Ecology
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ecology End of Unit Test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Population Density
Number of organisms / unit of area
Ecological successions
The series of predictable changes that occur in an ecosystem
Disturbance
Changes in environmental conditions that cause a change in an ecosystem
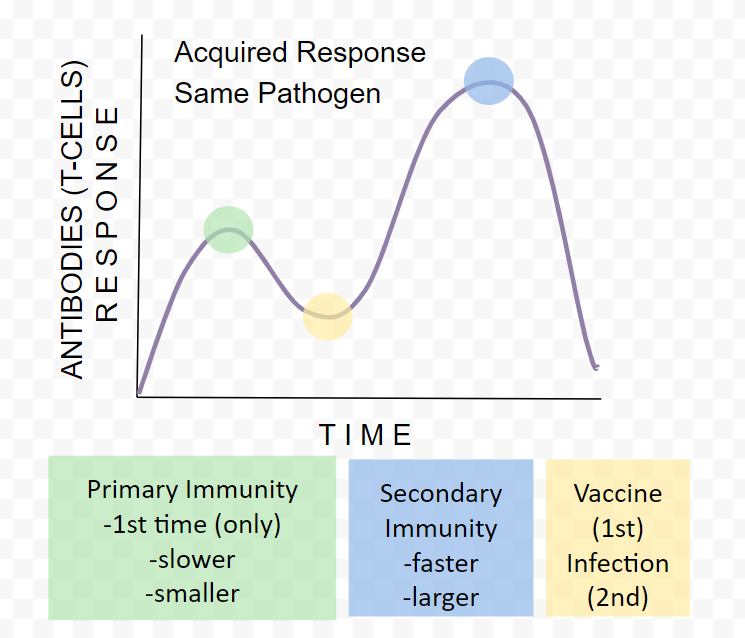
Acquired response
Non-Specific
1st, 2nd, lines
mucus - tears - skin - fever - macrophages
innate
Specific
3rd line of defense
T+B cells ← antibodies
primary and secondary
acquired
mRNA
Blueprint to produce antigens.
Live-Attenuated
Weakened, non-harmful portion of viruses
Inactivated
Killed version of virus
Vaccinations
Stimulate the immune response in body to viruses by producing antibodies and memory cells
trains body to fight and respond quicker
slows transmission
Immune System
Bodies defenses that attack and destroy pathogens
Disease Transmission
Direct Contact
Exchange of Fluids
Contamination
Airborne
Vector
Growth rate / change of population
Organisms per time
Density = # of organisms
Organism per area
Predator / Prey Cycle
Predation affects population size (density dependent)
Many show a cycle of increase/decrease over time (boom bust)
Fundamental to health of natural population and ecosystem
Limiting Factor
Causes population growth to decrease
Ecology
study of organisms and their environment, relationships and interactions
Ecological Hierarchy
Organism - species - population - community - ecosystem - biome - bioshphere
Community
Two of more different species occupying the same geographical location.
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area.
Ecosystem
A community or group of abiotic and biotic factors that live in and interact with each other in a specific environment.
Biosphere
The region on, above, and below the Earth's surface where life exists.
Biome
An area classified according to the species that live in that location. Temperature range, soil type, and the amount of light and water are unique to a particular place and form the niches for specific species
Autotroph
Gets energy by converting it themselves
Heterotroph
Gets energy from consuming other living things.
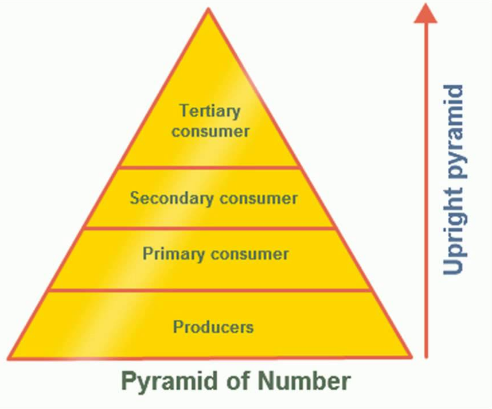
Trophic Levels
Consist of: primary producers (plants), primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and detritivores (decomposers)
Consumer
An organism that gets its energy by eating plants or animals
Producer
An organism that creates its own food or energy
10% rule
~10% of energy is transferred between trophic levels
90% is a heat emission
Biomass pyramid
Representation of total living biomass or organic matter present at different trophic levels in an ecosystem
Food chain
Direct map of what is eaten to what is doing the eating.
Food Web
Relationships of many different species consuming and crossing over one another.
Natality
Amount of births
Mortality
Amount of deaths
Emigration
Amount of organisms entering a location.
Immigration
Amount of organisms leaving a location
Exponential
Growth of a population means there are unlimited resources allowing the species to increase “infinitely.”
Logistic growth
Growth looks like an S and has a carrying capacity (K) which shows the maximum population an environment can maintain.
Density dependent
Impact is greater the more dense of population (predation)
Biotic factors - availability of food, space, disease, ect
Density independent
Impact is the same no matter the density
Abiotic factors - weather, natural disasters, ect.
Innate immunity
Physical Barriers. such as skin, the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract, the nasopharynx, cilia, eyelashes and other body hair.
Defense Mechanisms. such as secretions, mucous, bile, gastric acid, saliva, tears, and sweat.
General Immune Responses.
Acquired immunity
A person's immune system responds to a foreign substance or microorganism, or that occurs after a person receives antibodies from another source.
Active immunity
Acquired through infection/vaccine.
Own immune system
Competition
Occurs between organisms in an ecosystem when their niches overlap, they both try to use the same resource and the resource is in short supply.
Vector
Any organism (vertebrate or invertebrate) that functions as a carrier of an infectious agent between organisms of a different species
The study of insects that transmit pathogens, their interaction with (vertebrate) hosts or with the disease-causing parasitic organisms
Zoonotic
Infectious disease that spreads between animals and humans (rabies - West Nile - plague )
Epidemic
The widespread of an infectious disease.
Primary Succession
Establishing life in an area where no soil exists
Secondary Succession
The changes that occur (every time) after a disturbance
Keystone Species
Species that, if removed, affects the entire ecosystem (important and unique roles)
Trophic Cascade
Ecological event that changes structure of ecosystem
Indirect interactions between species, control the entire ecosystem
Increase in population
Birth rate (natality)
Immigration
Decrease in population
Death rate (mortality)
Emigration
Pathogen
Agents that cause disease
Ways in which diseases can transmit
Direct Contact
Exchange of Fluids
Contamination
Airborne
Vector
Passive Immunity
Immunity which is gained from someone else.
T-Cells
Helper T Cells - activates T + B cells
Cellular immunity
Killer T-cells - destroy infected cell
Both T & B Cells
Memory cells
Activated by helper T cells
Acquired immunity
3rd line or Specific
White Blood Cells - Lymphocytes
Primary AND Secondary immunity
B Cells
Antibodies - plasma
Proteins that “tag” antigen
Humoral immunity - fluids in the body