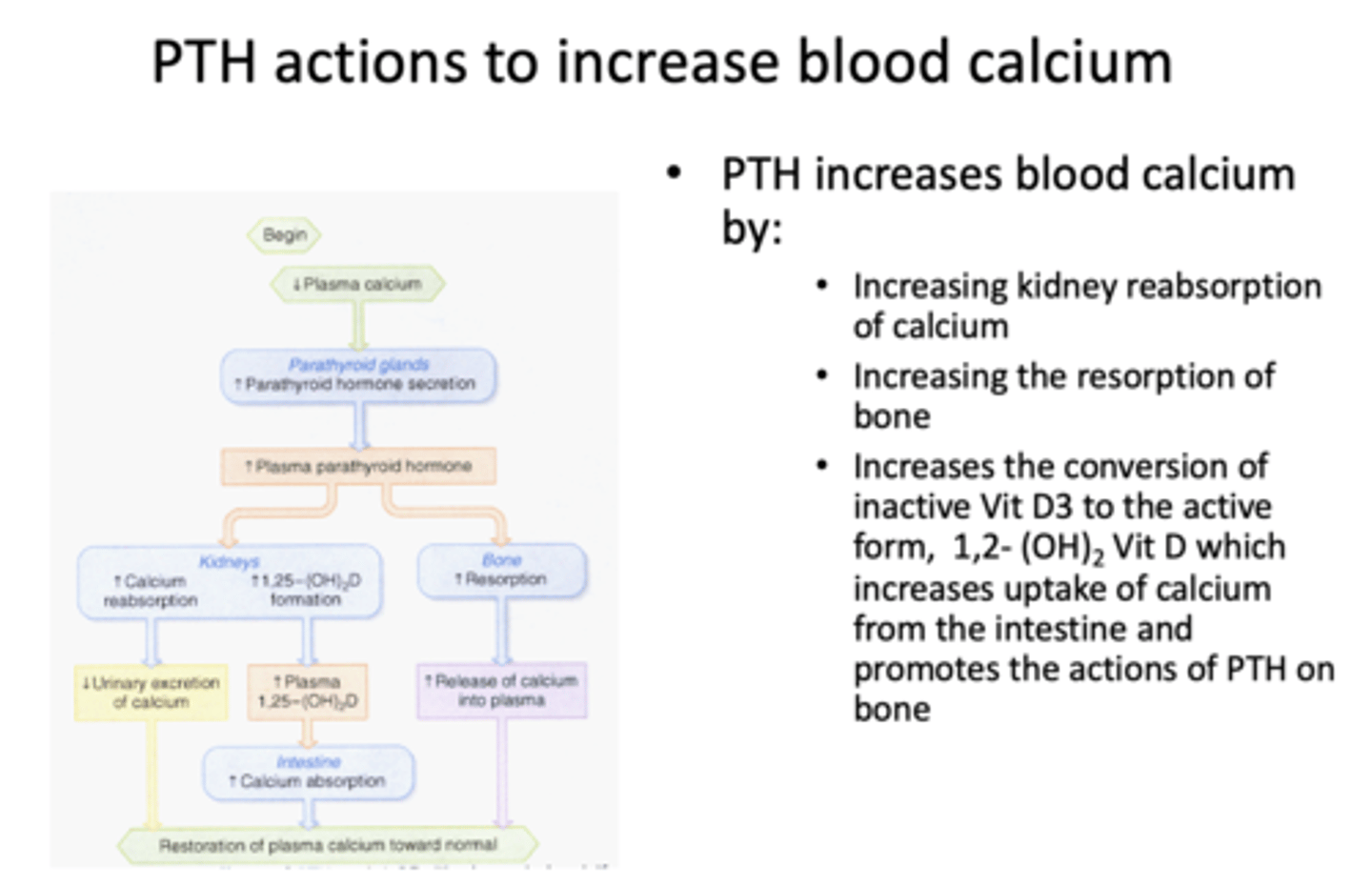
PTH increases blood calcium by what three things?
- Increasing kidney reabsorption of calcium
- Increasing resorption of bone
- Increases conversion of inactive VitD3 to active form (VitD3 increases uptake of Calcium)
PTH acts on what part of the kidney to increase Ca2+ reabsorption?
