Hearing and balance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 3:51 AM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
cerumen
ear wax
2
New cards
protects + cleans ear
what is the function of ear wax?
3
New cards
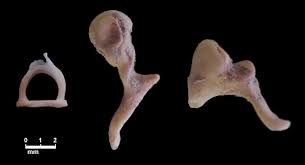
hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), stirrup (stapes)
auditory ossicles
4
New cards
amplify sound: sound moves the hammer which moves the anvil with moves the stirrup with punches the oval window and produces sound waves
what do the auditory ossicles do?
5
New cards
air
What is the middle ear filled with, normally?
6
New cards
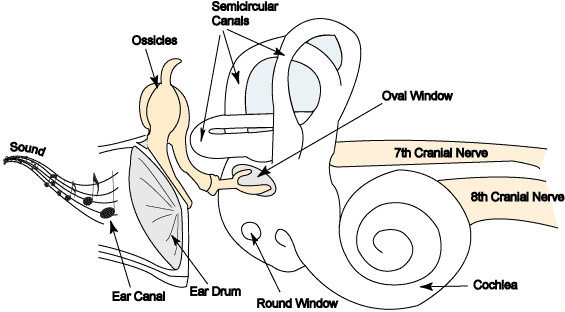
1. pinna
2. External acoustic meatus (auditory canal)
3. Tympanic membrane
2. Ossicles amplify the sound waves
3. Oval window
4. Basilar membrane in the spiral organ of Corti
5. Hair cells of the tectorial membrane are bent when the basilar membrane vibrates against it
path of conduction of sound waves
7
New cards
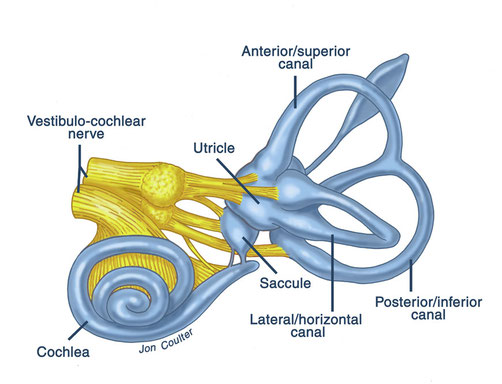
temporal bone
in what bone are the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals located?
8
New cards
hearing: inside spiral organ bathed in endolymph, resonance of basilar membrane and stimulation of hair cells to pitch of sound, hair cells detect vibrations in tectorial membrane
what stimulus is the cochlea designed to sense? How?
9
New cards
static equilibrium, linear acceleration
what stimulus is the vestibule designed to sense? How?
10
New cards
dynamic equilibrium, angular acceleration, sensation of gravity
what stimulus are the semicircular canals designed to sense? How?
11
New cards
spiral organ/organ of corti
part of cochlear duct
Hair cells (and support cells) sit on basilar membrane
Tectorial membrane sits on top of hair cells
As sound waves move through vestibuli they oscillate the tectorial and basilar membranes impacting the hair cell
Hair cells (and support cells) sit on basilar membrane
Tectorial membrane sits on top of hair cells
As sound waves move through vestibuli they oscillate the tectorial and basilar membranes impacting the hair cell
12
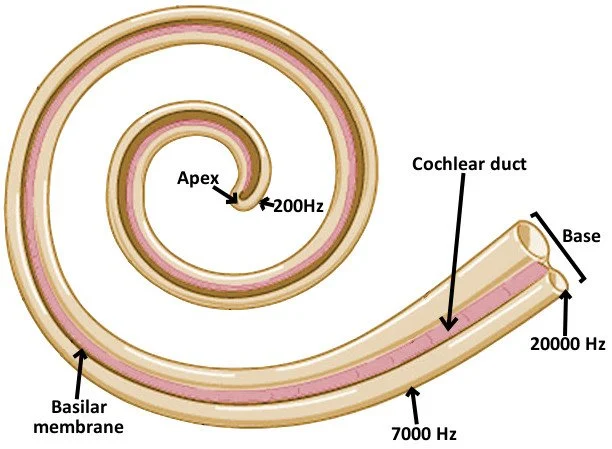
New cards
basilar membrane
Hair cells of the tectorial membrane are bent when the _____ ____ vibrates against it
hair cells sit on top
found in cochlea
hair cells sit on top
found in cochlea
13
New cards
tectorial membrane
found in cochlea
movement detected by hair cells
sits on top of hair cells
movement detected by hair cells
