Lab X Practice Exams
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
When given EMG data, want “best activates” the muscle
concentric action for several different exercises: look for the highest number (more EMG activity, taking more work) not as strong concentrically
When given EMG data, want “best isolates” the muscle
least amount of activation in the OPPOSITE muscle
Which of the following fiber types would tend to be the largest diameter fibers in men?
a) I
b) IIC
c) IIA
d) IIAX
e) IIX
c) IIA
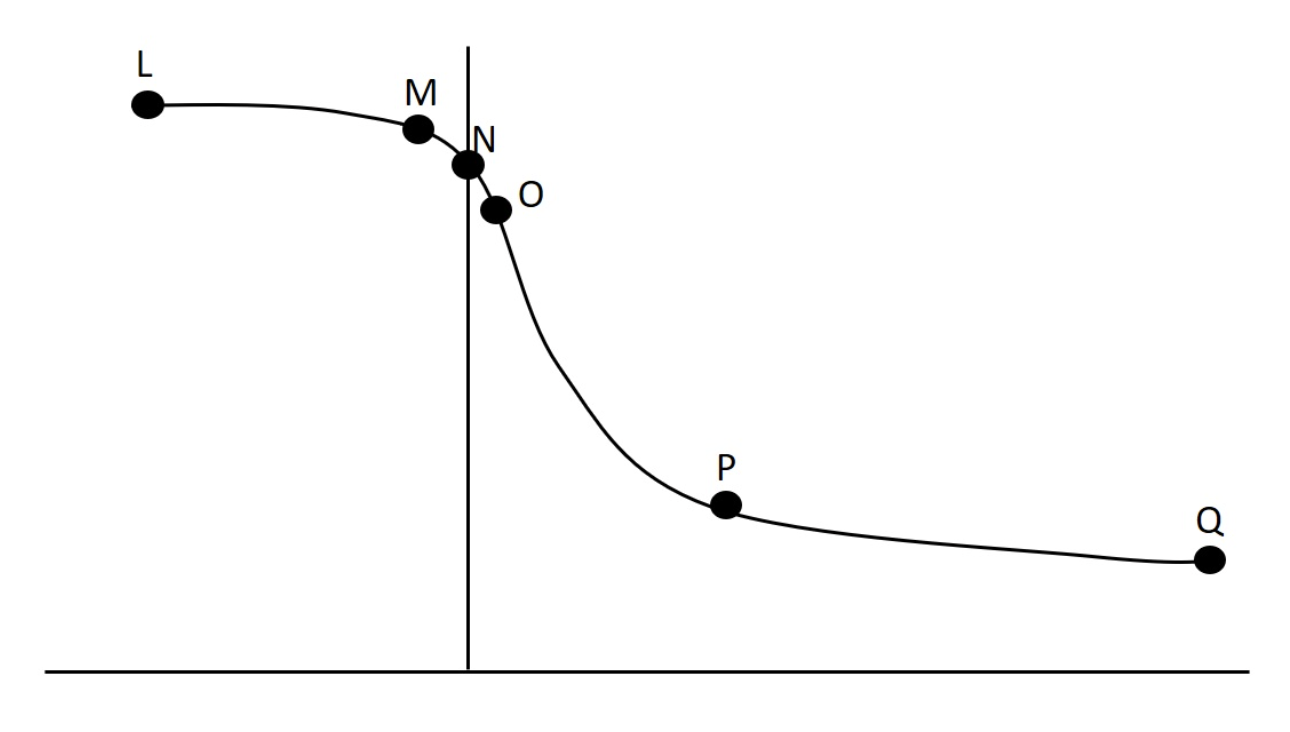
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. High speed resistance training would increase which concentric data point the most?
Q
How much power is produced when performing a military press, your subject moved a/n 29 pound weight a distance of 0.34 meters in 0.34 seconds. No units required
129.3
F = mass (kg) * 9.81 x V = distance (m) / time (sec)
Which of the following is NOT a potential mechanism that contributes to peripheral fatigue of skeletal muscle?
a) depletion of PCr stores can contribute to peripheral fatigue
b) H+ can inhibit phosphofructokinase and thus slow ATP production, and thus play a role in peripheral fatigue
c) during long duration activities, glycogen depletion can contribute to peripheral fatigue
d) an increase in Pi can potentially result in its precipitation with calcium in the SR and thus impair SR calcium release
e) lactate can directly interfere with actin - myosin interactions and thus reduce force production
e) lactate can directly interfere with actin - myosin interactions and thus reduce force production
During the hold relax PNF procedure, which of the following types of receptors is theoretically being used to help us improve range of motion?
a) group III and IV afferents
b) muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs
c) Ruffini endings and muscle spindles
d) joint kinesthetic receptors
e) muscle spindles
f) cutaneous Ruffini endings
g) golgi tendon organs
g) golgi tendon organs
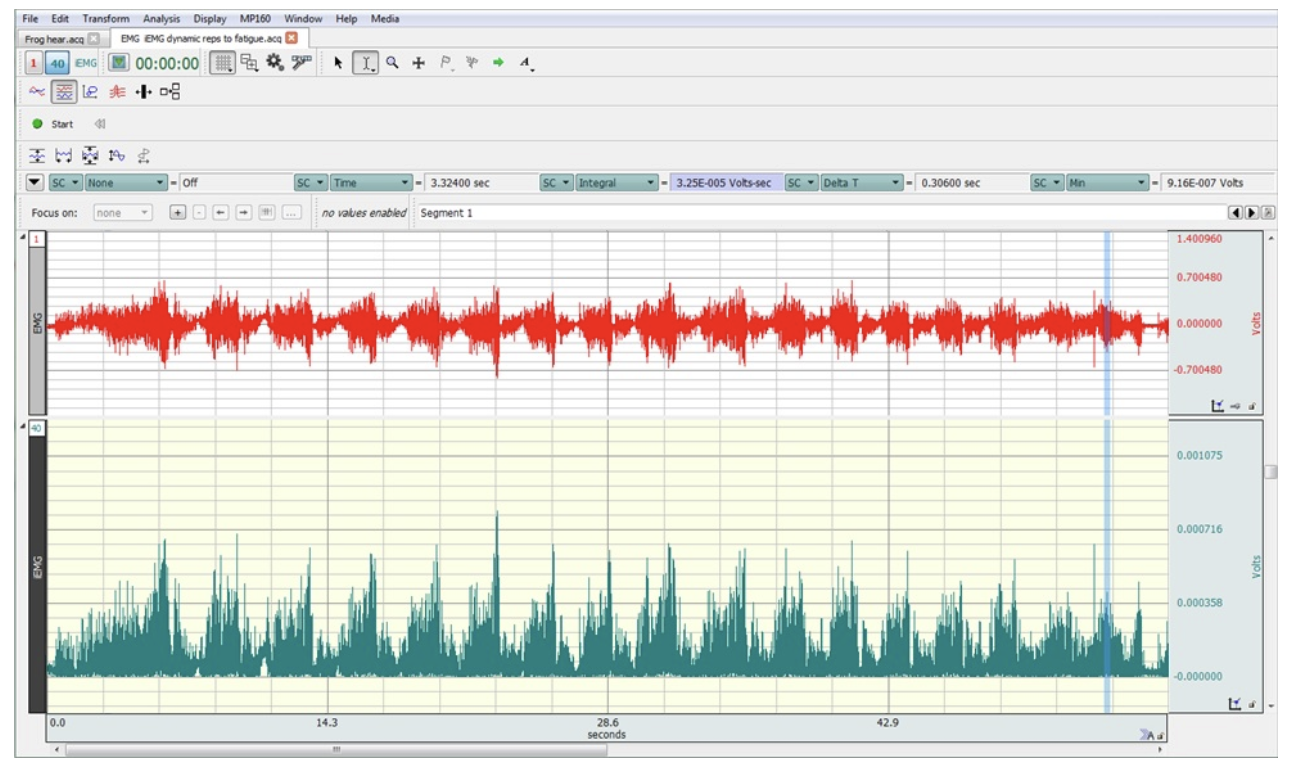
The following figure depicts EMG and iEMG activity during dynamic bicep curls until the subject could not lift the weight anymore. They lifted the weight 17 times before they fatigued. Which of the following mechanism(s) are most llikely to be contributing this fatigue, given this set of data?
