Data Analysis
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
In what cases should you use the median over the mean?
When outliers are present in datasets.

Find IQR
IQR=Q3-Q1
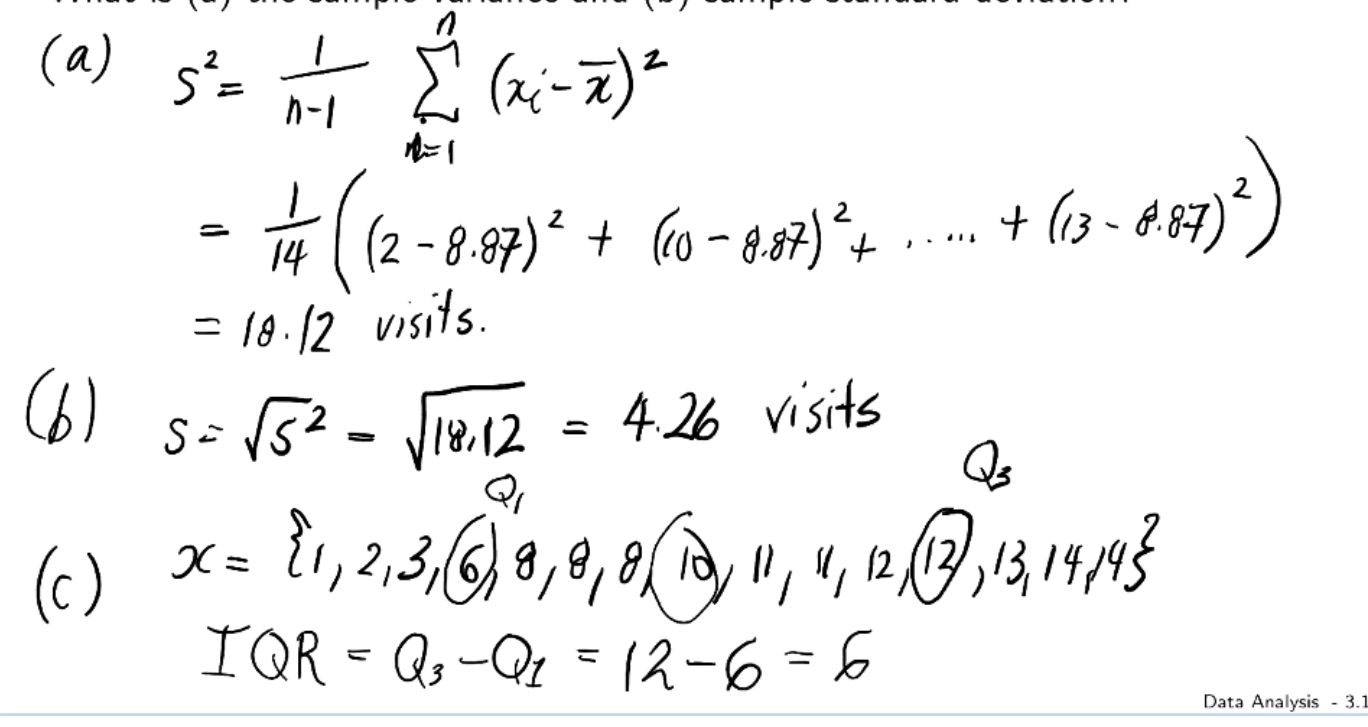


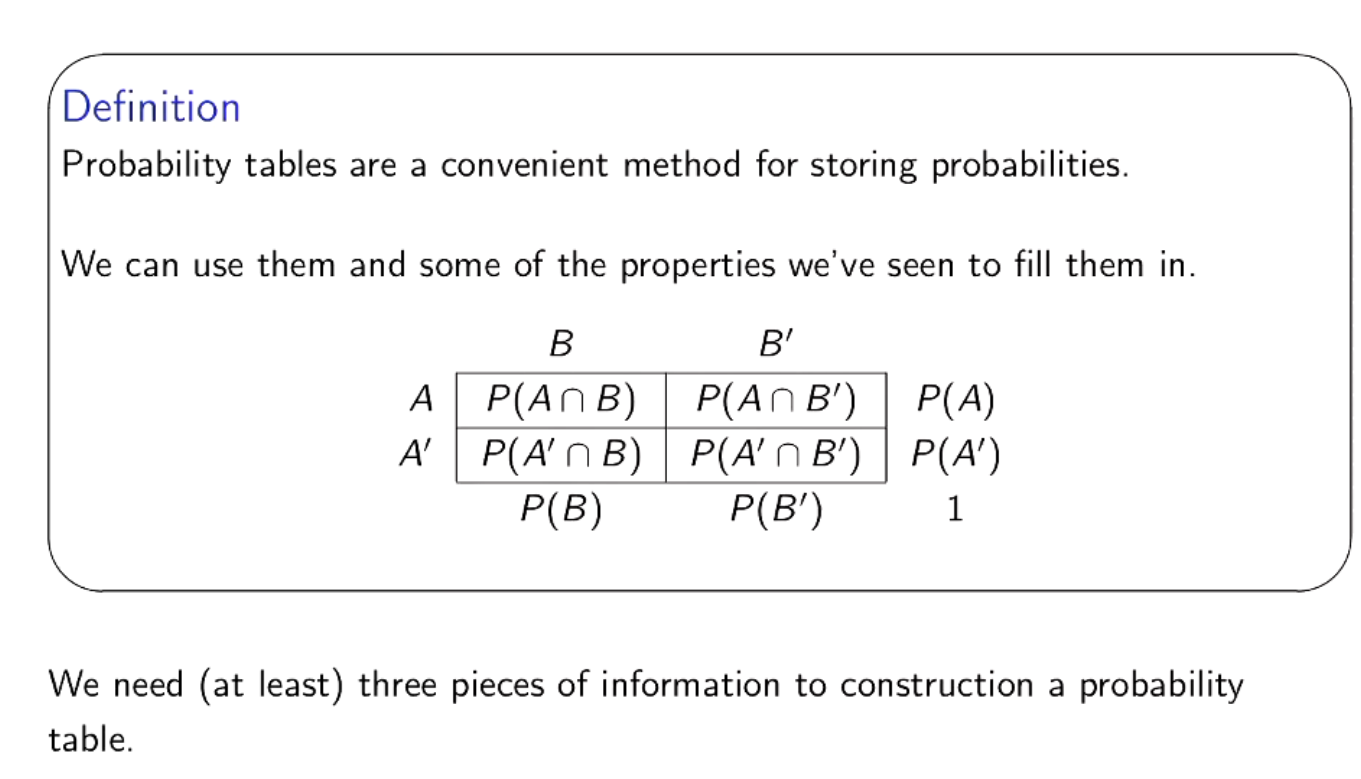
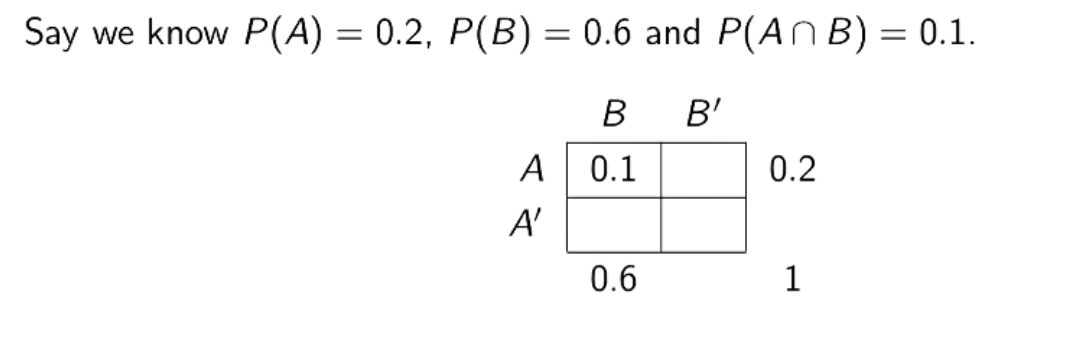
How to use probability table?
What is sensitivity?
What is specifcity?
What is precision?
True positive, yielded from probability table.
Actual positive (TP+FN).

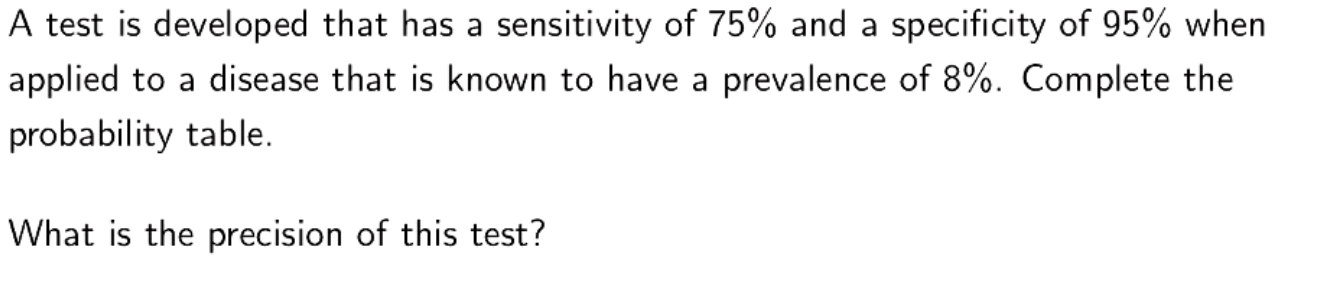
Precision= TP/(FP+TP)
0.566
Cannot trust the positives.

