pubhlth 264 environmental health - midterm
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1. What are the two major air pollution problems at global level?
a. Upper atmosphere ozone depletion
b. Climate change due to green house effect
2. What are the two major air pollution problems at regional level?
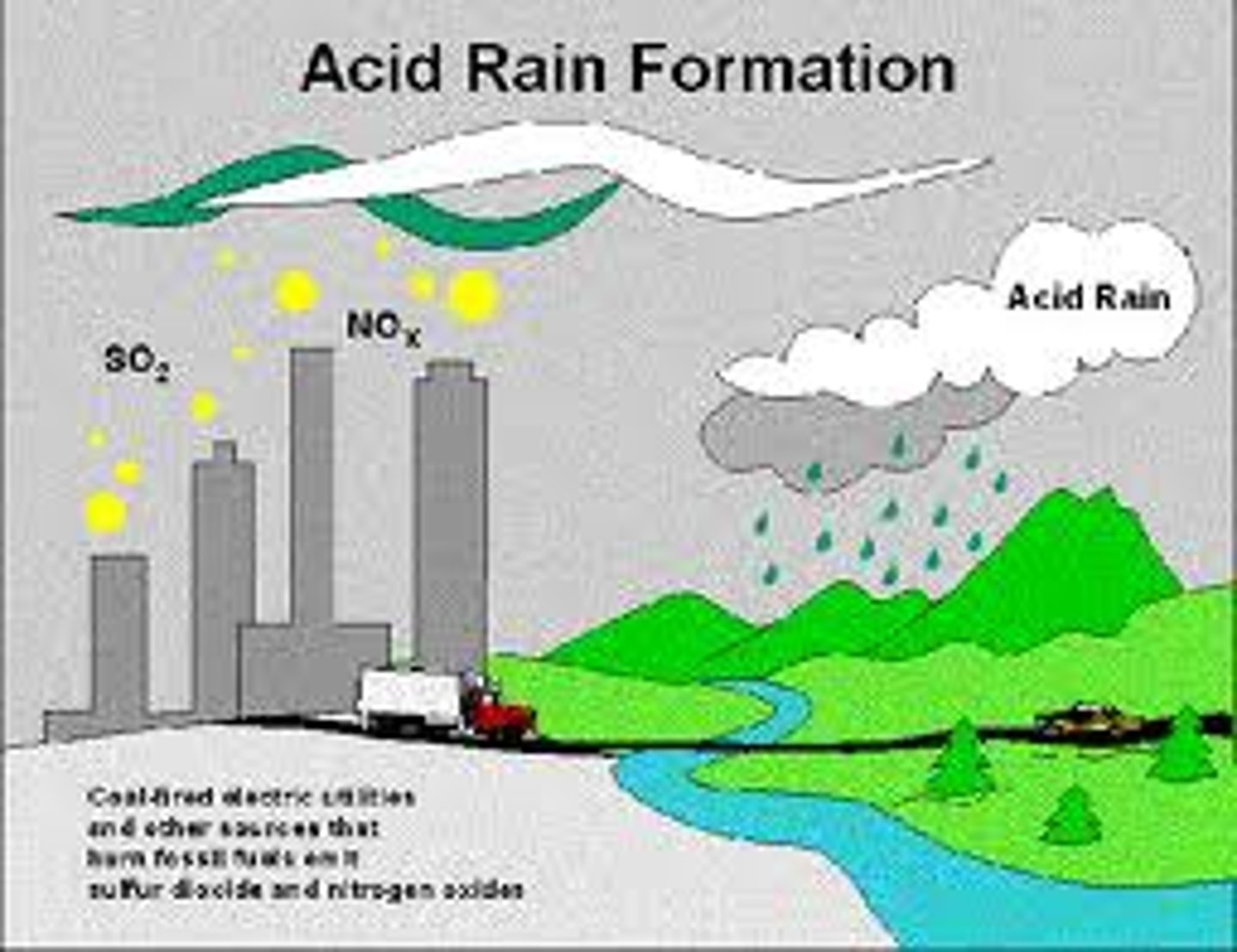
a. Acid rain
b. Photochemical smog
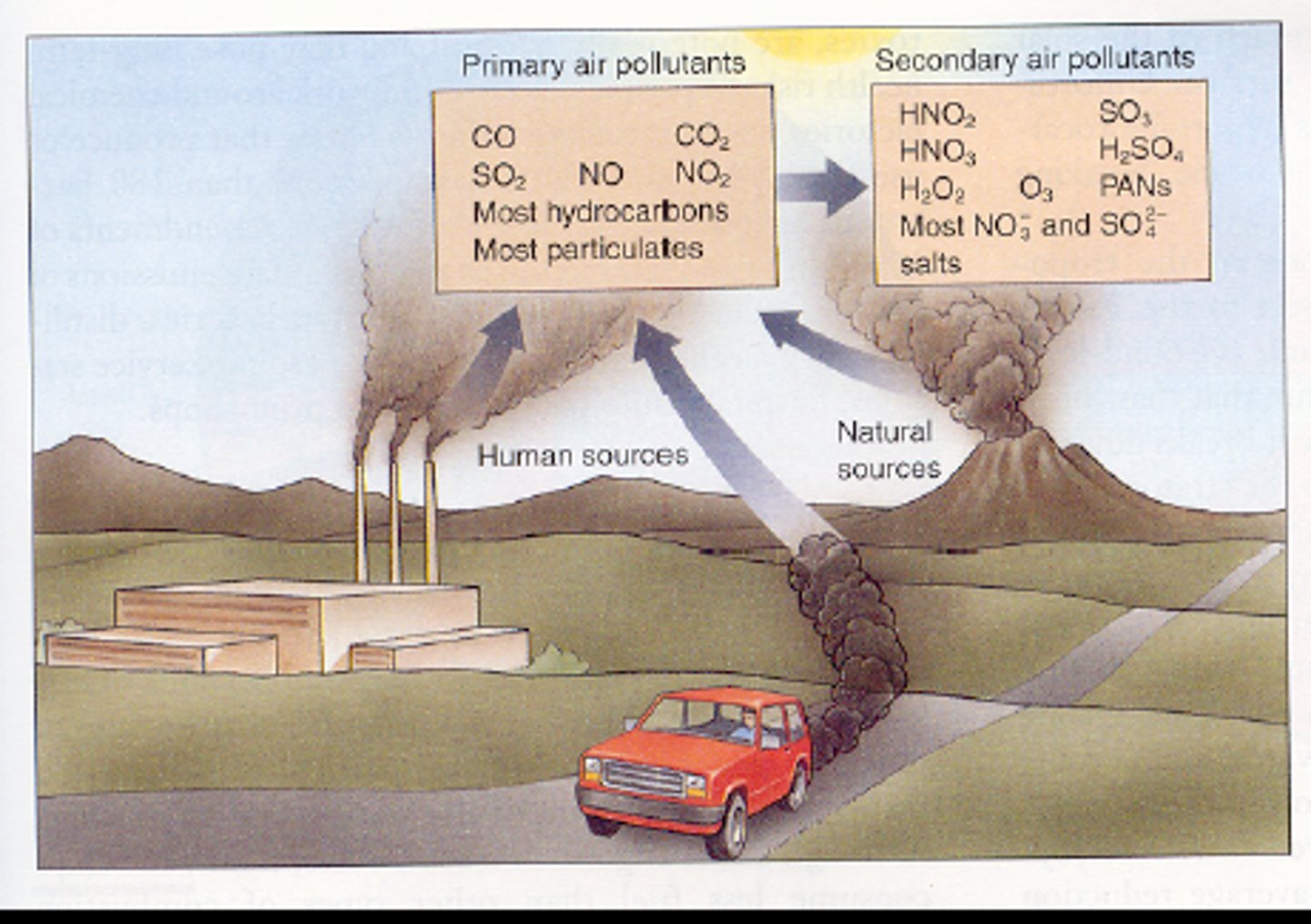
3. What are the major air pollution problems at local level?
a. CO, SO2, Pb, PM
b. Air toxics
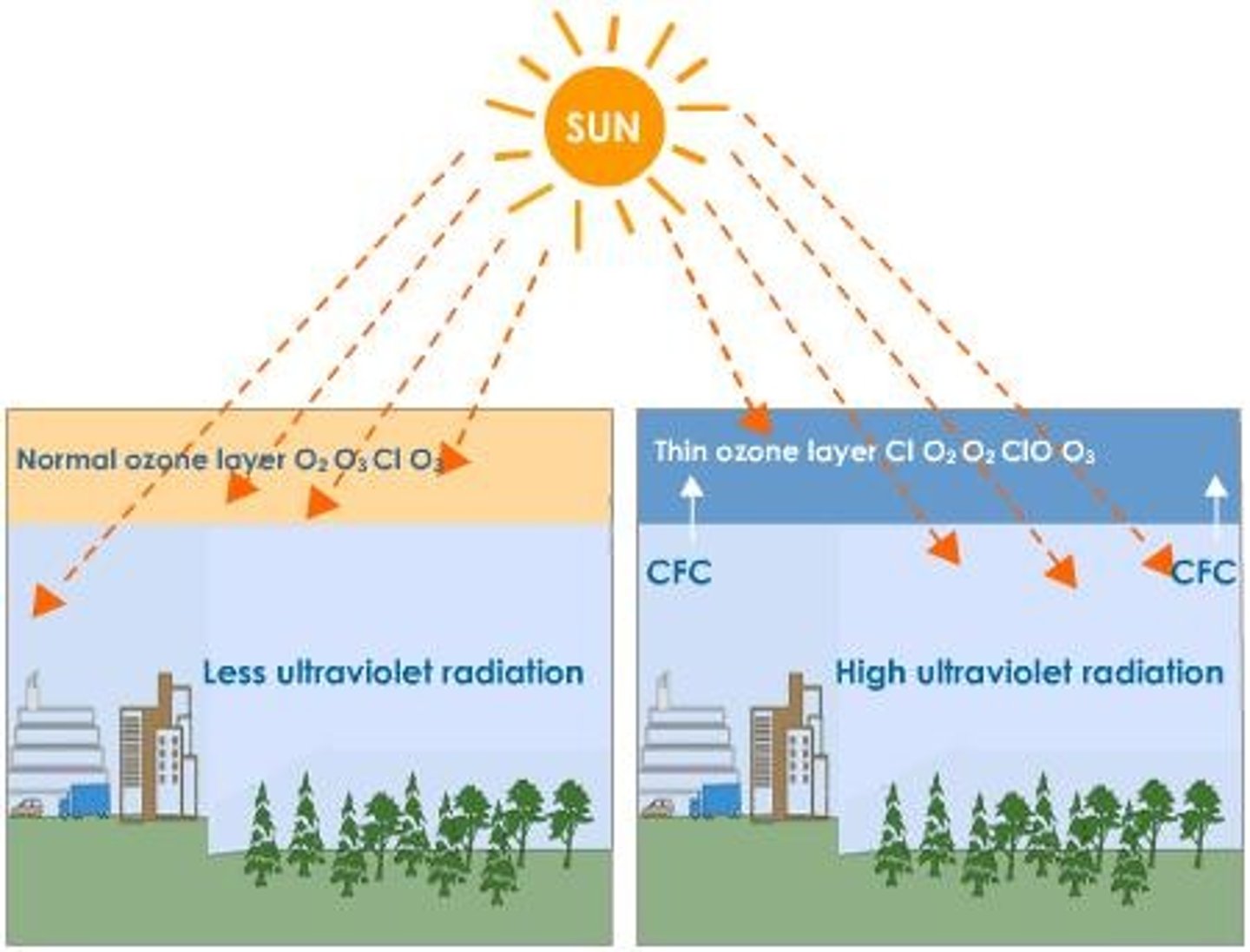
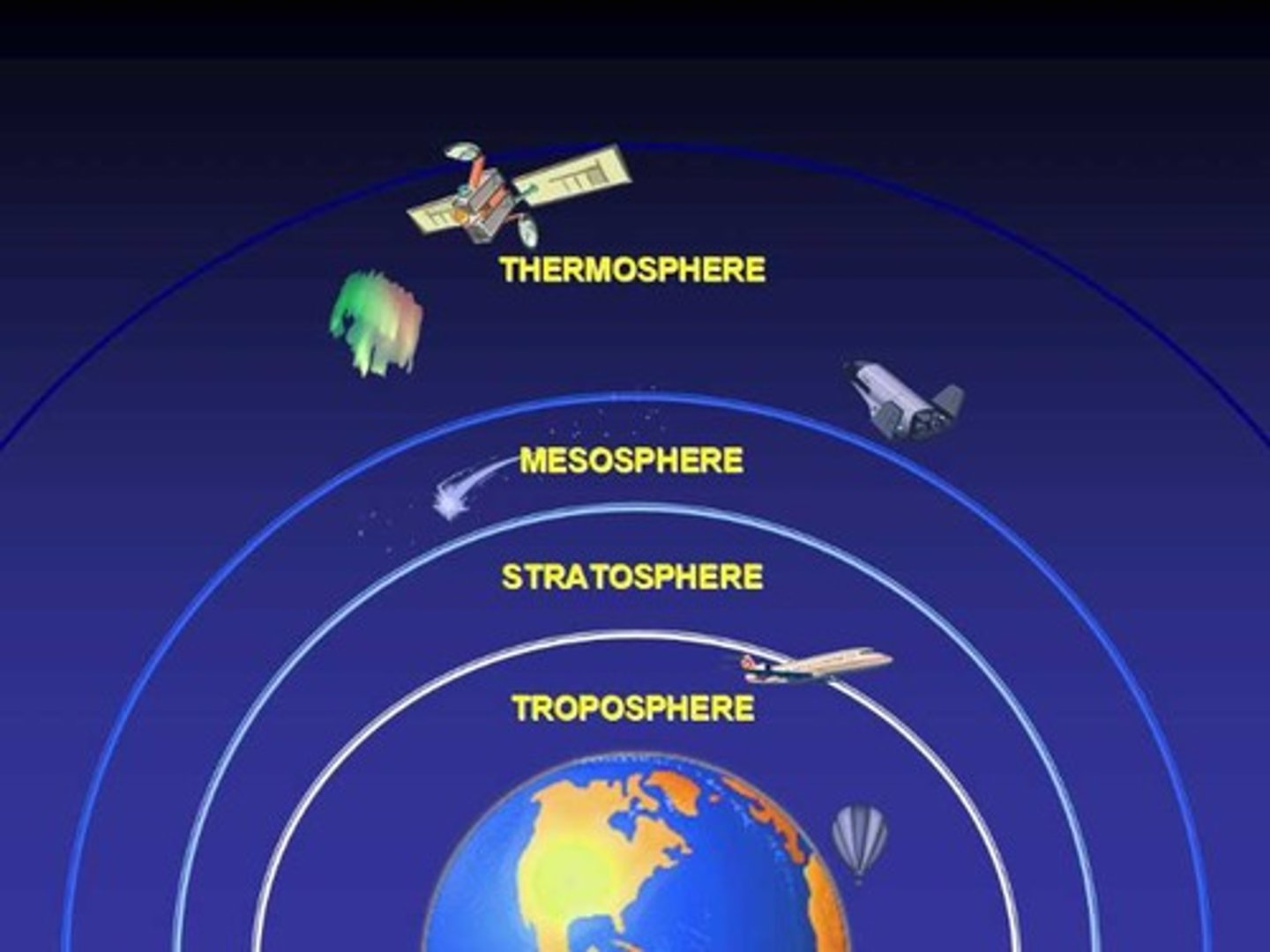
4. In which atmospheric region does the ozone layer occur and what would be the human health consequences of ozone layer destruction?
a. Stratosphere and troposphere
b. Health effects: Sunburn, skin cancer, eye damage, cataracts, suppress immune system, DNA mutation
c. Additional:
i. Chest pain, coughing, throat irritation, and congestion.
ii. Worsen bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma.
iii. Reduce lung function and inflame the linings of the lungs.
iv. permanently scar lung tissue.
5. On an overcast or cloudy day, would you expect any O3 buildup due to smog? Explain why.
a. No...