- Thick ascending loop of Henle
- DCT cells
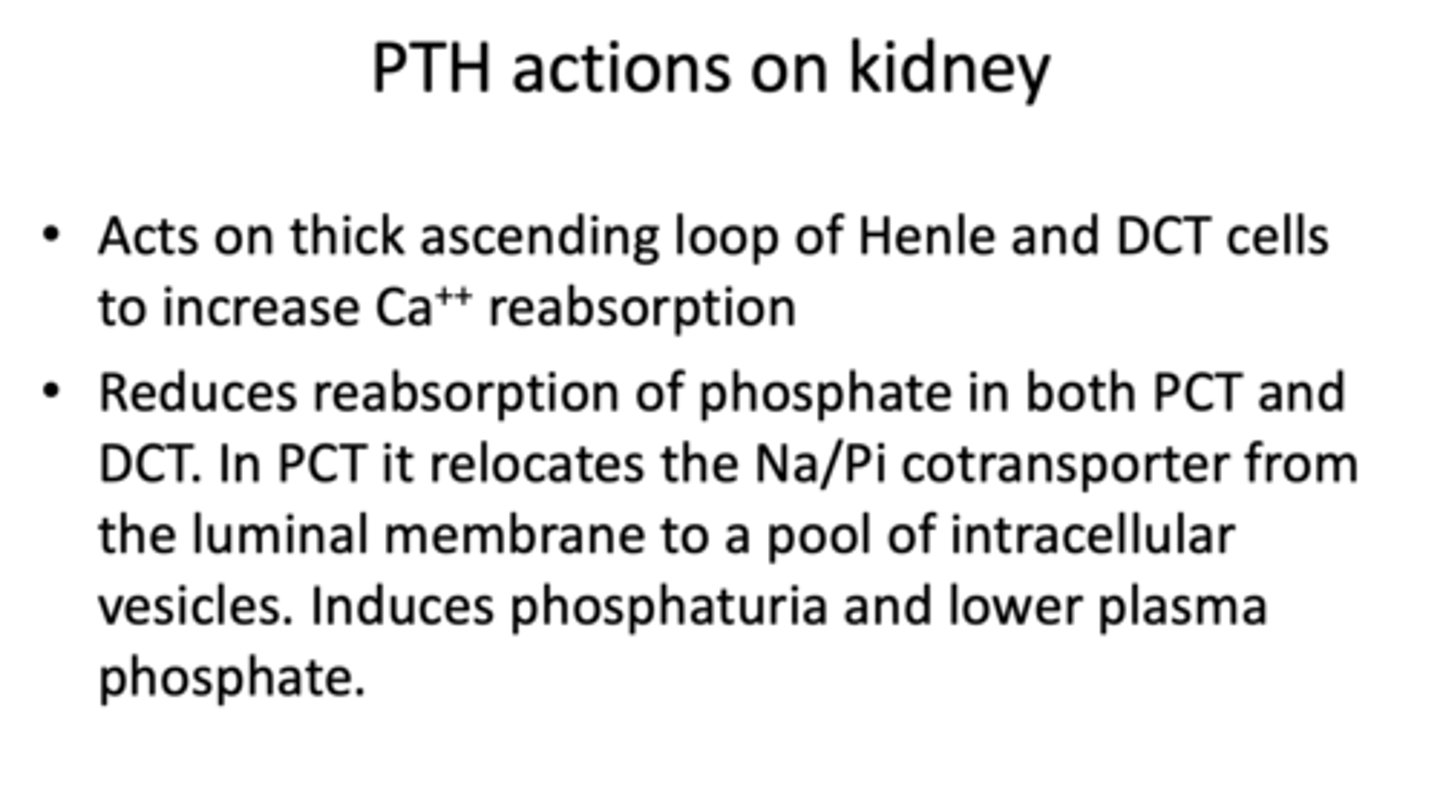
PTH reduces resorption of _______ in both PCT and DCT. In PCT, it relocates the Na/Pi cotransporter and induces phosphaturia and lower plasma volume
phosphate
What has the following characteristics?
- Acts to increase bone resorption and mobilize Ca++ and phosphates, thus increasing both in the plasma
- Binds to osteoblasts to induce secretion of cytokines that increase the number and activity of bone-resorbing osteoclasts
PTH

What promotes proliferation of monocyte/macrophages?
M-CSF (macrophage colony stimulating factor)

What promotes differentiation of precursor cells into osteoclasts?