What are random variables?
The outcome of a random process.
Flipping a coin.
Rolling a dice.
Discrete: random variables are restricted to a certain value.
Continuous: can take ny value in an interval.
Eg. the outcome of measuring an individuals time in a 100m sprint.
What is a probability mass function?
Probability that X takes on a particular value.
Pr(X=x)=1/6 for x=1,2,3,4,5,6 and Pr(X=x)=0 otherwise.
How to calculate mean?
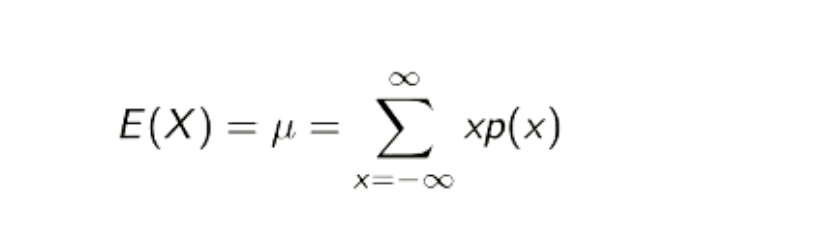
What is variance and how do you calculate it

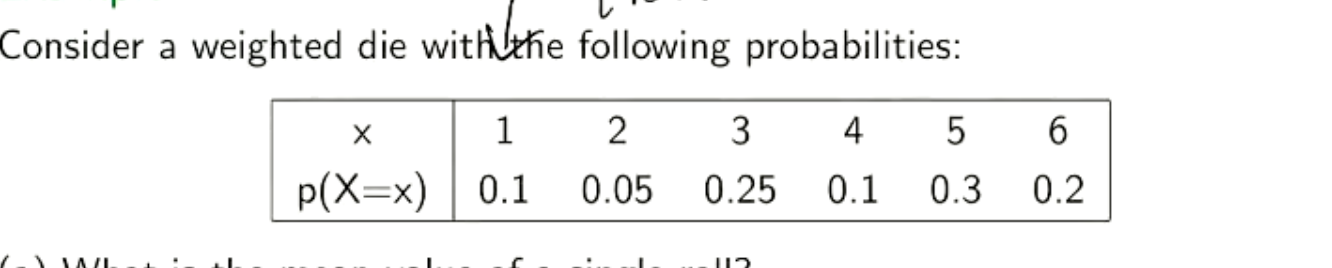
Find mean and variance.
E(x)=4.05
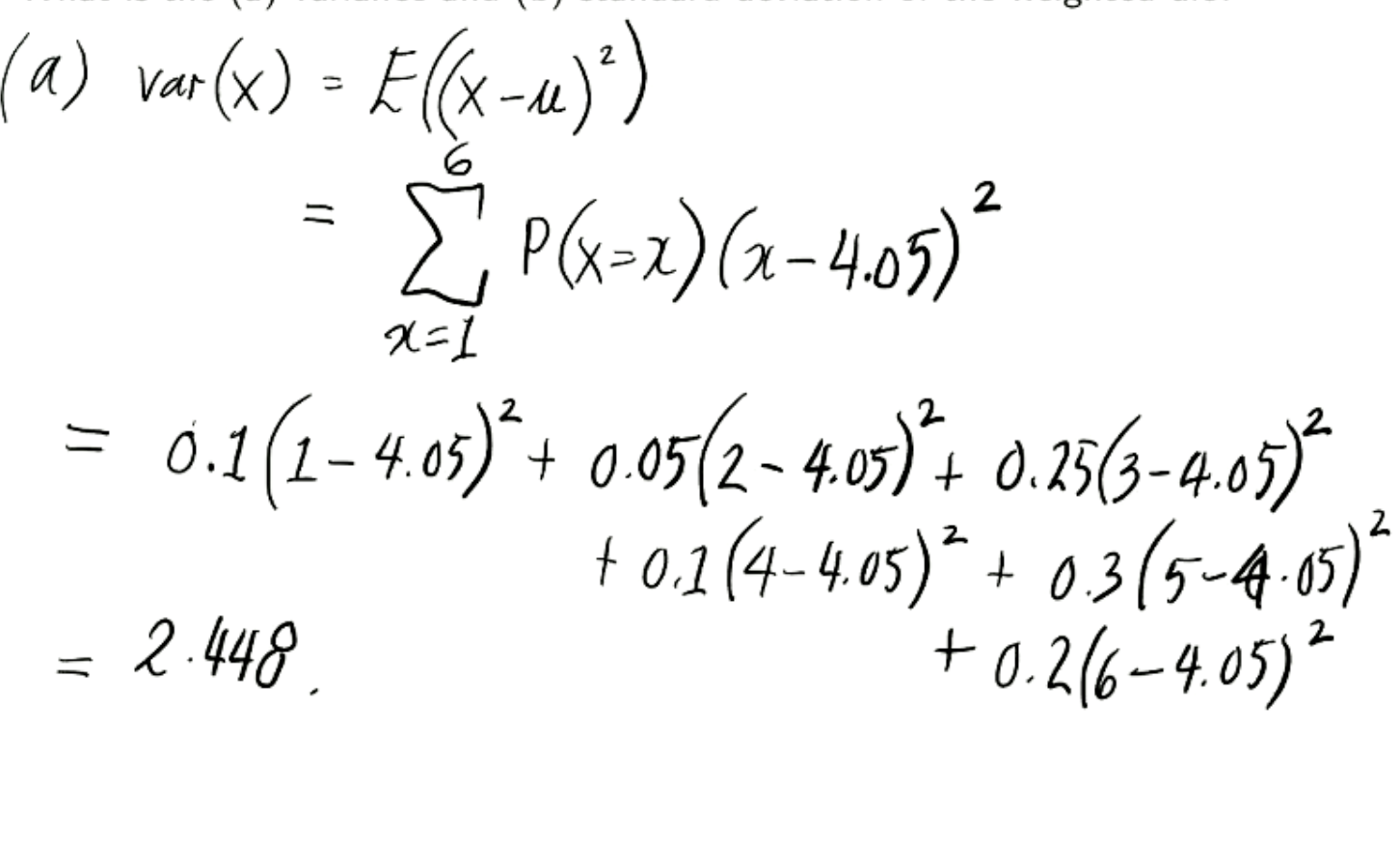

Whilst E(x) is lower for A, distribution of numbers suggests that it might not be the better treatment.
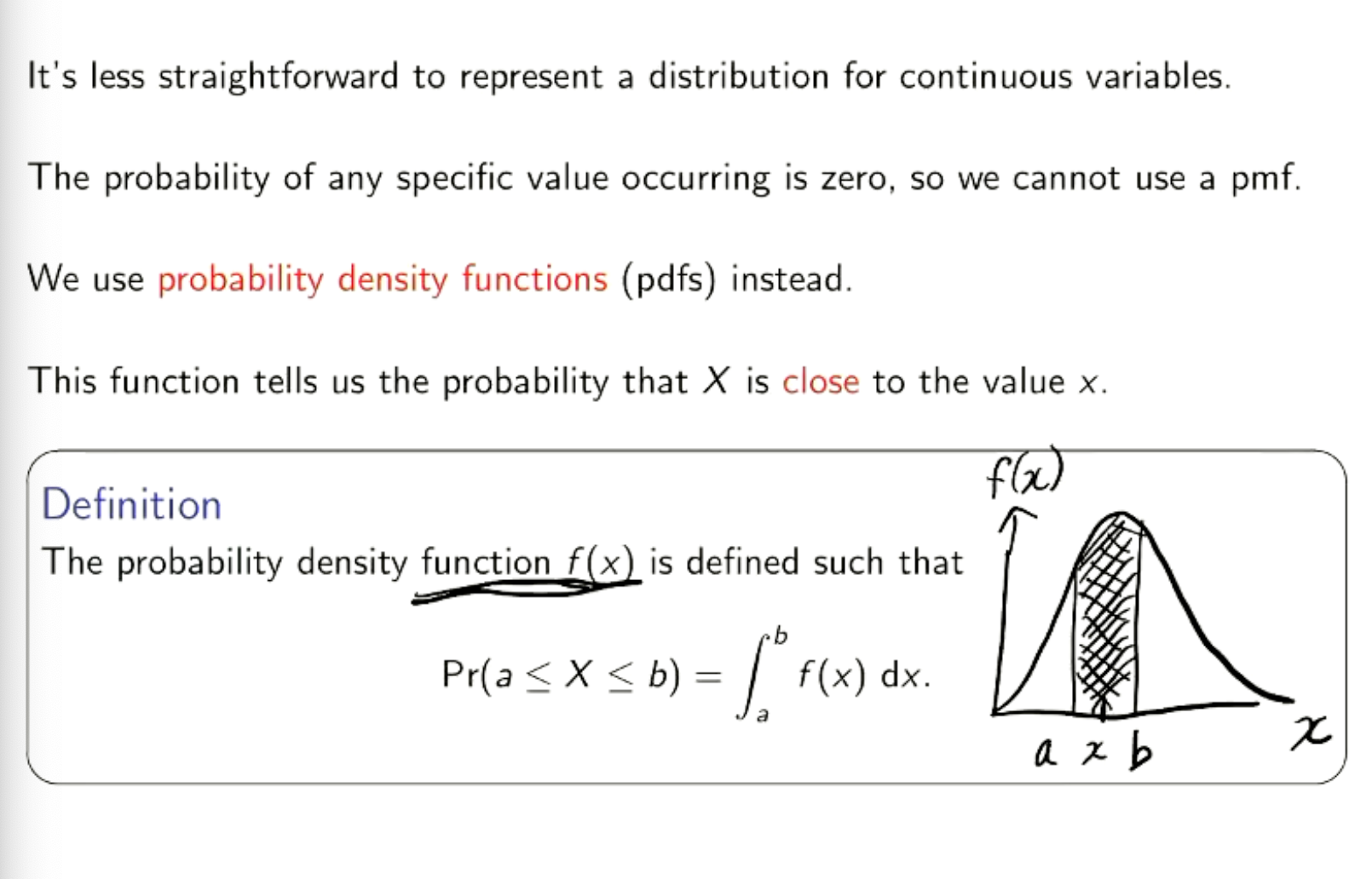
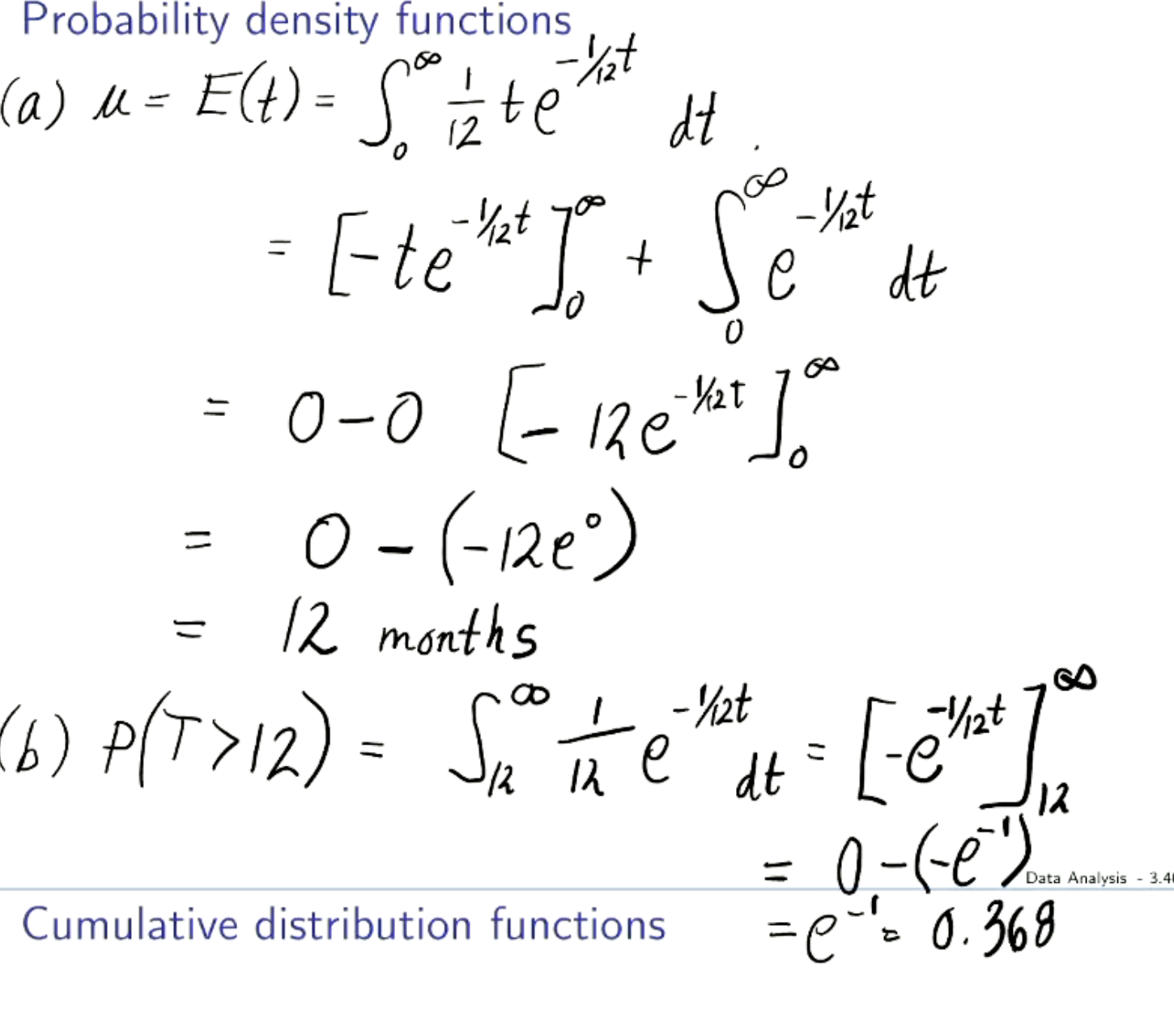
How to do probability density functions?
Mean is integral from - infinity to infinity x*f(x)
Var is integral infinity (x-u)²*f(x)

