Transport in Animals - B9
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is the defintion of a circulatory system
The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals transporting oxygen through blood and is made up of different vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one way blood flow.
Single circulatory system
A circulatory system where the heart only has two chambers and blood passes through the heart only once seen in fish.
double circulatory system
A circulatory system where the heart has four chambers and blood passes through the heart twice seen in all mammals.
Advantages of a double circulatory system
A double circulatory system provides more oxygen and a higher blood pressure.
Describe the flow of blood starting from the vena cava
Vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, left atrium, left ventricle and then aorta
coronary arteries (fucntion)
the coronary artieries provide oxygen to the heart
Veins (function)
Veins pump blood to the heart
arteries (function)
Arteries pump blood away from the heart to the body
Valves (definition)
Prevents the back flow of blood
Septum (function)
The septum is a wall of muscle that keeps oxygenated and deoxygentaed blood seperate
How does the heart function
The heart functions by contracting the muscles of the ventricles and atria to pump blood and also by using valves
What happens to the heart during physical activity?
During physical activity the heart pumps blood faster as muscles demand more oxygen for energy production.
Veins (characteristics)
Veins carry deoxygenated blood, have larger lumen, thin wall, has valves to prevent backflow, low blood pressure.
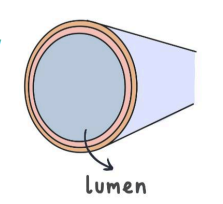
Arteries (characteristics)
Arteries carry oxygenated blood, have smaller lumen, thick wall, has no valves, high blood pressure.
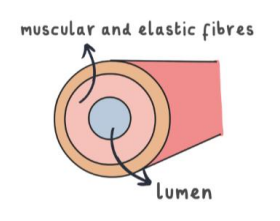
What is the lumen?
The lumen is the hollow part of a blood vessel
What is coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a build up of cholesterol in the coronary artery which narrows the artery and can lead to blockage.
What causes coronary heart disease?
Coronary heart disease is caused by an unhealthy diet with high amounts of fat and a lack of exercise as exercise helps lower blood pressure which lowers the risk of coronary disease. And other factors such as smoking, age, sex and genetics.
How can a heart be monitored?
The heart can be monitored with an electrocardiogram which records the electrical signals in the heart that cause contraction of the atria and ventricle. Or can be monitored by listening to the pulse rate and listening to sounds of valves closing.
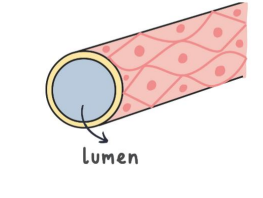
Capillaries (functions)
Capillaries are used to exchange substances with tissues such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and other nutrients.
capillaries (characteristics)
Capillaries have narrow lumen and diameters, large surface area, are branched and have slow blood flow to allow time for exchange.
Components of blood
Plasma, platelets, red blood cells, white blood cells
Red blood cell (function)
Red blood cells transfer oxygen by having haemoglobin to which oxygen can bind to.
White blood cells (function)
White blood cells are part of out immune system and fight off pathogens.
Plasma (function)
Plasma transports many things such as blood cells, hormones, urea, nutrients, carbon dioxide and ions.
platelets (function)
Platelets stick to a broken vessel wall and clump together blocking the cut by forming a scab which prevents blood loss , allows healing and prevent pathogens from entering the wound
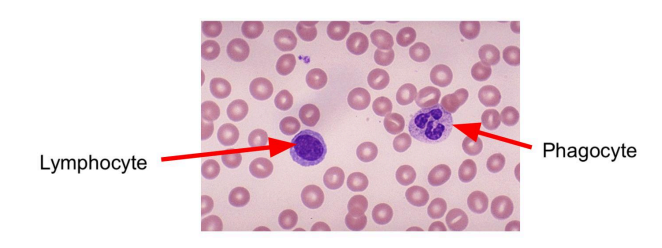
What are the types of white blood cells in our blood?
lymphocytes and phagocytes
lymphocytes (function)
lymphocytes produce antibodies, these antibodies bind to antigens which cause foreign cells (pathogens) to clump together making them harmless.
phagocytes (function)
phagocytes engulf pathogens by first attaching them and then trapping them inside its membrane where it then release enzymes which break down (kill) the pathogen.
What do phagocytes look like?
phagocytes have a wonky shape in their center
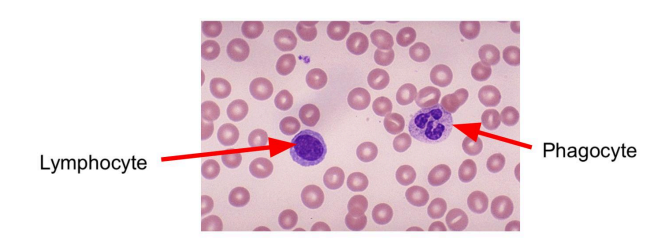
What do lymphocytes look like?
lymphocytes have a smooth circle in their center