3.6a Social-Emotional Development in Infancy and Childhood
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
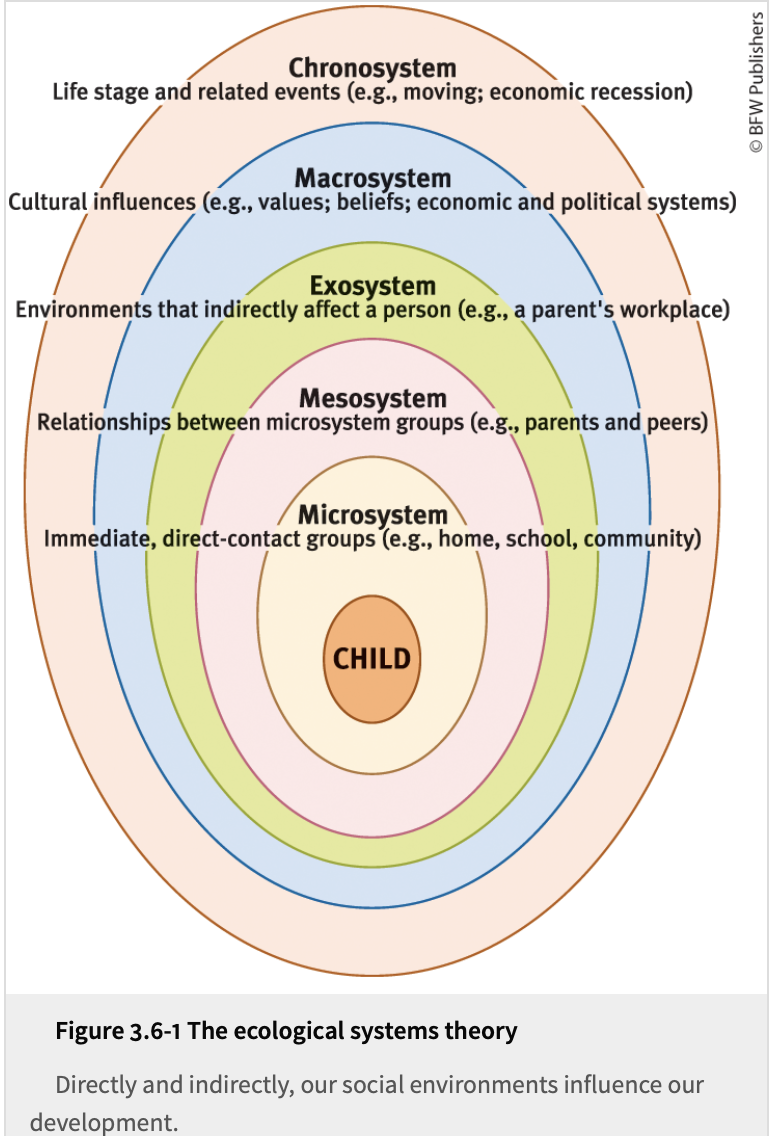
Ecological systems theory
A theory of the social environment’s influence on human development, using five nested systems (microsystem; mesosystem; exosystem; macrosystem; chronosystem) ranging from direct to indirect influences
Ecological systems theory (visual)
Stranger anxiety
The fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
Attachment
An emotional tie with others; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to caregivers and showing distress on separation
Strange situation
A procedure for studying child-caregiver attachment; a child is placed in an unfamiliar environment while their caregiver leaves and then returns, and the child’s reactions are observed
Secure attachment
Demonstrated by infants who comfortably explore environments in the presence of their caregiver, show only temporary distress when the caregiver leaves, and find comfort in the caregiver’s return
Insecure attachment
Demonstrated by infants who display either a clinging, anxious attachment or an avoidant attachment that resists closeness
Temperament
A person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
Basic trust
According to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
Self-concept
All our thoughts and feelings about ourselves in answer to the question, “Who am I?”
Authoritarian parents
Coercive; they impose rules and expect obedience
Permissive parents
Unrestraining; they make few demands, set few limits, and use little punishment
Neglectful parents
Uninvolved; they are neither demanding nor responsive. They are careless and inattentive, and do not seek a close relationship with their children
Authoritative parents
Confrontive; they are both demanding and responsive, exerting control by setting rules, but, especially with older children, they encourage open discussion and allow exceptions