variance also.
integral(0,6)(x-4)²*x/18dx=2
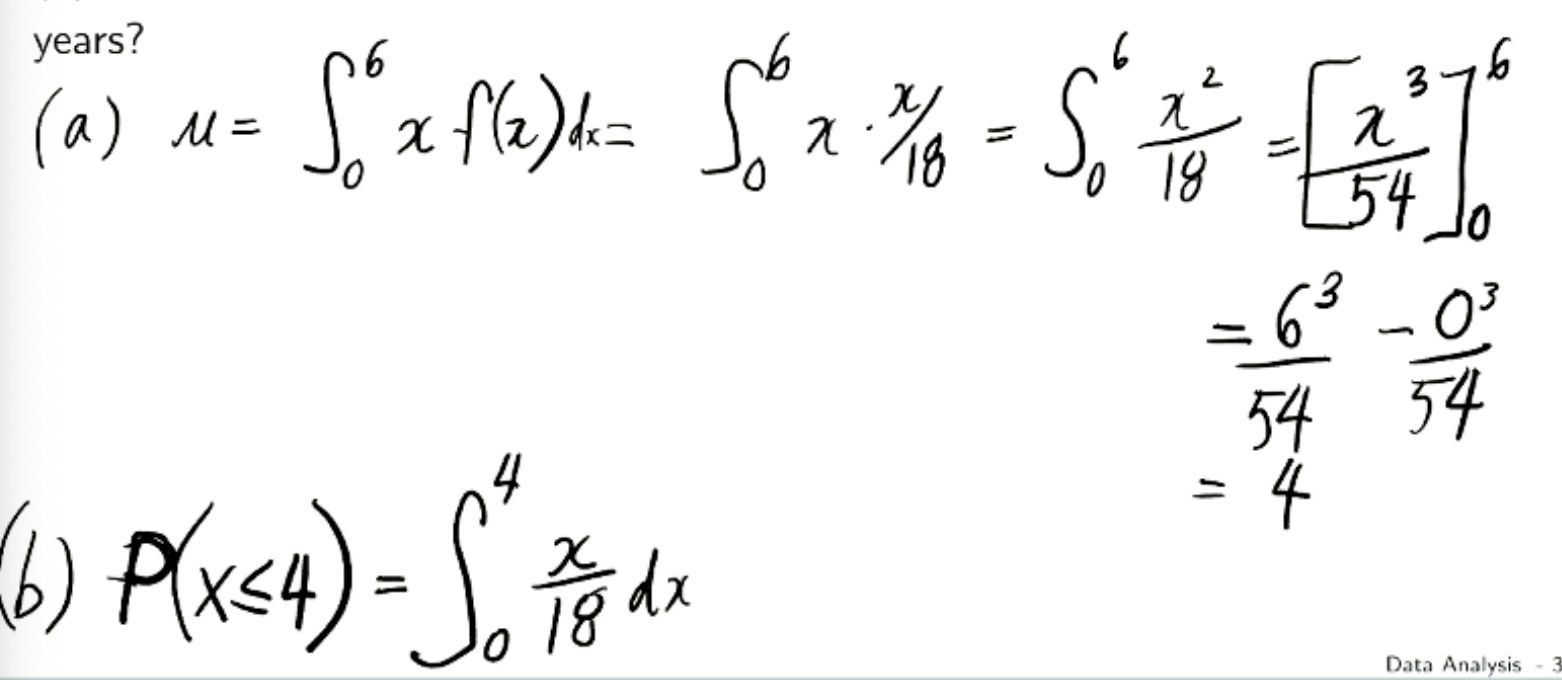

Must know how to do by hand. First part is integration by parts.
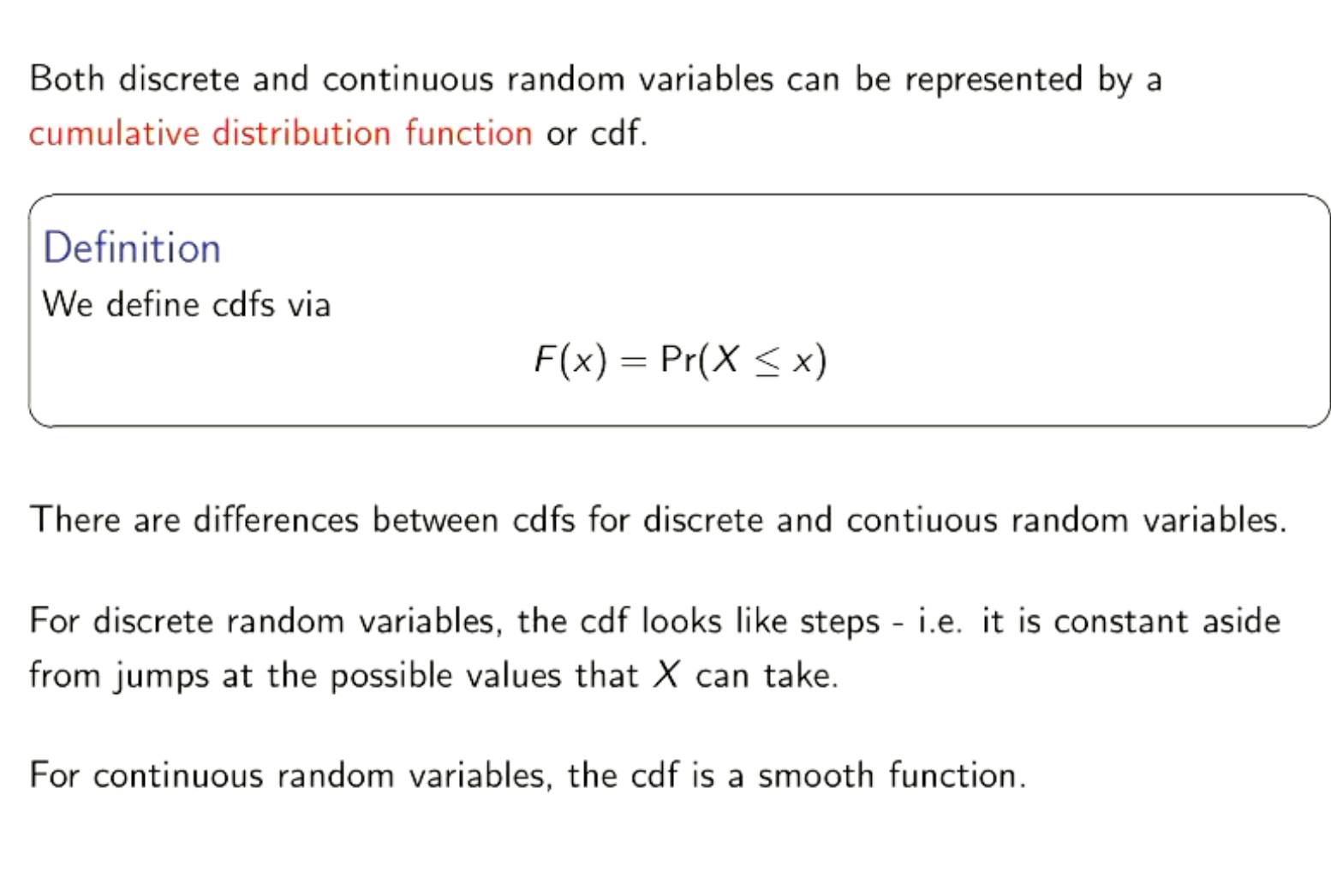
What is a cumulative distribution function?

