Topic 8: Posttranscriptional Gene Regulation
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Where is newly transcribed precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) processed to translatable mature mRNA in eukaryotes?
Nucleus
5’-UTRs and 3’-UTRs are part of what?
The first and last exon, and are untranslated regions
What do UTRs do?
Regulate mRNA stability and translational initiation
When is the 5’-CAP and 3’ poly-A tail added?
5’-CAP is added early in transcription and 3’ poly-A tail is added soon after cleavage of mRNA by CPSF
What does pre-mRNA contain?
Alternating coding segments and UTRs (exons) and non-coding segments (introns)
What does the removal of introns by splicing during transcription do?
Generates the open reading frame (ORF) consisting of a continuous stretch of codons (flanked by start and stop codons) and the UTRs
What is RNA processing coordinated by?
Recruitment of enzymes to CTD of RNA pol II
Once processed, where is mRNA transported?
Exported from nucleus into cytoplasm to associate with ribosomes (for translation)
What does the 5’-CAP contain?
7-methylguanosine (7-MeG) is added to 5’ end of pre-mRNA via 5’,5’ triphosphate linkage by guanylyltransferase after the first 20-30 nt of the transcript have been added
What does 5’-CAP do?
Protects mRNA from degradation by 5’-3’ exoribonucleases because a 5’ phosphate has been replaced with a methylated guanosine (steric hindrance)
Also acts as a ribosome binding site whereby the 5’ cap recruits the cap binding complex (CBC)
What does the CBC do?
Helps recruit a small ribosomal subunit (40S) to the mRNA which then scans for the start codon (and to the right end)
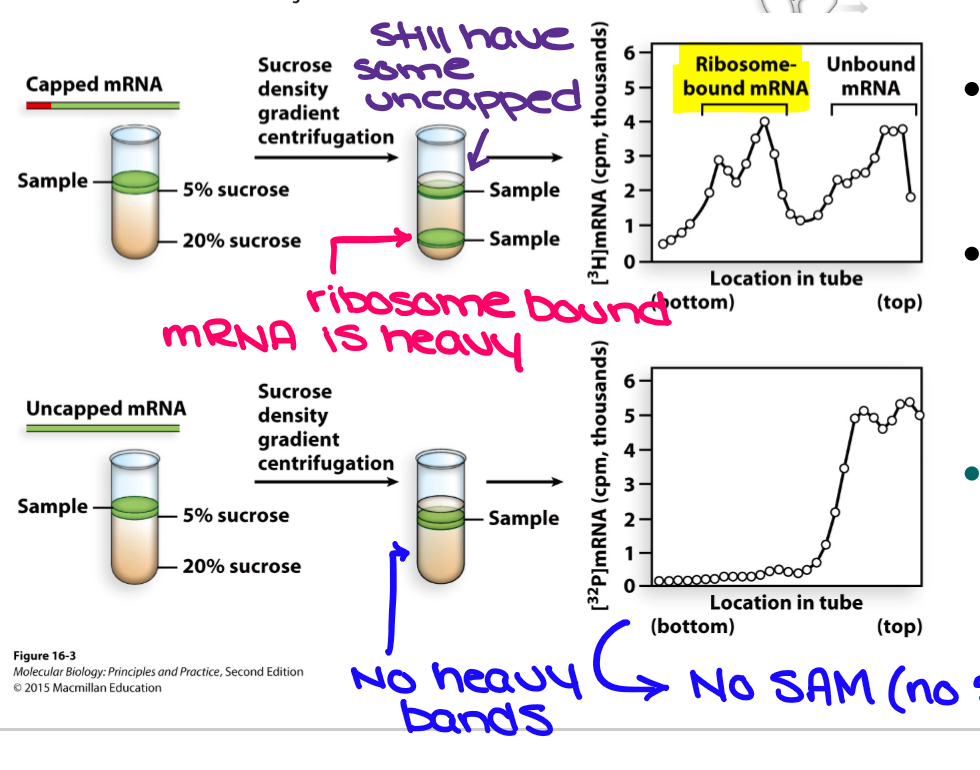
What did the classical studies of 5’ cap do?
Synthesized 5’-capped and uncapped mRNA by transcription assay using wheat cell extracts with labels labeled GTP and SAM (produces 7-meG)
sucrose density gradient centrifugation showed that only 5’-capped mRNAs were bound to ribosomes
What is a poly A tail?
String of adenines added to 3’ end of eukaryotic mRNA by poly-A-pol (PAP)
What does the poly A tail do?
Protects mRNA from degradation and promotes translation
What binds to the poly A tail and protects it from degradation by 3’-5’ exonuxleases?
