Aspects of Medical Imaging and Technology
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
What does traditional MRI image?
proton content
What are specialised, newer MRI machines image?
noble gases
What is an analogue measurement?
When a quantity is continuous
What is a digital measurement?
When a quantity is discrete
What does ADC stand for?
Analogue-Digital Converter
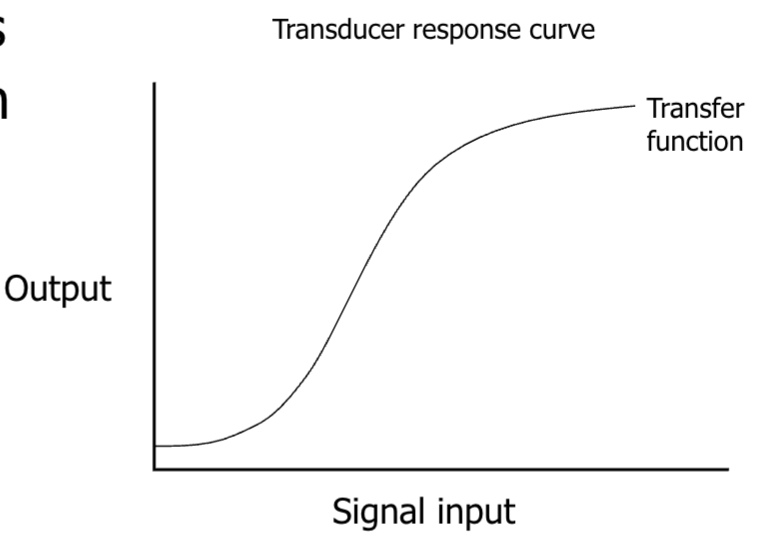
What is the role of the transducer?
To convert the physical interaction into an analogue mA or mV signal that can be passed to the ADC
What is the shape of pretty much every transducer response curve?
What is noise?
about randomness - for the same input do you get the same output, how reproducible is it?
What is saturation?
The point at which a change in input solicits no change in output, often associated with overdriving the input
What is linearity?
The extent to which a doubling of the input provides a doubling of the output
What is the best place of the transducer response curve to operate the transducer?
The central, most linear part
What is dynamic range?
The range over which the response of the transducer is dynamic
What is dynamic range limited by?
Limited by ADC min/max input
What is clipping?
When the signal exceeds the min/max limit of the ADC
What is resolution?
how fine-grained the response is
What is the resolution of an analogue system limited by?
Noise
How do you maximise resolution (bit depth)?
Large num of samples
Steps as small as possible
What is the risk for medical imaging if the bit depth is too small?
Doctors cannot distinguish differences in image (e.g. differences in tissue density) for diagnosis
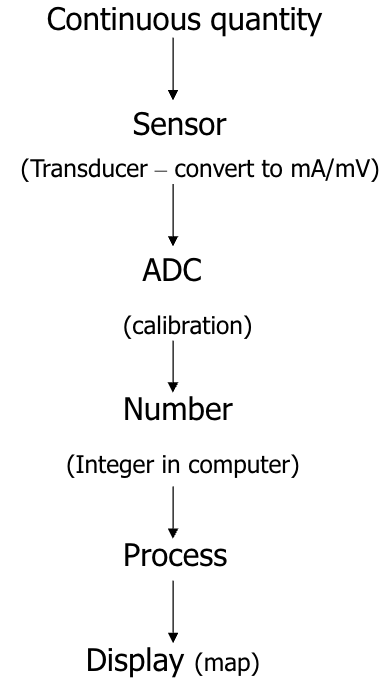
What is the digital acquisition chain?
Analogue interaction
Transducer(converts to mA or mV)
ADC (converts to binary)
Computer
What is the purpose of the latch?
The latch sits between the ADC and the computer and holds the most recent digital value
It helps to control the rate at which data is fed to the computer so it has adequate time to process it
What is the Nyquist sampling limit?
Nyquist sampling limit says that you must sample at twice the frequency of interest
What is the full flow chart of imaging from acquisition to image? (6)
What is an image?
A distribution of points of different intensities
What does the curve shifting principle do?
Moves the delta point away from the origin to any arbitrary position, in Dirac-Delta function
What is a line intensity function?
A quantitative description of the intensity distribution, provides a mechanism for describing the images as a general mathematical function
What is conjugacy?
The extent to which the object point is accurately reproduced in image space - imaging systems need good conjugacy to be effective
What does PSF stand for and what is it?
Point Spread Function = the function that represents the point object in image space
Denotes how much the point object is spread in image space by the imaging system
How do you derive the convolution?
Energy of f at any point is defined by f(x)dx
Image: δ at each fdx is replaced by g
Sum up the energy (probability) at point z whilst shifting g
What is the convolution integral?
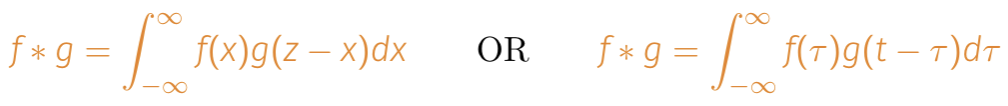
What are the three key properties of the convolution integral?