RANKL

What is stimulated by PTH and VitD which stimulates existing osteoclasts to resorb bone?
Interleukin-6

____________ inhibits collagen synthesis by osteoblasts and promotes production of bone matrix proteases
PTH

T/F: Vitamin D3 is actually a hormone
True
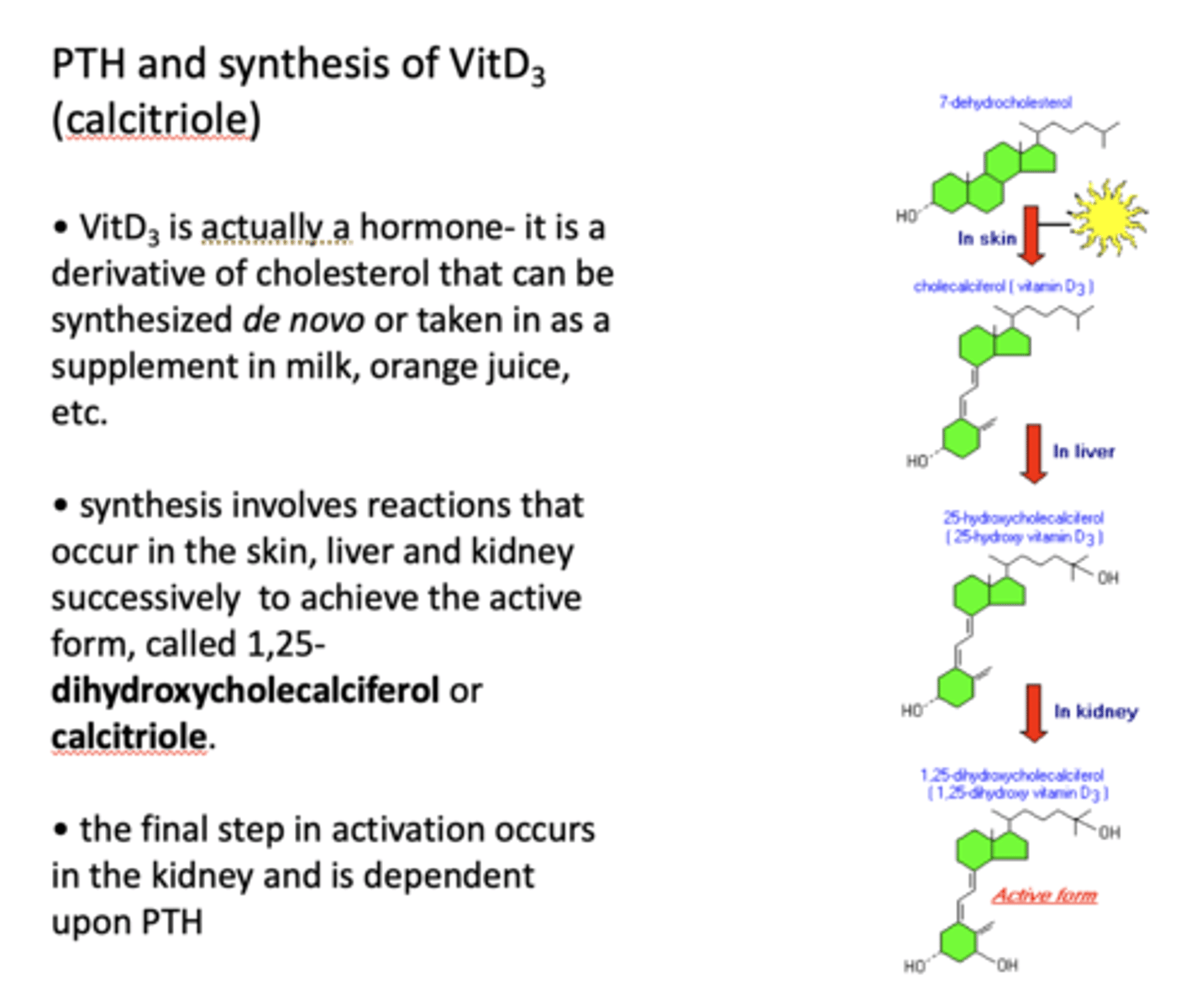
____________ is a derivative of cholesterol that can be synthesized de novo or taken in as a supplement in milk, orange juice, etc
VitD3
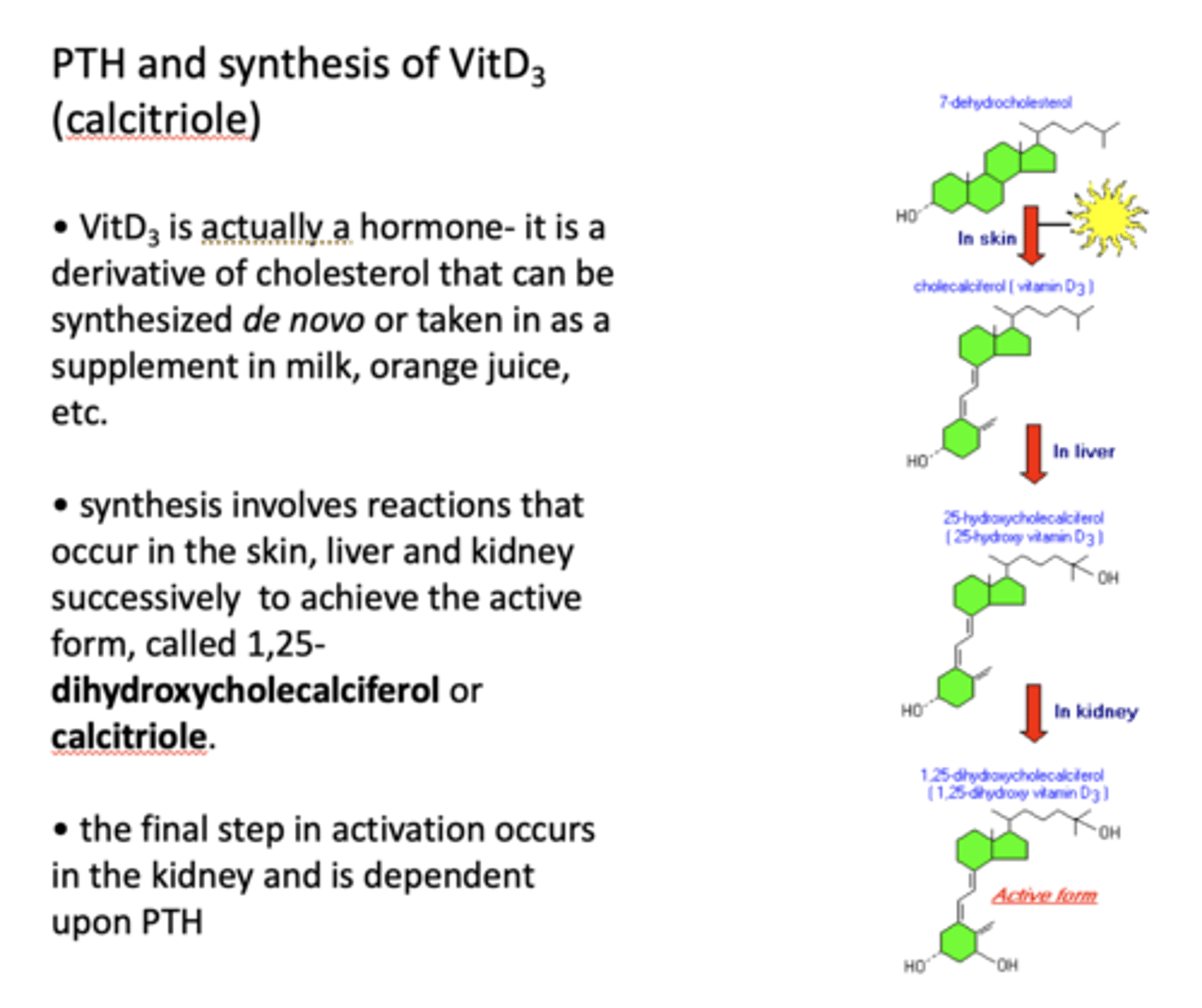
synthesis of vit D3 involves reactions that occur in the _______ successively to achieve the active form, called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or _____
skin, liver and kidney
calcitriole
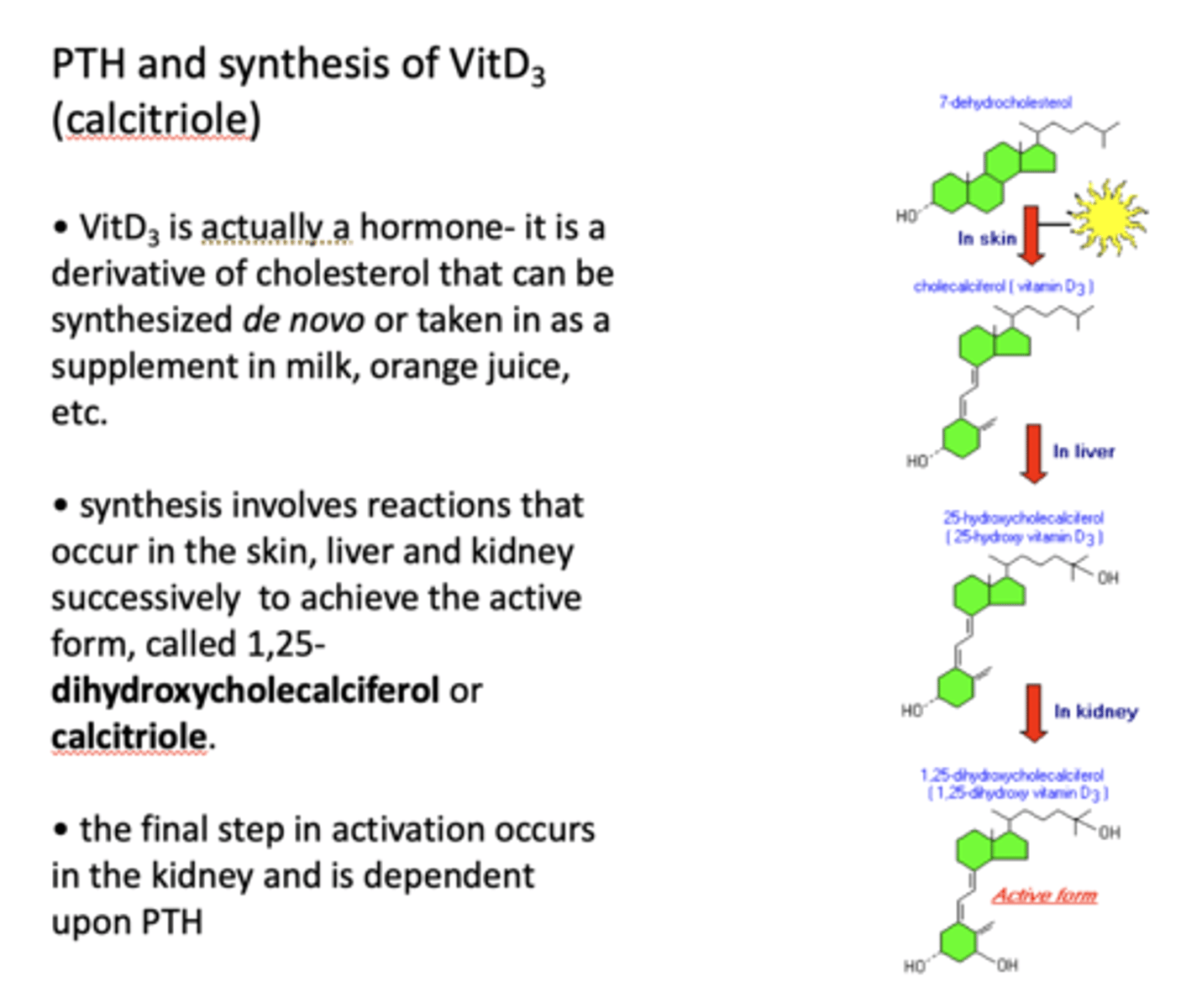
Where does the final step of activation of vitamin D3 occur? What is it dependent on?