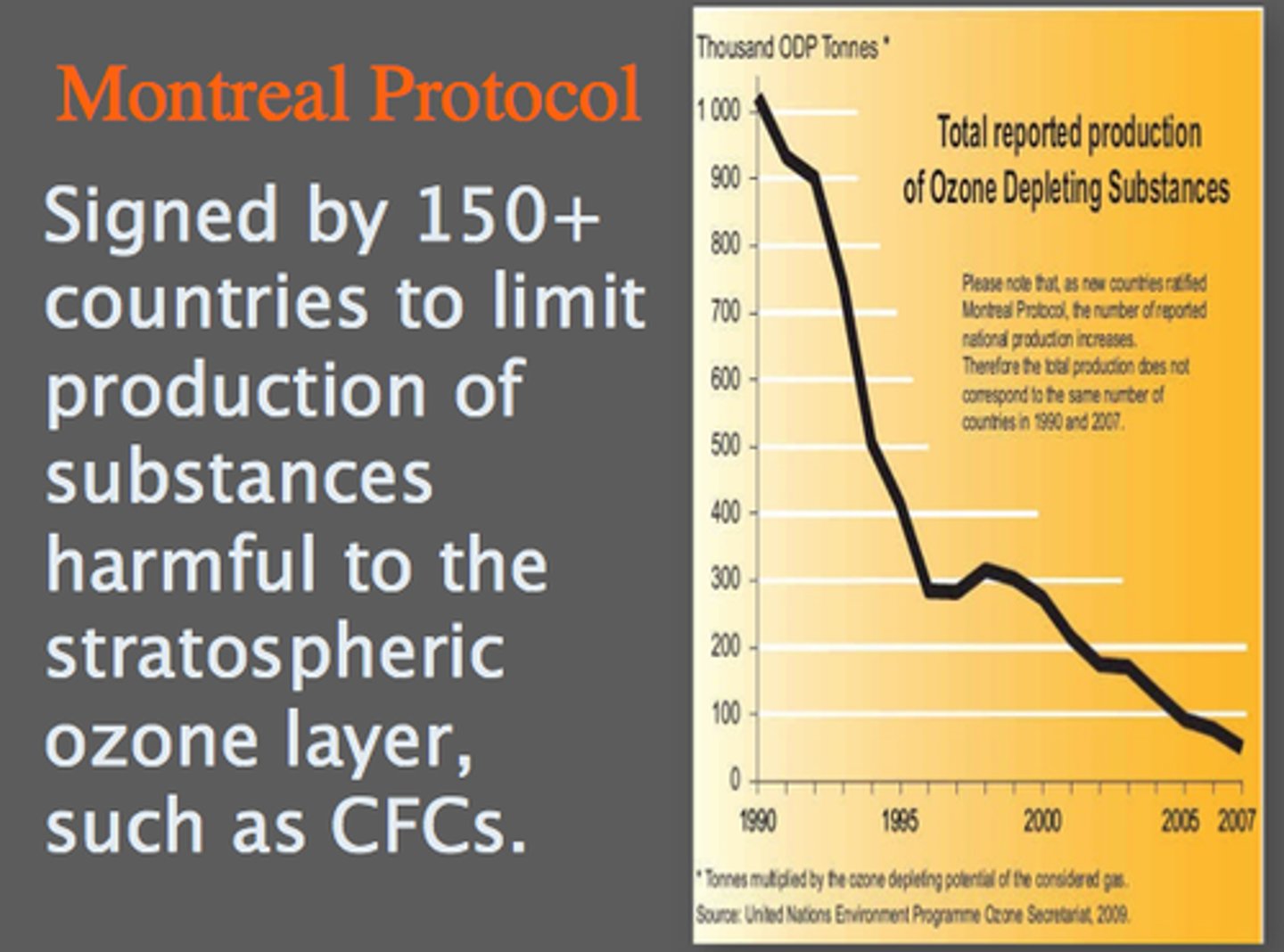
6. What international treaty went into effect in 1987, aiming at mustering worldwide effects to protect the ozone layer? What is the major action called by this treaty?
a. 1987 Montreal Protocol: Restricted CFCs and halons
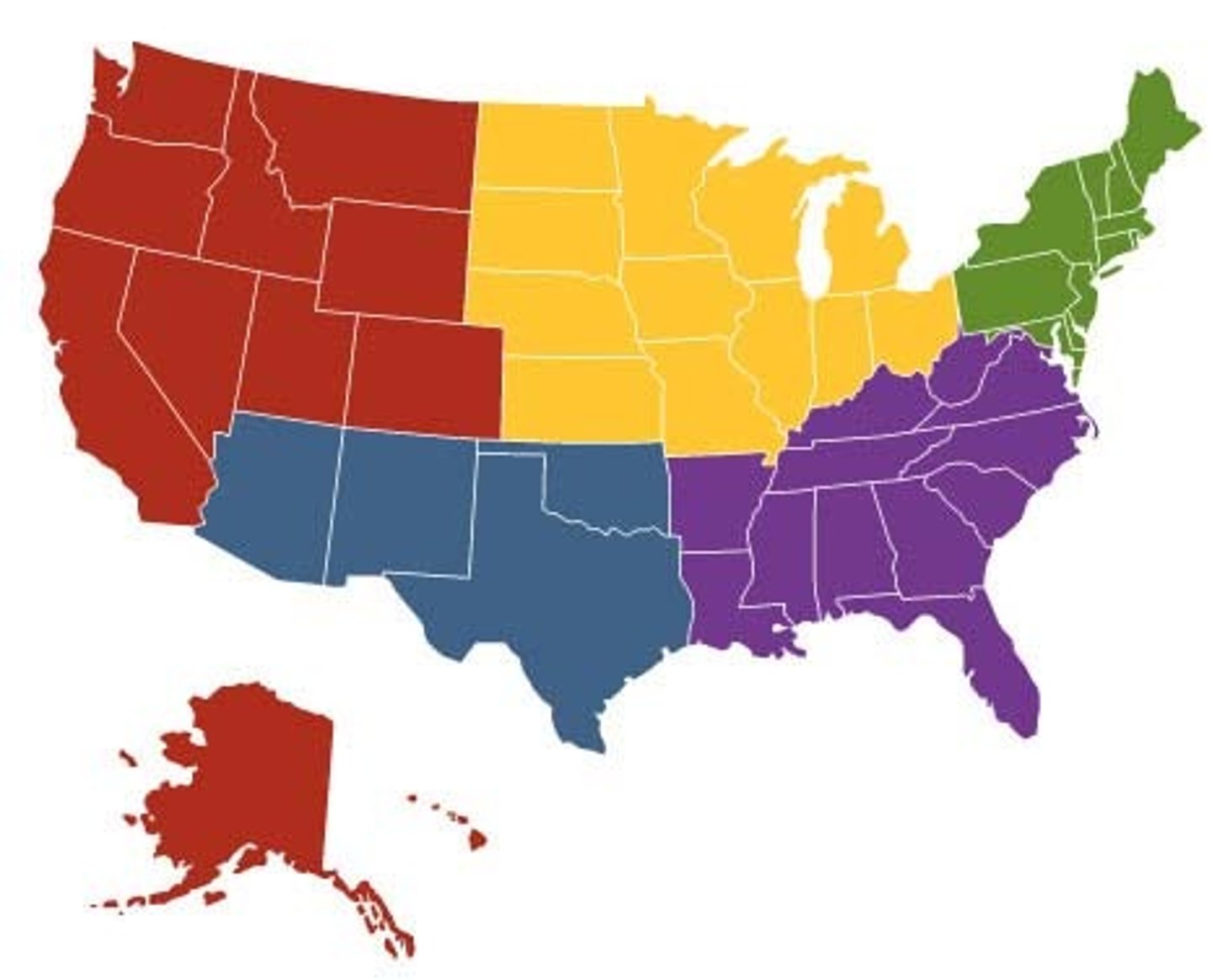
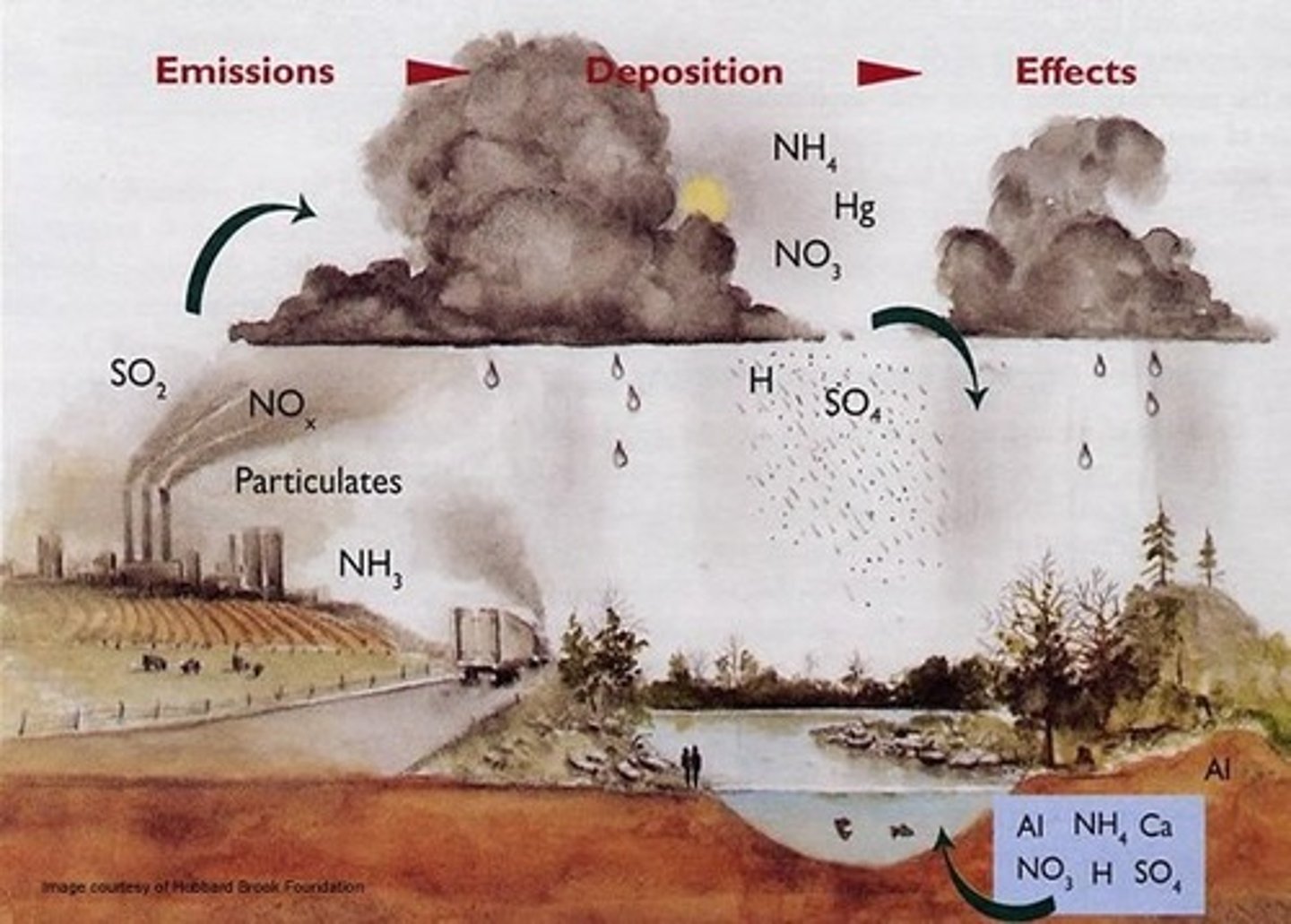
7. Which geographical area in the U.S. has the most significant acid rain problem and what are the environmental and human health effects of acid rain?
a. Northeast
b. Environmental effects:
i. Impaired forest growth -> reduced ecosystem productively
ii. Increased acidity for lakes, rivers
iii. Death of fish and wildlife
iv. Weathering of monuments and buildings
c. Human health effects: respiratory illness
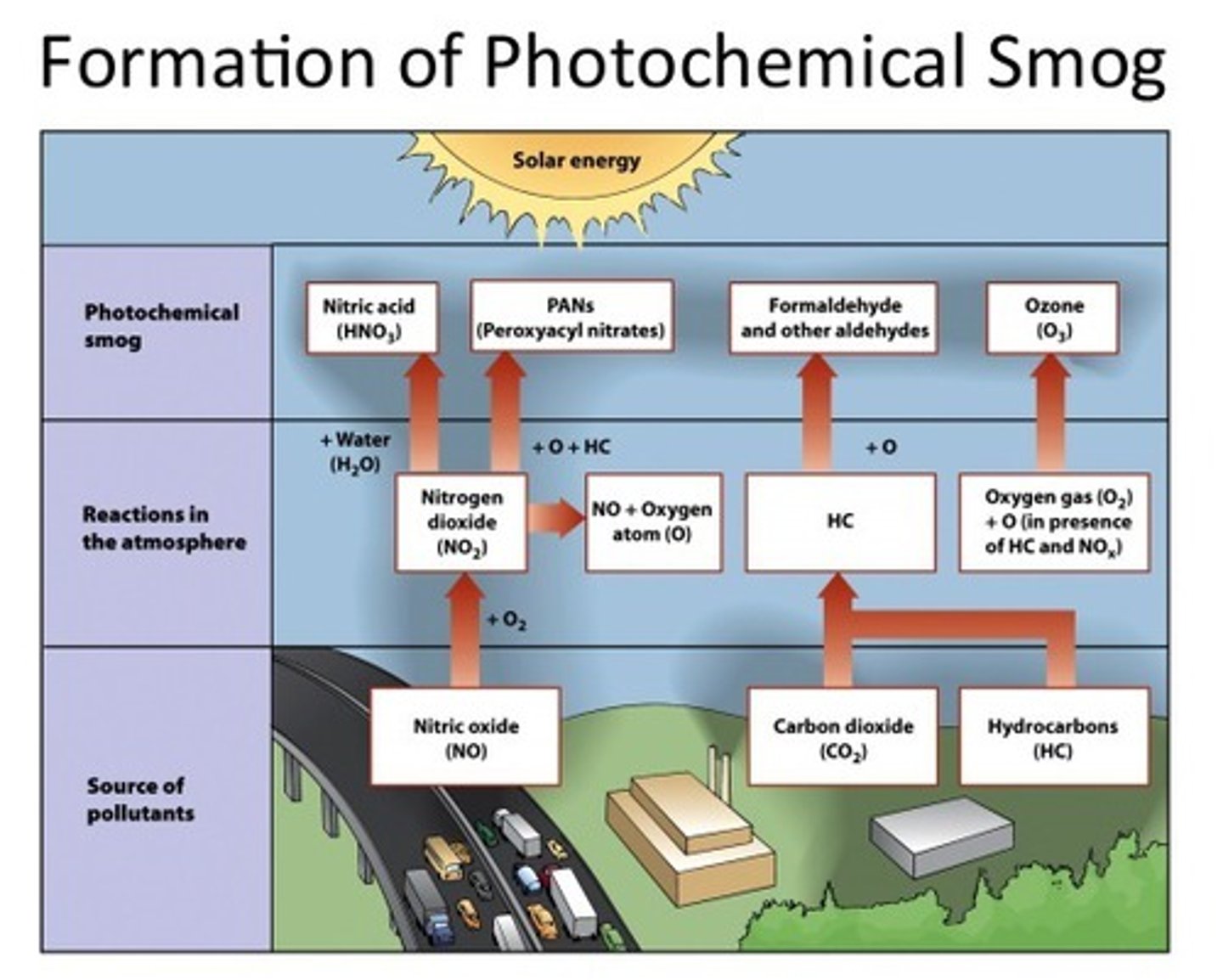
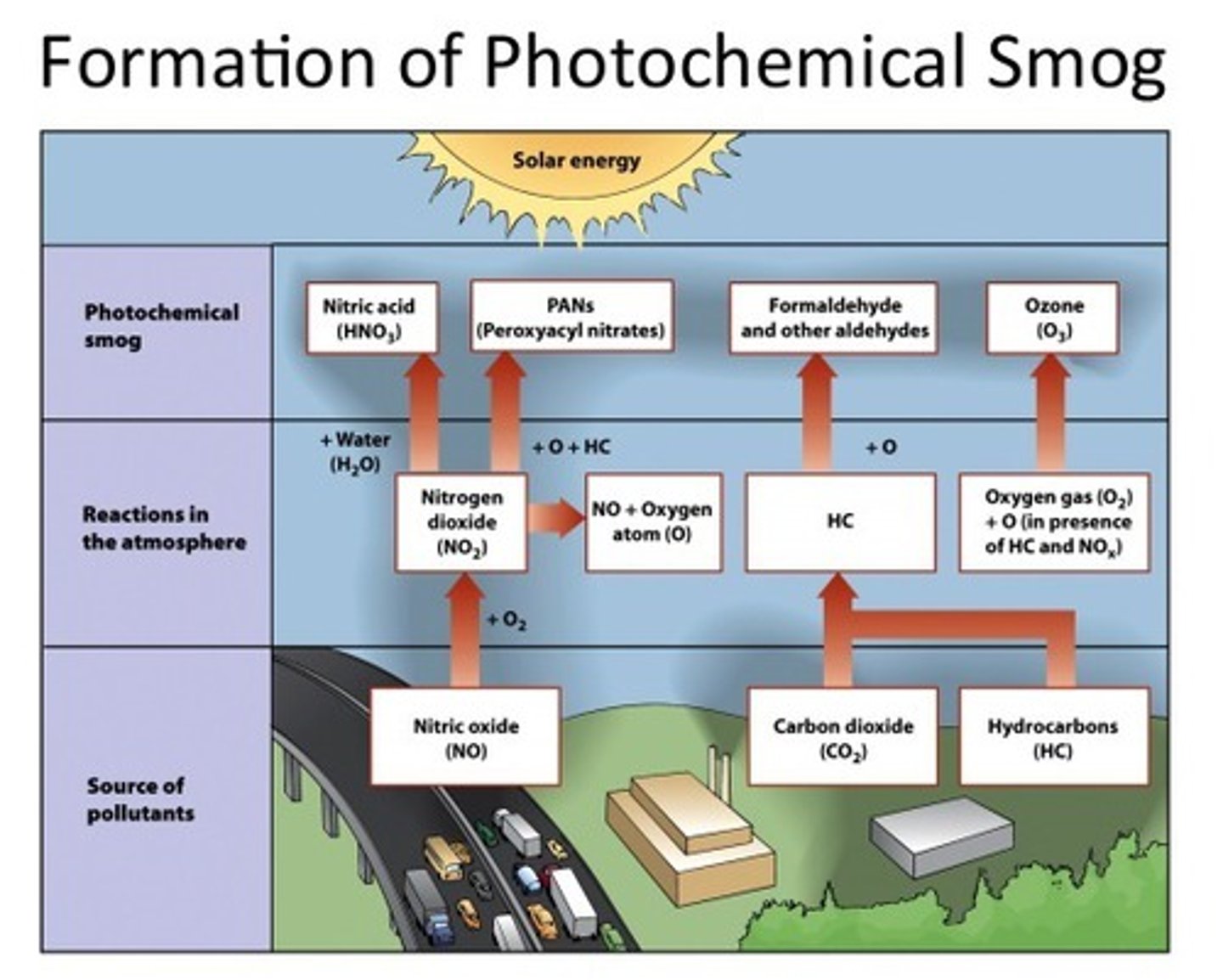
8. What are the differences between industrial smog and photochemical smog?
a. Industrial smog:
i. Burning sulfur-rich oil or coal creates SO2, SO3, sulfuric acid, ammonium sulfate.
ii. Carbon leads to CO2 and CO.
iii. Days with stagnant air, usually winter.
b. Photochemical smong:
i. Smog from reaction of sunlight with pollutants
ii. Prevalence in many American cities
iii. "Brown air smog"
iv. Contains tropospheric ozone, NO2, VOCs, 100 more