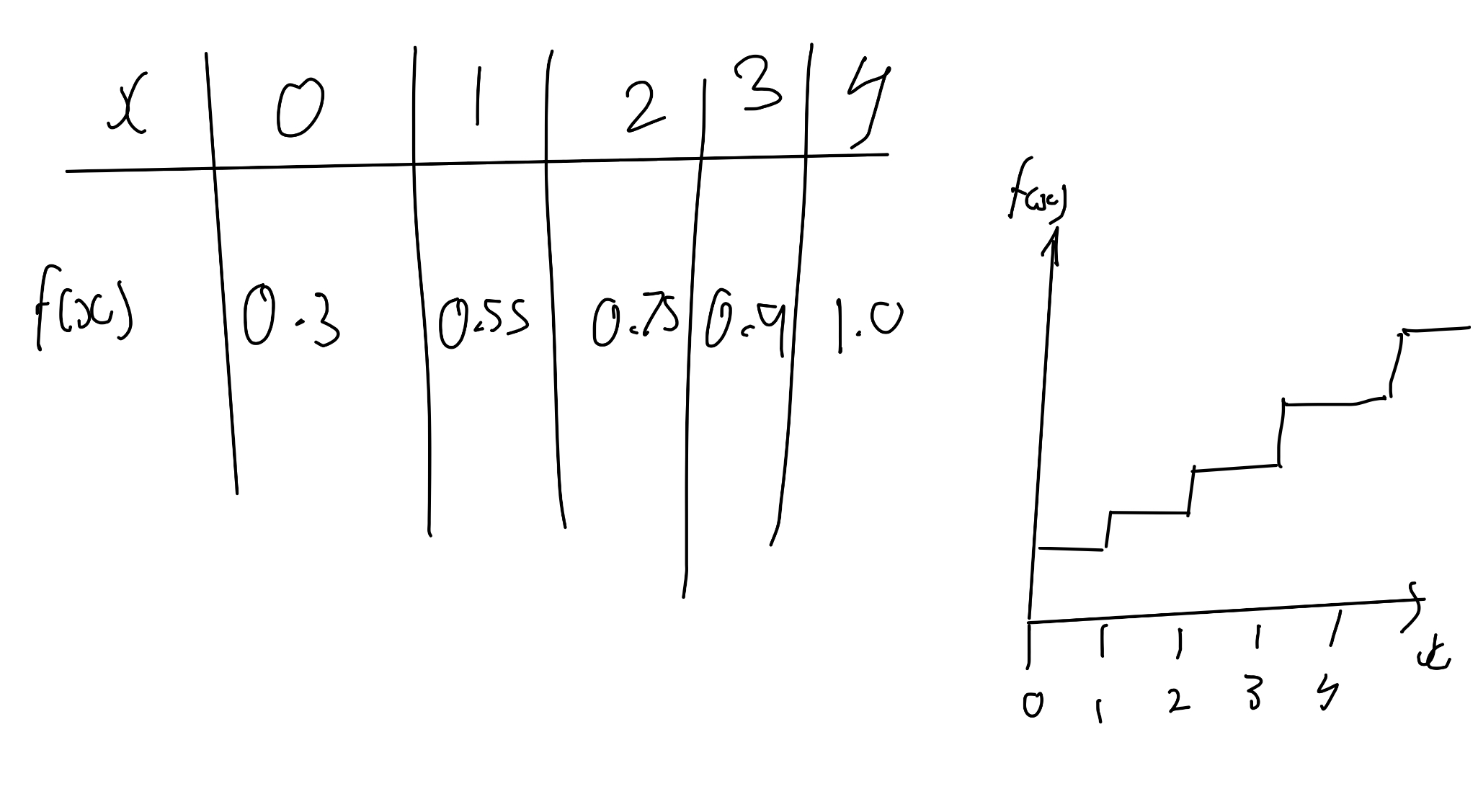

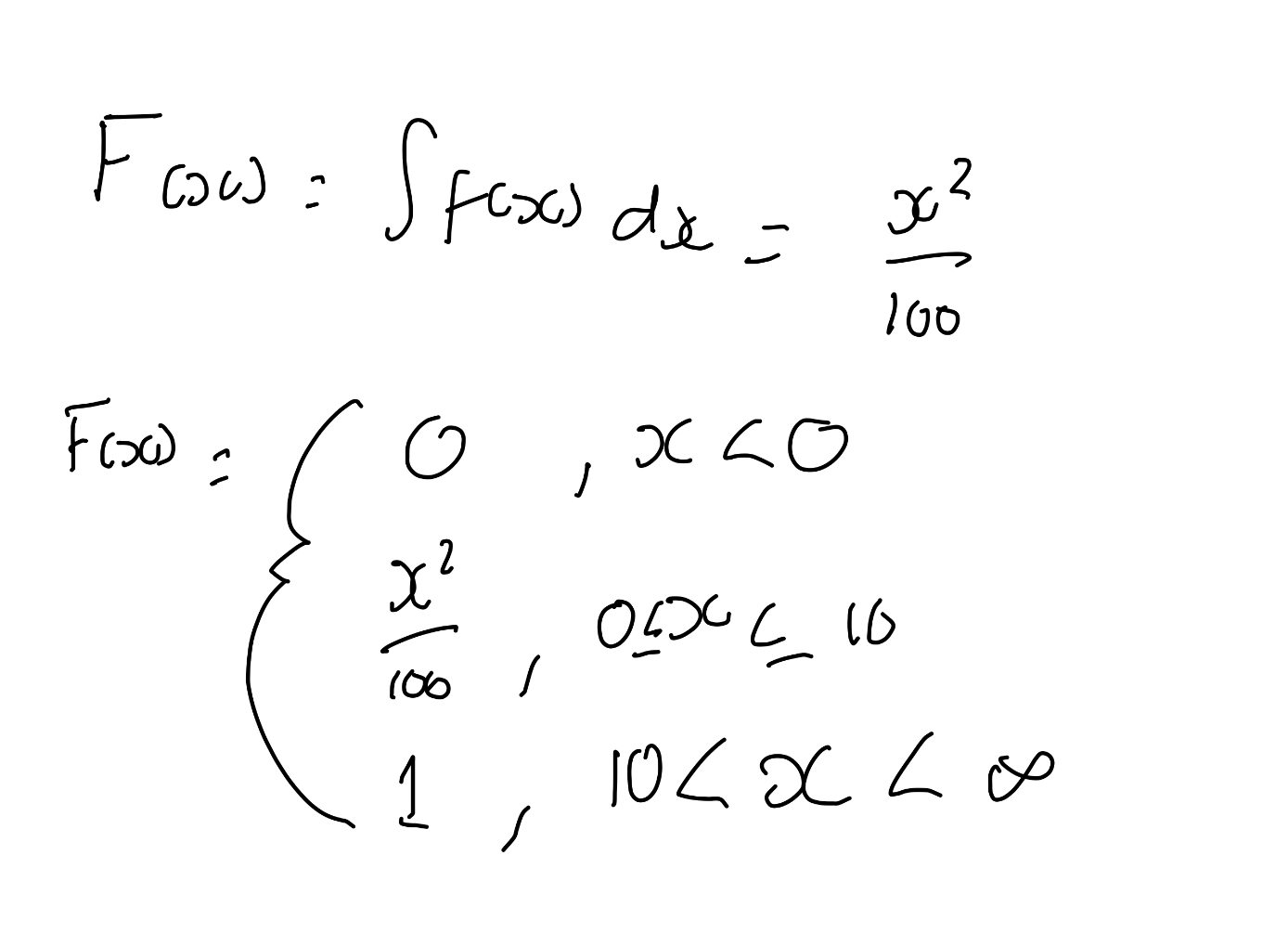
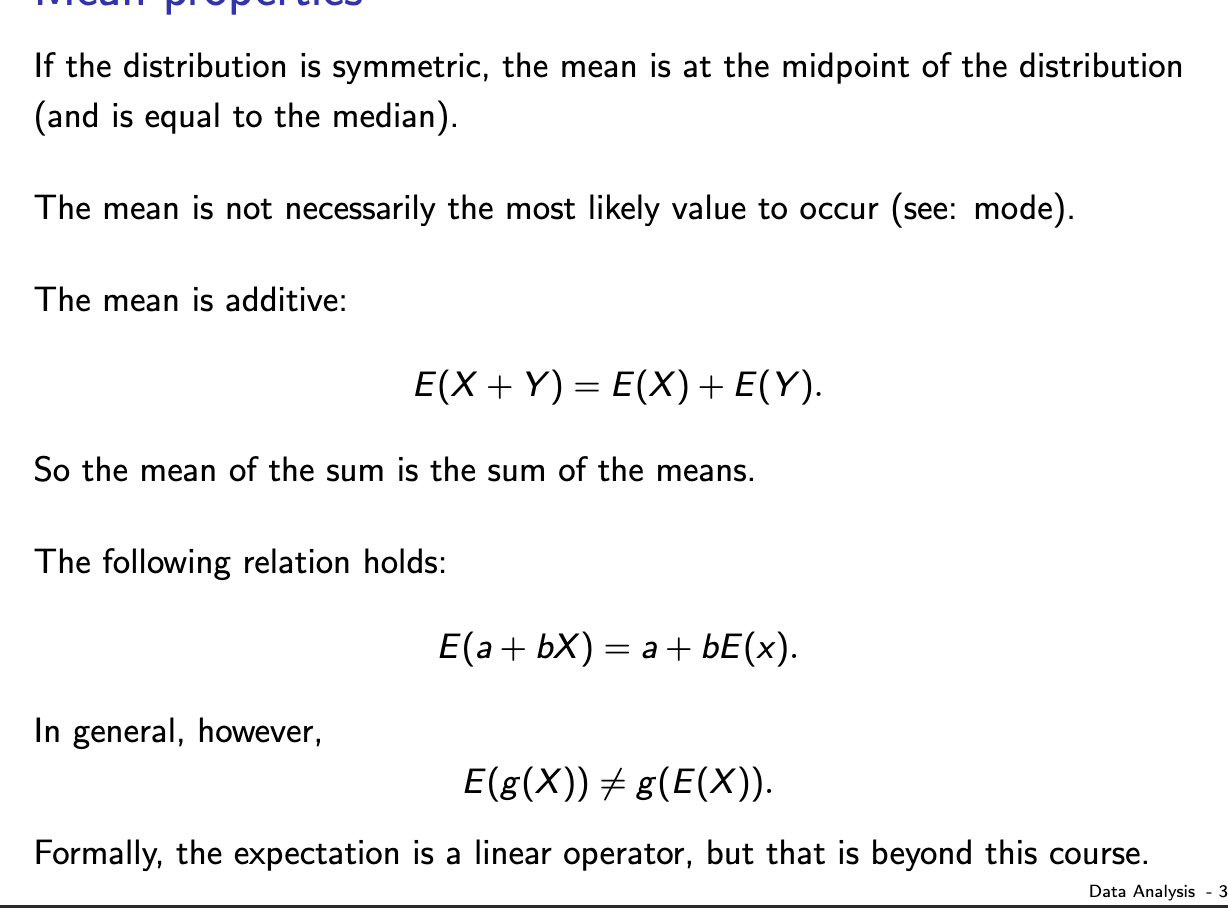
What are the properties of mean?
Bell curve: means = median.
What are the properties of variance?
Independent: result of one trial does not impact any other.


