Lecture 18 - Viral Diseases
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Bornavirus
What avian virus causes PDD, and affects psittacines? It is an RNA virus, is transmitted fecal-oral and possibly vertical, and causes lymphoplasmocytic ganglionueritis, causing progressive destruction of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The nerves of the GIT are most commonly affected, especially in the esophagus, crop, proventriculus, and ventriculus, leading to impairment of peristaltic function and food accumulation in the proventriculus and crop.
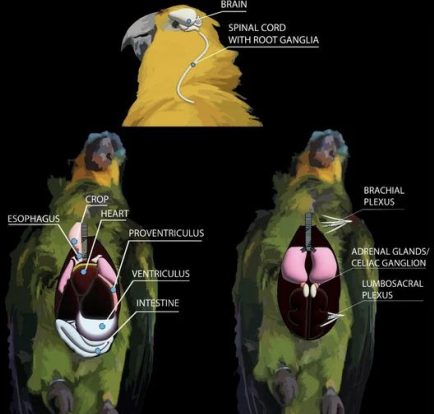
Proventricular Dilation
What disease is caused by bornavirus in psittacines? Signs include weight loss, normal appetite, undigested seeds in feces, and vomiting/regurgitation. CNS signs can include tremor, incoordination, blindness, and seizures, as well as lethargy and ruffled feathers. The course is unpredictable, as positive birds can remain healthy for years, signs may be induced during stress, and a poor prognosis occurs once disease develops.
GI
What body systems’ nerves are affected by bornavirus/PPD, leading to accumulation of food?
Proventriculus
PPD/Bornavirus is diagnosed by an enlarged which organ on radiography? Fluoroscopy, GI biopsies, RT-PCR on crop swab, serology, and post-mortem exam are also used.
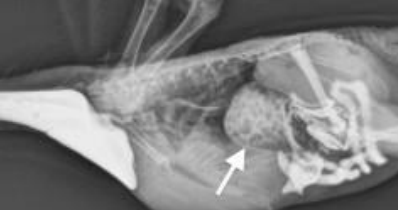
Celecoxib
What NSAID drug can be given PO daily for long-term periods to help manage PPD? Nutritional support, antiemetics, control of secondary infections, and switching to extruded diets can also be done.
No
Can life expectancy be predicted for PPD/Bornavirus?
Circovirus
What virus causes PBFD (Psittacine beak and feather disease), is a DNA virus, affects many wild and captive psittacines worldwide, may have originated in Australia, is common in pet stores, and affects birds at varying rates of susceptibility? Horizontal transmission via feces, dander, and regurgitation will occur.

PBFD
What disease (abbreviated) is caused by Circovirus in psittacines and has more susceptibility in young birds, and has acute and chronic forms?
Young
Are young or old birds more susceptible to PBFD/Circovirus?
Budgerigars
Which birds are commonly asymptomatic to PBFD/Circovirus?
Lorikeets
Which birds may recover from, and become carriers and spreaders for, PBFD/Circovirus?
Yes
Are cockatoos and African gray parrots especially susceptible to PBFD/Circovirus?
Acute
Which form of PBFD occurs in nestling/fledgling birds especially in African gray parrots and black cockatoos? Fractures of developing feathers, intrapulp hemorrhage, edema of wing tips, leukopenia, anemia, green diarrhea, regurgitation, and rapid death from hepatic necrosis will all occur.
Chronic
Which form of PBFD occurs with gradual loss of plumage bilaterally, along with dystrophic feathers (short, retained sheath, bloody), secondary infections, and difficulties in eating, leading to hypoproteinemia, weight loss, and death?
Cockatoos
What birds with chronic PBFD will get loss of powder down, bare skin patches, glossy beak, abnormal beak/nails, and skin hyperkeratosis?
Leukopenia
What condition is diagnostic of acute PBFD?
Hypoproteinemia
What condition is diagnostic of chronic PBFD?
PCR
What diagnostic method is best for PBFD, other than clinical signs? Serology, postmortem exams, and skin biopsies/histology are also used.
No
Is there any good treatment for PBFD besides supportive treatment? Recovery is possible in some birds with protective immunity, and biosecurity is very important, while a vaccine is still experimental.
Polyomavirus
Which virus is a DNA virus, is also called APV, mainly affects young psittacines, and has affinity for epithelial, lymphoreticular, and endothelial cells? It is also called Budgerigar fledgling disease but also affects other young psittacines. It is shed in feces, crop secretions, skin, and feather dander, and is spread by ingestion and inhalation. Surviving birds will continue to shed for months. It is also called French moult.