sits on top of hair cells
14
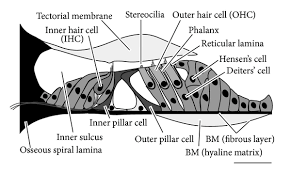
New cards
3 outer rows of hair cells
1 of 2 types of hair cells in spiral organ
MOTOR
DANCE
served by motor Efferent fibers
possibly modulate movement of tectorial membrane
protect from overstimulation
MOTOR
DANCE
served by motor Efferent fibers
possibly modulate movement of tectorial membrane
protect from overstimulation
15
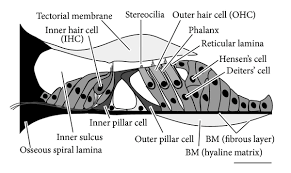
New cards
1 inner row of hair cells
1 of 2 types of hair cells in spiral organ
SENSORY
link to sensory Afferent fibers
primary output of nerve impulse
SENSORY
link to sensory Afferent fibers
primary output of nerve impulse
16
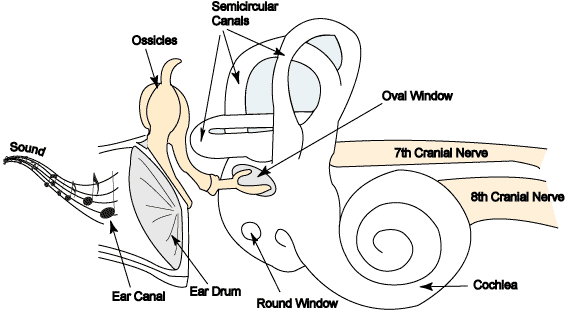
New cards
oval window
on the cochlea
entry for sound E
energy from the “stirrup” hitting it
entry for sound E
energy from the “stirrup” hitting it
17
New cards
round window
found on cochlea
exit for sound E
vestibule
**sound dissipates**
with aging: becomes more stiff
exit for sound E
vestibule
**sound dissipates**
with aging: becomes more stiff
18
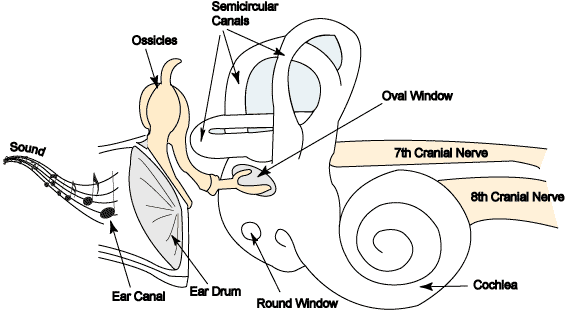
New cards
inside the cochlear duct
Where is perilymph found?
19
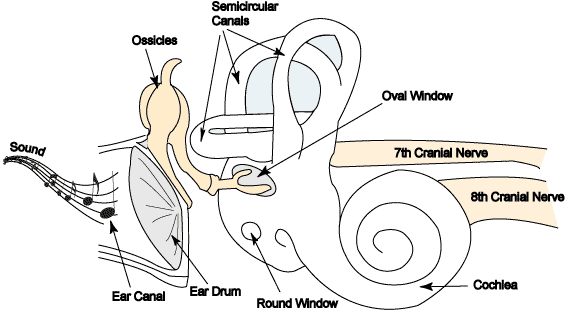
New cards
Inside the semicircular canals and the vestibule
Where is endolymph found?
20
New cards
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
cranial nerve for hearing and balance
21
New cards
vestibular and cochlear branch
branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve
22
New cards
nystagmus
vision condition in which the eyes make repetitive, uncontrolled movements because the brain and the eye aren’t on the same page and that affects the way our brains interpret movement signals from the eye
23
New cards
your middle ear can feel that you are moving, but if your eyes are focused on something unmoving, your balance and your sight don’t match up, and your brain can’t make sense of the signals, triggering a nauseous response
why do people get motion sickness?
24
New cards
pitch is set by frequency of sound waves, volume is set by intensity or amplitude of a sound wave
What determines a sound's pitch? volume?
25
New cards
pitch is determined by the location of the cells stimulated in the cortex (sympathetic vibrations), volume is determined by the frequency of the arriving impulses
longer cells=sense lower pitched sounds
longer cells=sense lower pitched sounds
How are pitch and volume "sensed" by the cochlea?