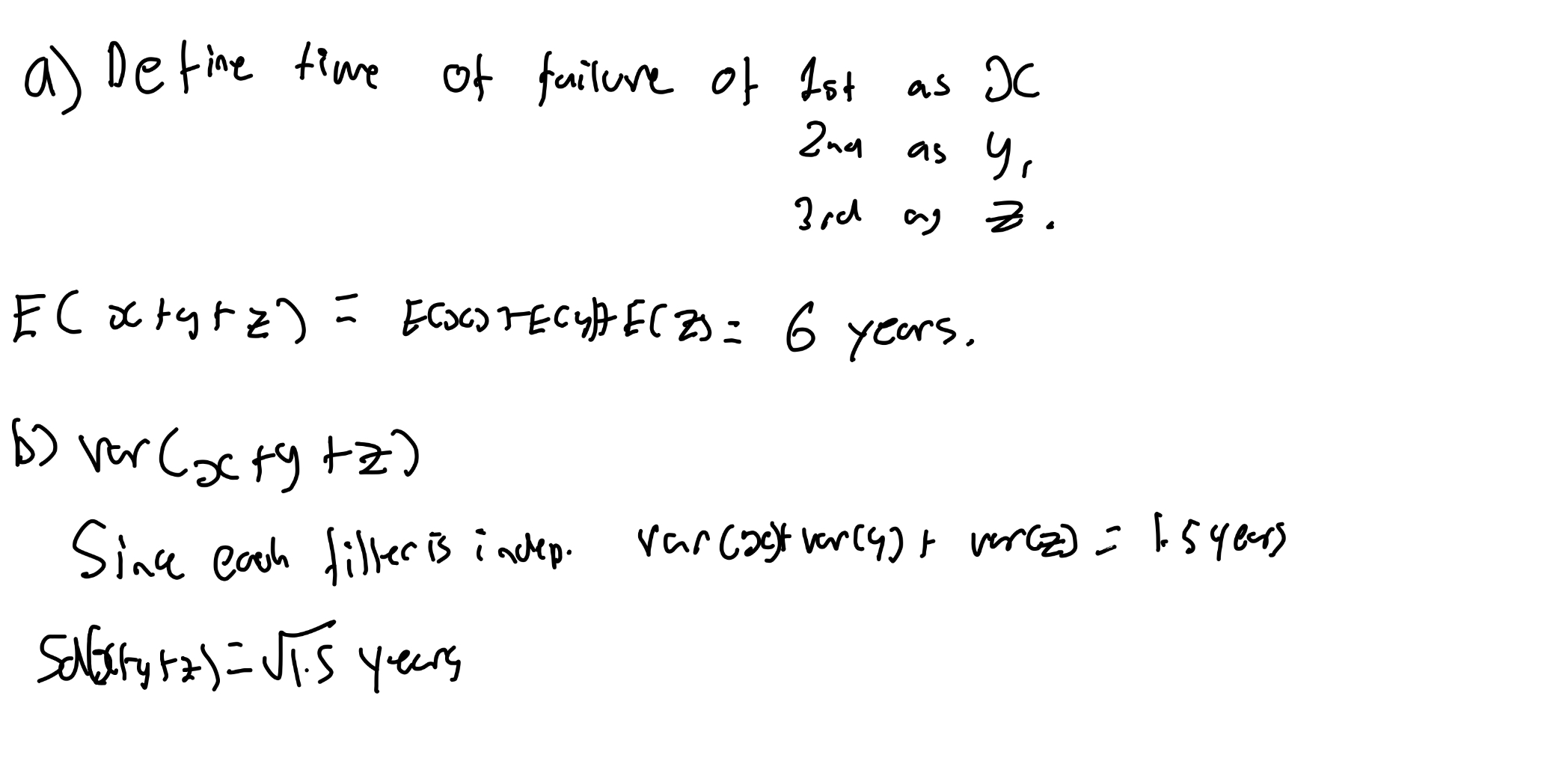
What are Bernoulli trials?
Experiment with two possible outcomes: success and failure.
p= success q= failure.
What is the binomial distribution?


Find µ and sd.
E(x)=np=500x.95=475
sd=sqrt(npq)=sqrt(np(1-p))=sqrt(500×0.95×0.05=4.87
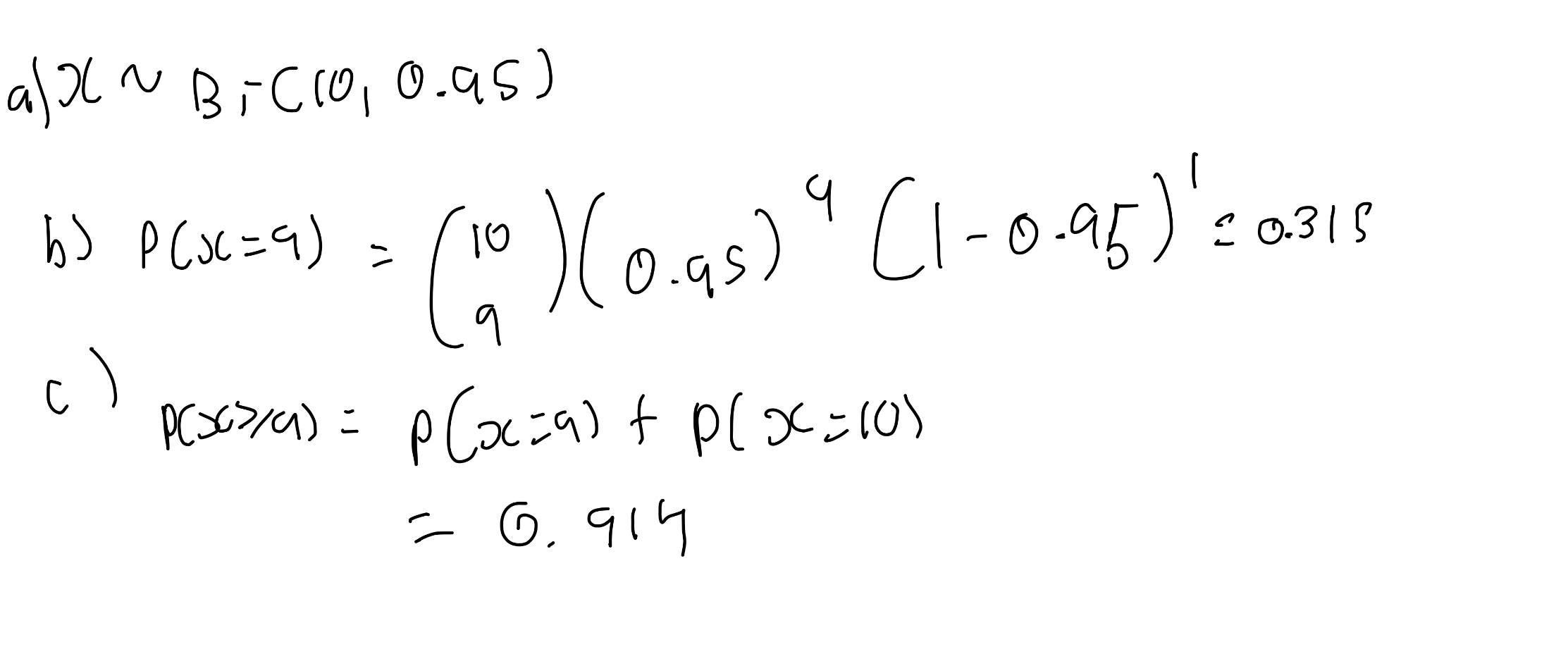

What is the probability that a person infects more than 17 people
(12+-2(2)=(8,12)
z=x-u/sigma = 15-12/2=1.5

What is a confounding variable?
Variable that affects the relationship between the variables in the question.
Like an uncontrolled variable.

Use CLT to find sample mean and sd.
Find 95% CI
N(10,4/100)
CLT is sd²/n
E(xbar)+-1.96*sd(xbar)=10+-1.96×0.2

From CLT, xbar - N(µ,100/400)
µ≤xbar+0.98 and vice versa
49.82≤µ≤50.8




No, since 2.9µm does not lie within the 95% CI, we cannot say with 95% confidence that 2.9 lies within the population mean.

What is the t-distribution?
Used when sd is not known.
Looks similar to normal distribution, but there is more mass in the distribution tails (wider), as this accounts fort the extra uncertainty associated with not knowing the sd.

A new method for performing the above surgical procedure that seeks to
improve the consistency in the time required to complete the procedure. One
day, 18 surgeries are performed. The sample mean of the time taken for the
procedure is 29.47 minutes. What must the standard deviation be such that the
95% confidence interval for the mean does not include 30 minutes?
t score = 2.08 for t21 and 2.11 for t17

How to find variance for proportion?
var(p hat)=var(X/n)=1/n²8var(X), where var(X)=npq, thus var(phat)=pq/n
A disease is known to have a prevalence of 20%. If we randomly sample 200 members of the population, what is the 95% probability interval for the prevalence?
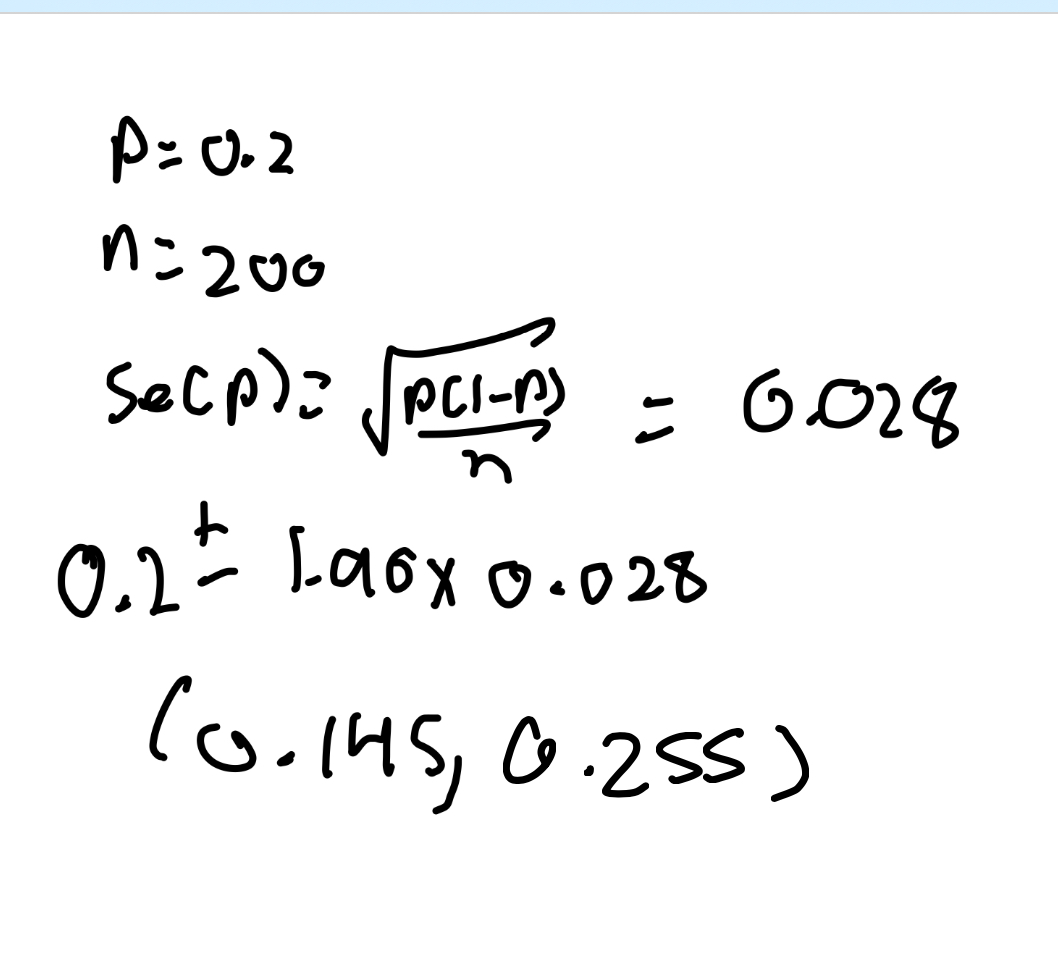
We suspect we have a positively biased coin. If we observe a sample proportion of ˆ p = 0.6, how many observations would we need such that the 95% confidence interval only contains values of positive bias?
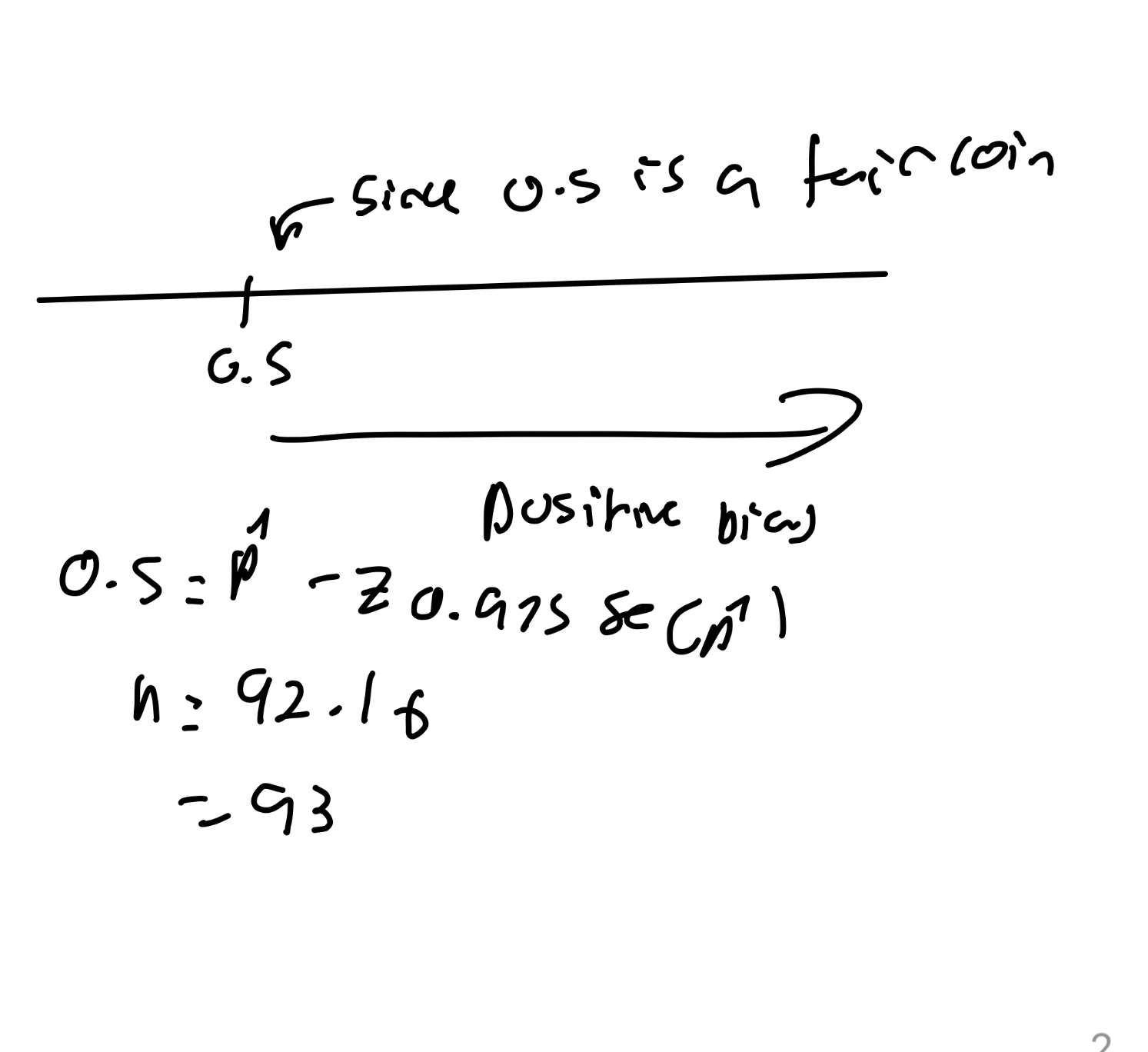
What is the null hypothesis?
Always an equality statement.
A new chemotherapeutic drug does not change the 5 year survival rate of lung
cancer.
Birth weight is not associated with the child’s IQ.
Rest days do not affect the chance of soft tissue injuries.
The alternative hypothesis, H1, is the opposite.
Prove by contradiction.


If it was true, say do not reject H0, not accept.
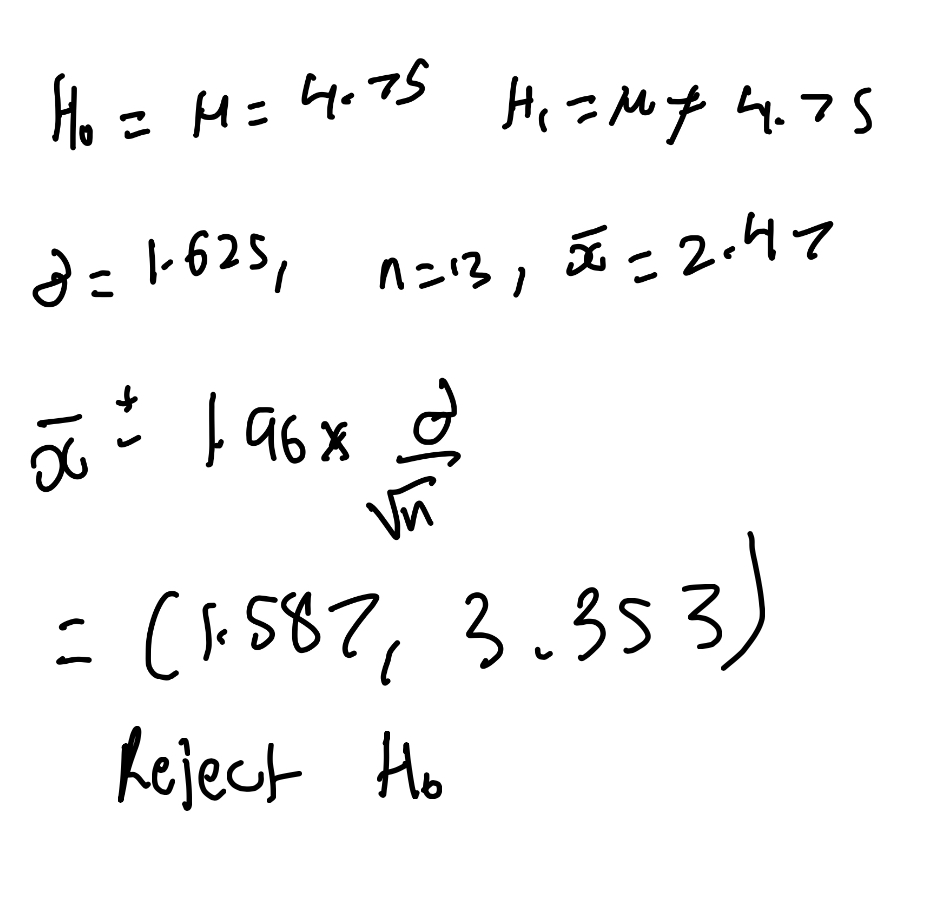
Suppose we flip a fair coin 100 times. We expect 50 heads. But in an experiment, 80 heads are observed.
What would the statement of the p-value?
If the coin was truly fair (H0), what is the likelihood that we would see a result this extreme or more?
If the probability is really low, like 0.001, then we assume that it isn’t feasible that the coin is fair.
The cutoff for rejecting the p-value is 0.05.
What is a type II error (ß)?
ß is when we do not reject H0 when H1 is true.
The power = 1-ß, which is the probability of avoiding the type 2 error.


Pr(Zs<0.017)=0.507
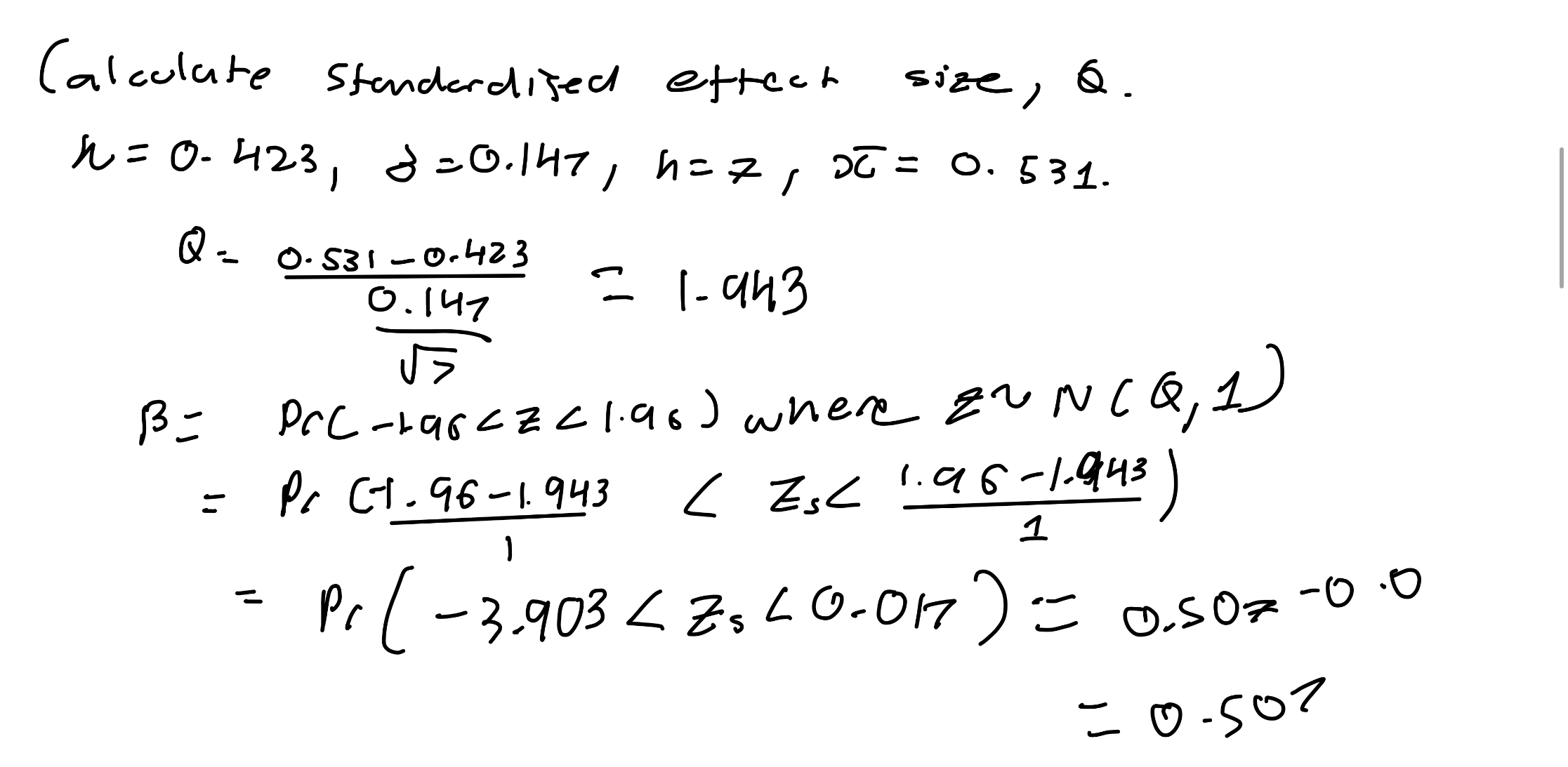
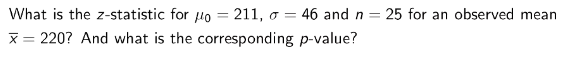
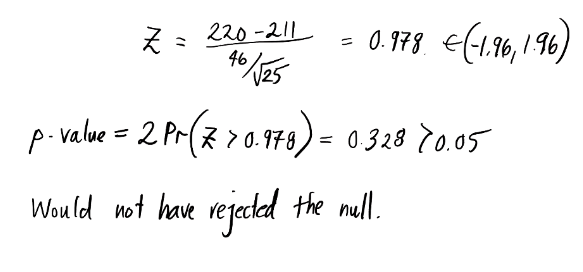

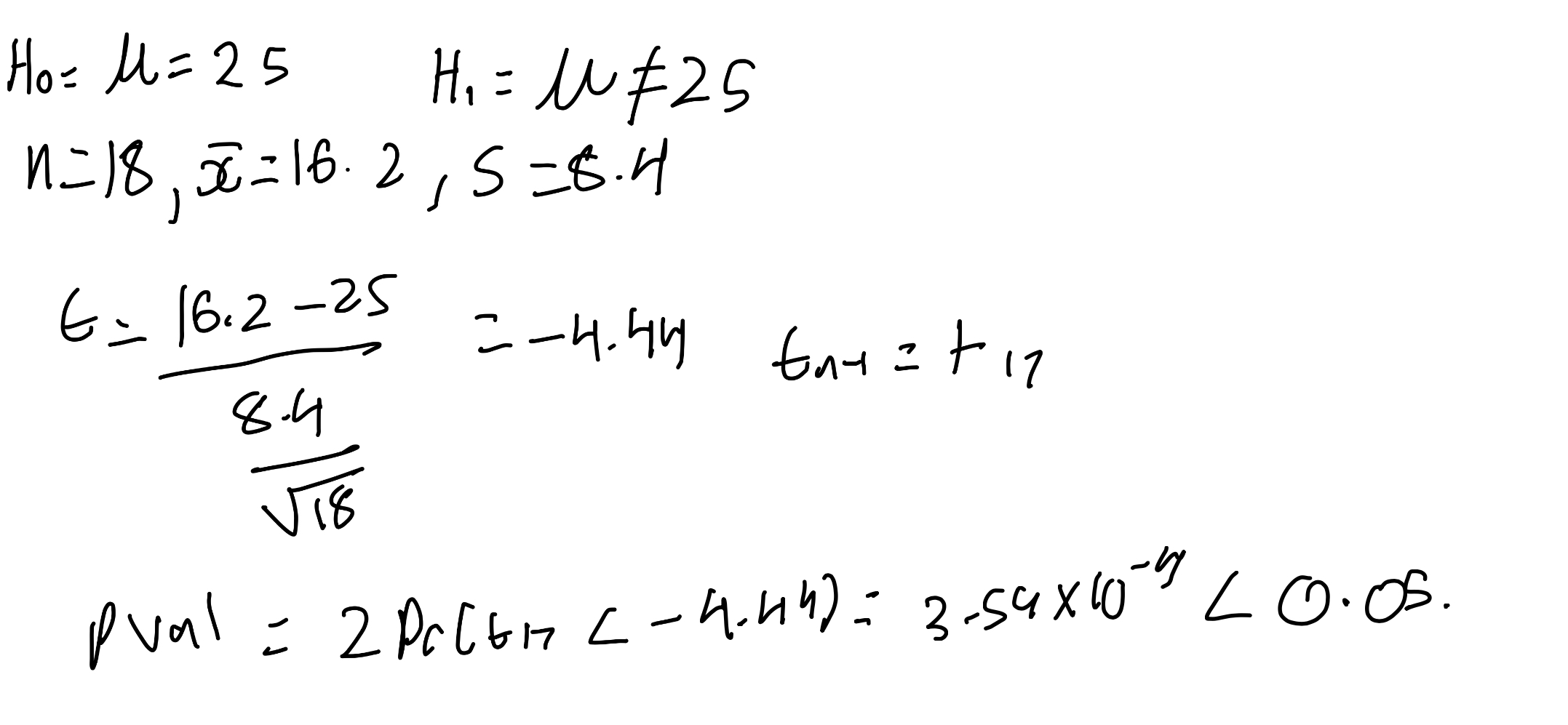

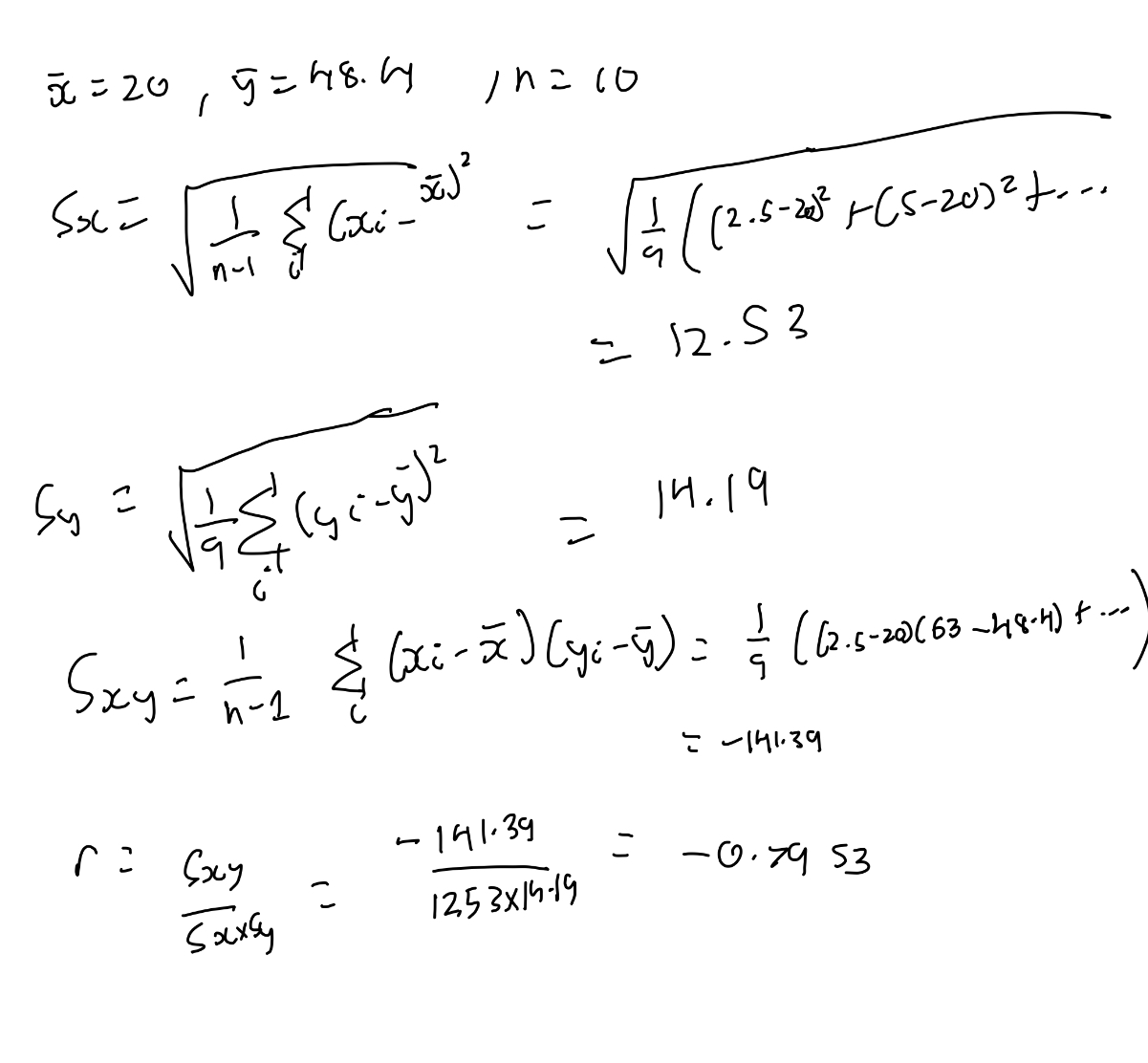

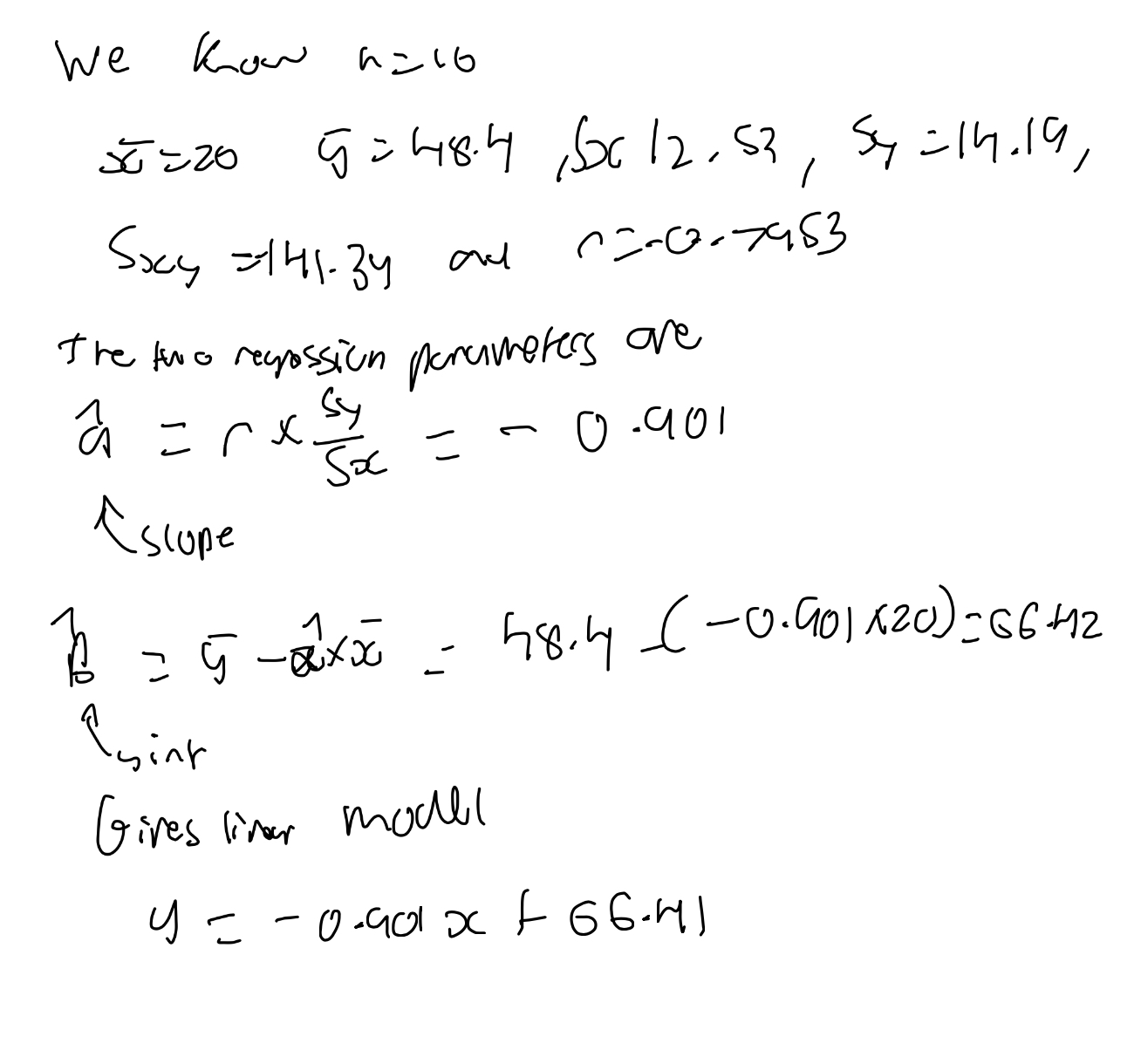
What are the things you need to check before you proceed with regression?
No patterns should arise from the residual plot.


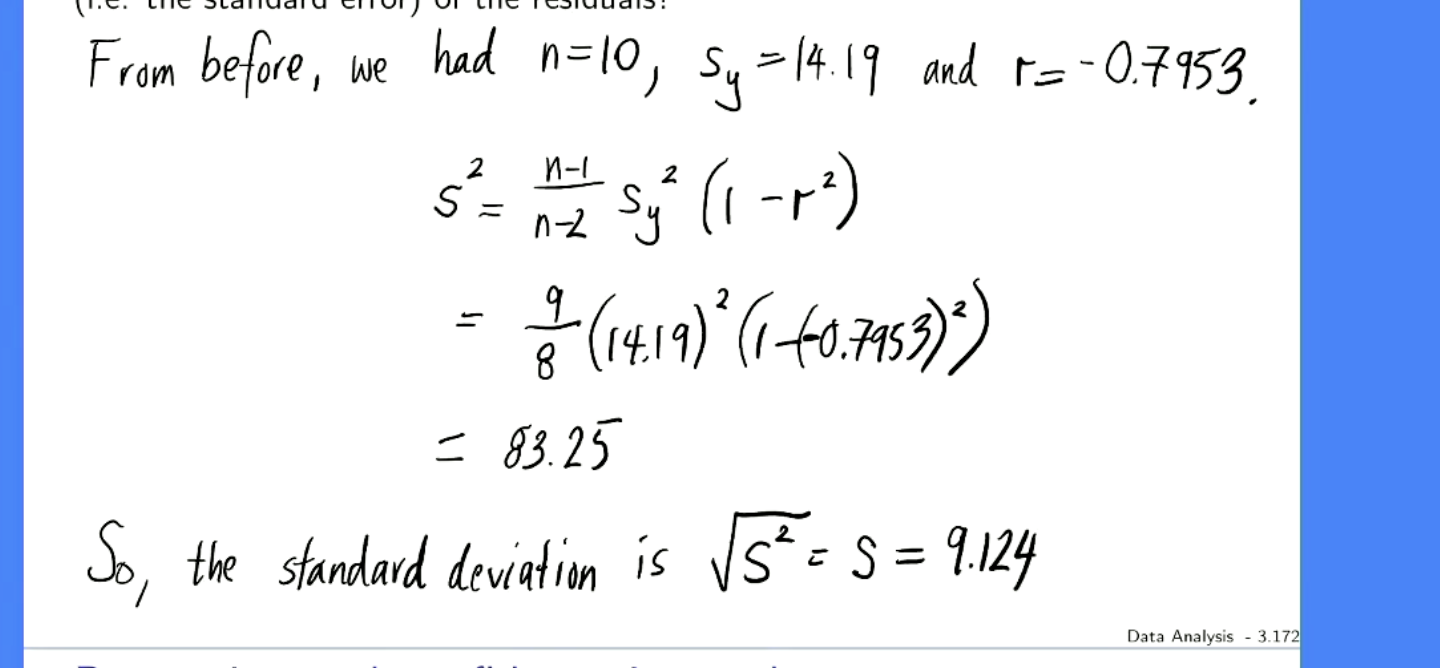
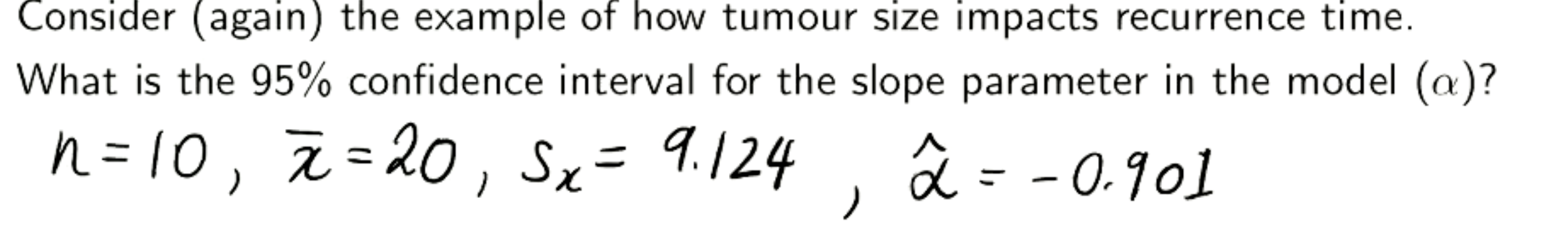
t8, bc these are 2 degrees of freedom n-2.