Budgerigars
Polyomavirus is also called fledgling disease of which birds, usually affecting 1-3 week old birds? It causes acute lethargy, crop stasis, and death, with cutaneous hemorrhage, ascites, and head tremors, while surviving birds will show feather dystrophy.
PCR
What diagnostic test is best for polyomavirus/APV, while serology, histopathology, supportive treatment, and prevention are also important? It can be done on blood, oral, or cloacal swab. A vaccine does exist but is recommended for older birds.
1
Which psittacid herpesvirus is a DNA virus, was first seen in SA, and causes both Pacheco disease and mucosal papillomatosis? It is spread by oral secretions and droppings, and by ingestion. Birds with lifelong infection can be spreaders, and repeat PCR testing and meticulous PE should be done before introducing new birds. Vaccines may be used but the main one has been discontinued.
Pacheco
What disease is caused by Psittacid herpesvirus 1 is highly contagious, causes sudden death, is sometimes preceded by depression and biliverdin-stained urates, can cause hepatic/splenic necrosis, is treated with acyclovir if symptoms are noticed in time, and can be a carrier condition in macaws, amazon parrots, and conures?
Acyclovir
What antiviral can be given to treat the pacheco disease form of psittacid herpesvirus 1?
Mucosal papillomatosis
What disease condition is caused by psittacid herpesvirus 1, affects mainly macaws and Amazon parrots, forms papillomas in the oral cavity and cloaca which can come and go and then spread to the GI tract? There will be blood in droppings, papilloma prolapses in the cloaca, upper GI signs (wasting disease, regurgitation), bile duct/pancreatic duct carcinomas in some birds, and chronic liver disease. It is diagnosed with PE or PCR, and is treated only with surgery, Acyclovir is not effective.
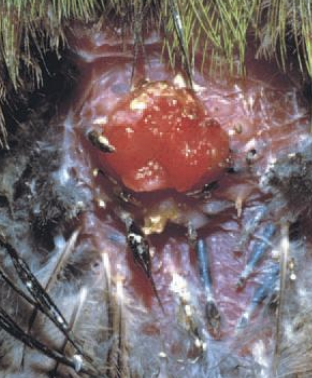
Poxvirus
Which virus can be transmitted by mosquito bites, fomites, bites, and skin injury? It is mostly found in birds housed outside, as well as domestic pigeons and free-range birds. There are three forms of disease, it is diagnosed with clinical signs and histopathology, treatment is only supportive, and prevention is done with vaccines for pigeons and canaries as well as with biosecurity.

Drypox
Which form of poxvirus infection displays raised lesions on the face, feet, and under the wings? It is normally self-limiting and has low mortality, with lesions regressing in a few weeks.
Wetpox
Which form of poxvirus infection is also called mucosal pox, displays blepharitis, conjunctivitis, diphtheritic lesions of the oral cavity/trachea, and has high mortality in canary aviaries?
Systemic pox
Which form of poxvirus infection displays acute onset of depression, anorexia, dyspnea, and peracute death, along with air sacculitis and pneumonia?
1
Which type of Paramyxovirus causes both exotic Newcastle disease and Pigeon paramyxovirus? If this is suspected, the official vet must be contacted, as it is notifiable.

Exotic Newcastle
Which disease form of Paramyxovirus-1 has entered the US through smuggled parrots, is regulated by strict laws on movement of birds, and causes depression, anorexia, respiratory symptoms, diarrhea, ataxia, and torticollis, with mainly CNS signs?
Pigeon
Which paramyxovirus-1 disease form is endemic in feral pigeons and doves, is problematic for racing pigeon flocks, causes CNS signs, diarrhea, and polyuria, has high mortality, and requires vaccination of pigeons at 6 weeks prior to racing seasons?
Influenza
Avian what virus is of concern for birds housed outdoors, spread from contact with wild birds, is notifiable, requires strict biosecurity, has some temporary regulations, has a tightly regulated vaccine, and requires all zoos to have contingency plans for it?
Flavivirus
WNV and EEC are both what type of virus, is mosquito-borne, causes fatal encephalitis in humans, horses, and birds, causes unspecific signs and sudden death, is kept in birds as a reservoir, and is more susceptible in some birds than others, like sentinels? Eating infected birds can also be infective, while PCR, isolation, and serology are diagnostic and prevention requires avoiding mosquito exposure.
WNV
Which flavivirus affects birds of prey, crows, and jays?
EEE
Which flavivirus affects pheasants, partridges, cranes, and ratites?