In the kidney and is dependent upon PTH
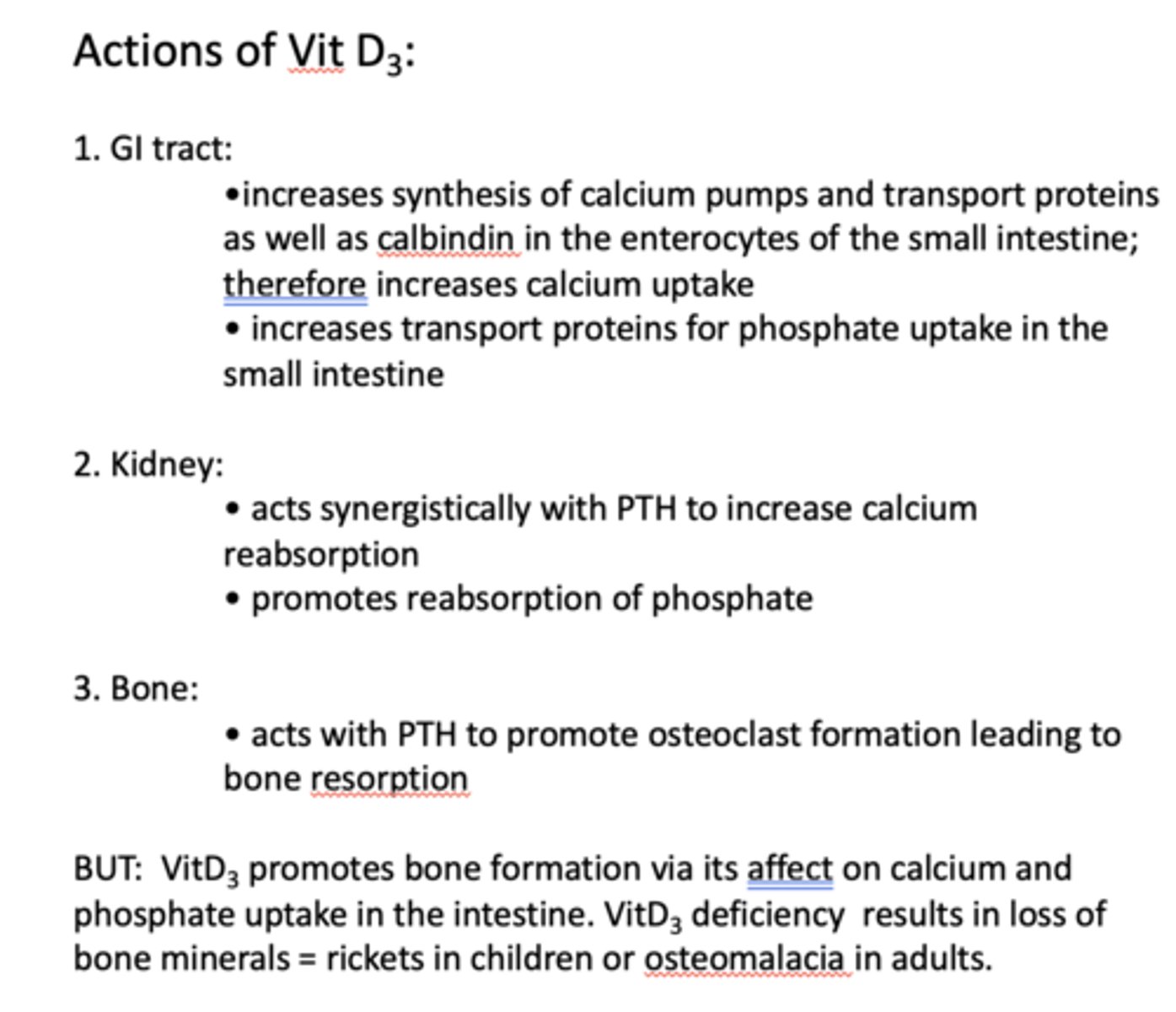
what is the action of vit D3 in GI tract?
- Increases synthesis of calcium pumps and transport proteins as well as calbindin in the enterocytes of the small intestine; therefore increases calcium uptake
- Increases transport proteins for phosphate uptake in the small intestine

what is the action of vit D3 in kidney?
