Postural Control In Sitting
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
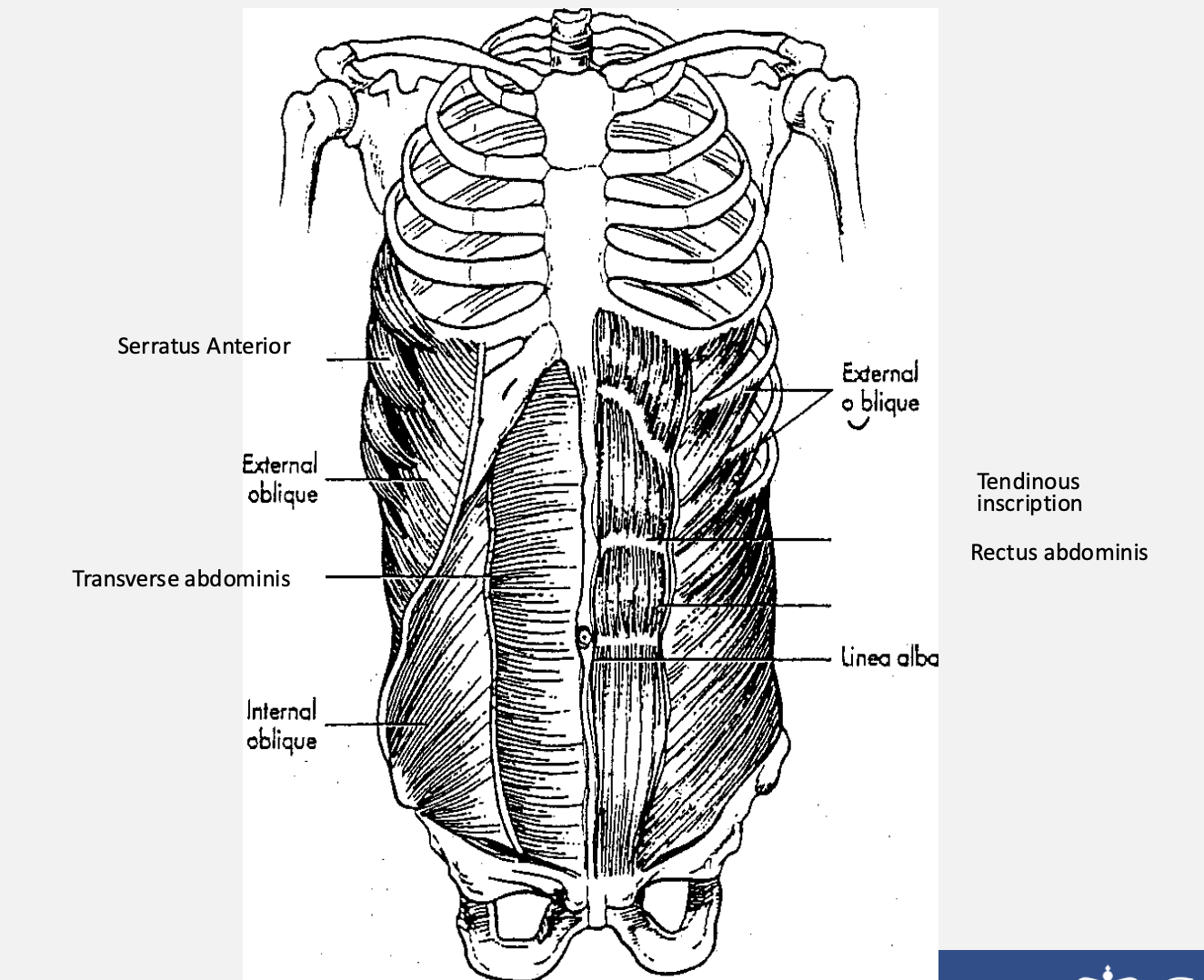
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE TRUNK:
MUSCLES OF THE ABDOMINAL WALL & LATERAL TRUNK
Purpose:
1. Support Vital Organs
2. Respiratory assist
3. Trunk control
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE TRUNK
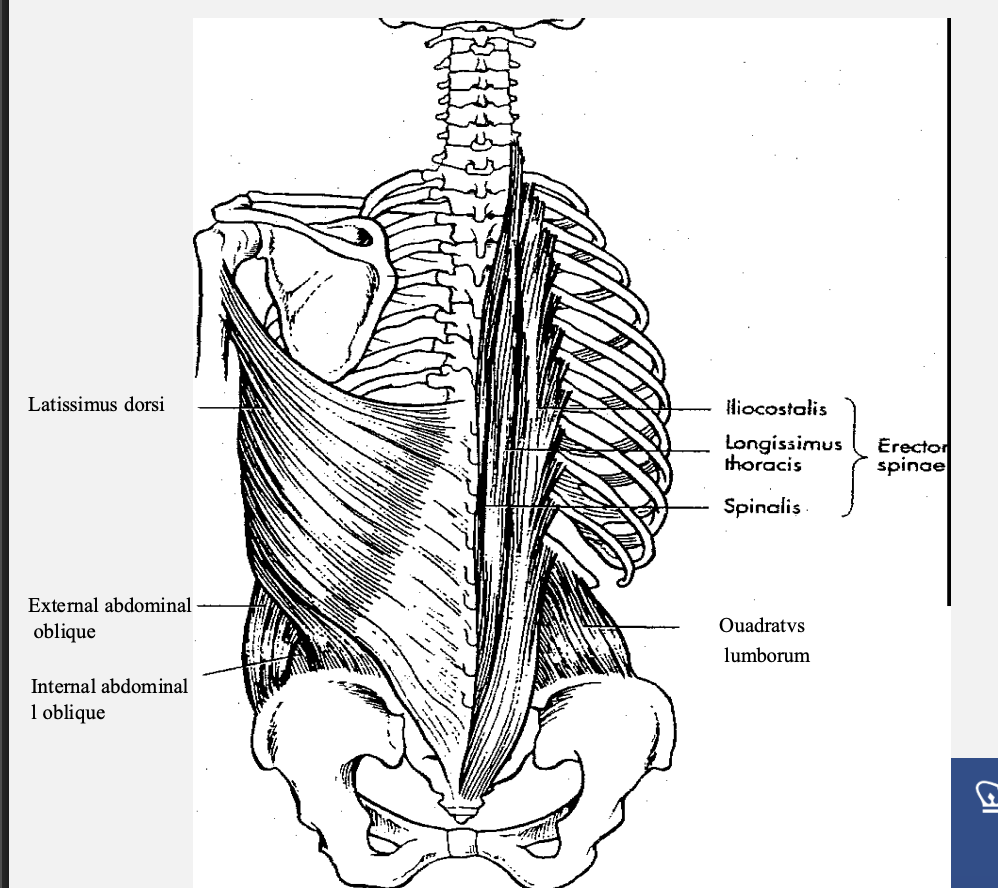
Posterior Trunk Muscles
Purpose:
1. Balance of the vertebral column
2. Trunk control (extension, lateral flexion, rotation)
3. Approximates head to sacrum and pulls pelvis to anterior tilt
4. Accentuates lumbar lordosis
MOTOR CONTROL CONSIDERATION
Types of muscle actions
***concentric contraction
***isometric contraction
***eccentric contraction
Movements in directions opposite the pull of gravity (concentric contraction)
Prevention of movement that would take place as a result of the pull of gravity (isometric contraction)
Controlling the speed of movement taking place in the direction of the pull of gravity (eccentric contraction)