Poly A binding protein (PABP)
What else does PABP bind?
Eukaryotic translational initiation factors (eIFs) at 5’ cap
What does PABP (3’) and eIF (5’) binding create?
Creates a “closed-loop'“ interaction which brings 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA together
this helps the 40S ribosomal subunit bind to the mRNAs 5’ end and begin translation more efficiently
increases the stability of mRNA
How does alternative splicing give rise to isoforms?
Splicing can occur in different combinations to generate two or more different mature mRNAs from a gene, which creates several related protein products (isoforms)
What are spliced out and what are kept?
Introns are spliced out, and certain exons are selected for inclusion
What are alternative polyadenylation sites?
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) sites that contain variant sequences that bind to CPSF (cleaves AUAA site) as well as other sequences such as GU-rich regions that determine choice of site
What do APA sites do?
Change lengths of 3’-UTR which affects stability, translation and localization of mature mRNA
What is the importance of isoforms created by alternative splicing and APA sites?
A single gene can produce different isoforms in different tissues generating tissue-specific phenotypes
Increases the number and variety of proteins (proteome) that can be encoded by the condensed genome
Minimizes # of genes and allows genome to stay compact
What are the 4 features of introns?
5’ splice site sequence
3’ splice site sequence + polypyrimidine tract
Begin with GU and end with AG (consensus sequences needed for efficient splicing)
Branch point site: located close to 3’ end of intron and is followed by the polypyrimidine tract
How are introns removed?
Two transesterification reactions where two phosphodiester linkages within pre-mRNA are broken and two new ones are formed (energetically neutral)
What is the first step in splicing the intron?
2’-OH of conserved A at branch site attacks the conserved G in the 5’ splice site resulting in an extra 5’-2’ phosphodiester bond (A has three phosphodiester bonds)
What is the second step in splicing the intron?
Phosphodiester bond between the sugar and the phosphate at the 5’ junction between the intron and exon is cleaved and the freed 5’ end of the intron is joined to the A within the branch point
What is the last step in splicing the intron?
The 5’ exon is freed and its 3’-OH attacks the phosphoryl group at the 3’ splice site of the intron joining the 5’ and 3’ exons
intron is liberated as a lariat and then rapidly degraded
What performs the splice reaction?
The spliceosome, consisting of 5 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins or snRNPs
What does each snRNP contain?
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA): U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, and U6 that form 2 prime structures
What do the snRNAs bind?
Sm proteins at the Sm-binding site near the hairpin loop at the 3’ end and other proteins unique to each snRNA
The spliceosome assembles from snRNPs and other proteins not associated with sRNAs such as….
SR (serine/arginine-rich) proteins that select and regulate splice sites in pre-mRNAs
What does selection of splice sites depend on?
Flanking sequences of the splice sites and branch point, as well as tissue specific splicing factors
How is correct splice site selected?
Base pairing between snRNA and pre-mRNA
What does spliceosome assembly on pre-mRNAs involve?
Base pairing to snRNAs
What is step #1 in spliceosome assembly?
U1 snRNP binds to GU at 5’ splice site and accessory protein U2AF binds AG and flanking sequence at 3’ splice site
What does U2AF then recruit?
U2 snRNP to the branch point
What binds to U2 at the branch site?
U6 of the U4-U6-U5 trimeric snRNP
What occurs after U6 of trimeric snRNP binds U2?
U1 is released, U5 base pairs with 5’ exon and U6 moves to base pair with 5’ splice site, then U4 is released
What happens after U4 is released?
U2 and U6 snRNPs catalyze nucleophilic attack of the 2’-OH of the branch point adenosine at the 5’ splice site cleaving the 5’ exon-intron junction and shifting U5 snRNP to the 3’ splice site
What happens after first nucleophilic attack?
U2-U6-U5 complex remains bound to intron lariat and catalyzes nucleophilic attack of the 3’-OH of the 5’ exon on the phosphodiester bind linking the intron to the 3’ exon
What happens last?
Lariat is cleaved and exons are joined
Why is ATP required for the splice reaction?
Required for unwinding of the snRNAs and proteins and snRNA base pairing with each other and the pre-mRNA
Where are self-splicing introns found?
Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and bacterial viruses
What are group 1 self splicing introns?
Requires a free guanine nucleoside whereby its 3’-OH forms a 3’-5’ phosphodiester bond with the 5’ end of the intron and releases the 3’ end of the first exon
Then the 3’-OH of the first exon attacks the 3'-end of the intron, releasing it and then joining the two exons together
What are group 2 self splicing introns?