v. Hot sunny days in urban areas create perfect conditions.
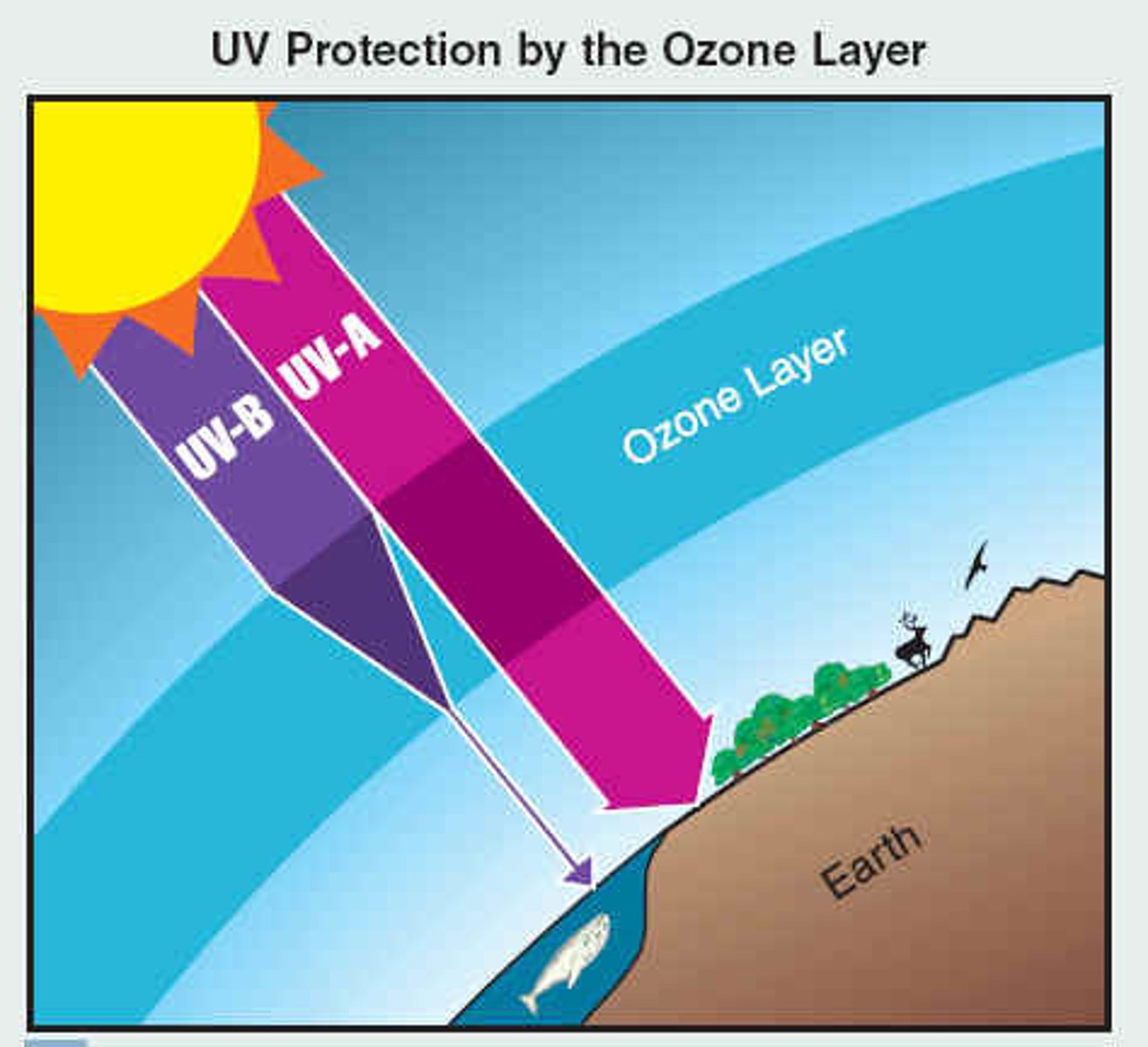
9. Why is O3 presence in the troposphere a paradox to O3 in the stratosphere?
a. O3 in stratosphere: protective layer that absorbs ultraviolent-B (wavelength of solar radiation)
b. O3 in troposphere: bad health effects
10. What does VOC stand for? What is the role of VOC in smog formation?
a. Volatile Organic Compounds
b. Precursor of ozone
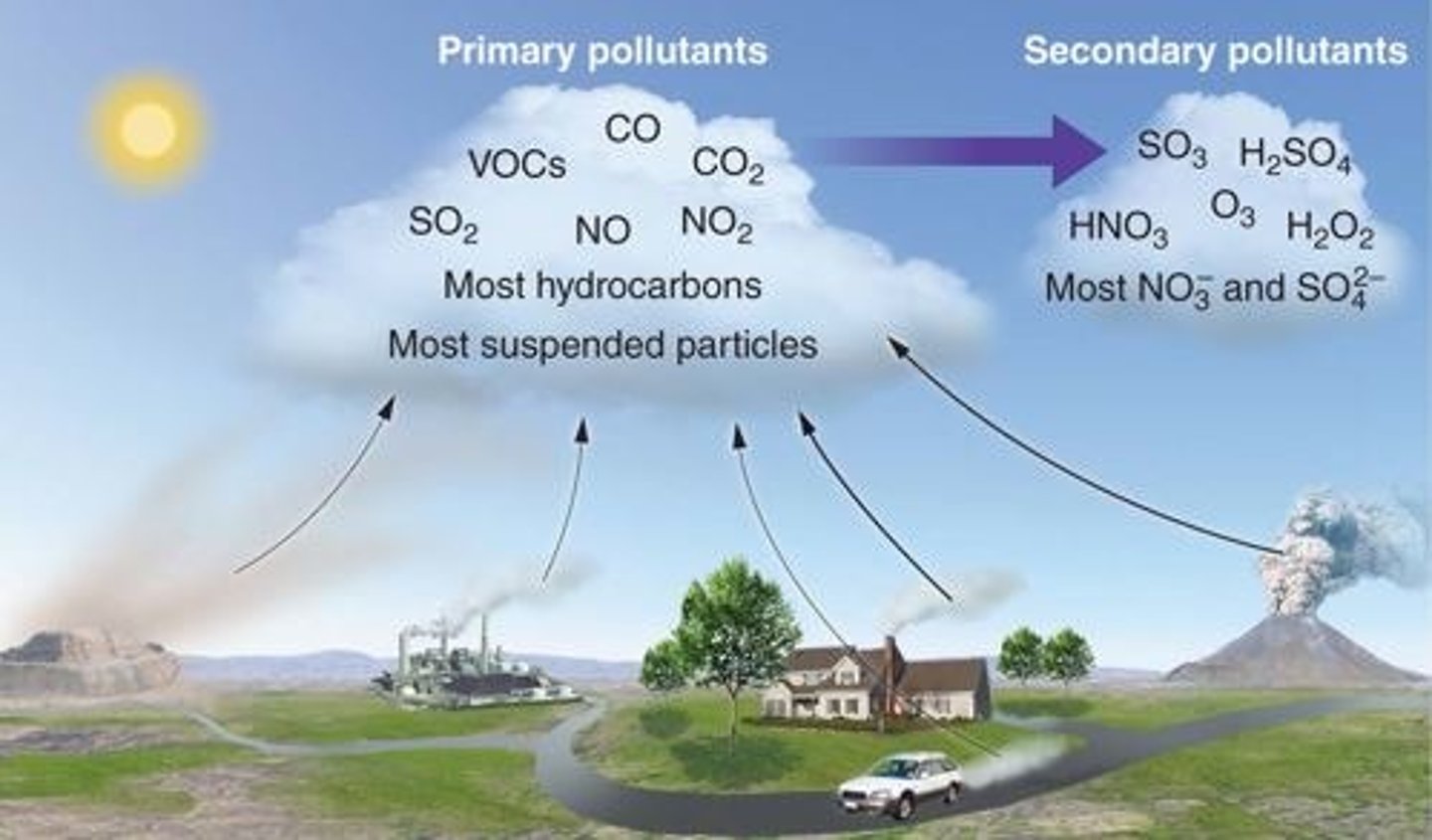
12. Cite two ways in which hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) differ from criteria pollutants.
a. Clean Air Act has primary and secondary standards that set limit in pollutant concentration in the air for criteria polluants (common air polluants)
b. For HAP (low concentrations) have regulation emissions from MACT (maximum achievable control technology)
13. Particulate matter (PM) air pollution is sometimes categorized as PM10, PM2.5, or ultrafine particles. Why is particle size an important factor determining the adverse human health effects?
a. Different sizes impact different areas of health.
b. PM2.5 is associated with mortality, respiratory illness, cardiovascular endpoints
c. UFP penetrates cell walls and blood brain barrier, absorbed into vital organs