Commutativity
Associativity
Distributivity
What does commutativity mean for the convolution integral?
f*g=g*f
What does associativity mean for the convolution integral?
f*(g*h)=(f*g)*h
What does distributivity mean for the convolution integral?
f*(g+h)=(f*g)+(f*h)
What is the equation for the Fourier series and what are the coefficients?
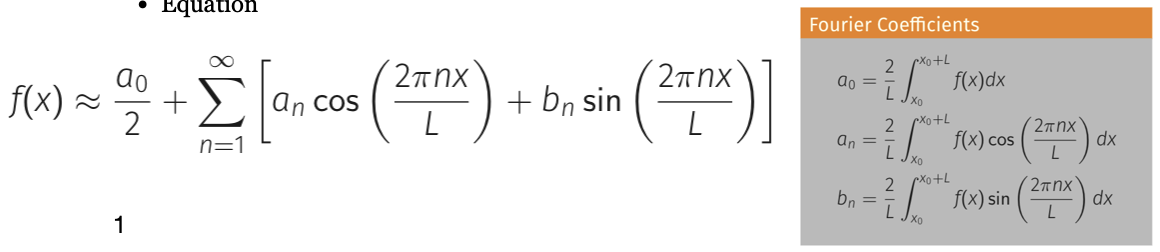
What is the equation for complex fourier coefficients?

What is the equation for an?
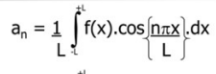
What is the equation for bn?
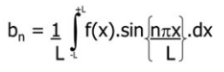
What is the equation for the Fourier transform?
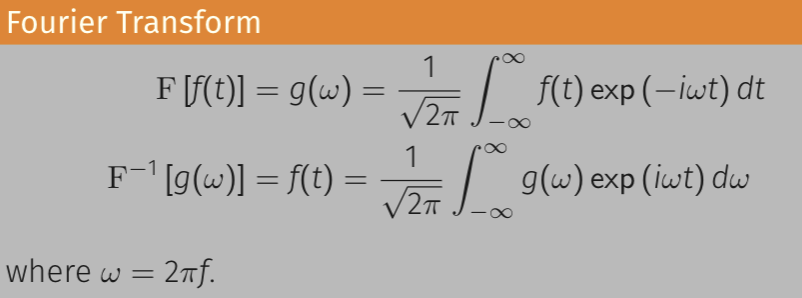
What does a phasor represent?
Amplitude and phase
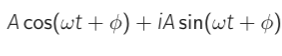
What is the phasor for this general complex exponential?
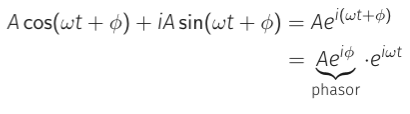
What is the definition of attenuation of an EM wave?
The decreasing photon flux resulting from interaction processes as light travels through a medium
What does the notation A represent on the periodic table?
A is the mass number
What does the notation Z represent on the periodic table?
Z is the atomic number, proton number
What is the order of magnitude of the atomic radius?
10-10m
What is the order of magnitude for the nuclear radius?
10-15m
What is the relationship between charge and strength of interaction?
The stronger the charge, the stronger the interaction
What is the relationship between mass and strength of interaction?
The larger the mass, the stronger the interaction
What is the relationship between speed and strength of interaction?
The slower the speed, the stronger the interaction
What is the linear energy transfer coefficient?
The energy deposited per unit distance travelled
What are the characteristics of x-ray radiation? (7)
Electromagnetic radiation
Emitted as a result of charge reconfiguration
A photon
>1keV
No charge
No mass
Not very interacting
What are the characteristics of gamma ray production?(2)
Many nuclear transitions do not deexcite directly to the lowest energy state
Gamma rays are an effective way of dealing with the remaining energy
Compare Maxwell, X-rays, and Gamma
Maxwell
An accelerating charge radiates (X-rays of many MeV is possible)
X-rays
Atomic in origin (up to ~100keV)
Gamma rays
Nuclear in origin (~8MeV)
What are the 3 electromagnetic interaction processes?
Absorption, scattering, and attenuation
What is absorption?
The transfer of a photon’s energy to surrounding material
What is scattering?
The random re-direction of a photon’s path
What is attenuation?
The decreasing photon flux resulting from interaction processes as EM waves travel through a medium
What is the attenuation coefficient of the absorber?
Probability of absorption per unit length, µ
What is mass attenuation coefficient represented by?
µ/ρ
What is Beer’s Law?
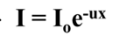
What does Beer’s Law show?
The dependence of transmitted flux on absorber thickness
How does flux, I, change with absorbing thickness x?
Changes exponentially, shown by Beer’s law
What is fluence?
The flow concentration per unit area
What is HVL?
Half Value thickness - it is 0.693/µ
What is reaction cross section?