- Acts synergistically with PTH to increase calcium reabsorption
- Promotes reabsorption of phosphate
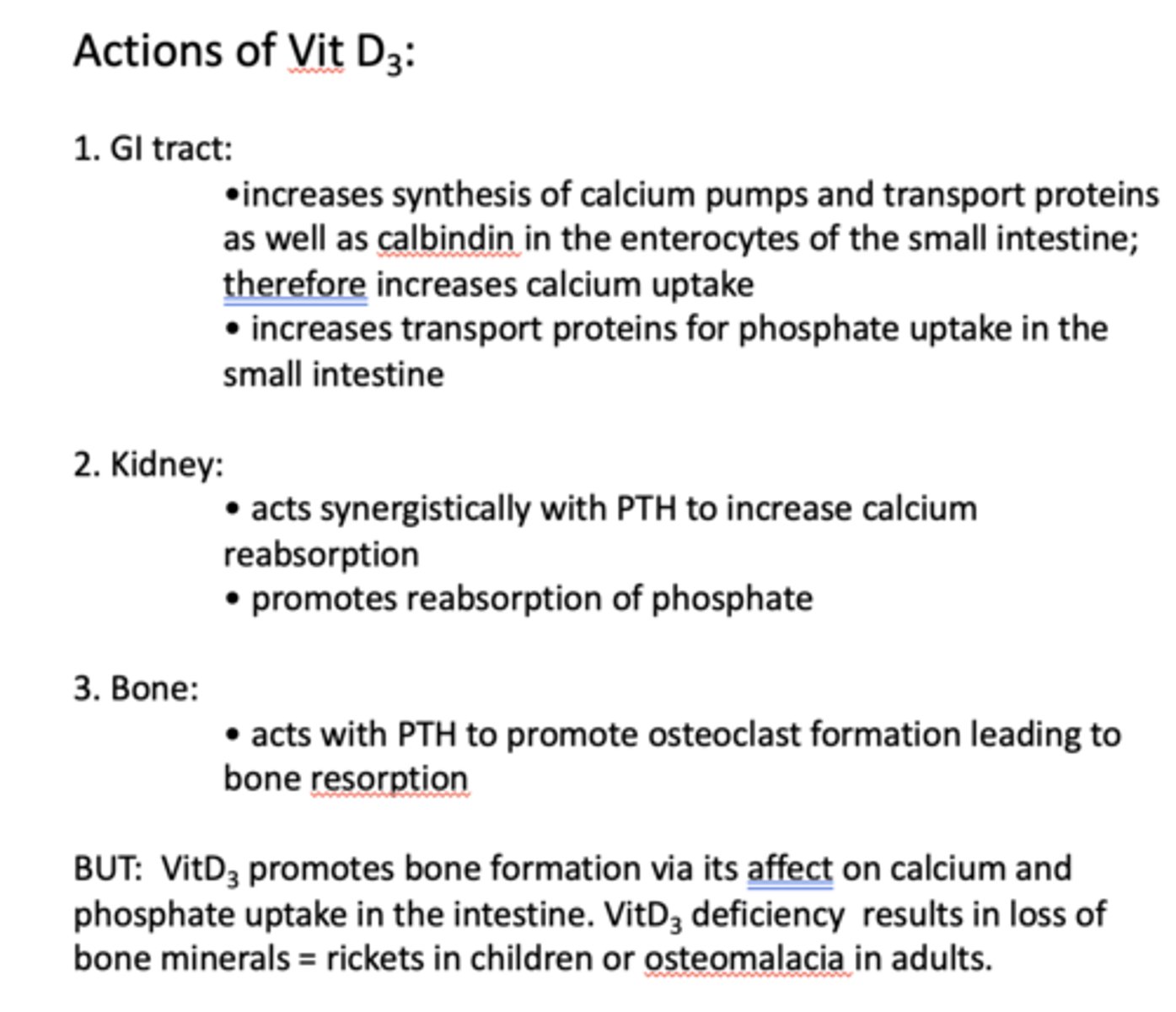
what is the action of vit D3 in bone?
- Acts with PTH to promote osteoclast formation leading to bone resorption
VitD3 deficiency results in loss of bone minerals known as what in children and adults?
rickets (in children)
osteomalacia (adults)
What has the following characteristics?
- Made in interfollicular cells in the thyroid gland and stored in secretory granules
- Secretion is triggered by increasing plasma Ca
- Effects are short-lived
calcitonin

In bone, what hormone binds to osteoclasts and inhibits bone resorption?
calcitonin

In kidneys, what increases calcium and phosphate elimination?
calcitonin

What does it imply when the removal of thyroid, which also removes the interfollicular cells, does not compromise the regulation of calcium blood levels?
Other sites must produce calcitonin

calcitonin: production
intrafollicular cells in thyroid gland
calcitonin: storage
secretory granules
calcitonin secretion is triggered by…?
increased plasma Ca2+ levels
what is the action of calcitonin in bone? in kidneys?
bone → bind to osteoclast to inhibit bone resorption
kidneys → increase calcium and phosphate elimination
(overall effect is to decrease blood calcium levles)