Self-splicing reaction is like spliceosomal splicing (lariat formation) and depends on RNA structure to create an active site for catalysis
6 domains whereby 1 contains binding sites for 5’ and 3’ splice sites and 6 contains the adenosine to initiate the splicing reaction
Why did RNA likely come before DNA?
RNA stores genetic information AND can also catalyze reactions like an enzyme
DNA developed later with advantages like increased stability, double stranded allows for complementary strand to be used as a template to repair damaged strand
What level is silencing at?
Posttranscriptional level (mRNA degradation and translation repression)
Where was silencing first observed?
Petunias where overexpression of a pigmentation gene resulted in its own downregulation (co-suppression of gene expression)
How are siRNAs generated?
Long dsRNAs are cleaved to 21-23 bp by the Dicer Rnase III
What is done once siRNAs are generated?
siRNAs are unwound and one of the strands functions as a template in RISC (RNA induced-silencing complex) to guide cleavage of the complementary mRNA
hunts down complementary sequence to stop translation → gene silenced
What is the purpose of chemically synthesizing siRNAs?
Partial LOF of a target gene
NOT 100% LOF, since not all mRNA will be degraded
What is gene silencing thought to have originated from?
Ubiquitous in almost all eukaryotes (developed early on in evolution)
thought to have been an ancestral antiviral mechanism to destroy viral dsRNA (viral RNA genome → dsRNA intermediates → Dicer Rnase III produces siRNA for RISC to use to stop viral RNA translation)
What are microRNAs?
Endogenous gene silencing regulatory RNAs
noncoding RNAs located in intergenic regions or within genes are transcribed by RNA pol II
What is the difference between siRNAs and microRNAs?
siRNAs are “foreign” whereas microRNAs are actually within the genome
Where are ssRNA (pri-miRNAs) cleaved?
Cleaved in the nucleus by Drosha generating a short hairpin mRNA (pre-miRNA) which is then processed by Dicer and RISC complex like siRNAs
What happens if there is high complementary between miRNA and mRNA?
mRNA is degraded by ribonucleases
What happens if there is lower complementary between mRNA and miRNA?
mRNA is translationally repressed and then eventually degraded (translation initiation factors replaced with mRNA decay factors)
What does CRISPR-Cas9 contain and what does it do?
Dual RNA molecules that guides DNA endonuclease (Cas9) to direct DNA cleavage (RuvC1 and HNH each cut one strand) at specific site in the genome
genetic engineering in unicellular and mutlicellular eukaryotes, as it allows for precise insertion, deletion, and tagging of genes
Genetic manipulation is permanent and heritable, and there is no transgene (eg antibiotic resistance; foreign DNA) remaining in mutant like seen in homologous recombination
For CRISPR-Cas9, where do the spacers originate?
From plasmid and viral sequences that once infected the bacteria, its like a record of past infection
In the CRISPR locus, there is a Cas9 operon, which is followed by the repeat-spacer array
What are the spacers transcribed to?
Transcribed to form crRNA which bind Cas endonucleases and direct them to cleave foreign DNA sequences by complementary base pairing
bacterio-adapted immune system
What does crRNA do?
Contains a repeated portion and an invader targeting portion (protospacer)
Why is tracrRNA required?
Required for crRNA maturation by forming a tracrRNA:crRNA duplex that is recognized by Cas9
How is RNA-guided Cas9 directed to target DNA?
Complementary base pairing of a 20 nt sequence in mature crRNA
both strands are cut if Cas9 is fully functioning
What does DNA targeting require?
A PAM sequence (5’-NGG-3’) which is required for initial binding of DNA target to Cas9
What is a single guide RNA (sgRNA) and what two features does it have?
Combine dual tracrRNA:crRNA to sgRNA that have:
20 nt sequence at 5’-end and dsRNA at 3’ end that is recognized by Cas9
20 nt of the sgRNA can be used to program CRISPR-Cas9 to target any DNA sequence IF it is adjacent to a PAM
When CRISPR-Cas9 creates a ds break, which two pathways can repair it and what does it create?
1) Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ): error prone and introduces indels
used to create LOF alleles
2) Homologous recombination uses the wild-type copy of the chromosome or donor DNA for gene correction
greater efficiency if nick is made by a defective Cas9 where one of the endonuclease subunits is nonfunctional
What is the only approved CRISPR based therapy so far?
Sickle cell anemia and beta thalassemia caused by a non-funcitonal beta hemoglobin gene
What gene is a transcriptional repressor of fetal gamma hemglobin?
BCL11A gene
What does CTX001 (Casgevy) do?
Inactivates BCL11A by CRISPR-Cas9 in extracted blood stem cells allowing production of gamma hemoglobin in place of beta hemoglobin
CRISPR-edited cells are then transferred into patient
$2.2 million USD for curative therapy