a) PCr depletion
b) failure to release enough calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
c) an increase in Pi inside the muscle fibers
d) low dopamine levels in motor areas of the brain
e) a decrease in pH in the muscle fibers
d) low dopamine levels in motor areas of the brain
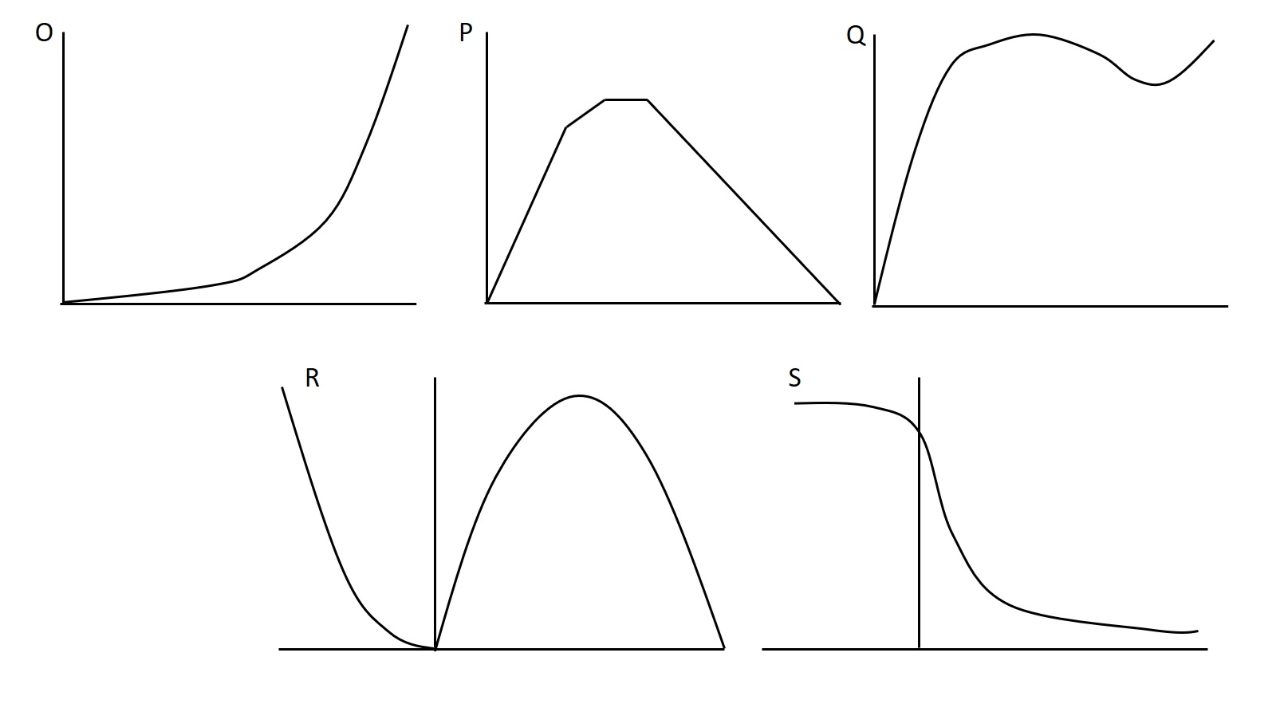
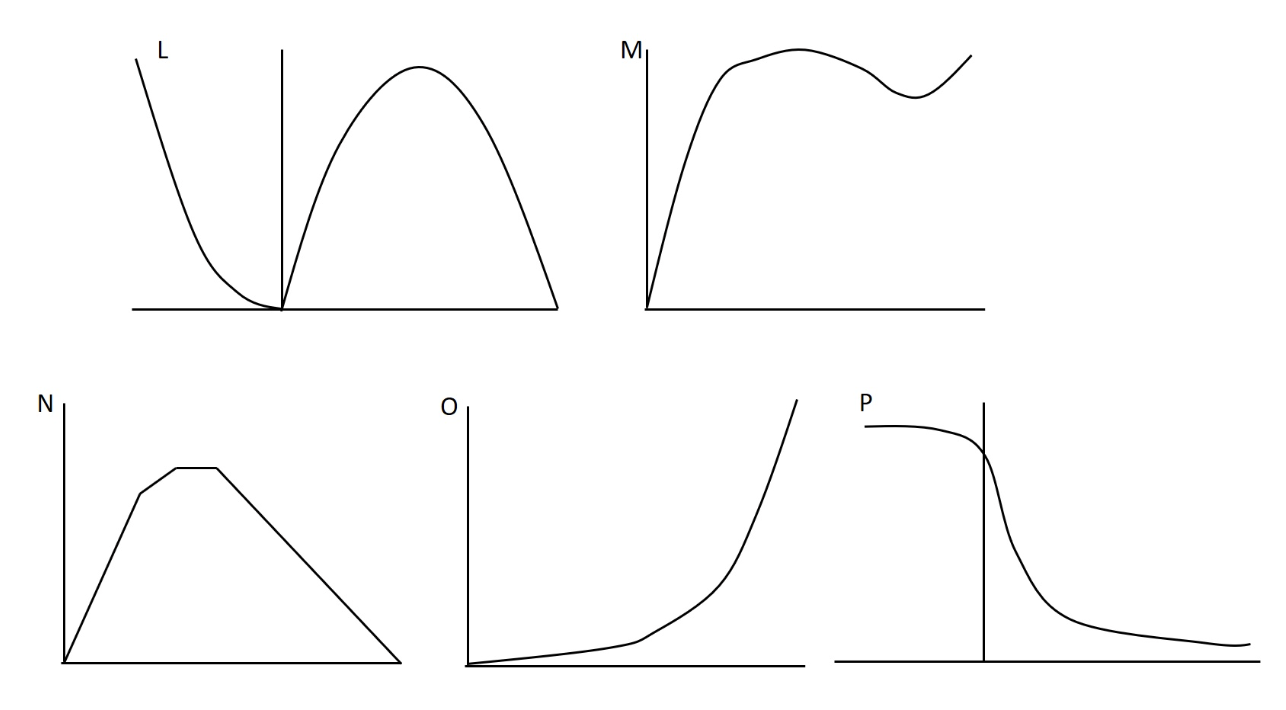
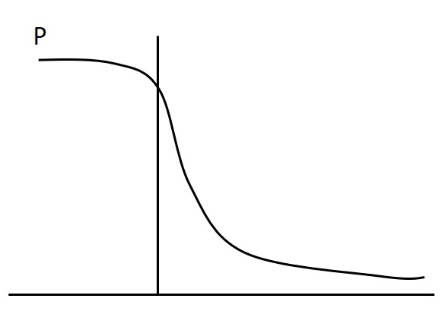
In our recent lab we did experiments related to several aspects of muscle performance including force, velocity, power, and muscle length. Which of the following figures best depicts the length-active tension curve?
P
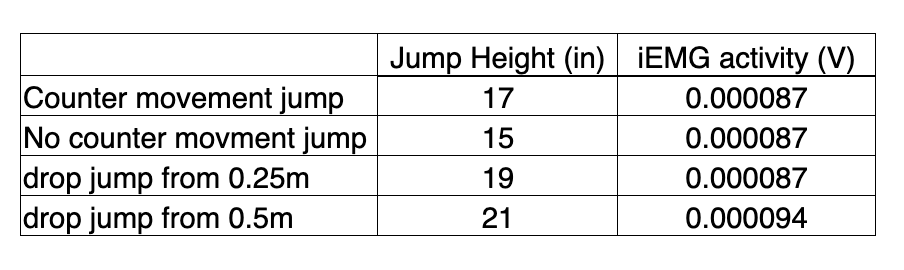
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the increase in jump height between the counter movement jump and the no-counter movment jump?
a) better use of the elastic components of the muscle
b) none of these answers
c) the initiation of an inverse stretch reflex
d) all of these answers
e) the initiation of a stretch reflex
a) better use of the elastic components of the muscle
If you were performing a hold relax with agonist contraction PNF procedure to try to improve gastrocnemius flexibility, which of the following muscles/muscle groups would we contract as during the first phase of this procedure?
a) quadriceps femoris
b) none of these
c) two of these
d) hamstrings
e) dorsiflexors (e.g. tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus)
f) gastrocnemius
f) gastrocnemius
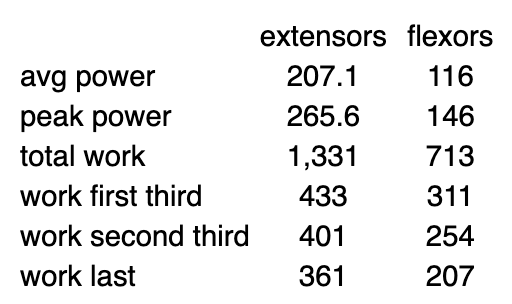
Below you can find data from your subject's Thorstenson test. Calculate the fatigue index (FI, as a %) of this subject's extensors.