MOTOR CONTROL CONSIDERATION
Motor Control:
Motor Control: how our neuromuscular system functions to activate and coordinate the muscles to perform a skill
Reciprocal innervation
Postural malalignment & normal muscle length
Dissociation
Voluntary vs. automatic
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR EVALUATION
Ask client to wear a gown
Subtle postural shifts will completely change muscle activity
everyone tends to sit in a posterior pelvic tilt
Evaluate at a variety of functional postures
Supine
eliminates gravity (e.g., are muscles misaligned, even when the person doesn’t have to work against gravity?; problematic, possibly tightness somewhere)
Sitting
have gravity now; see what kind of control they have against it, and if that impacts their asymmetries
Internal Perturbations
Caused when a person fails to control the base of support during voluntary movement (e.g., sitting and dressing)
nothing is externally forcing them; they just don’t have the internal strength to stay upright —> e.g., fall
External Perturbations
When the surface moves (e.g., sitting on a therapy ball) or something outside makes us move (e.g., being pushed by OT to test sitting balance, windy day)
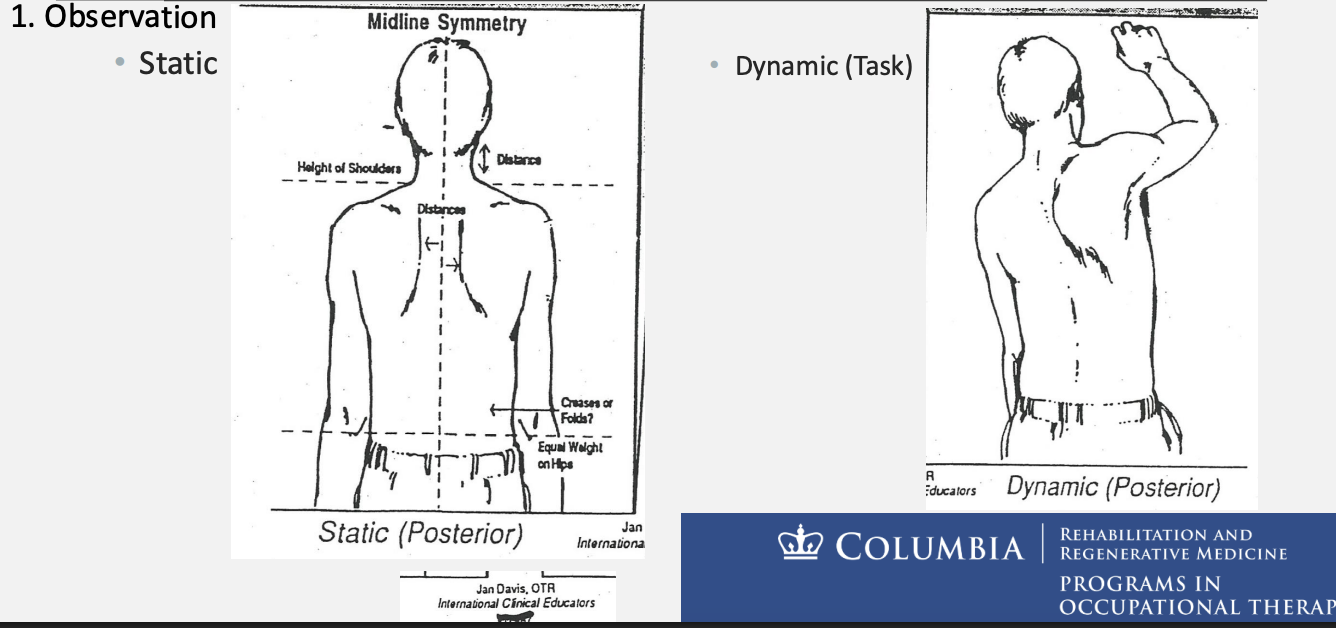
EVALUATION PROCEDURES
observations
static
dynamic (task)
Observed postures may be the result of a variety of problems:
Posterior pelvic tilt
Lateral flexion
Rotation
Control of selective movement patterns
Trunk flexors
Trunk extensors
Lateral flexion
Rotation
Assistance level for (1) static sitting balance/(2) dynamic sitting balance
Independent static/dynamic sitting balance: requires no physical or verbal cues
Supervision: requires supervision (verbal cues) with no physical assist
Contact guard (CG): touching assist
Minimal (min) assist: 25% assist
Moderate (mod) assist: 50% assist
Maximal (max) assist: 75% assist
Total assist: 100% assist
EVALUATION PROCEDURES
Control of selective movement patterns
Trunk flexors
Trunk extensors

EVALUATION PROCEDURES
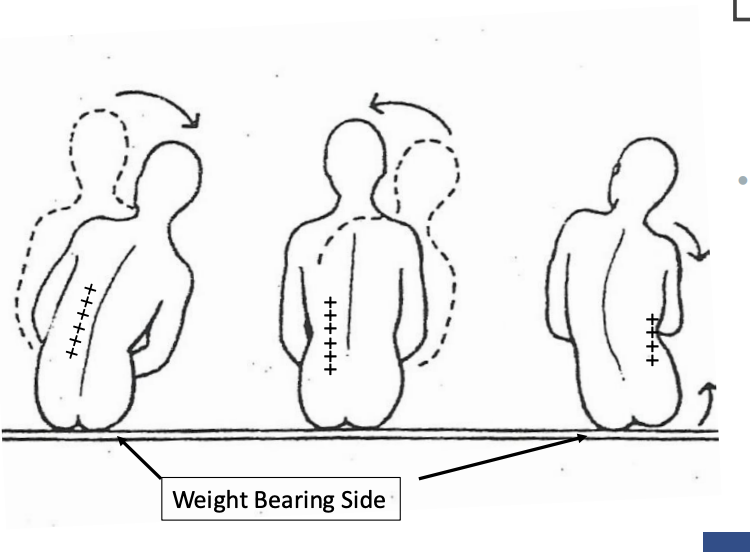
Control of selective movement patterns
Lateral flexion
leading with the shoulder to the right
weight-shift to the right
eccentric contraction of the left (so you don’t fall over)
left side is elongating
right side is shortening
going to sit back up
concentric activation of the left (to actively come back up)
hip hike of the right
concentric activation of the right side to lift it up
weight shift to the left
right side is shortening
left side is lengthening
EVALUATION PROCEDURES
Control of selective movement patterns
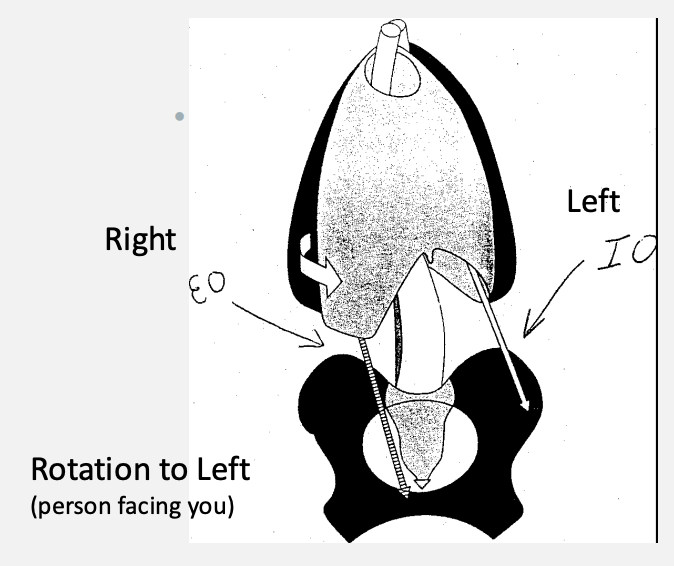
Rotation
rotating to left
left side: internal obliques
right side: external obliques
rotating to right
left side: external obliques
right side: internal obliques
EVALUATION PROCEDURES
static sitting balance
patient is not doing anything besides sitting (try to have their feet on the ground if they are lower level/need more help)
Assistance level for (1) static sitting balance/(2) dynamic sitting balance
Independent static/dynamic sitting balance: requires no physical or verbal cues
Supervision: requires supervision (verbal cues) with no physical assist
Contact guard (CG): touching assist
Minimal (min) assist: 25% assist
Moderate (mod) assist: 50% assist
Maximal (max) assist: 75% assist
Total assist: 100% assist

EVALUATION PROCEDURES
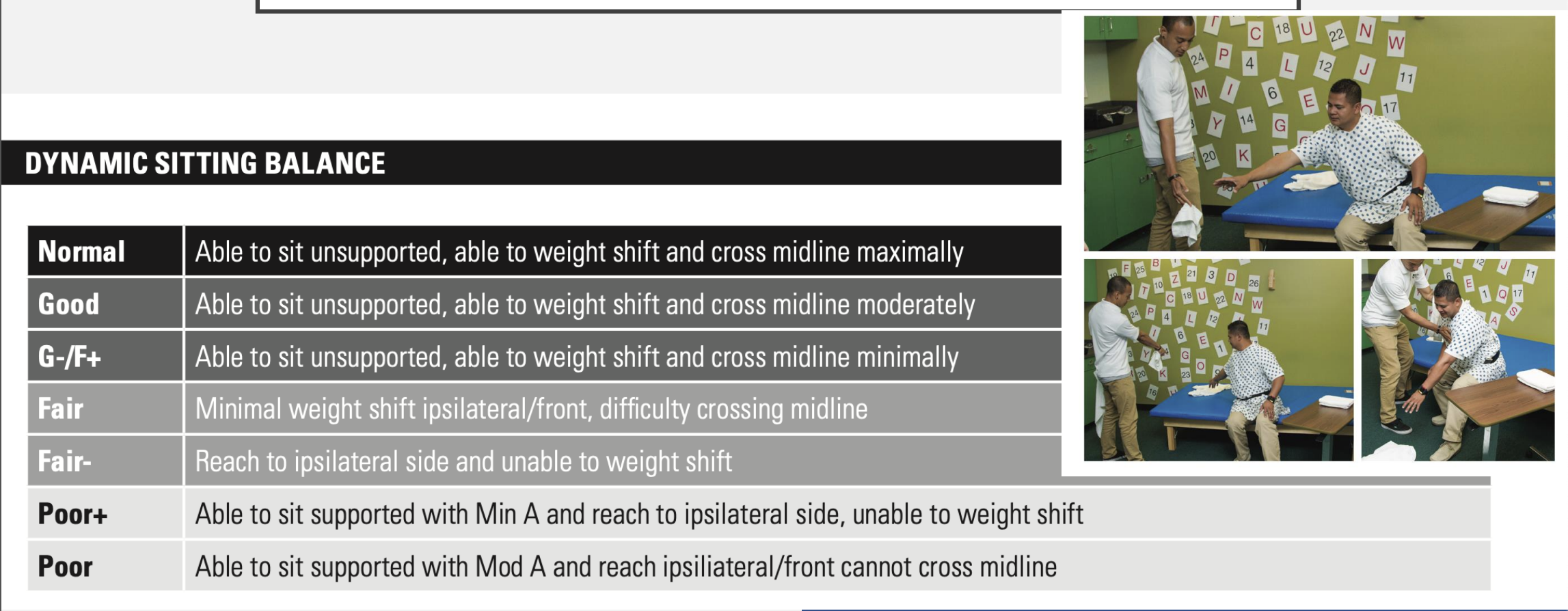
dynamic sitting balance
patient is doing something while sitting (e.g., dressing)
Assistance level for (1) static sitting balance/(2) dynamic sitting balance
Independent static/dynamic sitting balance: requires no physical or verbal cues
Supervision: requires supervision (verbal cues) with no physical assist
Contact guard (CG): touching assist
Minimal (min) assist: 25% assist
Moderate (mod) assist: 50% assist
Maximal (max) assist: 75% assist
Total assist: 100% assist
STANDARDIZED EVALUATIONS
Trunk Control Test
can be used to assess the motor impairment in a patient who has had a stroke; it correlates with eventual walking ability
testing done by patient lying in bed:
roll to weak side
roll to strong side
balance in sitting position on the edge of the bed with the feet off the ground for at least 30 seconds
sit up from lying down

STANDARDIZED EVALUATIONS
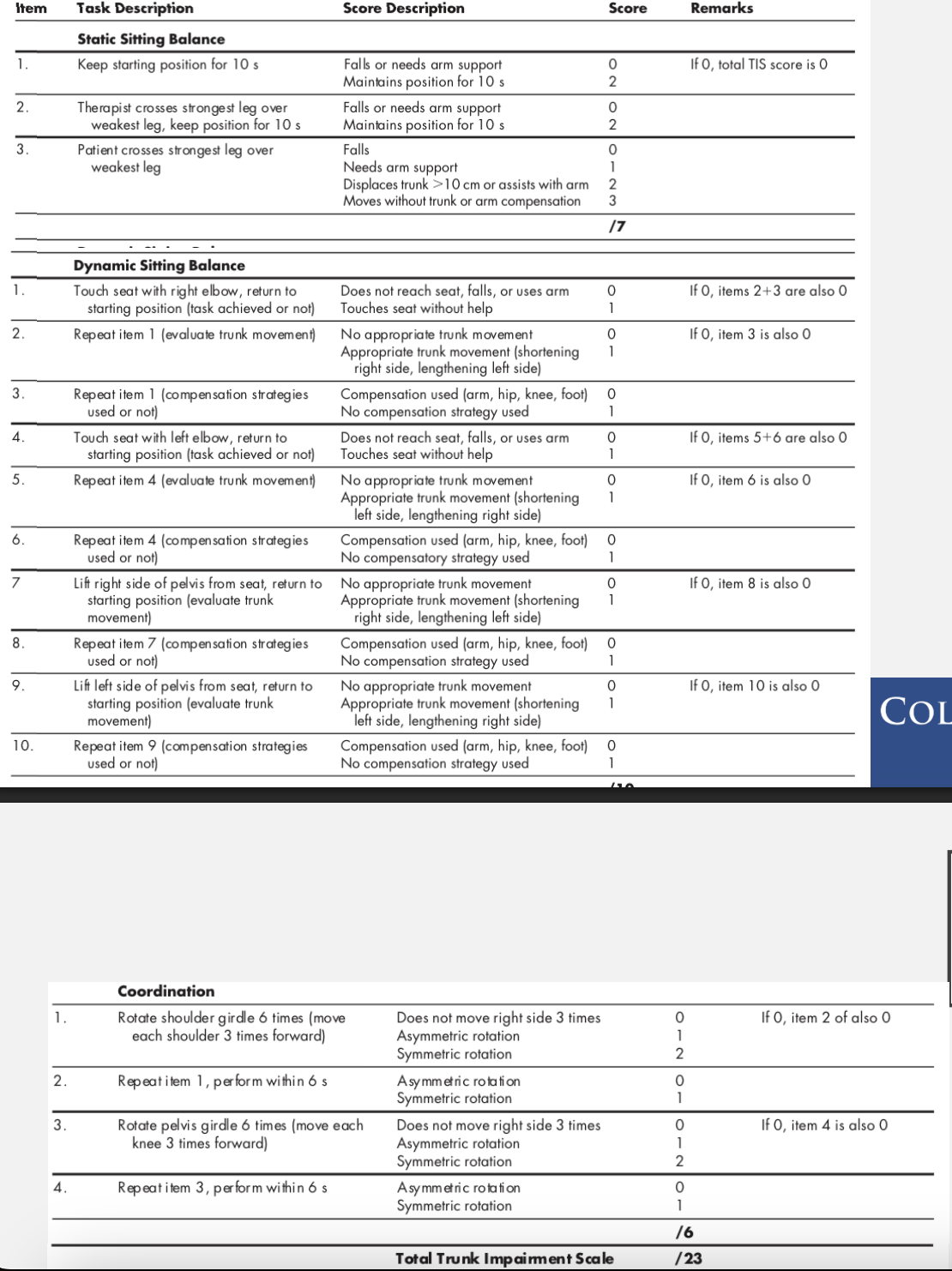
Trunk Impairment Scale (TIS)
scores
static sitting balance
dynamic sitting balance
coordination
TRUNK CONTROL AND ADL
Clear relationship between loss of trunk control and loss of functional independence
Prior evaluations focused on select movements of the trunk; however, the impact of impaired trunk control on functional tasks is more relevant to OT
Therefore, the evaluation of trunk control can take place during skilled observations
While there are infinite variations of observed movement patterns during task performance, the focus of evaluation and treatment should be observing, evaluating and treating patients with a variety of tasks and environments
e.g., Lower extremity dressing
Trunk flexion to reach down toward feet
Trunk flexion and rotation to reach to one side of body (ex., Right)
Trunk extension to realign to sitting position
Lateral flexion required when using a cross-leg method (ex,. Right leg over left leg)