14. Why air pollution is still a public health problem worldwide?
a. Prevalence in developing countries with lack of technologies

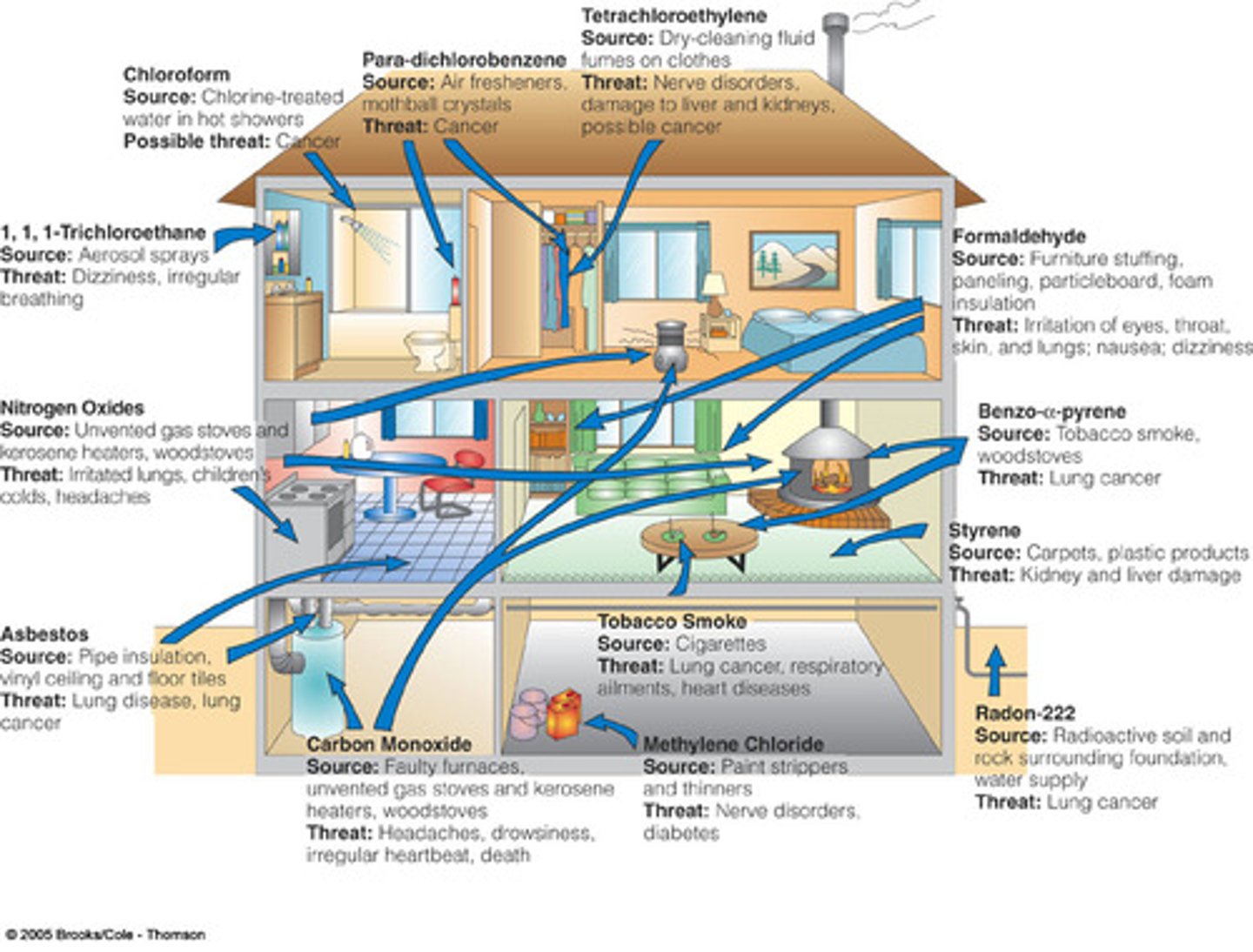
15. Why indoor air pollution is important?
a. People spend most of their time indoors (89% of time; 18 hours indoor every 1 outdoors).
b. Pollutant exposure, tobacco smoke and radon, occur mostly indoors
c. Indoor pollutant levels are 2-50 tines higher (formaldehyde, etc.)
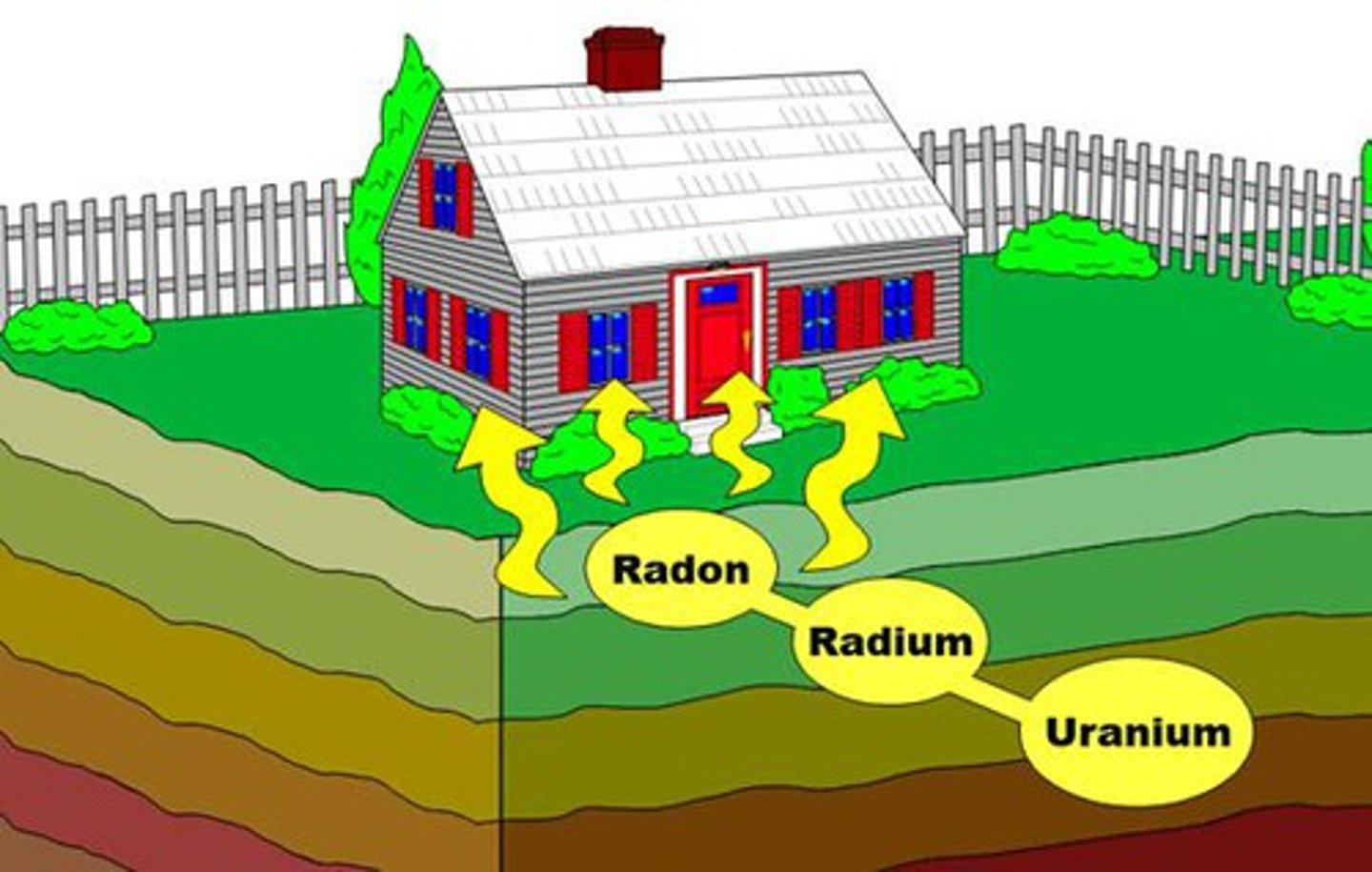
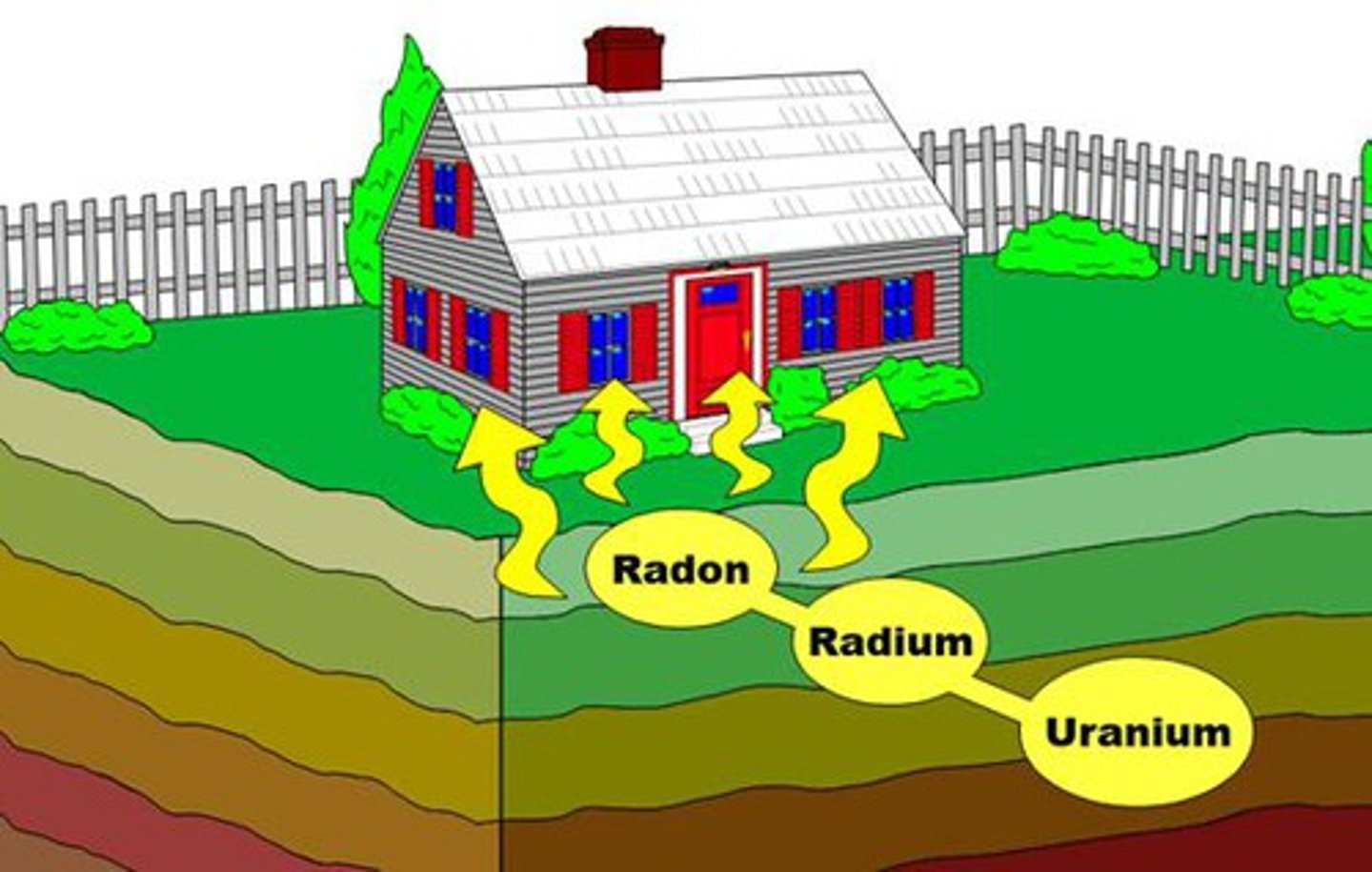
16. What health problem is associated with exposure to radon in homes? What is the source of radon in home?
a. Sources:
i. Permeable soils gas (85-90%)
ii. Well water supply (<1%)
iii. Natural gas
iv. Some building materials
v. Rocks
b. Health effect: lung cancer
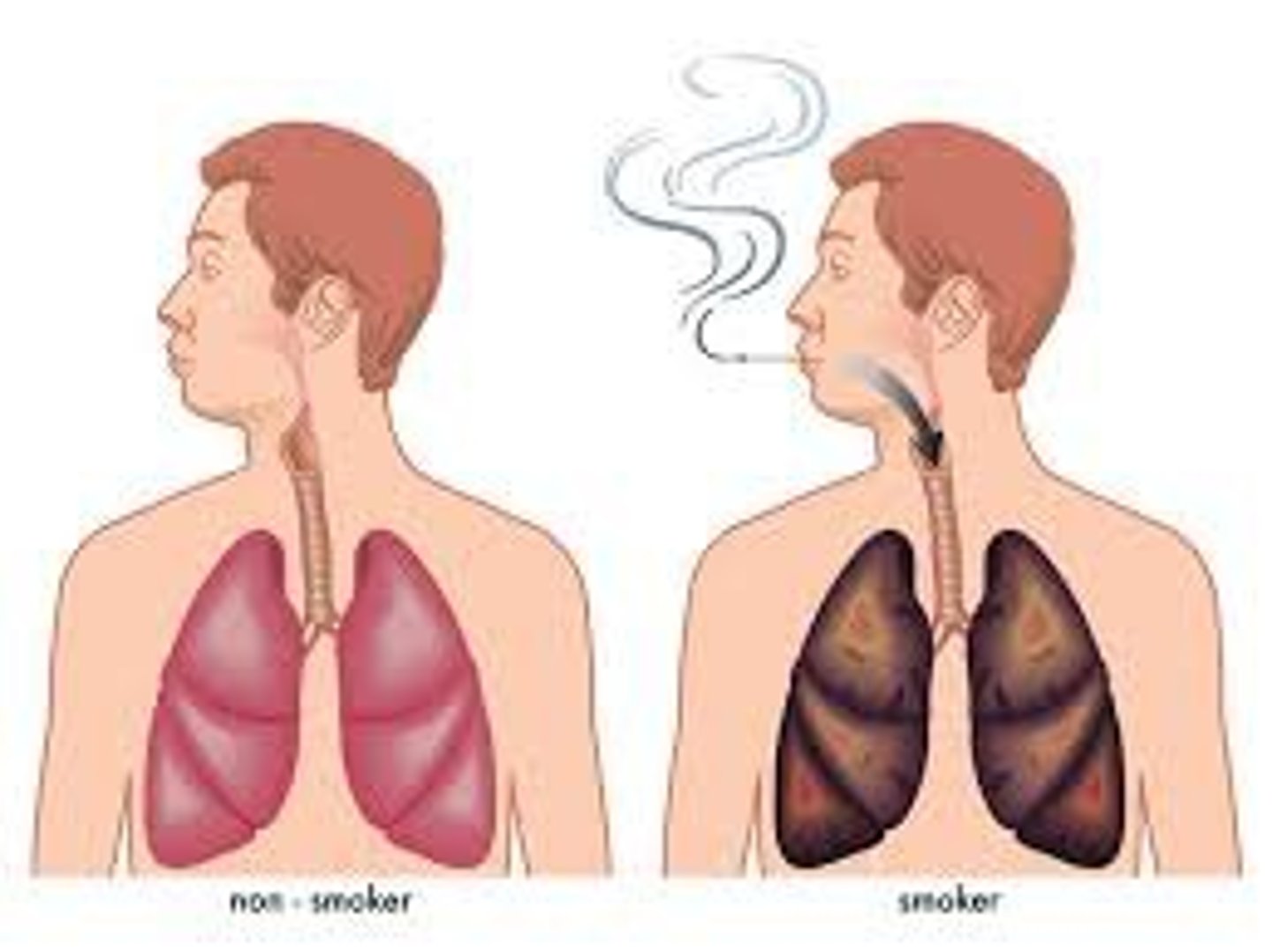
17. What health problems are associated with exposure to smoking, ETS, and vaping?
a. Smoking and environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) health effects:
i. Adults: lung cancer
ii. Fetus/infants: prenatal complications, low birth weight, infant mortality
1. Pneumonia and hospitalization in year 1 is 38% higher
2. Infant mortality is 80% higher
3. 5 times higher risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
4. 20% of all infant deaths could be avoided if all pregnant smokers stopped by the 16th week of gestation.
iii. Children whose mothers smoke: 70% more respiratory problems
b. Vaping
i. Contain: nicotine, VOC, PM, diacetyl (linked to cancer), cancer-causing chemicals
ii. Lung cancer
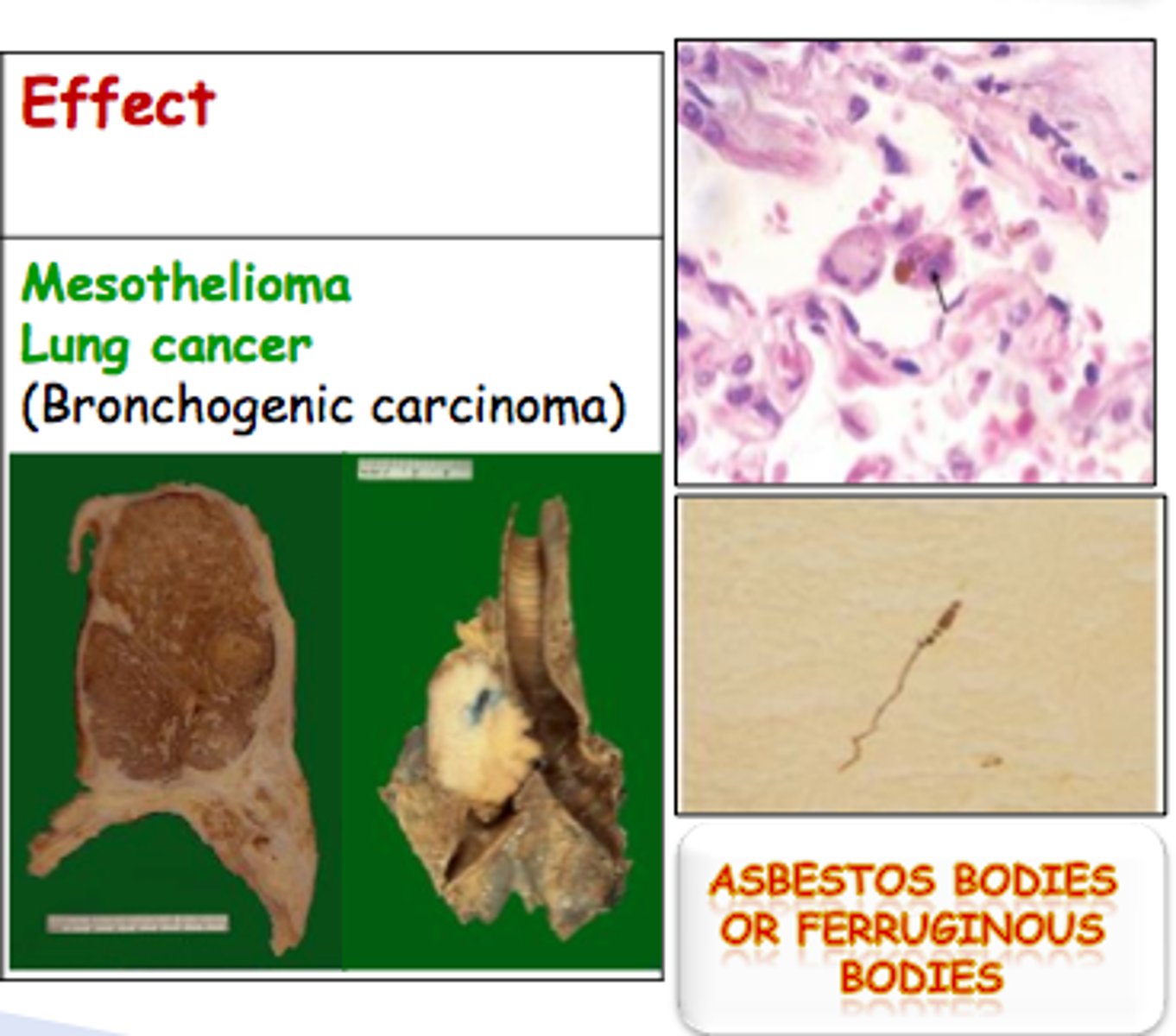
18. Explain how asbestos can be damaging to our health. What are the most common diseases associated with long-term asbestos exposure?
a. Health effects
i. Accumulate in lungs after inhalation
ii. Chronic toxicity = high
1. Asbestosis, lung cancer, mesothelioma, and tumor.
2. Symptoms years after exposure
3. Effects depend on length, diameter and composition of fiber
19. Particleboard, plywood, and wood paneling may emit significant amounts of what common indoor air pollutant?
a. Formaldehyde
i. Rate of emission changes depending on the age of the source (older = less emission)
20. What is PBDE? Describe the major source and health effects of PBDE.
a. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE): slows fires in upholstered furniture (mattress) and consumer electronics
b. Major source: fire-retardant, commercial products (electrical, construction products, clothes)
c. Health effects:
i. Thyroid hormone disruption
ii. Permanent learning and memory impairment, behavioral changes, hearing deficits, delayed puberty onset, decreased sperm count, fetal malformations and, possibly cancer

21. Why organic solvents and pesticides can be a problem indoors?
a. Common household products (cleaning, degressing, painting)
b. Health effects
i. Volatile lipid-soluble organic chemicals: cause general non-specific depression of the central nervous system
ii. Pesticides are neurotoxins, carcinogens, and endocrine disruptors
1. Target neurosystem
22. Describe the relationship of ventilation and air pollutant concentrations with significant indoor sources.
a. Increased ventilation rate reduces air pollutant concentrations

23. Understand the reasons for indoor air quality problems and strategies to improve indoor air quality.
a. Reasons for indoor air quality problems:
i. For office:
1. Inadequate ventilation
2. Pollutants from material processed inside the building
3. Pollutants drawn in from outside air
4. Biological contamination
5. Pollutants from building materials and furnishings
b. Strategies to improve indoor air quality:
i. Increased ventilation
ii. Pollutant source control
iii. Use of air cleaners (NOT air fresheners)
iv. Dust collectors/filters = remove some airborne particles
v. Gas adsorbing material = remove gaseous contaminants
vi. Ozone generators = air cleaners...
25. What are the main possible risk factor(s) of SARS-CoV-2 transmission indoors?
a. Direct contact
b. Indirect contact
c. Large droplet spray
d. Aerosols
26. How can we use mask, ventilation, air cleaner, and disinfection to minimize SARS-CoV-2 transmission indoors?
a. Mask: source control
b. Ventilation: reduce airborne transmission
i. Air should not be recirculated as far as practically possible.
c. Air cleaning
i. Portable air cleaning devices may be beneficial in smaller rooms, although they must be appropriately sized for the space.
d. Disinfection
i. UV germicidal irradiation = remove or deactivate potential viral contamination from the recirculated air.
ii. 'upper-room' UV lamps in crowded, poorly ventilated environments.

27. What ventilation rate in terms of liter/s/person is needed to reduce infection possibility indoors?
a. < 5 L/s per person = impact acute respiratory infection
b. < 25 = increase risk of sick building symptoms, increase short-term sick leave
c. <24 = reduce
28. What is an air (ex)change rate? How would you increase air (ex)change rate? Does air (ex)change rate of 0.5/hr indicate good indoor ventilation?
a. Air exchange rate: normalized value of ventilation that measures the outside air volume added to a space divided by volume of that space
b. Good ventilation system
c. Good indoor ventilation = varies during day and from environment
29. Why did the speaker recommend no more than 30 minutes of activity in a highly-occupied room, e.g. classroom?
a. Even with just one air exchange/hr, the risk of infection is low if you stay in one area for 30 minutes
b. Aerosols:
i. Travel beyond 6 feet
ii. Remain airborne for hours
iii. Virus remains viable for hours
31. List potential sources of water contamination and indicate control strategies that could be adopted to prevent such contamination from occurring.
a. Point sources: well-defined location where pollutants enter the waterway (sewage treatment plants)
b. Non-point sources
i. Agriculture: soil, manure, chemical fertilizer
1. Minimize soil erosion
ii. Construction
1. Not do construction during rainy days
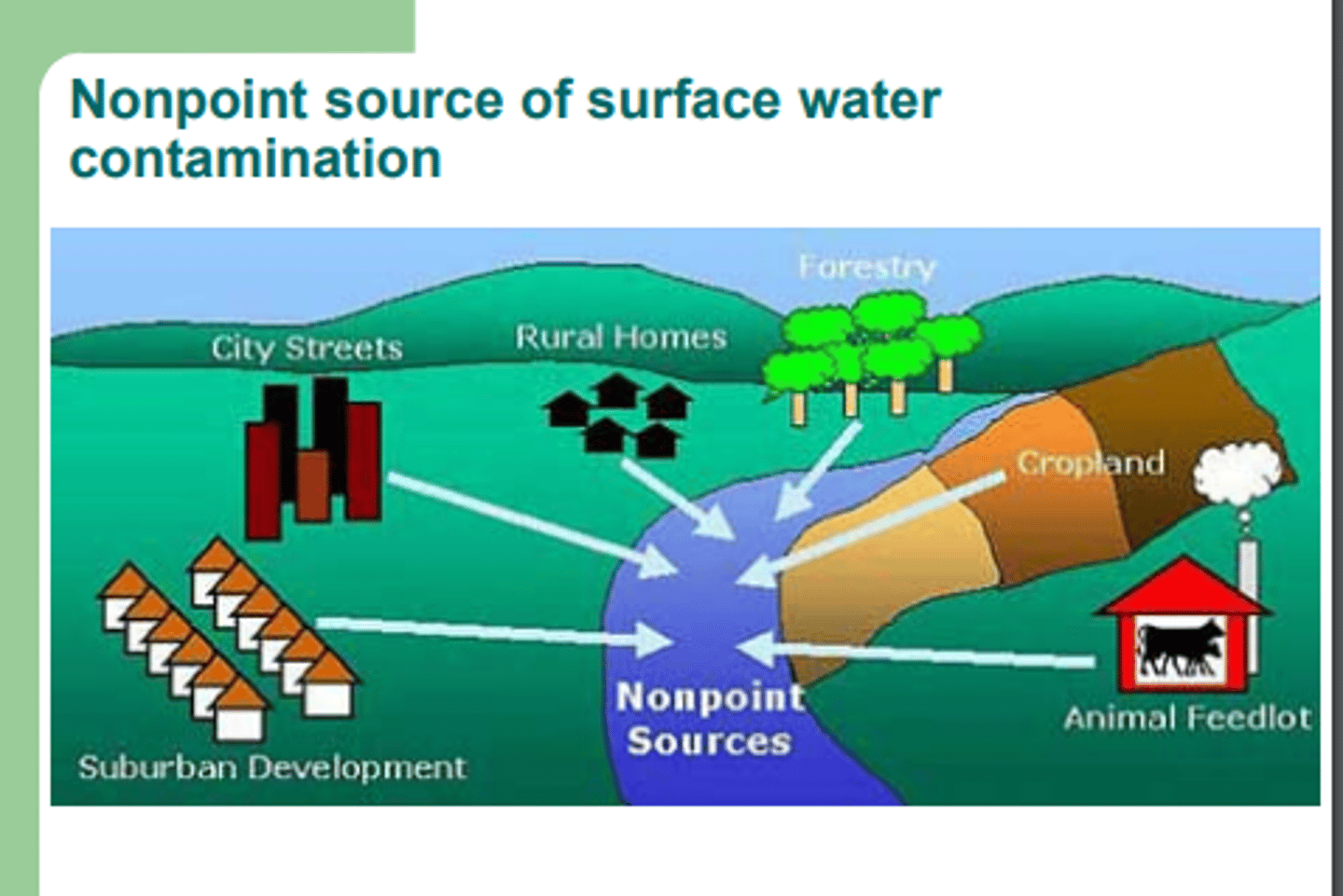
32. In the U.S. what federal law ensures the quality of drinking water and the quality of surface water pollution problems?
a. Safe Drinking Water Act
i. EPA established max contaminant levels (MCL) for more than 80 biological chemicals and radioactive pollutants
ii. MCL must be met by water supplied by every community water system
b. Clean Water Act: goven water pollution
i. Limit emission from point/non-point sources

33. What are the two major contaminant types of concern in drinking water?
a. Pathogenic microbial
b. Chemicals

34. What is the purpose of adding chlorine to drinking water? What are the advantages and disadvantages of chlorine and other disinfects in treating drinking water and waste water effluent?
a. Kills microorganisms
b. Cheap, convenient, residual
c. Doesn't kill all microorganism (protozoan cysts, etc.)
d. Lead to carcinogen effect
e. Other disinfectant
i. Ozone
1. Effective
2. Espensive, toxic, no lasting residual
ii. UV radiation
1. Effective, no known formation of disinfection by-product
2. No lasting residual, not effective against virus, expensive

35. What is the controversy about water fluoridation?
a. Led to bone tumor and bone fraction... but only some studies found that
i. Chronic exposure may led to this...
b. Ethical issue: need consent to add this to water
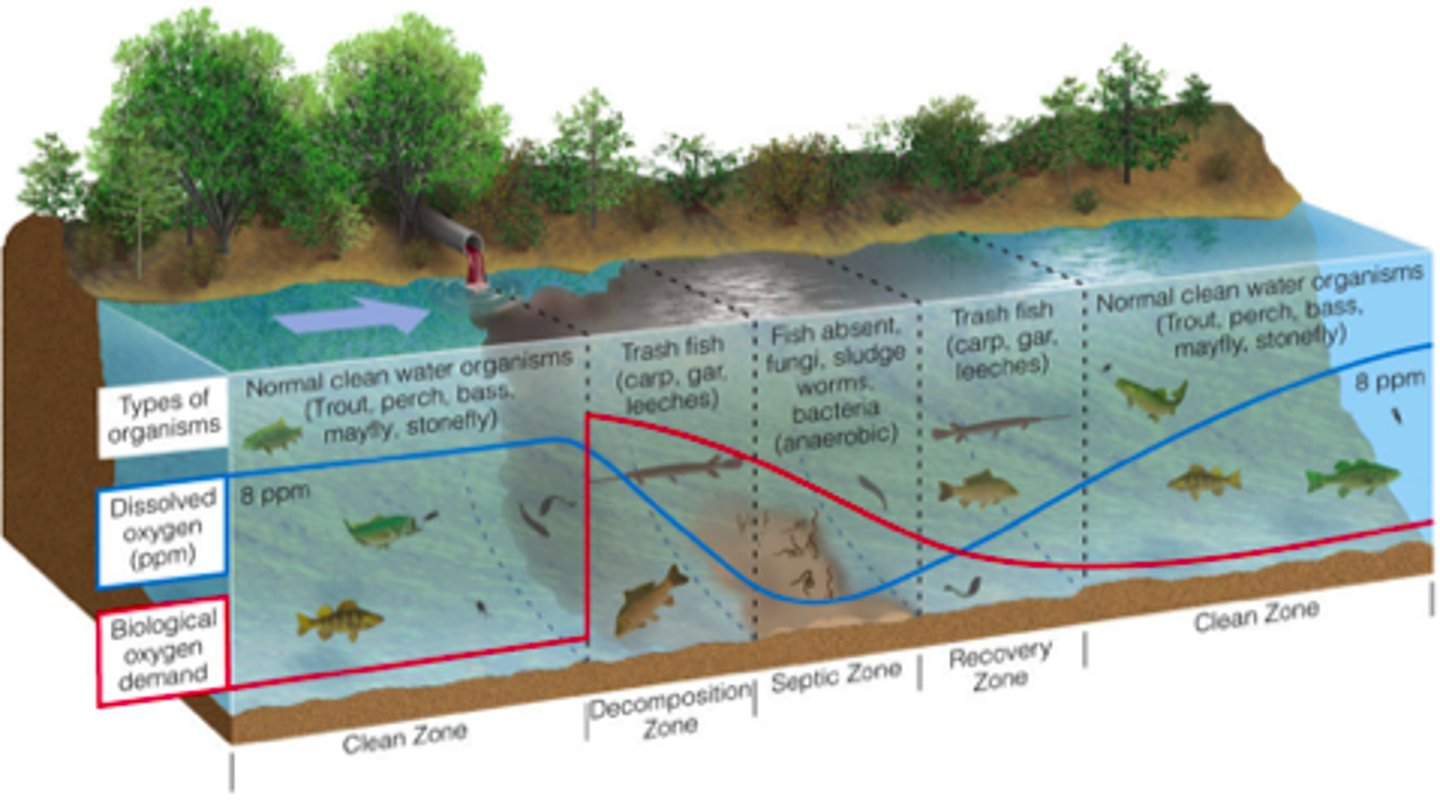
36. What is biological oxygen demand (BOD) and why do we want to have low levels of BOD in our waste treated discharge?
a. BOD: biochemical oxygen demand that comes from point source
b. BOD polluates the water area and decreases dissolved oxygen levels
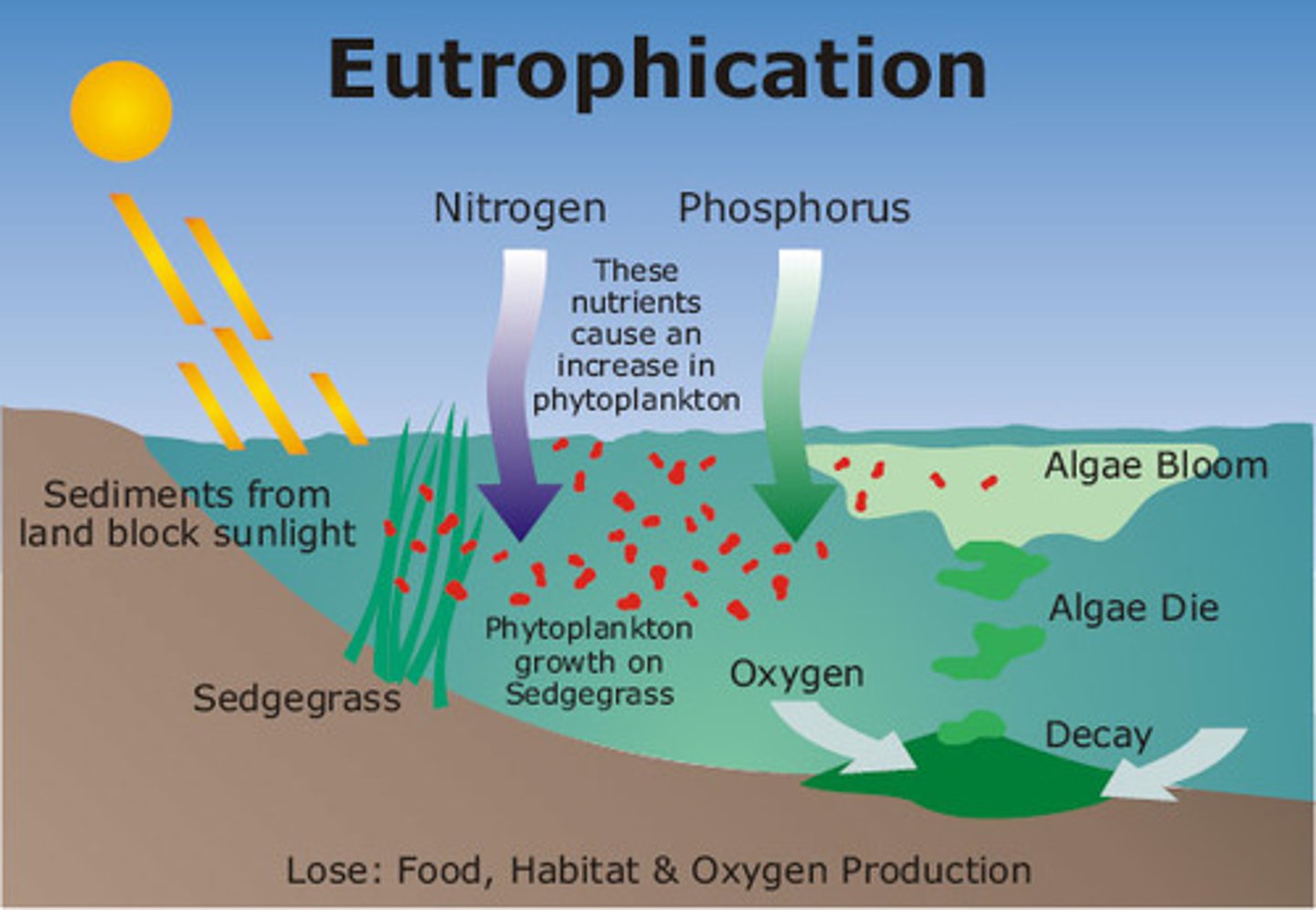
37. Explain eutrophication. What two pollutants are mainly responsible for initiating the process of eutrophication?
a. Too much nutrients in the water which leads to growth of algae that will fill up lake and transform to marsh/nog (become toxic and kill fish); consume a lot of oxygen -> death of aquatic system
b. Nitrates and Phosphates responsible
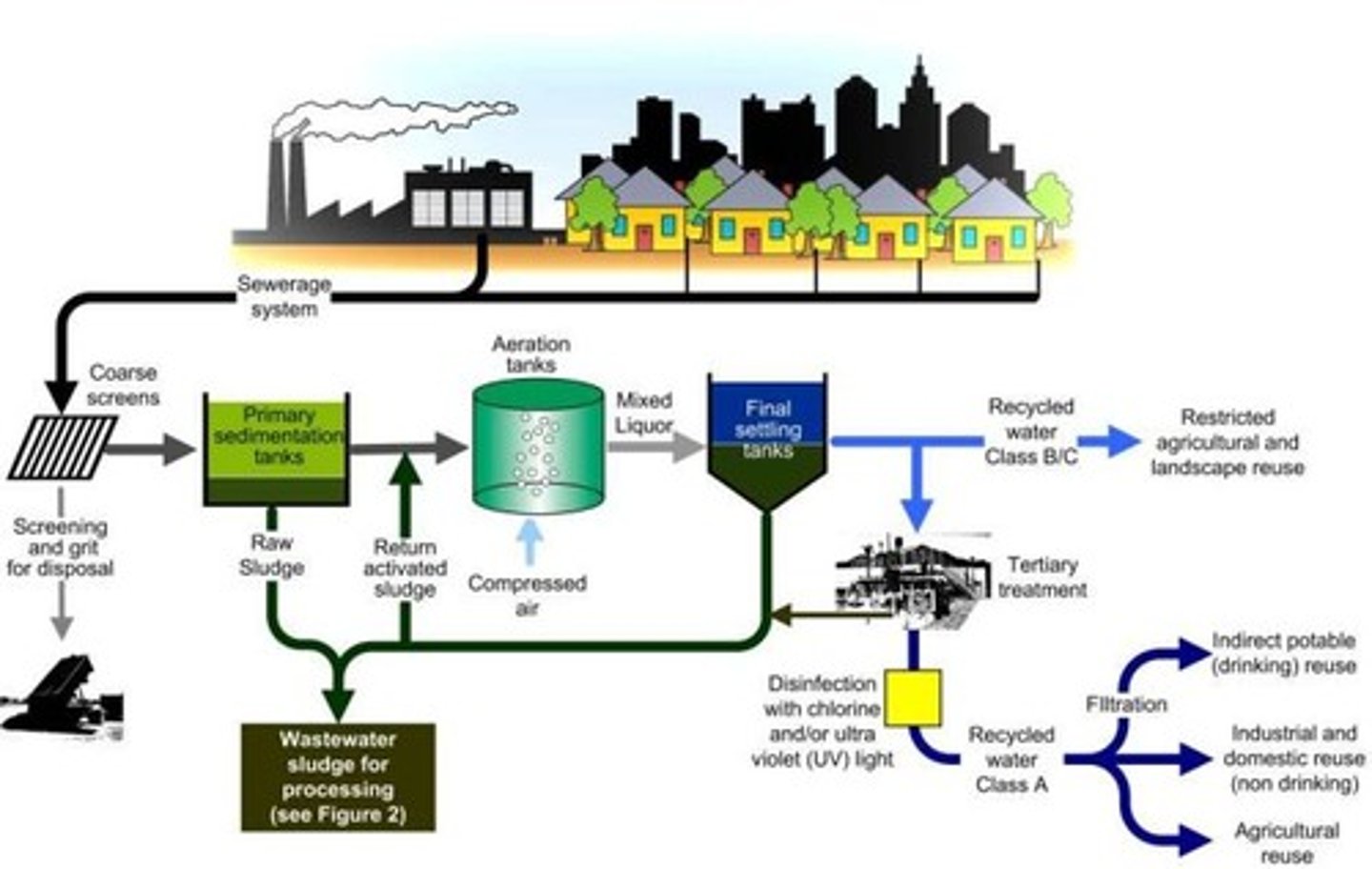
38. What are the steps used for treating drinking water and wastewater? What is the major difference in treating drinking water vs. wastewater?
a. Primary treatment: remove solids
b. Secondary: biological processes
i. Add oxygen
c. Terity: only required when final effluent must be clean that 95% or more contaminants must be removed by wastewater treatment
d. Differ in among of pollutants they must remove and degree of purification they must accomplish
39. What are the general indicators of water contamination? Why does EPA monitor indicator microorganisms rather than directly detect pathogens in the water?
a. Impossible to monitor for all pathogens
b. Demanding, expensive, time-consuming, can't tell if its live or dead
c. Indictor organisms
i. Microbial
ii. Bacterial
40. What are the four types of water-related diseases?
a. Water-borne: ingestion of water
b. Water-washed: poor personal hygiene
c. Water-based: parasites in intermediate organisms living in contamined water
d. Water-related: insect vector

41. Why safe drinking water is still a problem in developing countries?
a. They do not have access to safe drinking water; leading to infectious diseases, death lost work days, healthcare cost, drained family resources

42. Please list and describe three common water-borne diseases.
a. Water-borne: caused by ingestion of water that are contaminated by 1) pathogenic microorganisms (e.g. cholera, typhoid) and 2) chemicals that have an adverse effect on health (arsenic, pesticides).
b. Cholera: pathogenic microorganism that caused death (known in Soho, London)
c. Cryptosporidium:
d. Arsenic-associated disease: chemical

43. What are the three major transmission mechanism of cholera in the 1991-1993 outbreaks in Latin America? What are the corresponding control strategies?
a. Waterborne, foodborne, seafood
b. Strategies: ?

44. What are the two hypothesized causes of 2010 Cholera outbreaks in Haiti?
a. Climate causal hypothesis
b. Human causal hypothesis