83.4
FI = work last third / work first third x 100
FI = 361/433 × 100 = 83.4
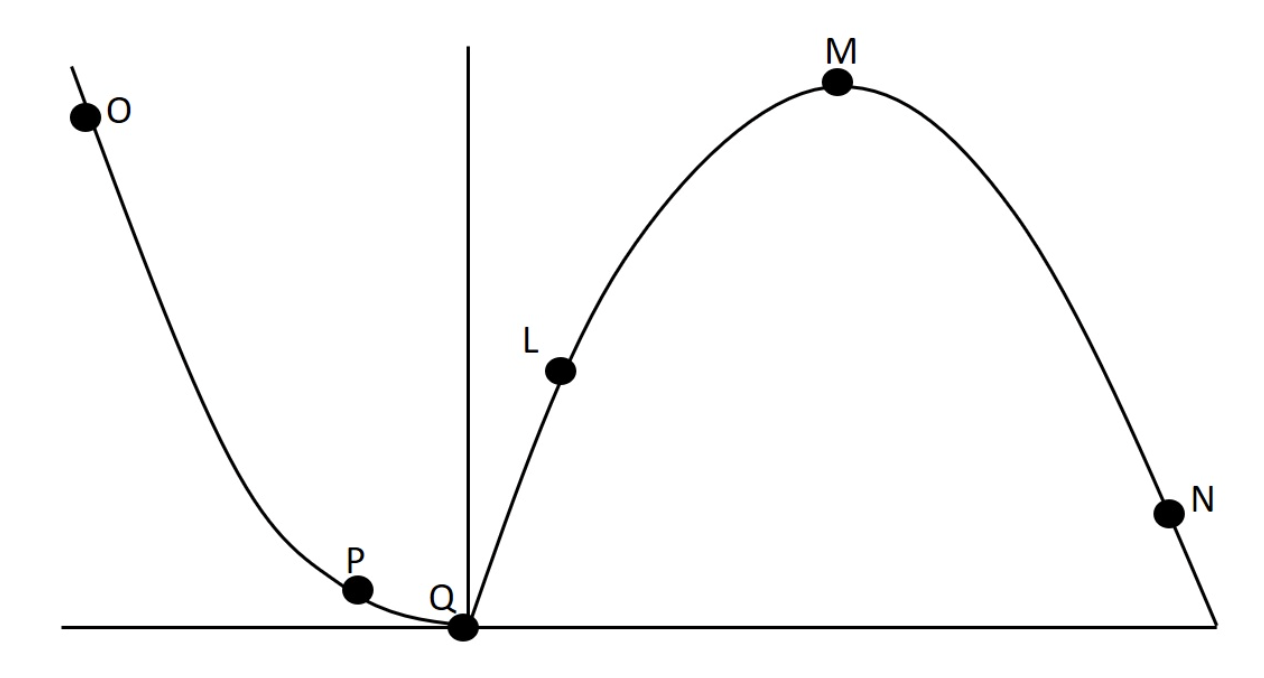
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Which point on this curve would probably be associated with the greatest eccentric forces?
O
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the greatest lactate dehydrogenase activity?
a) IIAX
b) I
c) IIC
d) IIX
e) IIA
d) IIX
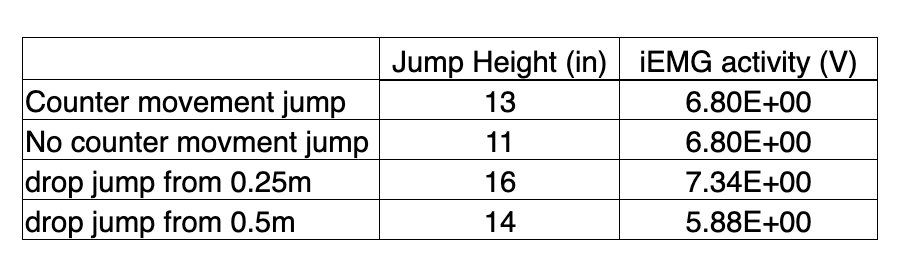
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the decrease in jump height between the 0.25m and 0.5m drop jumps?
a) better use of energy return from elastic proteins like elastin and titin
b) none of these answers
c) activation of muscle spindles, which may have increased motor unit recruitment
d) two of these answers
e) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have decreased motor unit recruitment
e) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have decreased motor unit recruitment
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the increase in jump height between the counter movement and no-counter movement jump?
a) better use of energy return from proteins like elastin and titin
b) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have decreased motor unit recruitment
c) two of these answers
d) activation of muscle spindles, which may have helped to increase motor unit recruitment
e) none of these answers
a) better use of energy return from proteins like elastin and titin
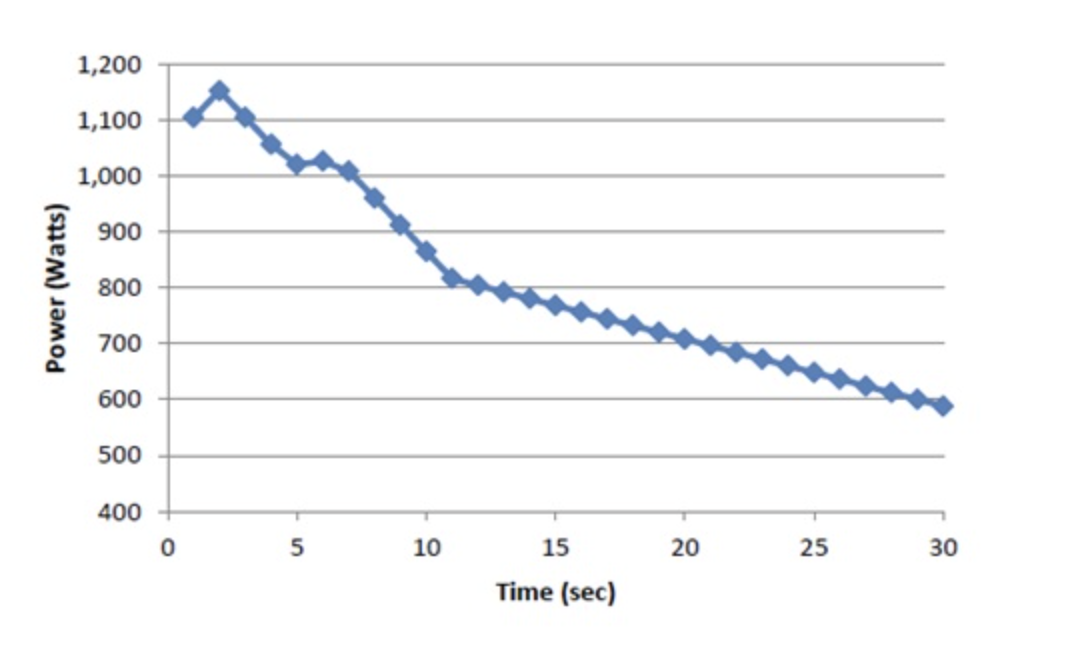
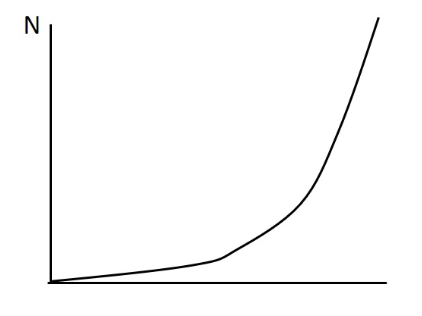
The following immage depicts the changes in power during a Wingate test. Which of the following are likely related to fatigue during this figure based on its appearance?
a) reduced excitability of motor areas of the brain
b) PCr depletion
c) glycogen depletion
d) central fatigue
e) two of these answers
b) PCr depletion
When using the hold-relax with agonist contraction procedure to try to increase the stretch of a muscle we make use of which of the following reflex phenomena?
a) reciprocal inhibition
b) withdrawal reflex and myotatic stretch reflex
c) inverse stretch reflex
d) crossed extensor reflex
e) withdrawal reflex
f) myotatic stretch reflex
g) inverse stretch reflex and reciprocal inhibition
g) inverse stretch reflex and reciprocal inhibition
Which of the following fiber types would tend to store the most intramuscular triglycerides (lipids)?
a) IIA
b) IIC
c) IIAX
d) I
e) IIX
d) I
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the lowest amount of SERCAs?
a) IIX
b) IIA
c) IIAX
d) IIC
e) I
e) I
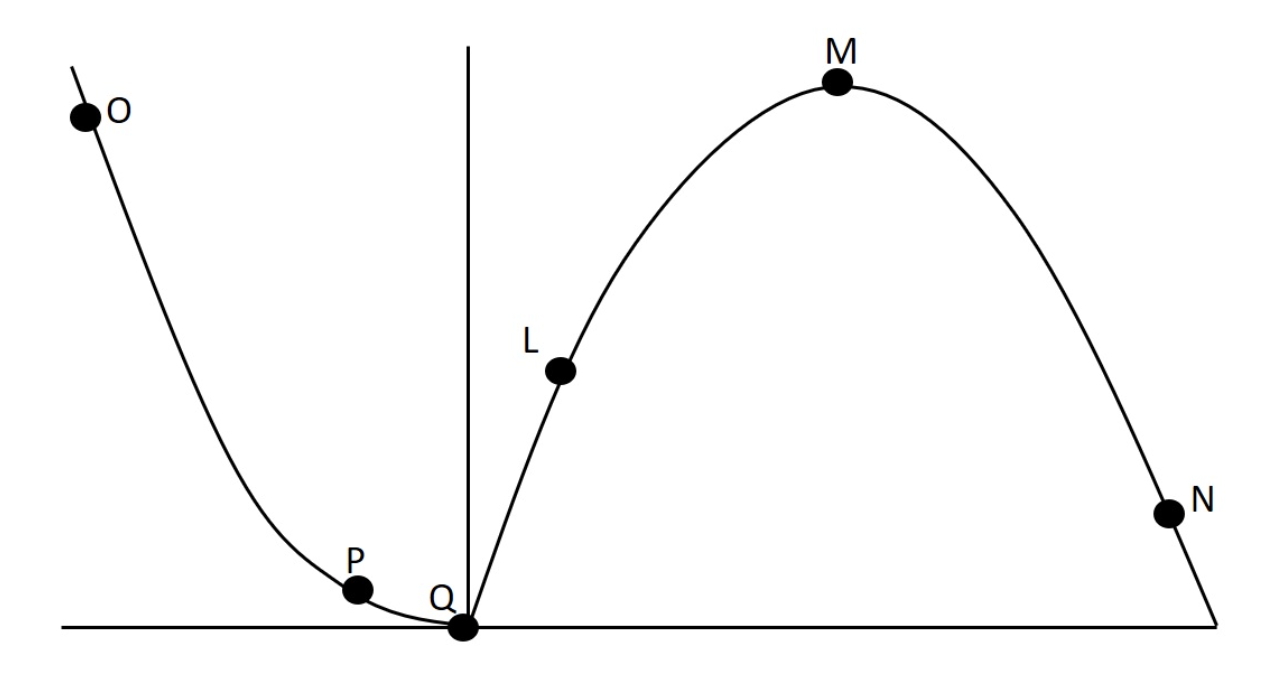
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. How would a muscle with more FT fibers compare to this subject at point Q?