26
New cards
frequency
sets pitch (high ______ = high pitch)
measured in Hz (cycles per second)
“wavelength”
measured in Hz (cycles per second)
“wavelength”
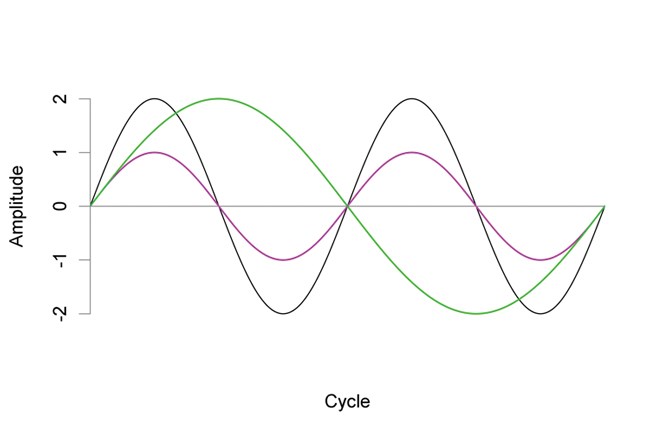
27
New cards
wavelength
determines frequency of sound (which sets the pitch)
measured in HZ
measured in HZ
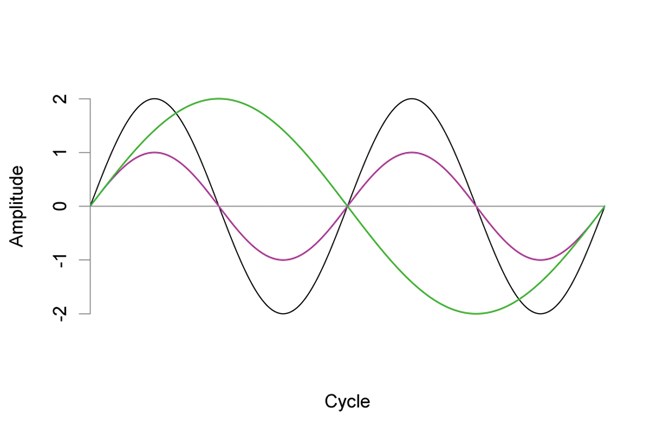
28
New cards
amplitude
“intensity” of a sound wave
determines volume (loudness)
measured on logarithmic scale decibel (dB)
determines volume (loudness)
measured on logarithmic scale decibel (dB)
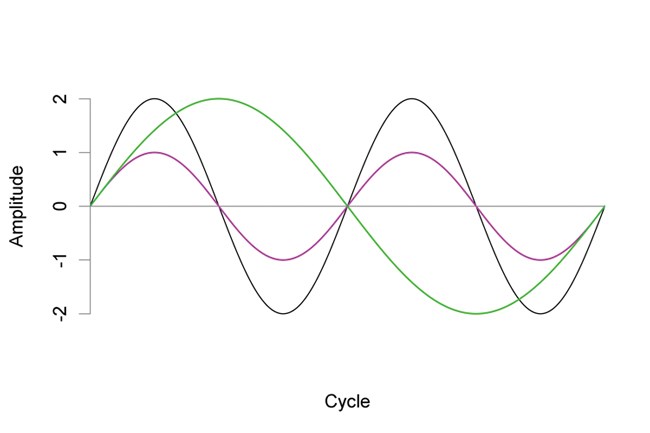
29
New cards
the location of the hair cells in the spiral organ that vibrate from a sound wave determines the pitch (longer cells=lower pitch)
How do we perceive pitch?
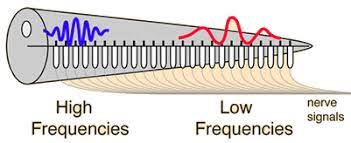
30
New cards
shorter hair cells
Where are high frequency sounds sensed in the cochlea?
31
New cards
long hair cells
Where are low frequency sounds sensed in the cochlea?
32
New cards
death of hair cells, defect with inner ear
Why does our sense of hearing decline as we age (Presbycusis)?
33
New cards
semicircular canals, vestibule
component parts of vestibular apparatus
34
New cards
hair cells + supporting tissue contain the otoliths which is the ear stone that slides over gel and bend hair cells as head moves
what’s the macula and what’s inside it?
35
New cards
otoliths
ear stones
made of calcium and carbonate
slide over gel and bend hair cells as head is moved
made of calcium and carbonate
slide over gel and bend hair cells as head is moved
36
New cards
utricle
one of otolith organs that senses forward tilt and acceleration
ex: Feeling when you slam on breaks
ex: Feeling when you slam on breaks
37
New cards
saccule
otolith organ senses vertical forces like gravity
ex: feeling when you drop in elevator
ex: feeling when you drop in elevator
38
New cards
semicircular canals
Where are the cristae ampullares?
39
New cards
cupula
gelatinous structure in the crista ampullaris that moves when hair cells around is move from changes in velocity of rotational movement
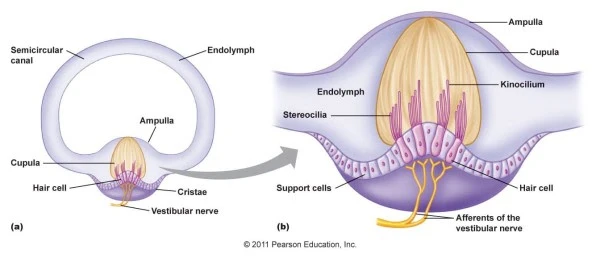
40
New cards
angular acceleration (gyroscope)
What type of motion is sensed by the semicircular canals?
41
New cards
deafness
hearing loss → no sound
42
New cards
conduction deafness
sounds cannot get through the outer and middle ear
43
New cards
sensorineural deafness
hearing loss as the result of damage to the inner ear
44
New cards
central deafness
hearing loss from damage to the cochlear nuclei or the central pathways that relay auditory information to the auditory cortex
45
New cards
tinnitus
the perception of sound that does not have an external source, so other people cannot hear it
ex: ringing, humming, buzzing in your ear
ex: ringing, humming, buzzing in your ear
46
New cards
Meniere’s syndrome
a disorder caused by build of fluid in the chambers in the inner ear
symptoms: vertigo, nausea, vomiting, loss of hearing, ringing in the ears, headache, loss of balance, and sweating
mom
symptoms: vertigo, nausea, vomiting, loss of hearing, ringing in the ears, headache, loss of balance, and sweating
mom
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago