Grade 11 Biology: Genetics
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Interphase
-Cell is metabolizing and growing
-All organelles double, including DNA
Prophase
-Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
-Chromosomes condense
-Centrioles move to opposite poles
Cytokinesis
-Divides the cytoplasm of parental cell into two daughter cells
-occurs in both mitosis and meiosis
P generation
Parent generation
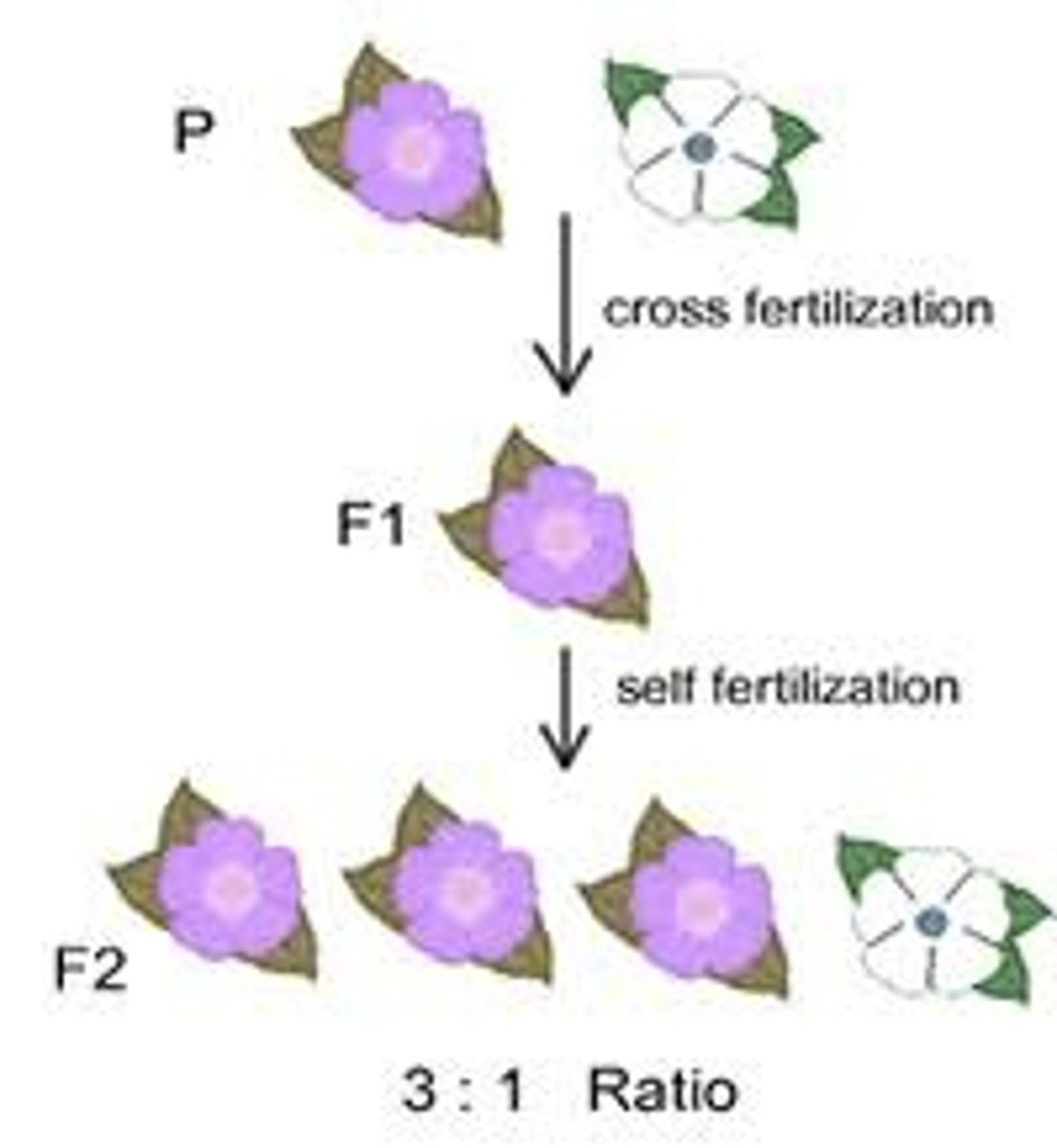
F1 generation
Offspring of the parent generation (First Filial generation)
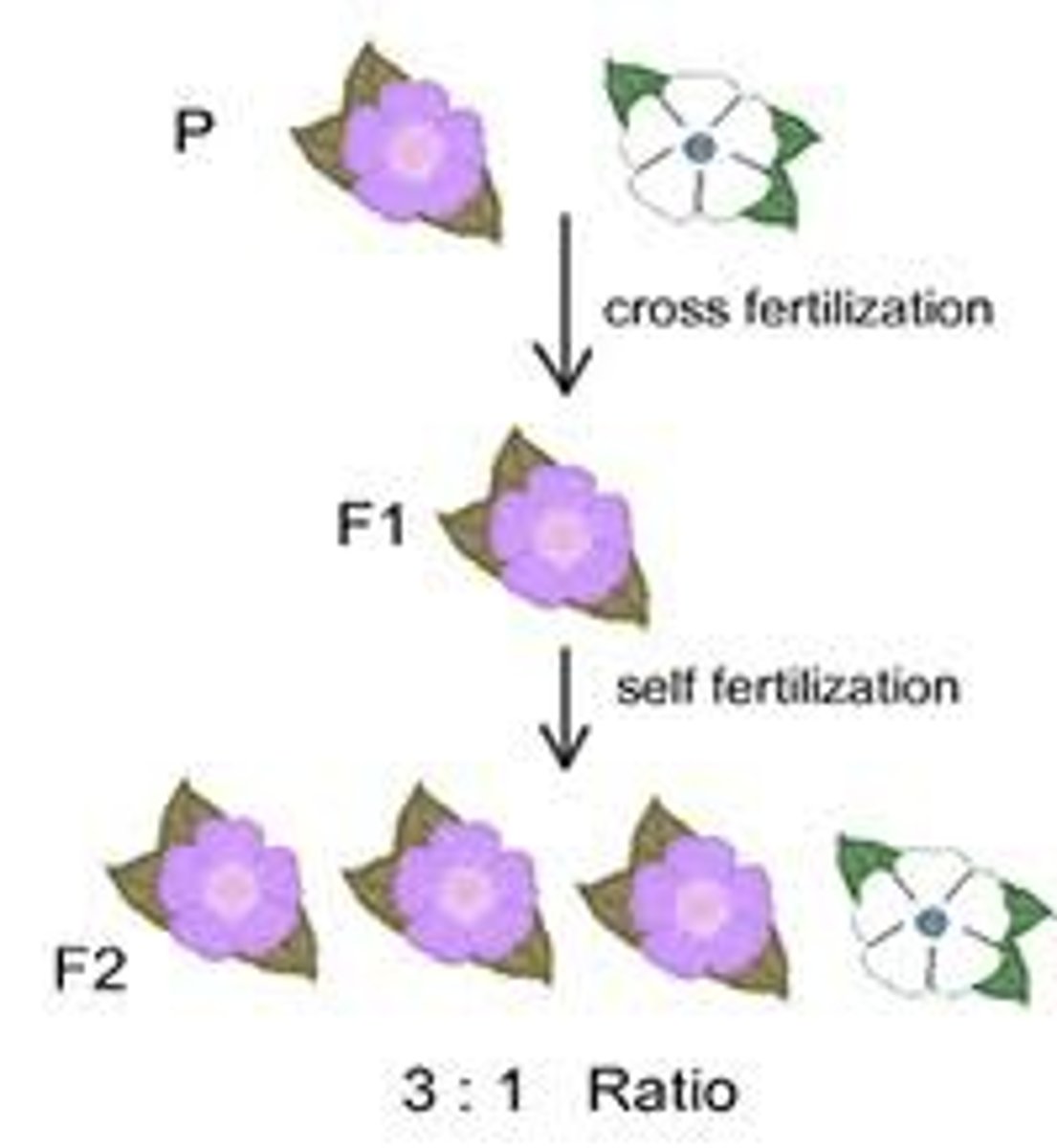
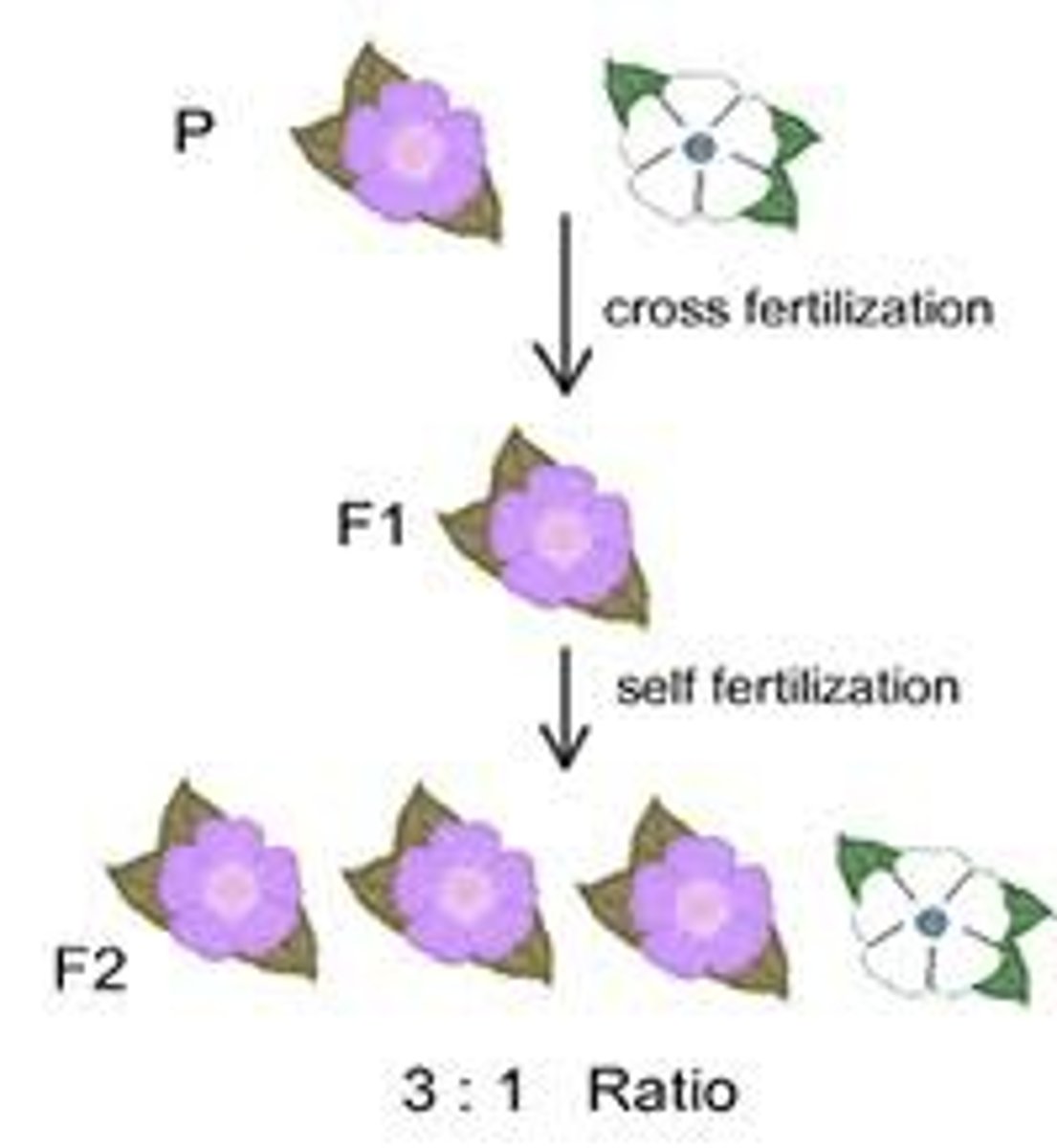
F2 generation
Offspring from a F1 x F1 cross (Second Filial generation)
Gregor Mendel
Father of Genetics; conducted experiments using pea plants

Metaphase
-Chromosomes move to the equator via centromeres attached to a spindle fibre
Anaphase
-Spindle fibres contract pulling sister chromatids to opposite poles
Telophase
-Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear
-Chromosomes relax; cytokinesis occurs
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that determines an inheritable specific characteristic.
Alleles
Different variations of the same gene
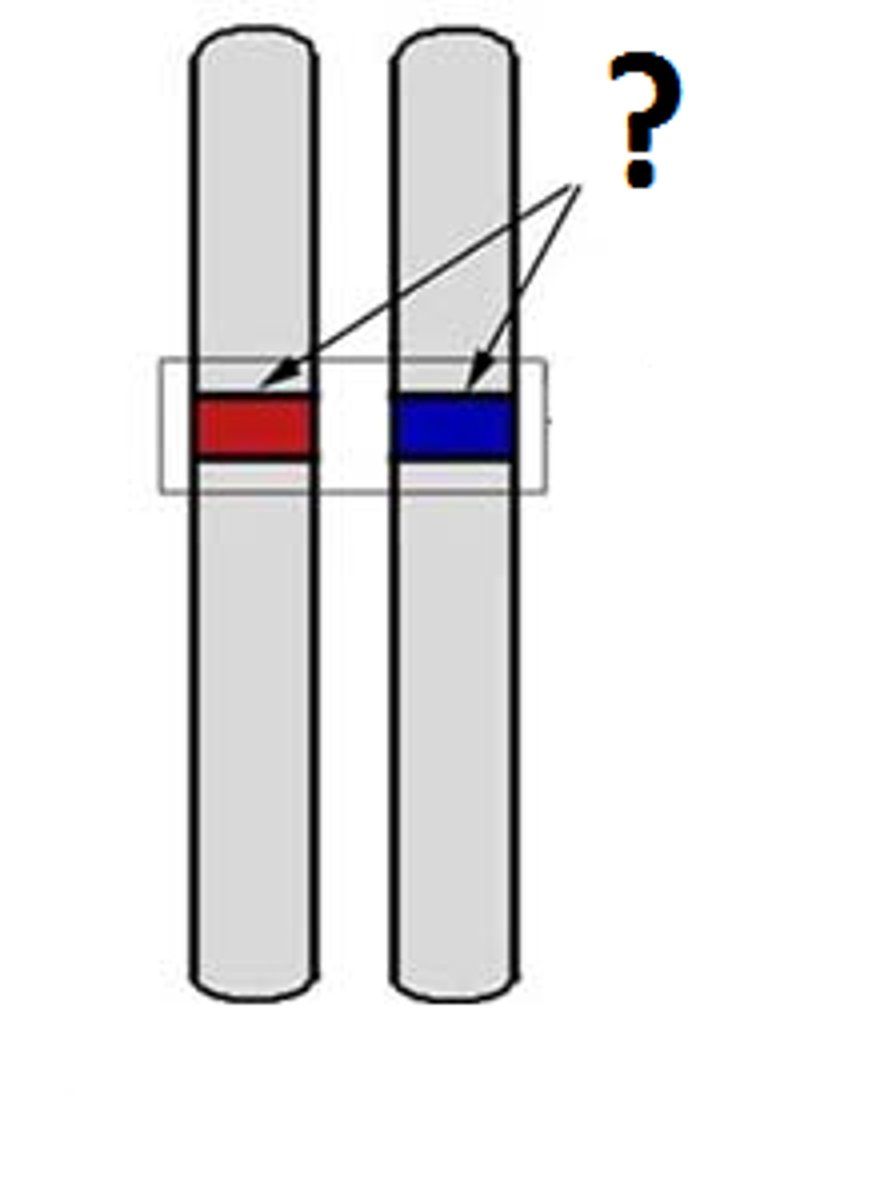
The Law of Segregation
For each trait, an organism carries two genes; one from each parent. Parents donate only one copy of each of their genes ( creating alleles)
Dominant
Allele that is visible regardless of the other allele being dominant or recessive and is represented by an uppercase letter in the genotype
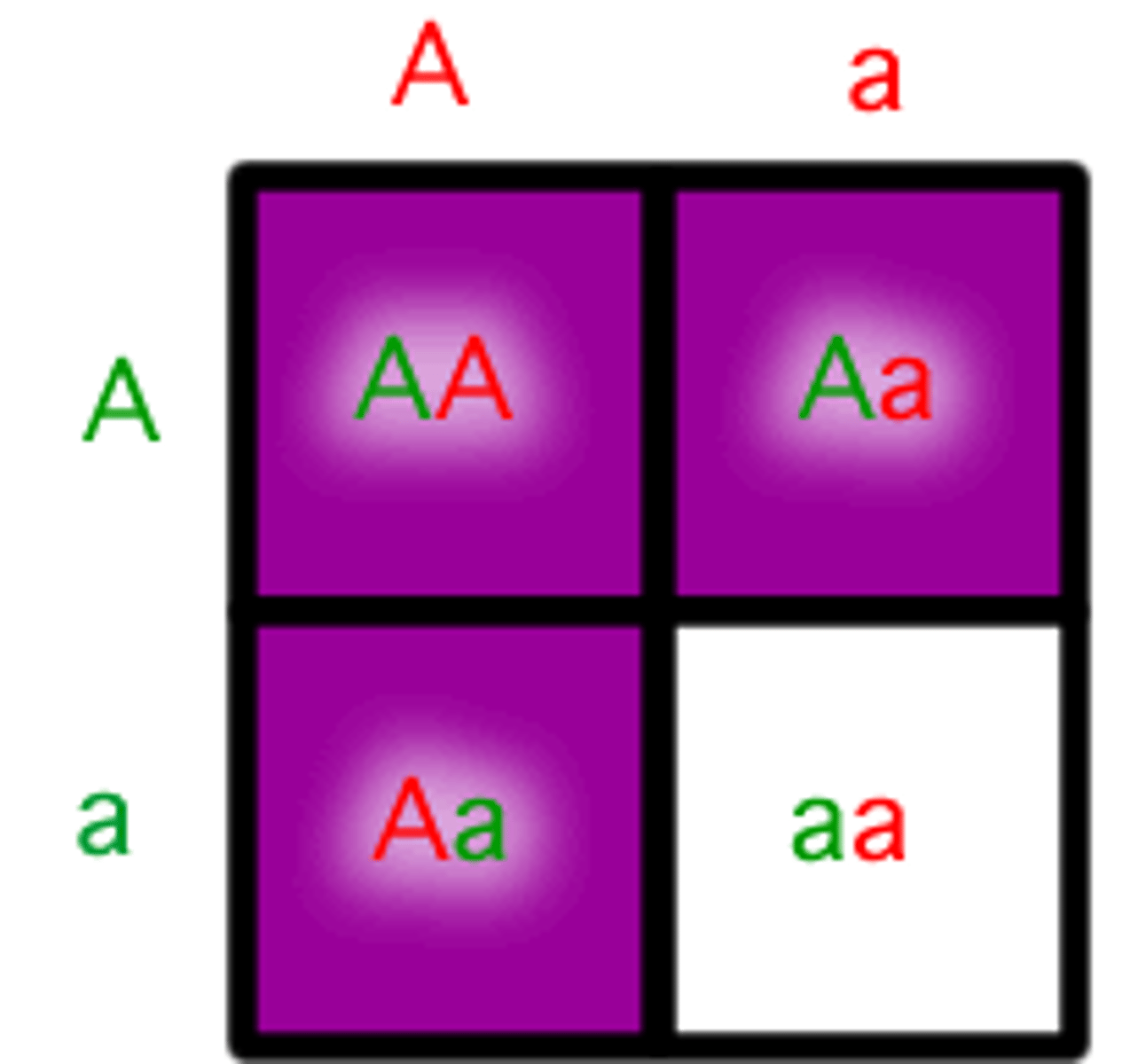
Recessive
Allele that is only expressed when two recessive alleles are present, but masked (hidden) when a dominant allele is present and is represented by a lowercase letter in the genotype
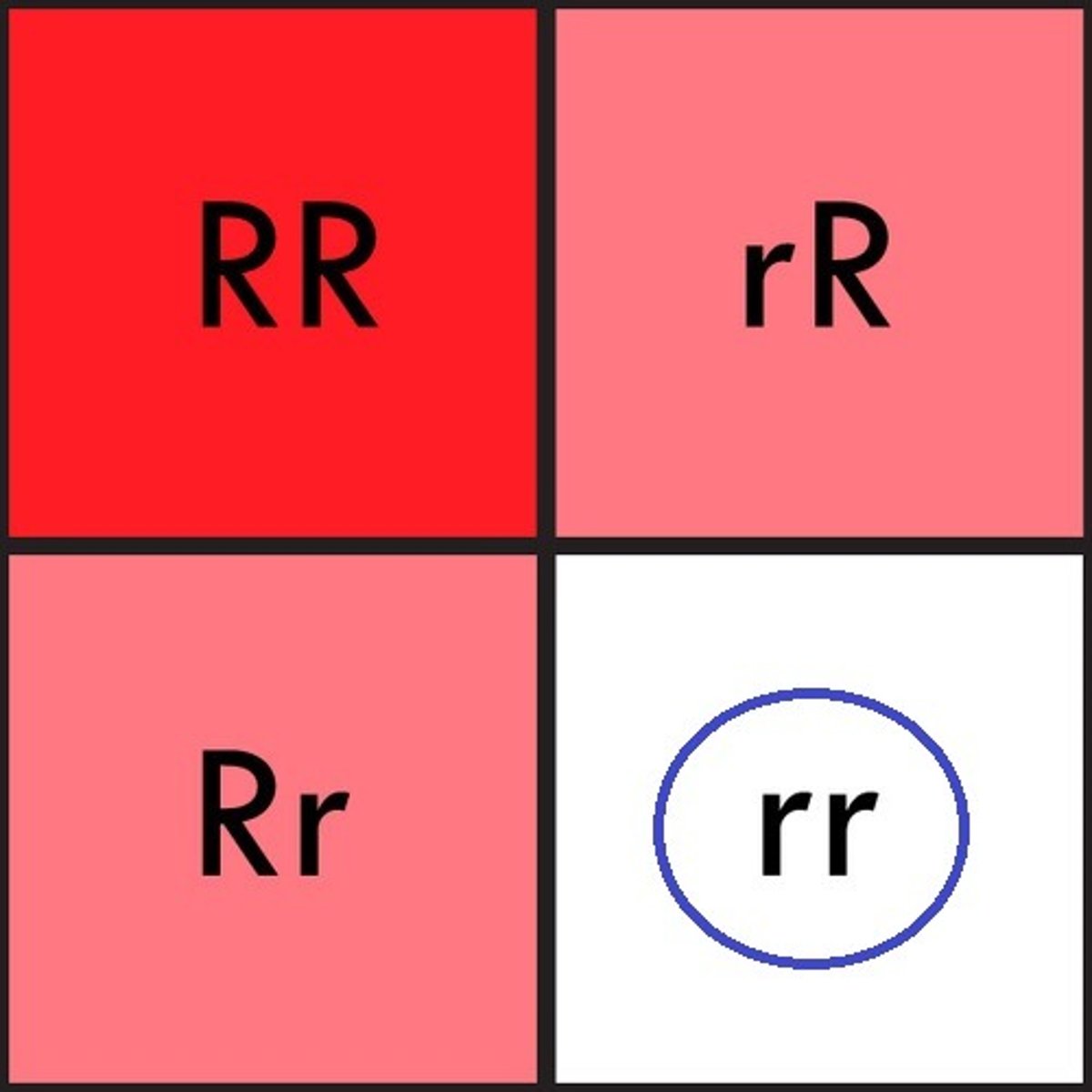
Phenotype
Observable (physical) characteristics resulting from the combination of alleles in the genotype
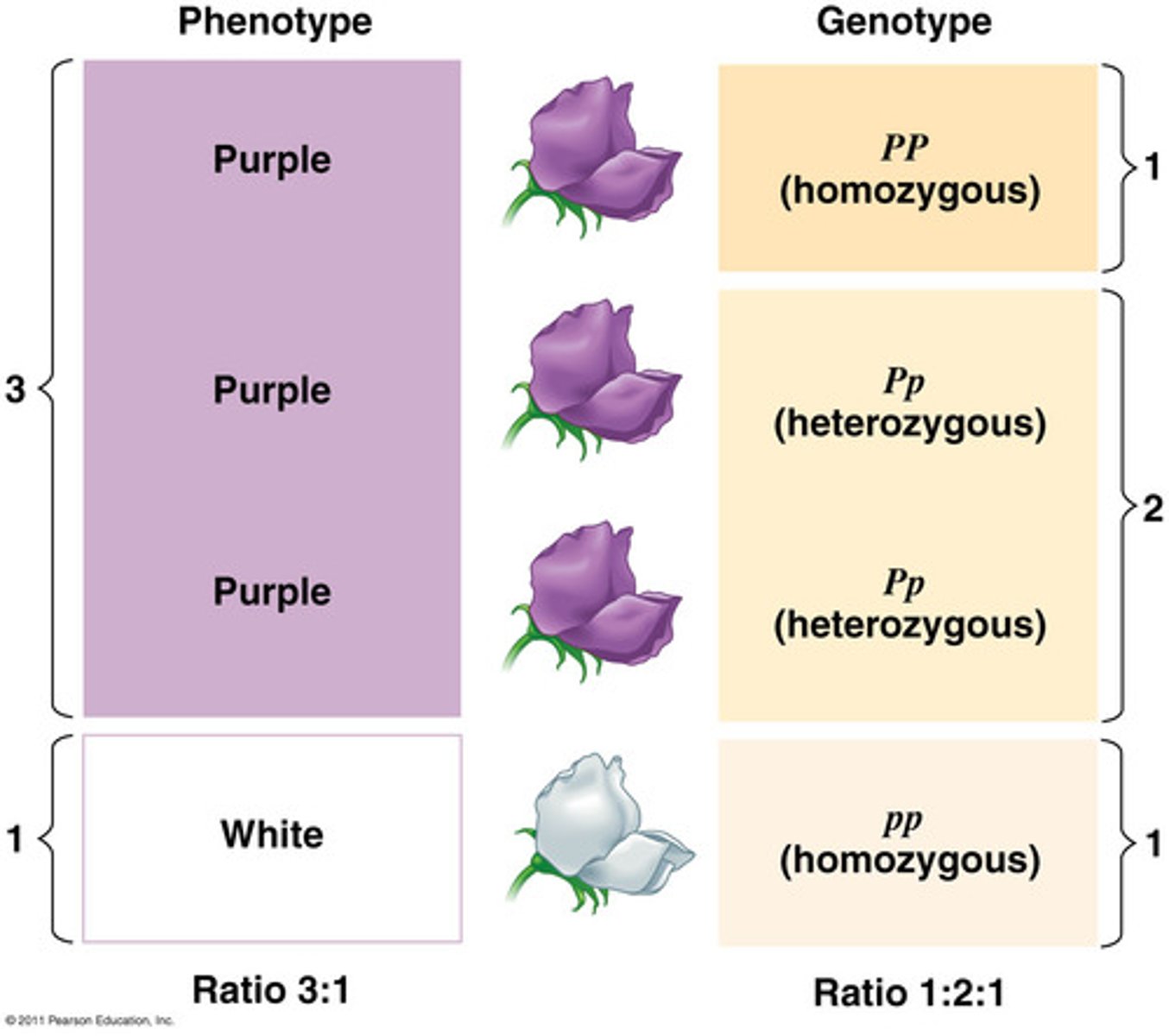
Genotype
Specific combination of alleles of a trait in an organism represented by a set of letters
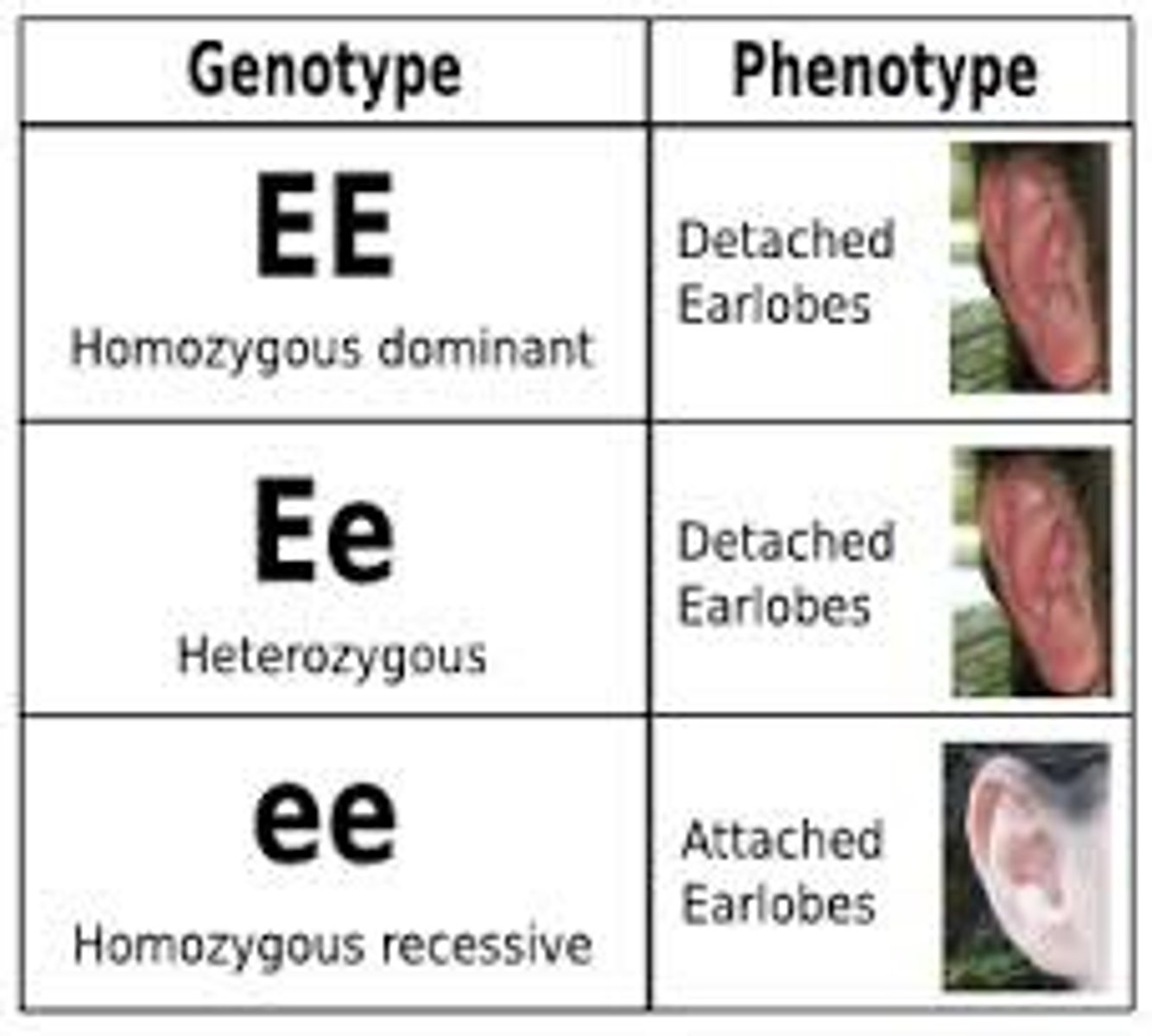
Homozygous
A combination of alleles where both alleles in the set are identical
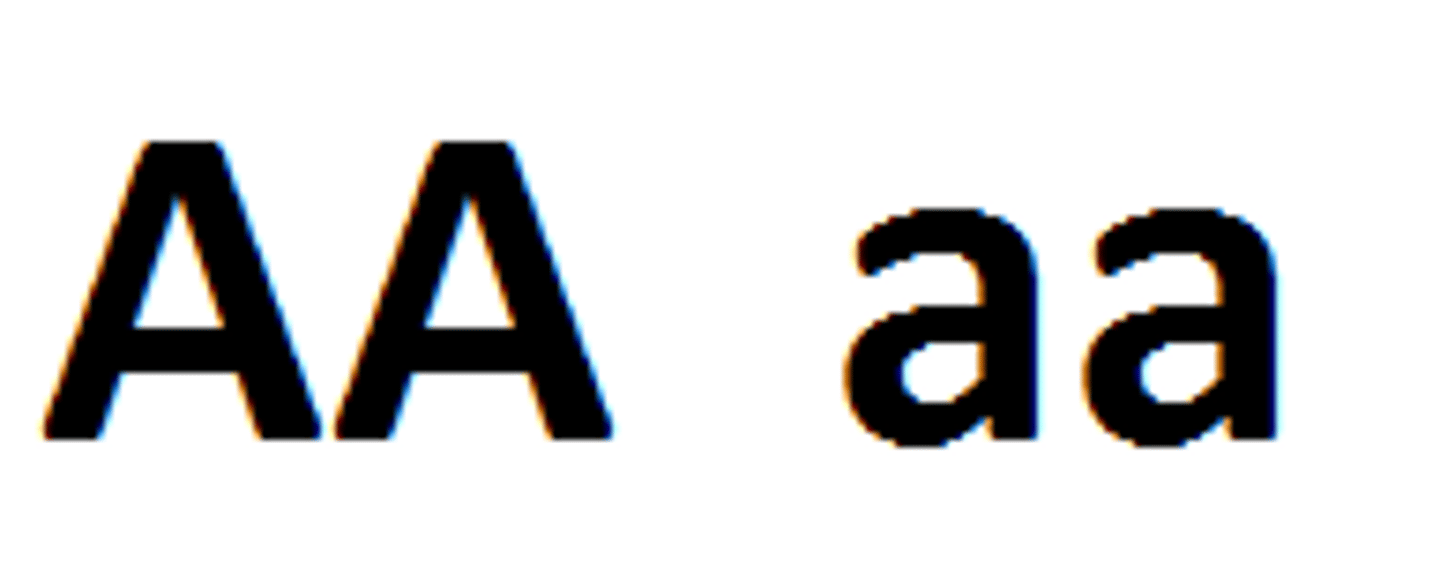
Homozygous Dominant
A set of dominant alleles that are identical
Homozygous Recessive
A set of recessive alleles that are identical
Heterozygous
A combination of alleles where the two alleles are different with one dominant allele and one recessive allele
Monohybrid Cross
A simple genetic cross where the parents have different alleles of a specific trait
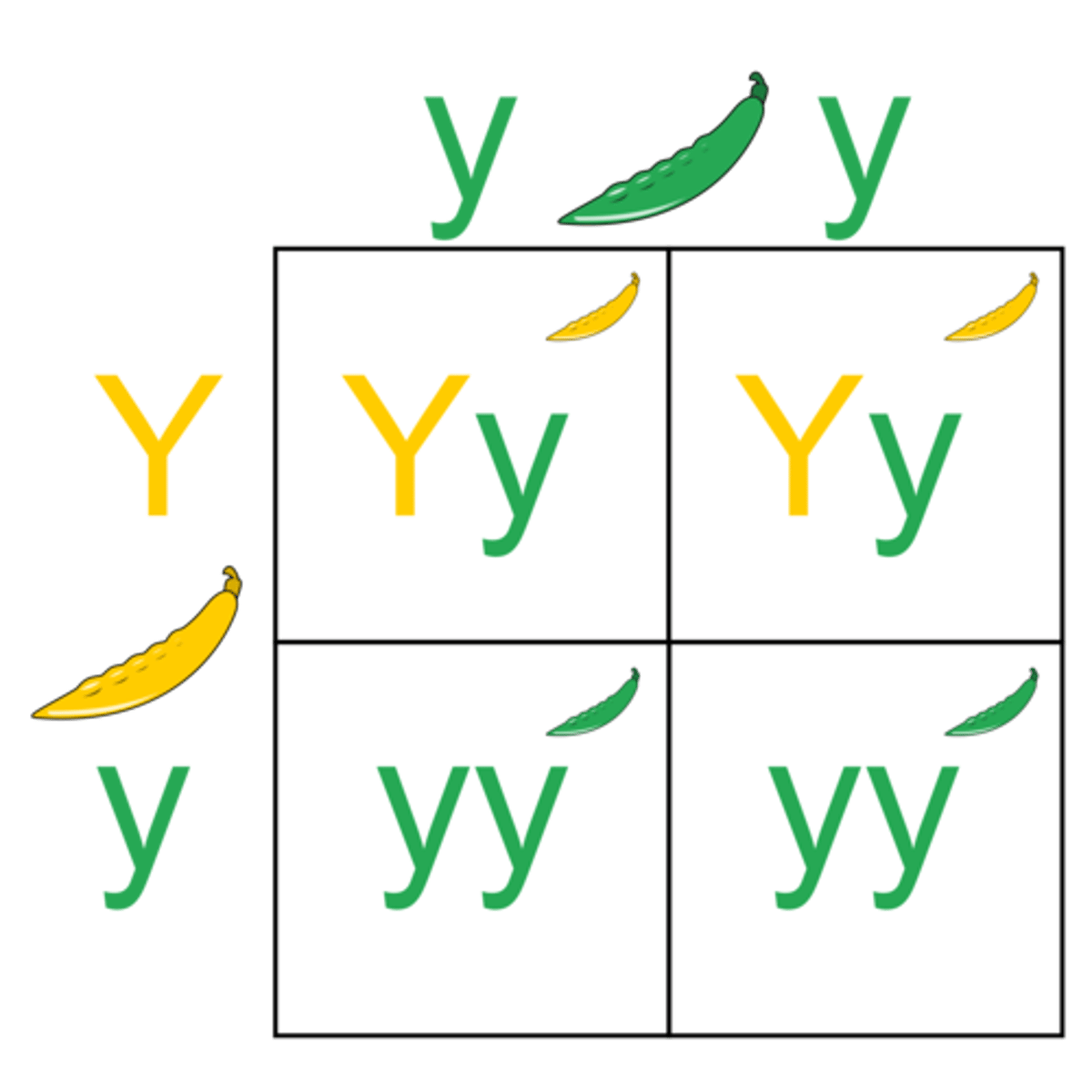
Punett Square
Simple grid that is used to represent the possible genotypes of offspring in monohybrid crosses
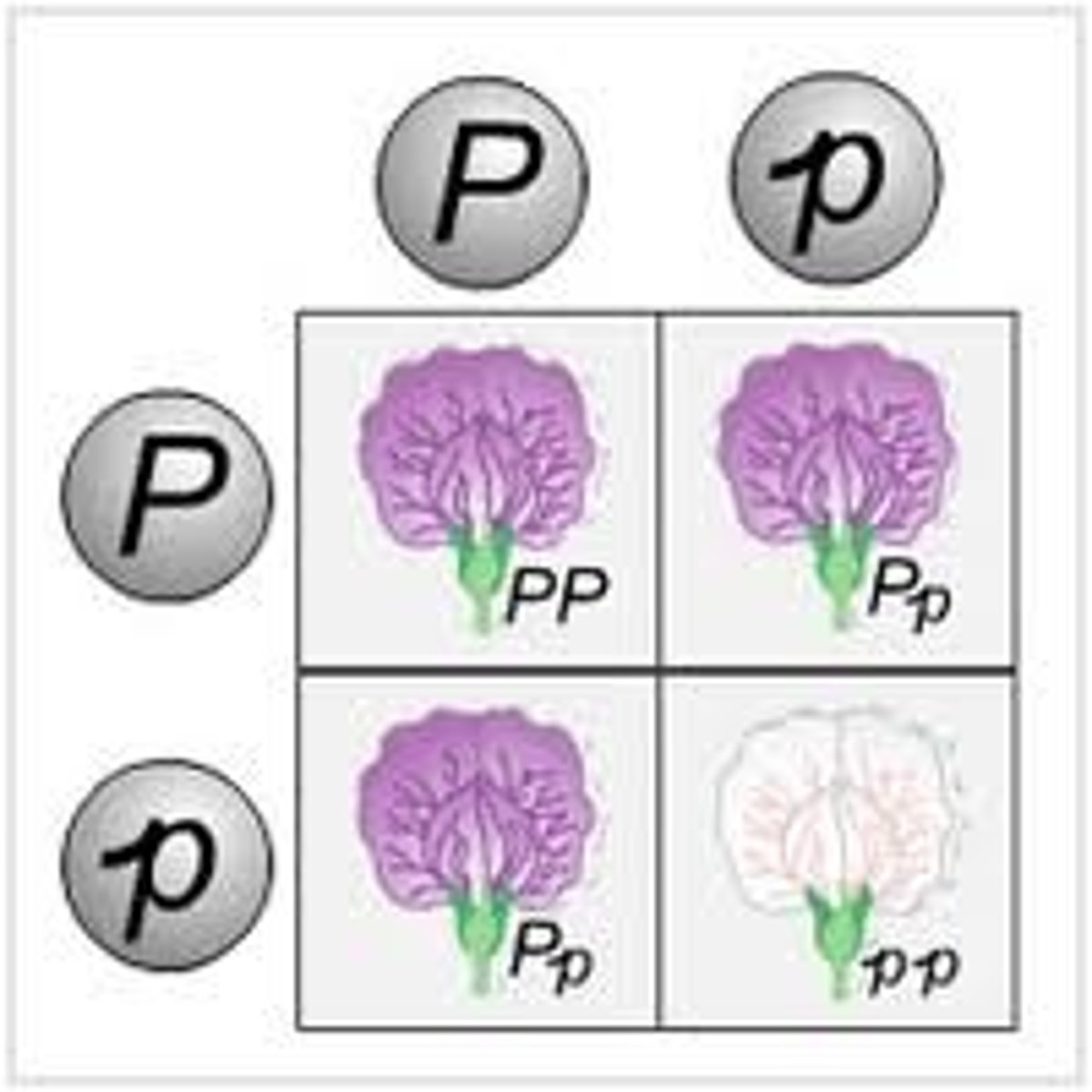
Dihybrid Cross
A genetic cross where the parents have different alleles of two specific traits
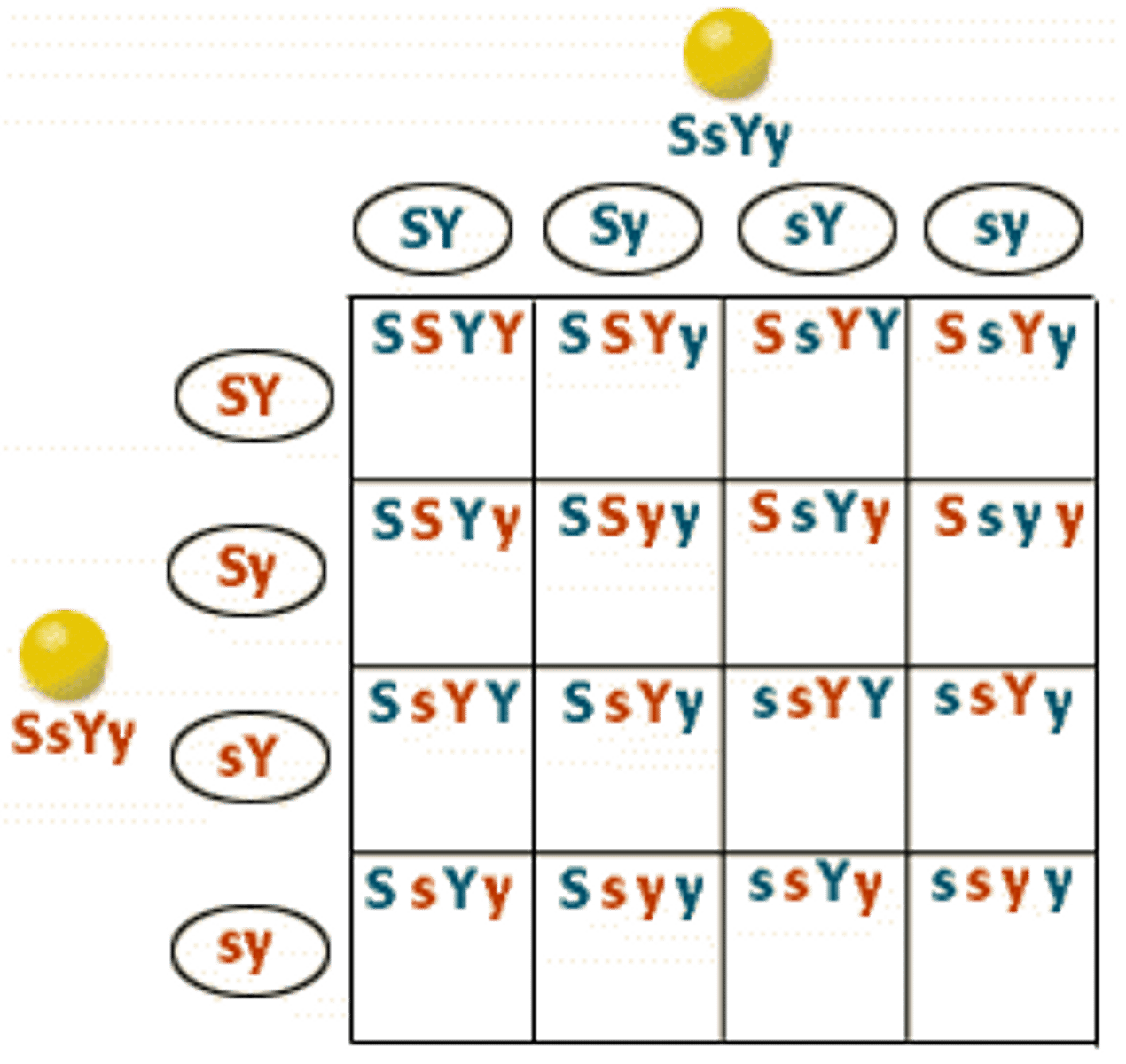
The Law of Independent Assortment
Two alleles of one gene segregate without influencing the segregation of two alleles of a different gene and the probability of the phenotype of the offspring will always have the ratio 9:3:3:1 regardless of which two genes
Complete Dominance
One trait fully dominates and is expressed in the phenotype
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygote has an intermediate trait between the dominant and recessive phenotype due to neither of the alleles fully dominating the other and this is represented by superscript in the genotype
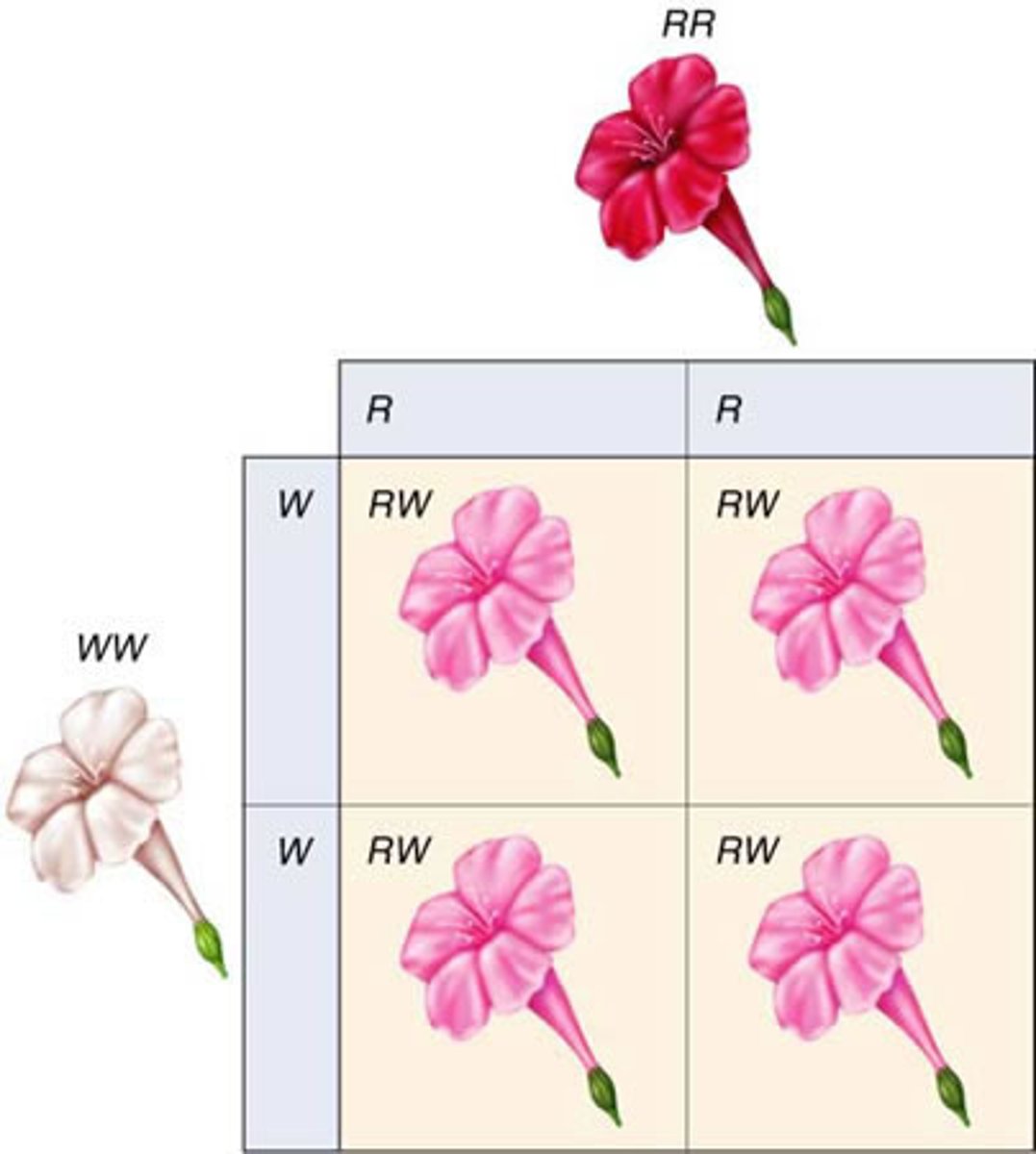
Codominance
Heterozygote fully expresses the traits of both alleles and this is represented by only having captial letters in the genotype since there is no recessive allele
Multiple Alleles
When there are more than two variations of the same gene

Sex-Linked Inheritance
Traits controlled by genes located on the sex chromosomes
Autosomes
A chromosome that is not involved in determining the sex of an organism. ex. humans have 22 autosomes in a human cell.
Centromere
The region where two sister chromatids are held together in a chromosome.
Chromosome
A structure in the nucleus that contains DNA
Crossing over
The exchange of chromosomal segments between a pair of homozygous chromosomes.
Gamete
A male or female reproductive cell
Haploid
-A cell that contains only one set of chromosomes and the same sequence of genes as another chromosome
-Produced in meiosis
-Half the number of chromosomes found in the nucleus
Diploid
-Two sets of chromosomes
-Double the number of chromosomes found in the nucleus
-non-sex cells
A
Adenine
T
Thymine
G
Guanine
C
Cytosine
Karyotype
A photograph of pairs of homologous chromosomes in a cell
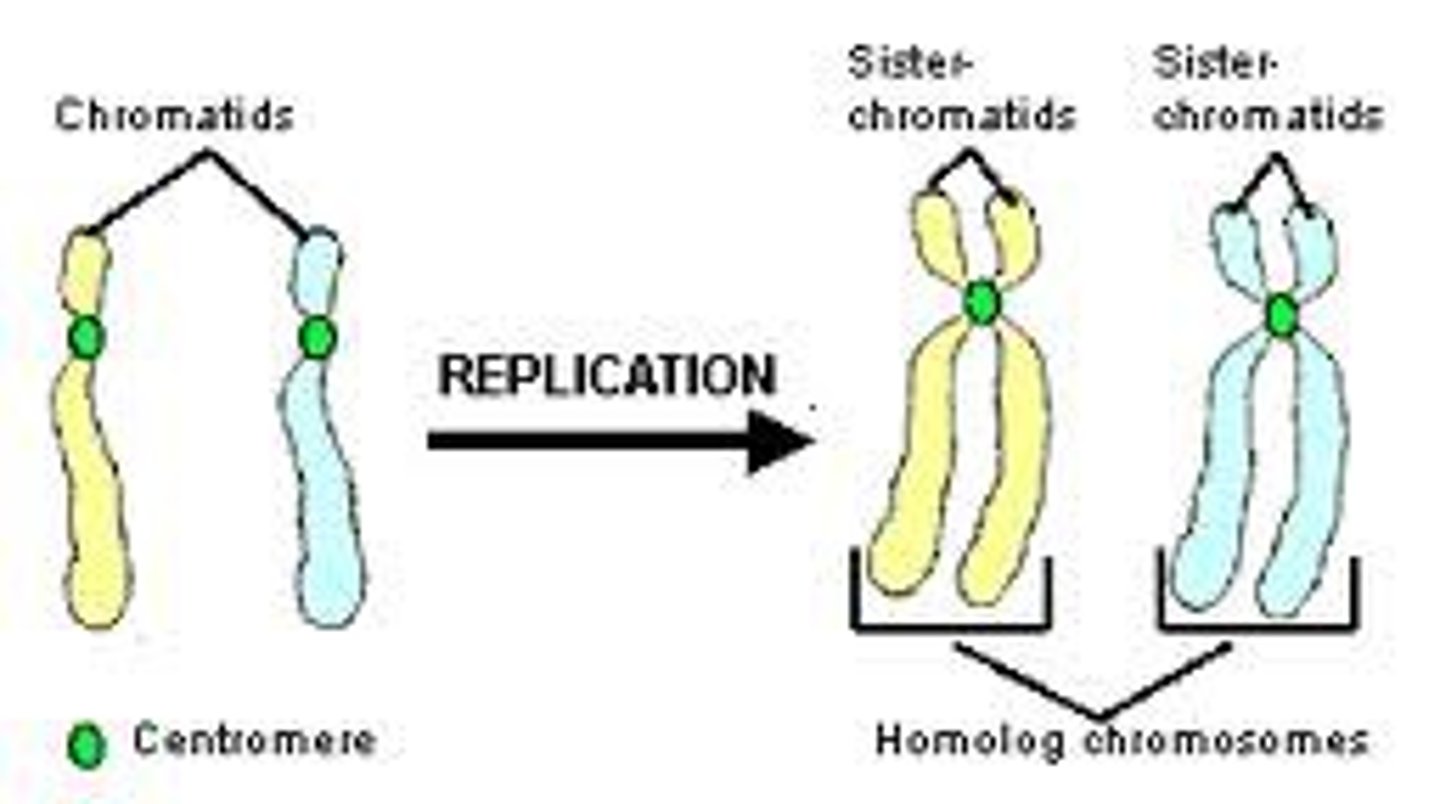
Sister Chromatids
one of two chromosomes that are genetically identical and held together in a chromosome
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosome pairs or sister chromatids to separate during meiosis
Type A blood
- Can accept A because it has A antigens
- Can accept O blood because there are no antigens
- Can't accept B or AB blood because it has B antibodies
Type B blood
- Can accept B because it has B antigens
- Can accept O blood because there are no antigens
- Can't accept A or AB blood because it has A antibodies
Type O blood
- Can accept O because it has no antigens
- Can't accept A, B, and AB because it makes A and B antibodies
Type AB blood
- Can accept AB because it has AB antigens
- Can accept O because it has no antigens
- Can accept A and B because of no antibodies
Genetics
The study of heredity and variation
Homologous Chromosomes
Carry information for the same genes and are similar in size and shape
Monosomy
a daughter cell is missing a chromosome (non-disjunction
Trisomy
a daughter cell has an extra chromosome (non-disjunction)