a) the subject with more fast twitch fibers would have lower values
b) none of these answers are true
c) the subject with more fast twitch fibers would have higher values
d) they would be about the same
d) they would be about the same
During the first phase of the hold relax with agonist contraction PNF procedure, which of the following types of receptors is theoretically being used to help us improve range of motion?
a) joint kinesthetic receptors
b) Ruffini endings and muscle spindles
c) cutaneous Ruffini endings
d) muscle spindles
e) group III and IV afferents
f) golgi tendon organs
f) golgi tendon organs
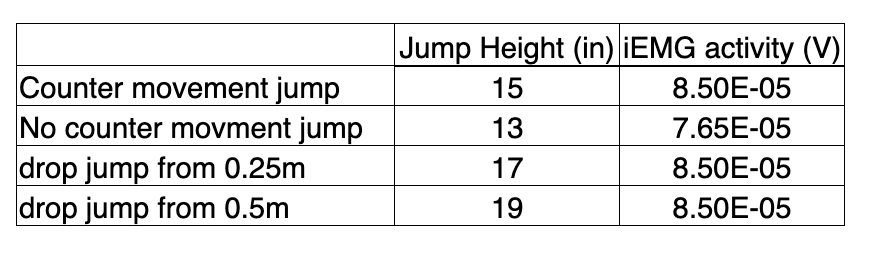
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the increase in jump height between the 0.25m drop jump and the 0.5m drop jump?
a) better use of the elastic components of the muscle
b) the initiation of a stretch reflex
c) none of these answers
d) the initiation of an inverse stretch reflex
e) all of these answers
a) better use of the elastic components of the muscle
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the greatest lactate dehydrogenase activity?
a) IIX
b) IIAX
c) I
d) IIC
e) IIA
a) IIX
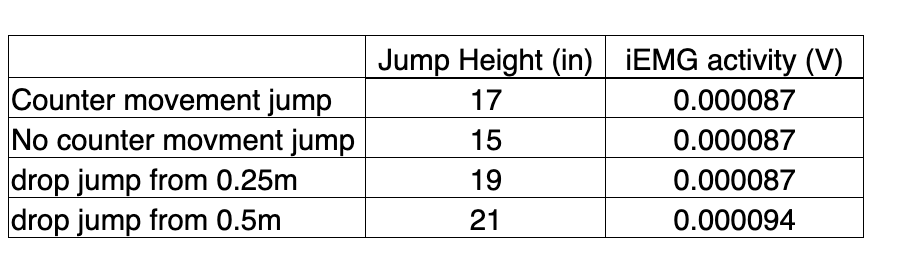
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the increase in jump height between the 0.25m drop jump and the 0.5m drop jump?
a) all of these answers
b) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have increased motor unit recruitment
c) activation of muscle spindles, which may have increased motor unit recruitment
d) none of these answers
e) better use of elastic energy return from proteins like elastin and titin
c) activation of muscle spindles, which may have increased motor unit recruitment
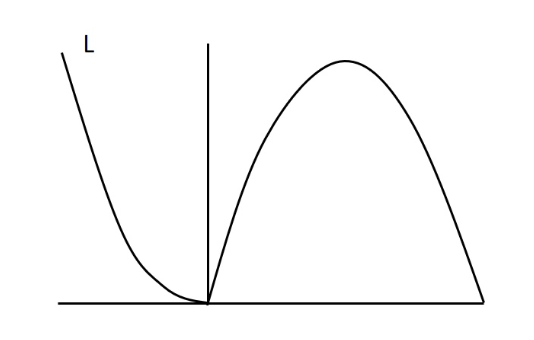
In our recent lab we did experiments related to several aspects of muscle performance including force, velocity, power, and muscle length. Which of the following figures best depicts the power-velocity curve during concentric and eccentric actions?
L
Myosin heavy chain IIX would be the predominant type of myosin in which fiber type?
a) IIC
b) I
c) IIAX
d) IIA
e) IIX
e) IIX
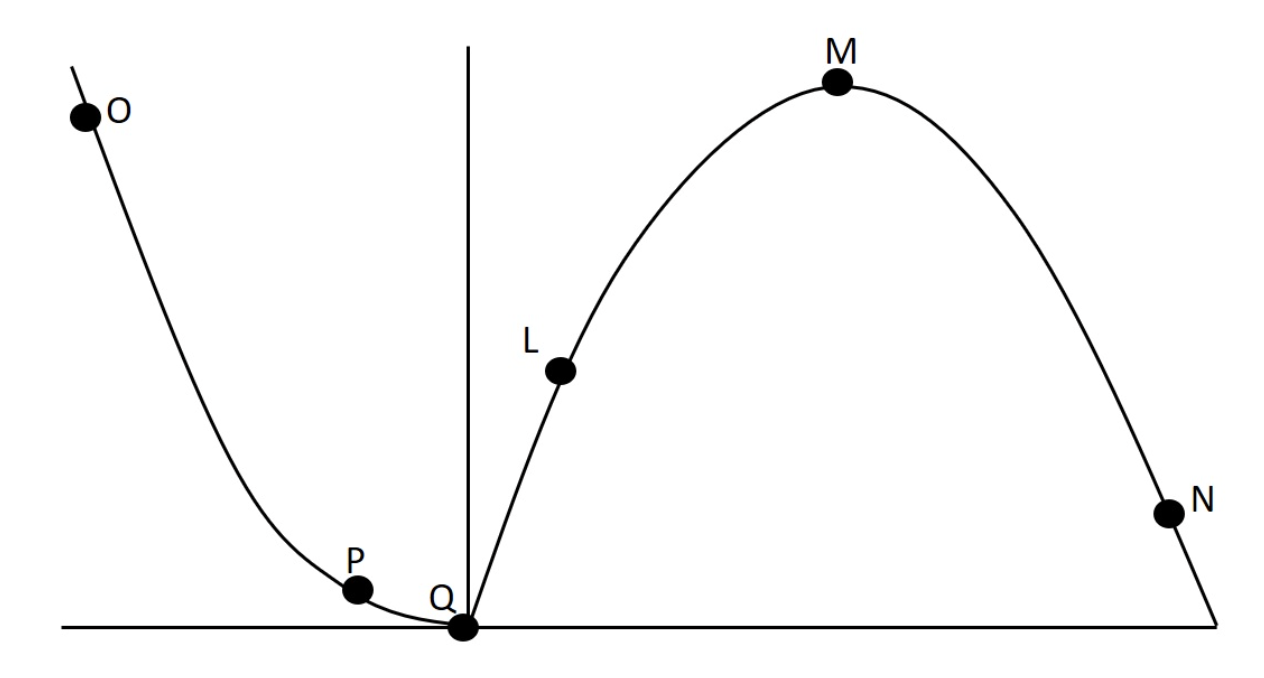
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Why does point O have a high value on this figure?
a) power is high; with concentric actions force increases as velocity decreases
b) power is high here because force increases as velocity increases with eccentric actions
c) during eccentric actions low velocity is associated with higher forces
d) none of these answers are true
e) the power is high because intermediate velocities and forces are best for producing power during eccentric exercises
b) power is high here because force increases as velocity increases with eccentric actions
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Considering all labelled data points on this curve, which has the lowest potentnial for producing power?