The probability of an interaction interpreted as an effective area of interaction per particle
What is differential cross section?
A refined version of the reaction cross section to account for dependence on other parameters
What is photoelectric absorption proportional to?
Z4/E3
What happens in photoelectric absorption?
Incoming photon interacts with an electron, resulting in disappearance of photon and ejection of electron
What are the three attenuation processes?
Photoelectric absorption, compton scattering, pair production
What happens in photoelectric absorption?
Resonant coupling between radiation and inner electron shell
Electron ejected with excess kinetic energy
What is photoelectric absorption used for?
Diagnostic imaging, produces contrast in an x-ray image
What is photoelectric absorption proportional to?
Z4/E3
What is RBE?
Relative biological effectiveness
What is the equation for relative biological effectiveness?

What is the equation for Dose equivalent? and what does Q represent?
Dose Equivalent = Absorbed dose x Q x modifying factor
where Q is the radiation weighting factor
What are the principles for an acceptable dose?
Minimise time of exposure
Maximise distance from source
Shielding and effective working protocols
What is an early effect?
Cell damage may lead to cell death
Sometimes compromise the genetic data sufficiently
→ subsequent and immediate generations are non viable
What is a late effect?
Cell imperfectly repairing itself with errors encoded into the DNA
Can lead to generations of cells (years) before the error visibly manifests itself into e.g. cancer
What are stochastic effects?
Probabilistic, no safe dose
What are deterministic effects?
Threshold, severity related to dose
In a GM tube, what are the four modes A-D?
A - low voltage region
B - ionisation chamber region
C - proportional counter region
D - Geiger counter region
What happens in the low voltage region of the graph of log of detected current against voltage(??)?
(Mode A)
Gamma ray ionises gas
Ions drift towards cathode/anode
Ions recombine before reaching anode/cathode
-
ionise, drift, recombine
What happens in the ionisation chamber region of the graph of log of detected current against voltage(??)?
(Mode B)
Gamma ray ionises gas
No time for ion recombination
Ions attracted to anode/cathode
What happens in the proportional counter region of the graph of log of detected current against voltage(??)?
(Mode C)
Gamma ray ionises gas
Ions accelerated to cathode/anode
Collisions along their path produces further ionisation
Single gamma ionisation produces a many-ion current pulse
Gas amplification factor up to 106
What happens in the Geiger counter region of the graph of log of detected current against voltage(??)?
HT set to place tube just below the threshold of spontaneous discharge
Gamma ray ionises gas
Ions greatly accelerated to cathode/anode
Collisions produce ion avalanche
Gas amplification factor 1010
-
threshold, ionises, greatly accelerated, avalanche, amplification
Describe the process of Compton scattering (4)
Billiard ball type interaction (relativistic)
Between photon and free electron
Incident photon deflected with energy transfer to electron
Produces scatter/noise in diagnostic image
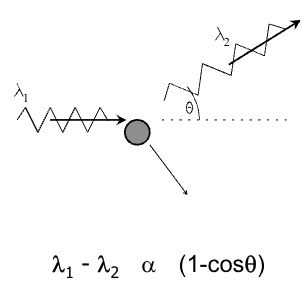
What is Compton scattering proportional to?
Z/E2
Describe pair production(2)
Photon in excess of 1.02MeV passes close to nucleus of an atom
Spontaneous conversion into electron positron pair
What is the process that happens in the GM tube? (3)
Gas in glass envelope, includes two electrodes
ionisation of gas by incoming photon generates ion pair, both are attached to electrodes responsible for generating an electric field
Result is pulse of charge down electrode wire that signifies an ionisation has occurred
What is the efficiency of the GM tube at few MeV?
<2%
What does TLD stand for?
Thermoluminescence Dosimetry
What is thermoluminescent dosimetry? (6)
Energetic structure of crystal includes energy traps
Ionisation causes some electrons to be caught by the traps
Has regular crystalline structure but when impurities are added imperfections arise in the lattice which act as energy traps
Following an interaction with radiation most excited electrons rapidly return to the ground state, but some remain trapped in the impurity levels
Upon heating, the trapped electrons are released and de-excite with an emission of light
These de-excitations occur in a well defined “glow curve”
What is the advantage of TLD?
Can measure accurately (2%) a dose over a very wide range (10^-5 to 10^3 Gray)
What is Kerma?
Kinetic Energy Released in the Material
dE/dm
What is absorbed dose?
Distributed energy transfer
What is the difference between KERMA and absorbed dose?
KERMA is at the point of interaction, absorbed dose is the effect
What does Bremsstrahlung mean?
Radiation that decelerates
What is LET?
Linear Energy Transfer coefficient
LET = dE/dm
What is a direct mechanism of damage?
Refers to an incident in which ionising radiation strikes the DNA directly
Why are direct mechanisms of damage unlikely?
DNA is a very small target
When do indirect mechanisms of damage occur?
When water molecules inside the cell become ionised and then can go onto cause damage to DNA