N
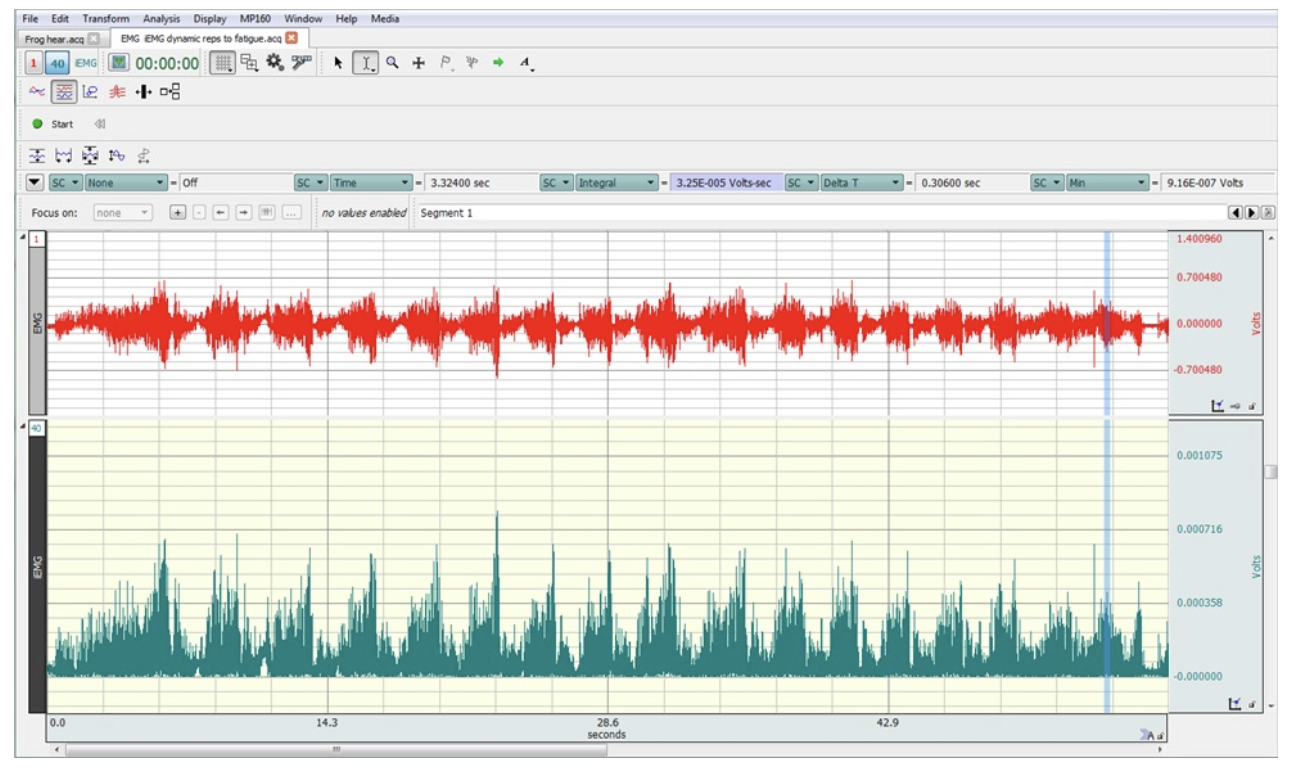
The following figure depicts EMG and iEMG activity during dynamic bicep curls until the subject could not lift the weight anymore. They lifted the weight 17 times before they fatigued. Which of the following mechanism(s) are most llikely to be contributing this fatigue, given this set of data?
a) failure to release enough calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
b) PCr depletion
c) a decrease in pH in the muscle fibers
d) reduced excitability in motor areas of the cerebral cortex
e) an increase in Pi inside the muscle fibers
d) reduced excitability in motor areas of the cerebral cortex
How much power is produced when performing an isometric bench press, your subject held a/n 102 pound weight a distance of 0.42 meters off the floor for 0.42 seconds. No units required
0
** held
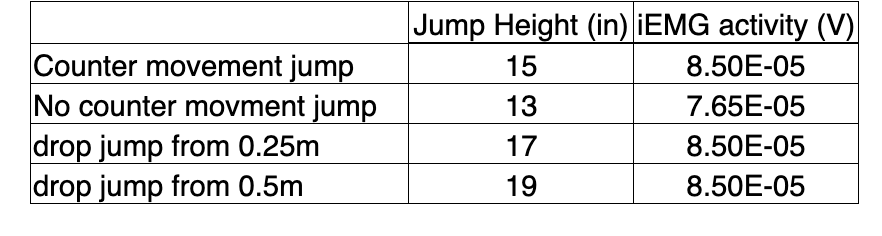
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the increase in jump height between the counter movement jump and the no-counter movment jump?
a) the initiation of an inverse stretch reflex
b) the initiation of a stretch reflex
c) none of these answers
d) better use of the elastic components of the muscle
e) all of these answers
b) the initiation of a stretch reflex
During the course of the entire hold relax with agonist contraction PNF procedure, which of the following types of receptors is theoretically being used to help us improve range of motion?
a) group III and IIV afferents
b) cutaneous Ruffini endings
c) muscle spindles
d) joint kinesthetic receptors
e) golgi tendon organs
f) muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs
g) Ruffini endings and muscle spindles
f) muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs
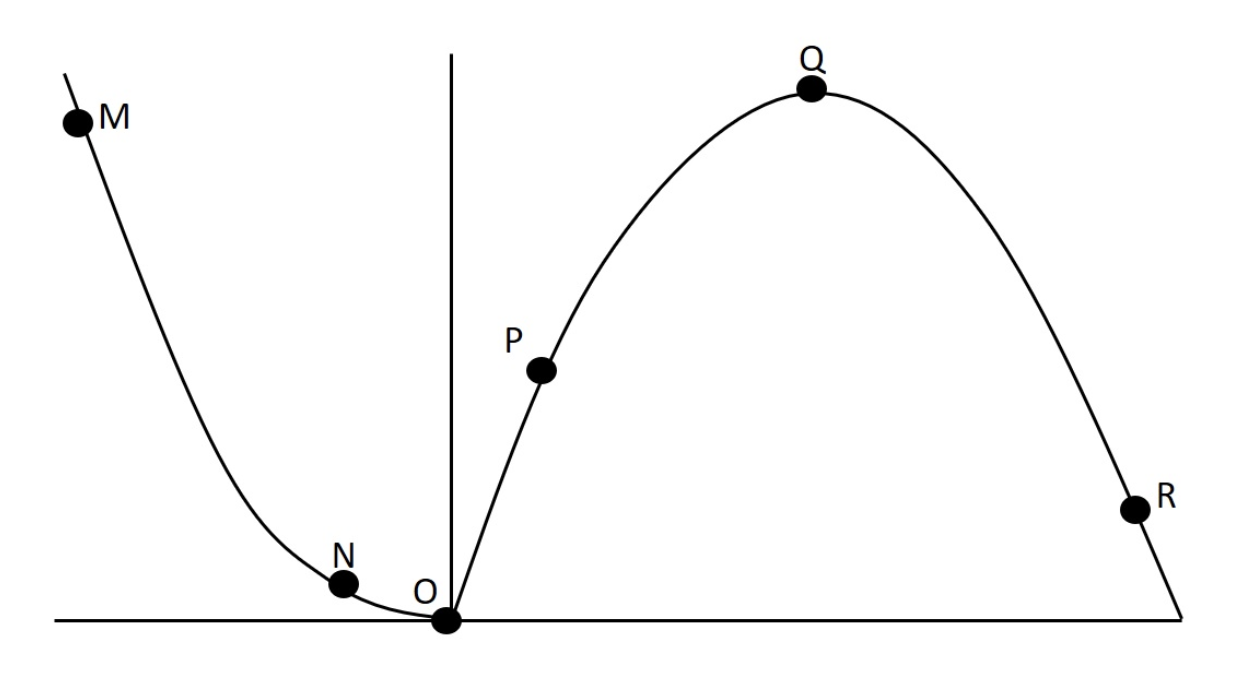
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Why does point P have a low value on this figure?
a) none of these answers are true
b) at that point force is low because velocity is low
c) at that point velocity is low so power is low; power = force x velocity
d) at that point power is low because force is low; force decreases as velocity increases during concentric actions
e) this is a force-velocity curve, and at that point velocity is high, so force is low
c) at that point velocity is low so power is low; power = force x velocity
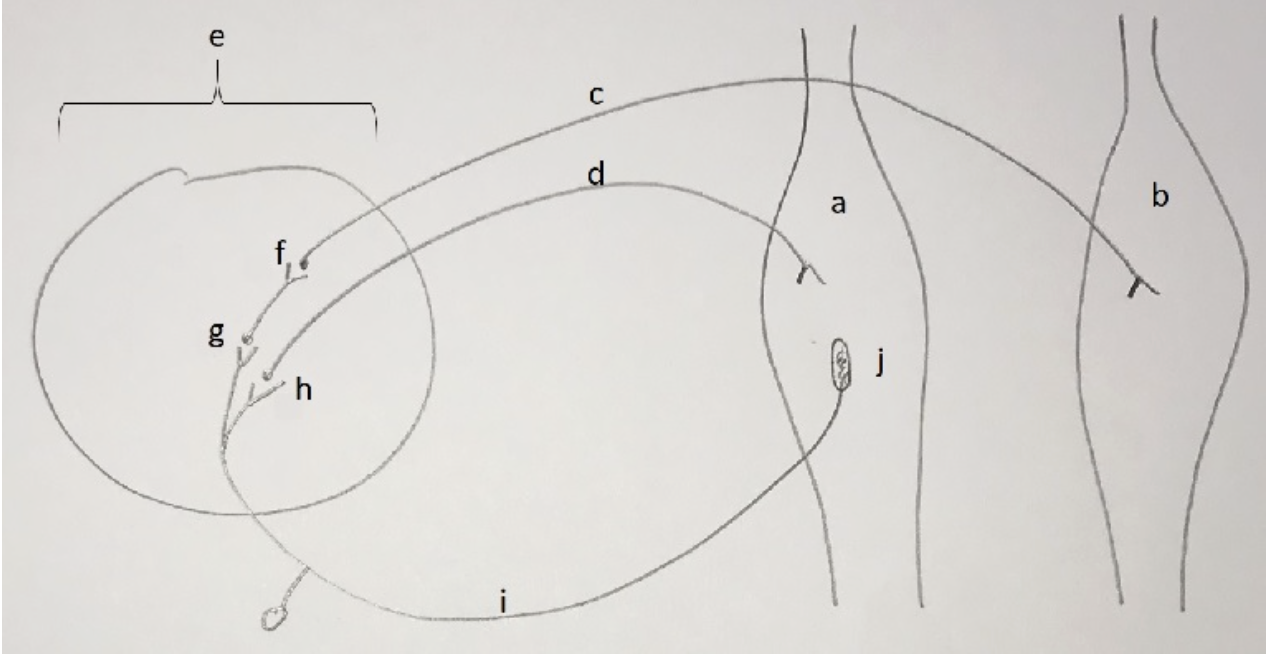
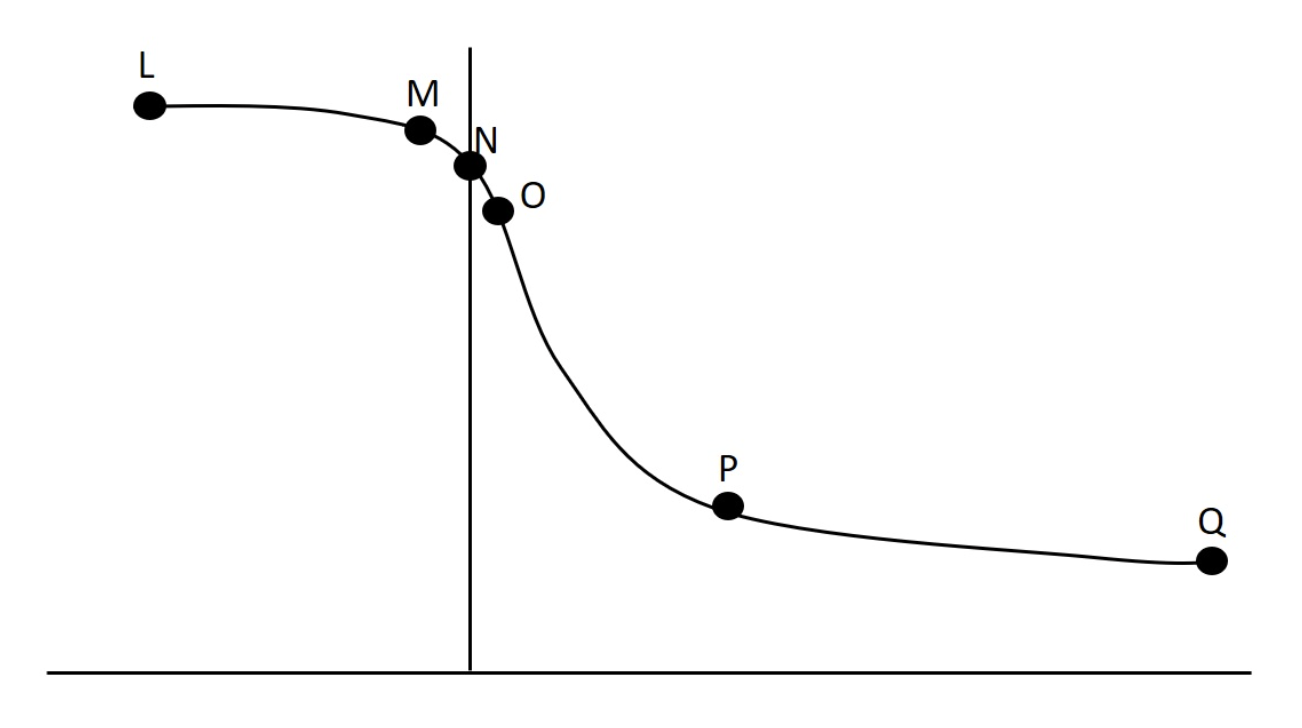
In one of our lab activities we used proprioreceptive neuromuscular facilitation, PNF, to try to inhibit muscle contraction and thus improve the ability to stretch a muscle (in our experiment we were stretching the muscle). The following depicts the reflex arc for reciprocal inhibition of the hamstrings. Match the letters with the most appropriate description. Note: hamstrings are innervated by the sciatic nerve and quadriceps femoris by the femoral nerve.
i hamstrings
ii muscle spindle
iii afferent nerve
iv inhibitory synapse
v sciatic nerve
vi excitatory synapse
hamstrings = b
muscle spindle = j
afferent nerve = i
inhibitory synapse = f
sciatic nerve = c
excitatory synapse = g
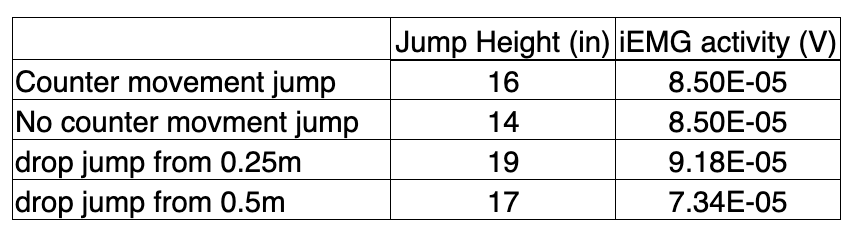
During our “jumping” experiment we had our subject jump with or without a counter-movement, and we also had our subject perform some “drop jumps”. We recorded EMG activity from the vastus lateralis and jump height during each. Here are some sample results from these experiments. What is a likely explanation for the decrease in jump height between the 0.25m and 0.5m drop jumps?
a) activation of muscle spindles, which may have increased motor unit recruitment
b) two of these answers
c) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have decreased motor unit recruitment
d) better use of energy return from elastic proteins like elastin and titin
e) none of these answers
c) activation of golgi tendon organs, which may have decreased motor unit recruitment
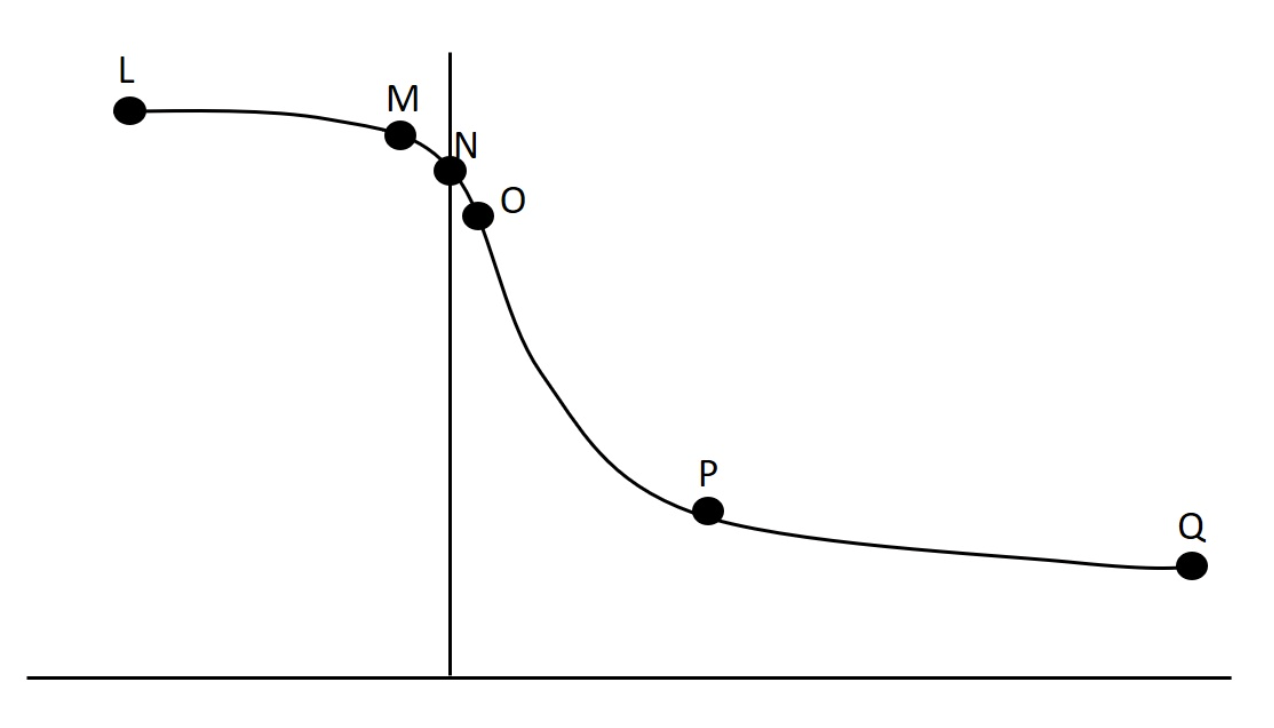
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Considering all labelled data points on this curve, which has the greatest potentnial for producing power?
L
If you were performing a hold relax with agonist contraction PNF procedure to try to improve hamstring flexibility, which of the following muscles/muscle groups would we contract during the second phase of this procedure?
a) hamstrings
b) gastrocnemius
c) dorsiflexors (e.g. tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus)
d) none of these
e) quadriceps femoris
f) two of these
e) quadriceps femoris
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the highest PFK (phosphofructokinase) activity?
a) IIA
b) IIX
c) IIC
d) I
e) IIAX
b) IIX
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the lowest PFK (phosphofructokinase) activity?
a) IIX
b) IIC
c) IIAX
d) IIA
e) I
e) I
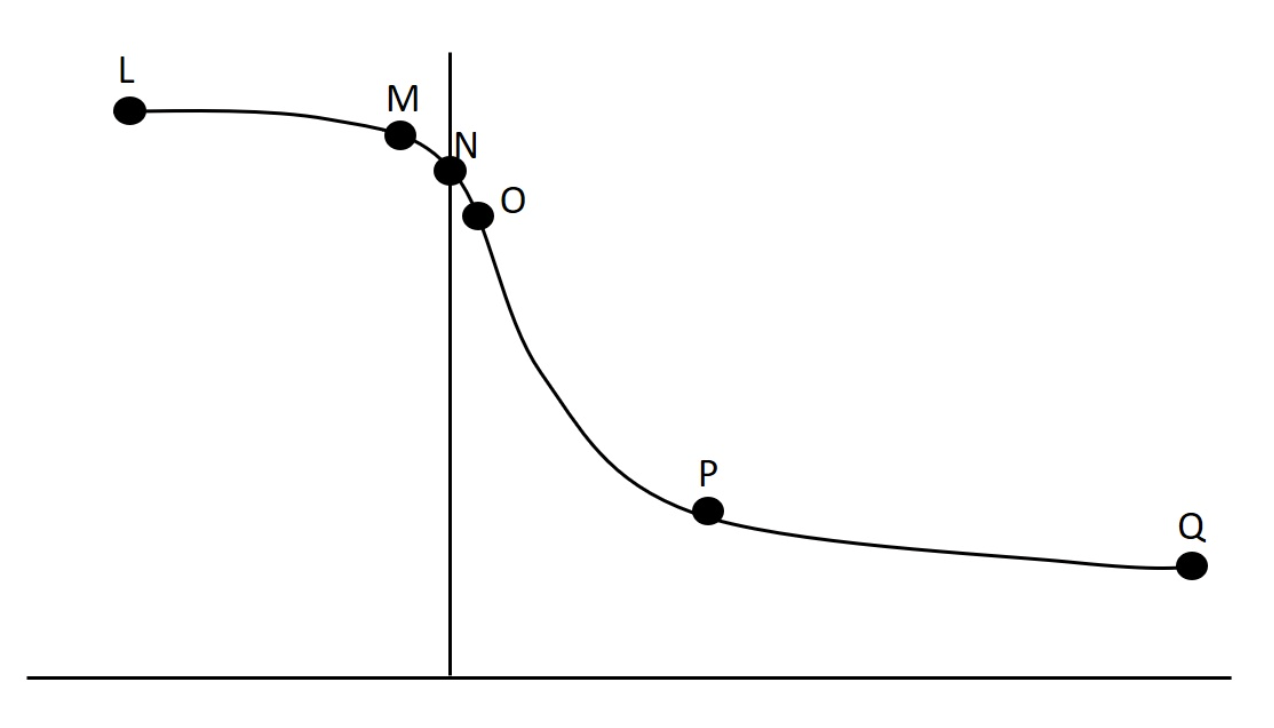
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. If we were comparing knee extensors and knee flexors, the extensors would be most likely to have higher force production at which concentric data point?
O
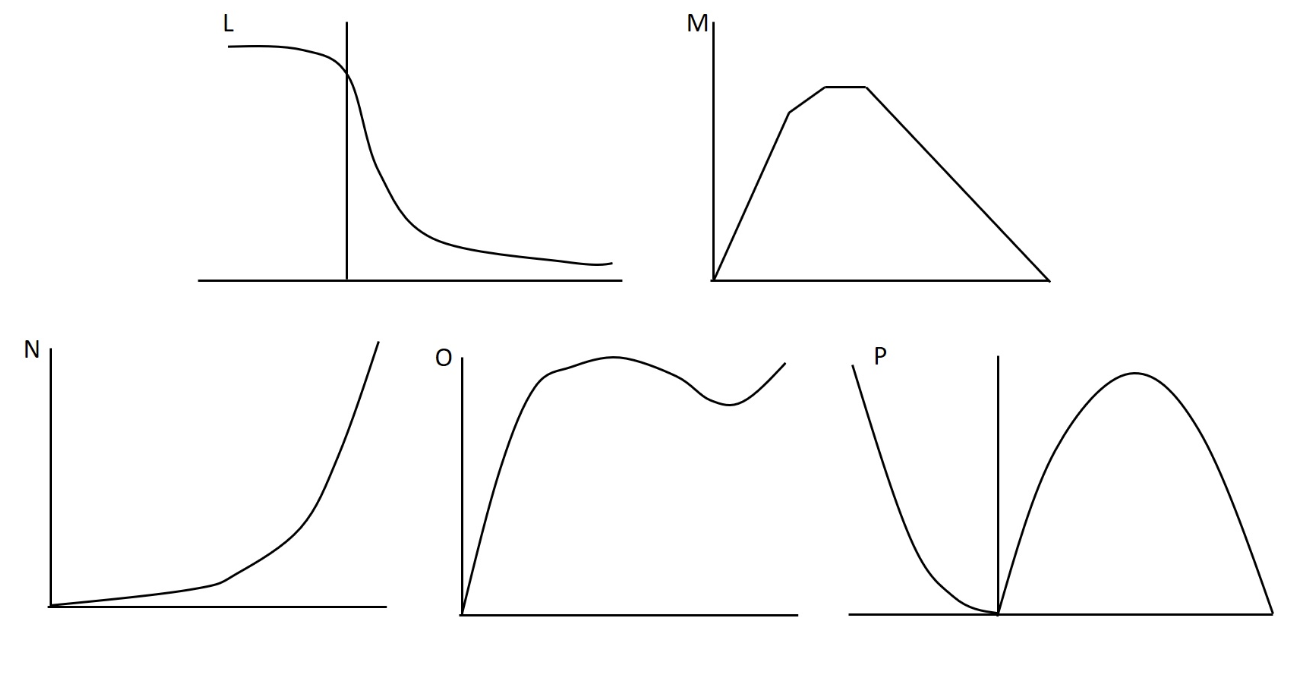
In our recent lab we did experiments related to several aspects of muscle performance including force, velocity, power, and muscle length. Which of the following figures best depicts the passive length tension curve?
N
Which of the following best describes the hold relax PNF procedure if the goal is to improve stretch of the hamstrings?
a) none of these answers
b) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their hamstrings submaximally and then maximally while we slowly lowered their leg down to the table - then had them relax while we re-raised their leg - then we passively stretched their hamstring
c) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their quadriceps submaximally and then maximally while we held their leg in place - then had them relax while we pushed their leg further
d) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their hamstrings submaximally and then maximally while we held their leg in place - then had them relax while we pushed their leg further while the subject contracts their quadriceps muscles
e) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their quadriceps submaximally and then maximally while we held their leg in place - then had them relax while we pushed their leg further while the subject contracts their hamstring muscles
f) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their hamstrings submaximally and then maximally while we held their leg in place - then had them relax while we pushed their leg further
f) - we stretched the subject’s hamstring passively until we reached the limits of its ROM - then we had the subject contract their hamstrings submaximally and then maximally while we held their leg in place - then had them relax while we pushed their leg further
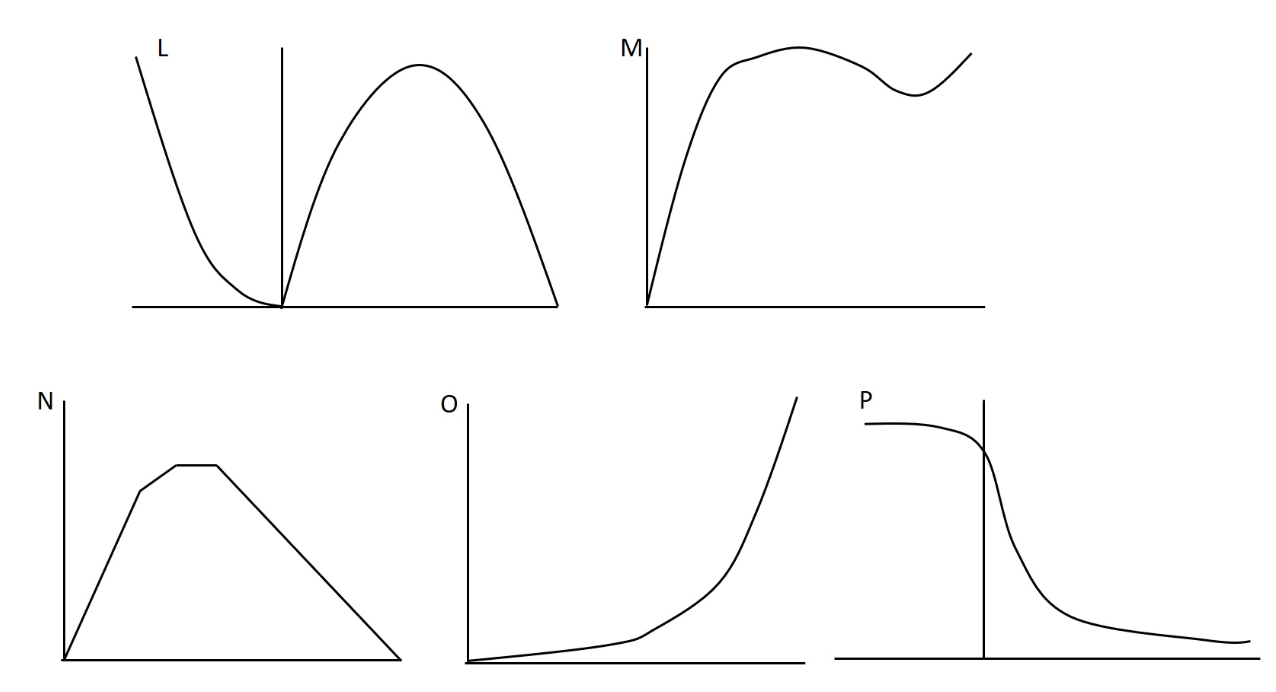
In our recent lab we did experiments related to several aspects of muscle performance including force, velocity, power, and muscle length. Which of the following figures best depicts the force-velocity curve during concentric and eccentric actions?
P
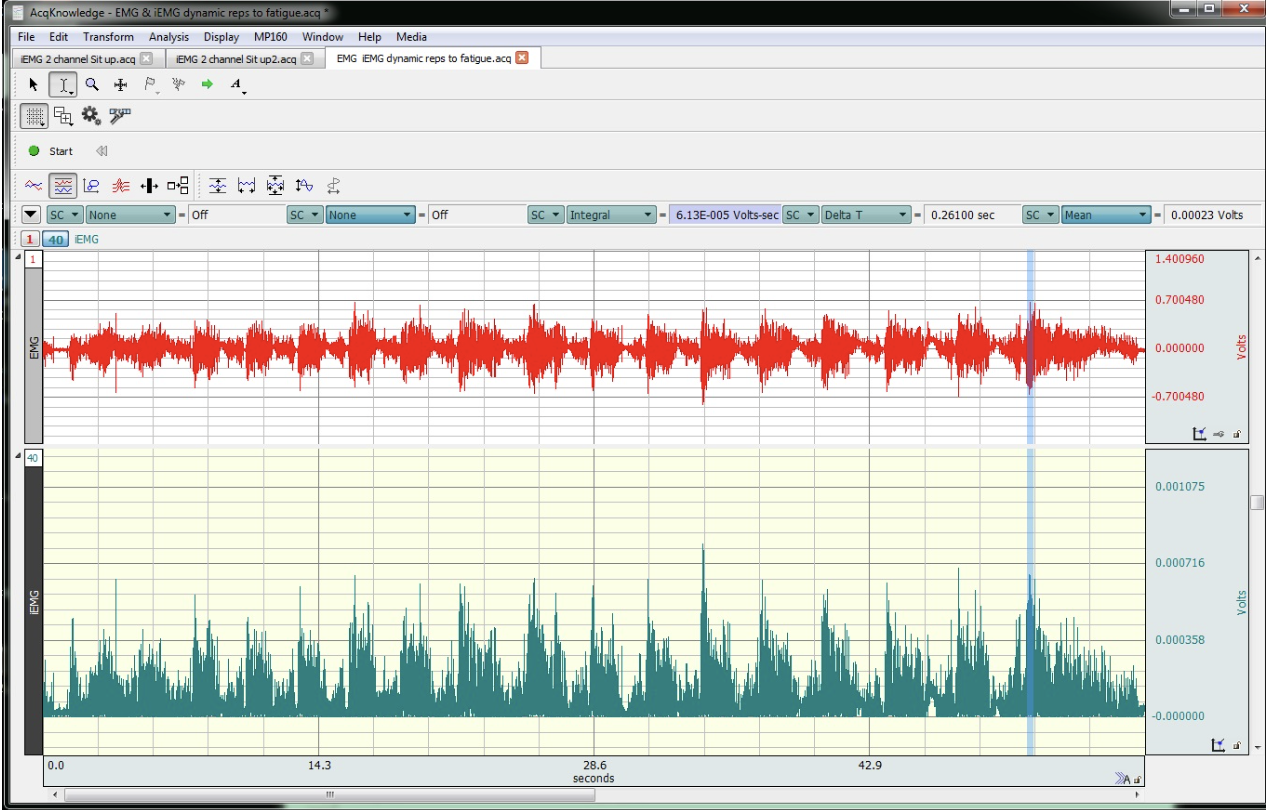
The following figure depicts EMG and iEMG activity during dynamic bicep curls until the subject could not lift the weight anymore. They lifted the weight 17 times before they fatigued. Which of the following mechanism(s) are LEAST likely to be causing this fatigue, given this set of data?
a) an increase in Pi inside the muscle fibers
b) glycogen depletion
c) failure to release enough calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
d) a decrease in pH in the muscle fibers
e) PCr depletion
b) glycogen depletion
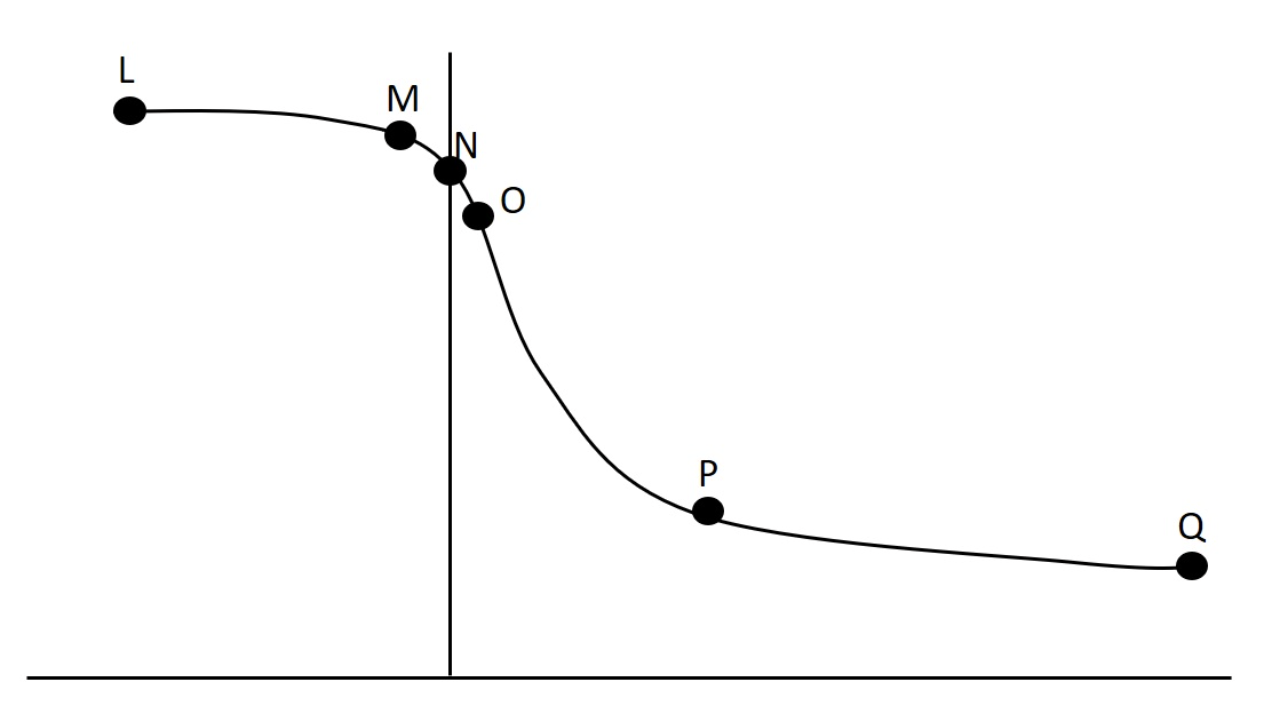
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. High speed resistance training would increase which concentric data point the most?
Q
During the second phase of the hold-relax with agonist contraction procedure to try to increase the stretch of a muscle we make use of which of the following reflex phenomena?
a) crossed extensor reflex
b) myotatic stretch reflex
c) reciprocal inhibition
d) none of the above
e) inverse stretch reflex
f) withdrawal reflex
c) reciprocal inhibition
In lab we collected data related to force-velocity and power-velocity relationships. One such set of data is presented graphically below. Why does point Q have such a low value on this figure?
a) none of these answers are true
b) this is a force-velocity curve, and at that point velocity is zero, and since power = F x velocity, power would be zero
c) this is a power-velocity curve, and at that point velocity is zero, and since power = F x velocity, power would be zero
d) this is a force-velocity curve, and at that point mass is zero, and since force = mass x acceleration, force would be zero
e) this is a power-velocity curve and at that point force is zero, and since power = F x velocity, power would be zero
c) this is a power-velocity curve, and at that point velocity is zero, and since power = F x velocity, power would be zero
Proprioceptive information that is perceived by the subject is brought up the spinal cord via ascending spinal cord tracts called the ____________________________
a) corticospinal tracts
b) afferent nervous system
c) dorsal columns/lemniscal system
d) pyramidal tracts
e) anterolateral spinothalamic tracts
c) dorsal columns/lemniscal system
The following figure depicts EMG and iEMG activity during dynamic bicep curls until the subject could not lift the weight anymore. They lifted the weight 17 times before they fatigued. Which of the following mechanism(s) are LEAST likely to be causing this fatigue, given this set of data?
a) PCr depletion
b) failure to release enough acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction
c) a decrease in pH in the muscle fibers
d) failure to release enough calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
e) an increase in Pi inside the muscle fibers
b) failure to release enough acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction
Which of the following fiber types would tend to have the greatest succinate dehydrogenase activity? (SDH catalyzes a step in the citric acid cycle)
a) I
b) IIC
c) IIAX
d) IIA
e) IIX
a) I
When we perform a drop jump to try to jump higher, one issue that might reduce jump height is that motor unit recruitment might be inhibited by which of the following reflexes?
a) crossed extensor reflex
b) inverse stretch reflex
c) reciprocal inhibition
d) none of the above
e) stretch reflex
f) withdrawal reflex
b) inverse stretch reflex