45. Please describe the 1993 Milwaukee Cryptosporidium outbreak in the U.S.
a. 1.61 million people were affected; over 400,000 with significant symptoms; 100 people died.
b. Median duration of illness was 9 days.
c. Clinical manifestations included watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever, vomiting.
d. $31.7 million in total medical costs and $64.6 million in total lost productivity.
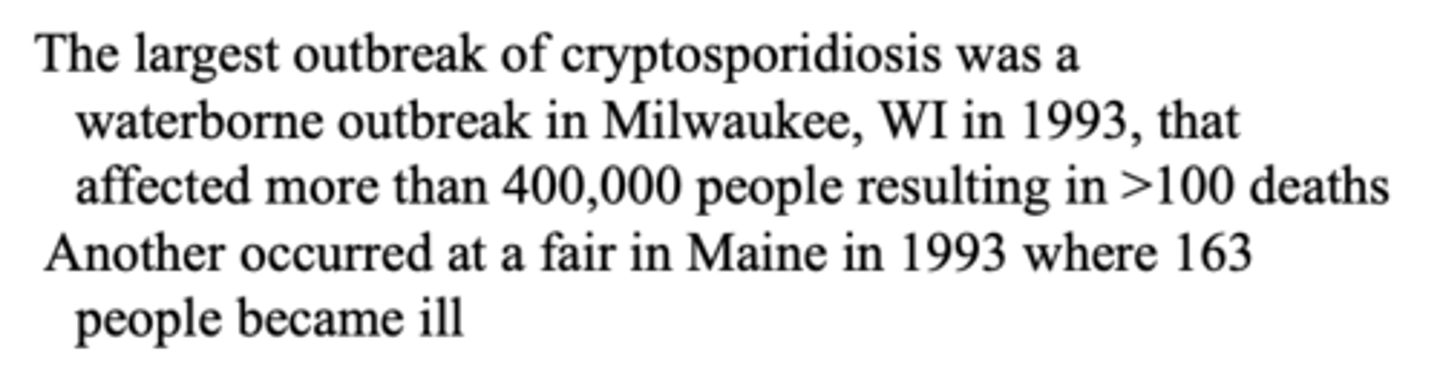
46. Please describe the potential relationship between extreme precipitation and waterborne disease outbreaks.
a. Rainfall: transport and dissemination of infectious agents
b. Flooding: sewage treatment plants overflow; water sources contaminated, secondary shortage of clean drinking water
47. What are the major sources of inorganic arsenic exposure? What are the health effects of inorganic arsenic? What's Bowen's disease?
a. Drinking water (minor include: wood preservative, electronic industry, medicine)
b. Bowen's disease (cancer with growth of cell of skin), cancer (skin, liver, lung, kidney, bladder, prostate), non cancer (circulatory problems, stocking, kidney damage, keratosis, nerve damage)
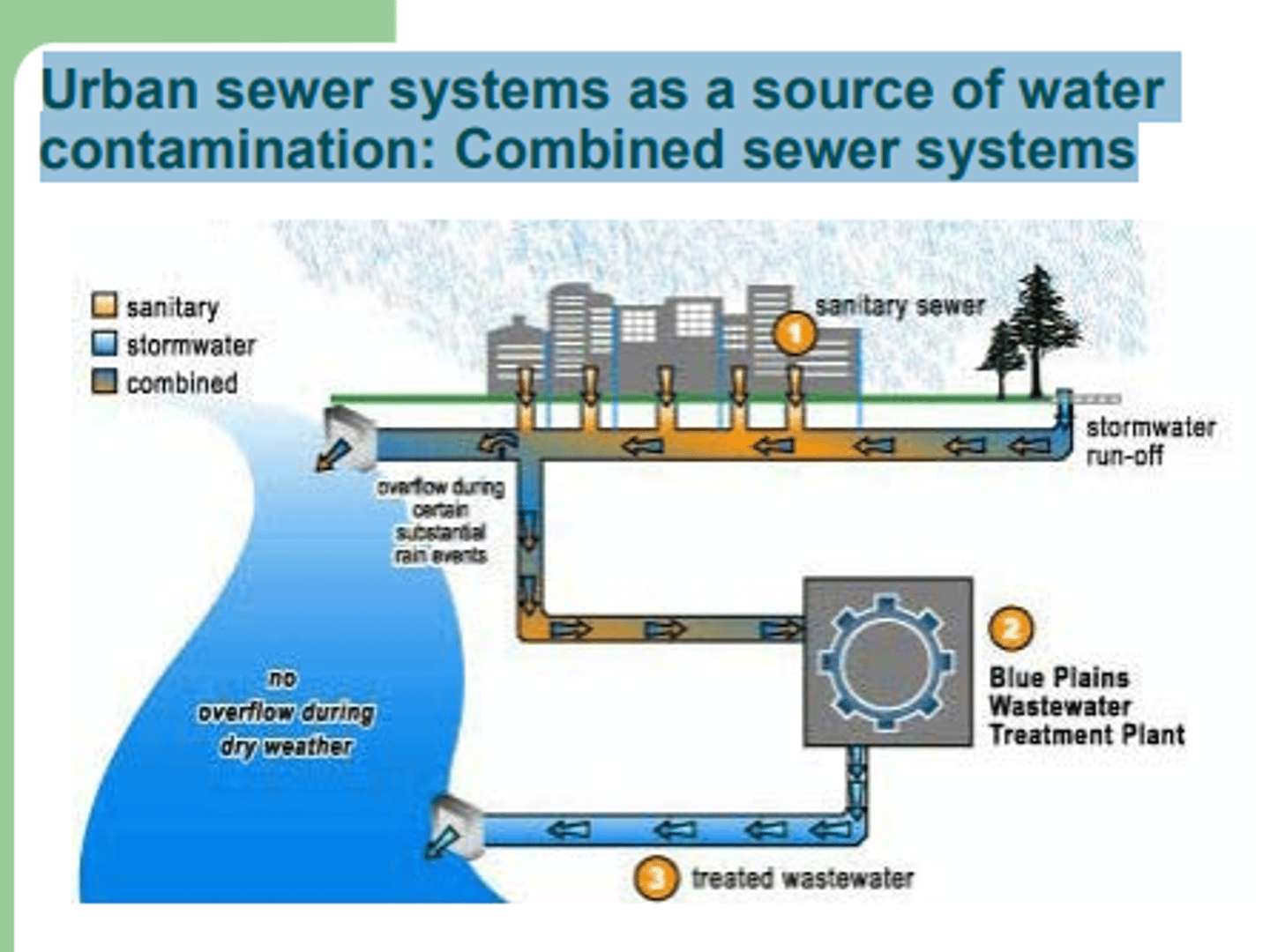
31. List potential sources of water contamination and indicate control strategies that could be adopted to prevent such contamination from occurring.
a. Point sources: well-defined location where pollutants enter the waterway (sewage treatment plants)
b. Non-point sources
i. Agriculture: soil, manure, chemical fertilizer
1. Minimize soil erosion
ii. Construction
1. Not do construction during rainy days
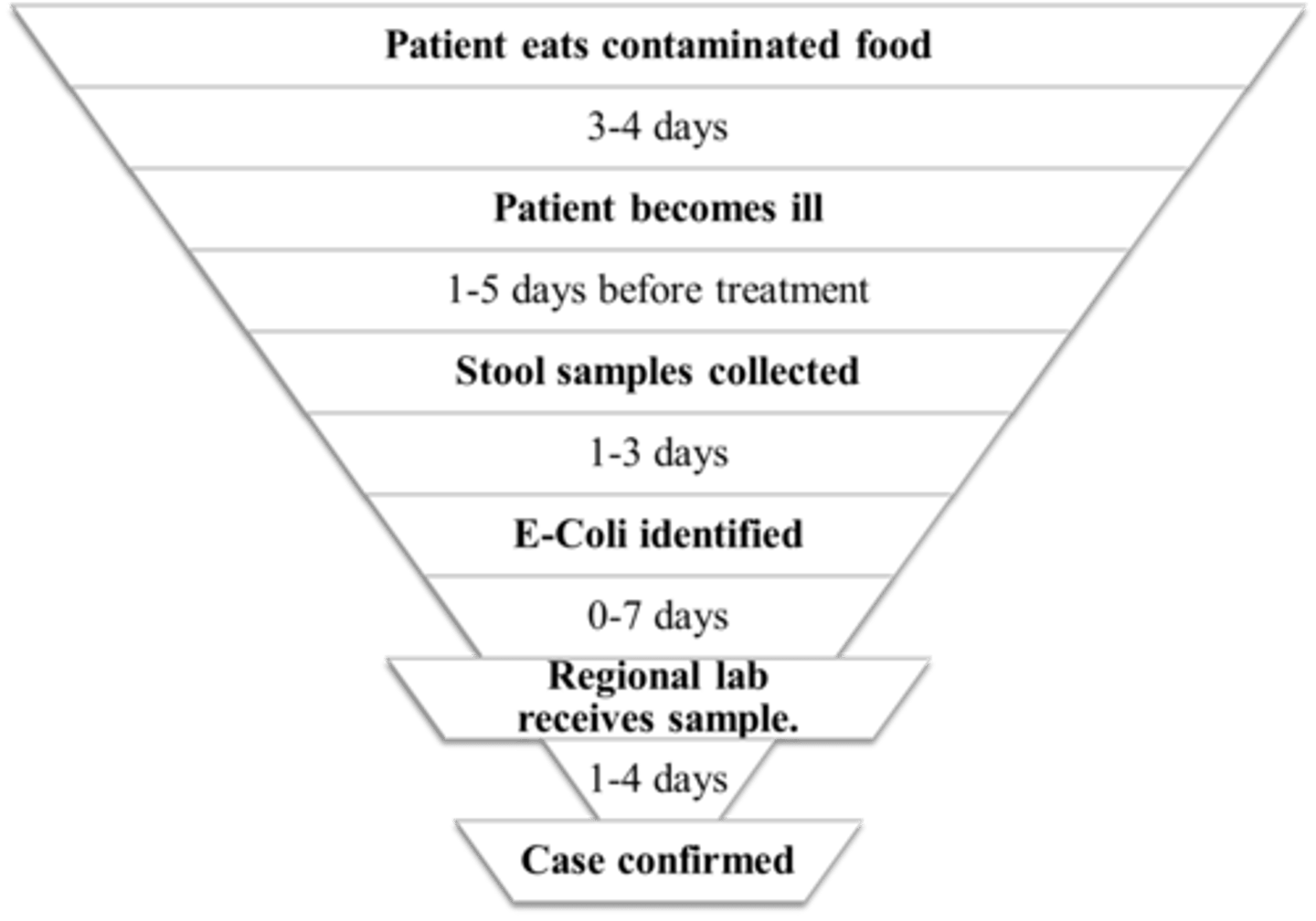
1. How would you determine a food-borne disease outbreak?
a. Two or more cases of a similar illness among individuals who have had a common exposure

2. The food-borne disease is significantly under-reported. Why?
a. Most household infections are not recognized or reported.
i. The person with the illness may not go to a doctor
ii. The doctor may not submit a specimen to a lab
iii. The lab may not test for the appropriate agent
iv. The lab might not report a confirmed case to CDC
b. Same pathogens in water and person to person
c. Emerging pathogens unidentifiable
d. Passive surveillance system
3. What is the major cause of foodborne-disease outbreaks with confirmed etiology?
a. Bacterial
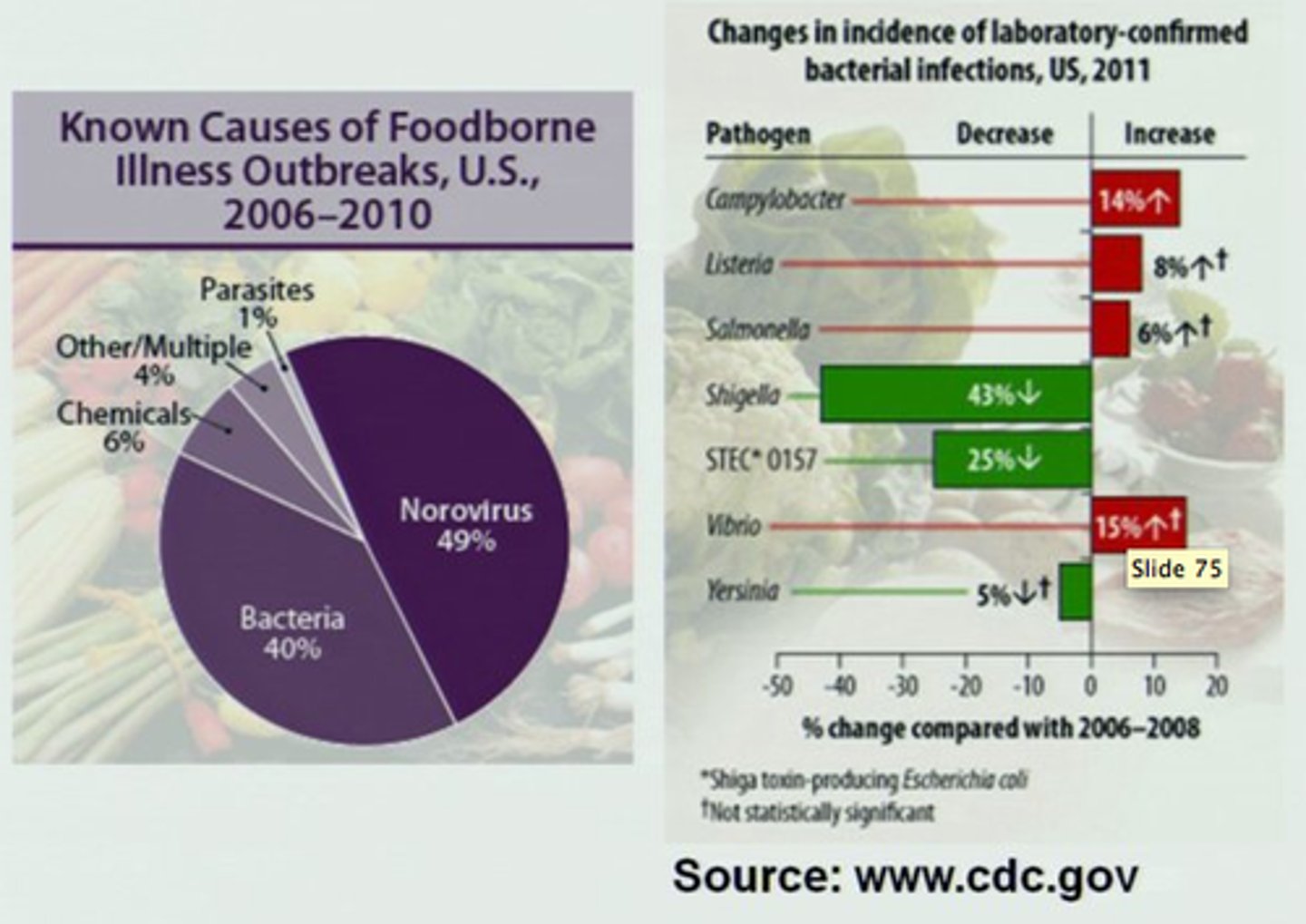
4. What are the major types of microorganisms associated with foodborne-disease outbreaks?
a. Norovirus
b. Salmonella

5. What are the major types of chemicals associated with food borne diseases?
a. Scombroid toxin/histamine
b. Ciguatoxin
c. Mycotoxins

6. What is the farm to table approach in controlling food-borne disease?
a. Implementation of good manufacturing practice and hazardous analysis critical control points.
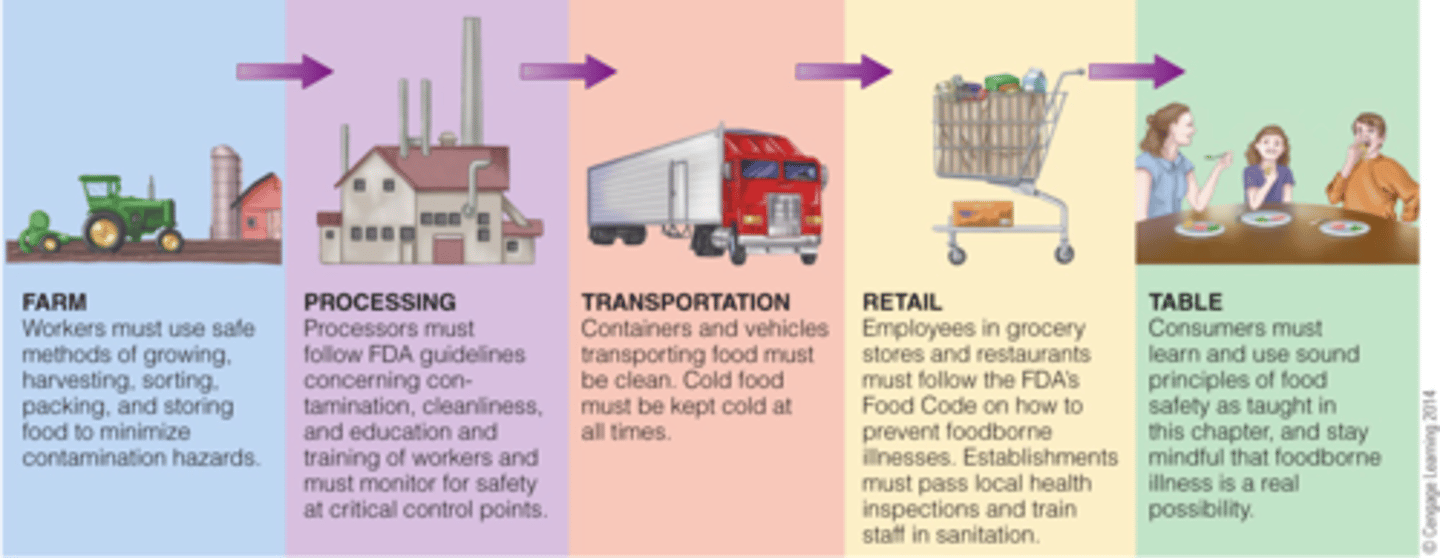
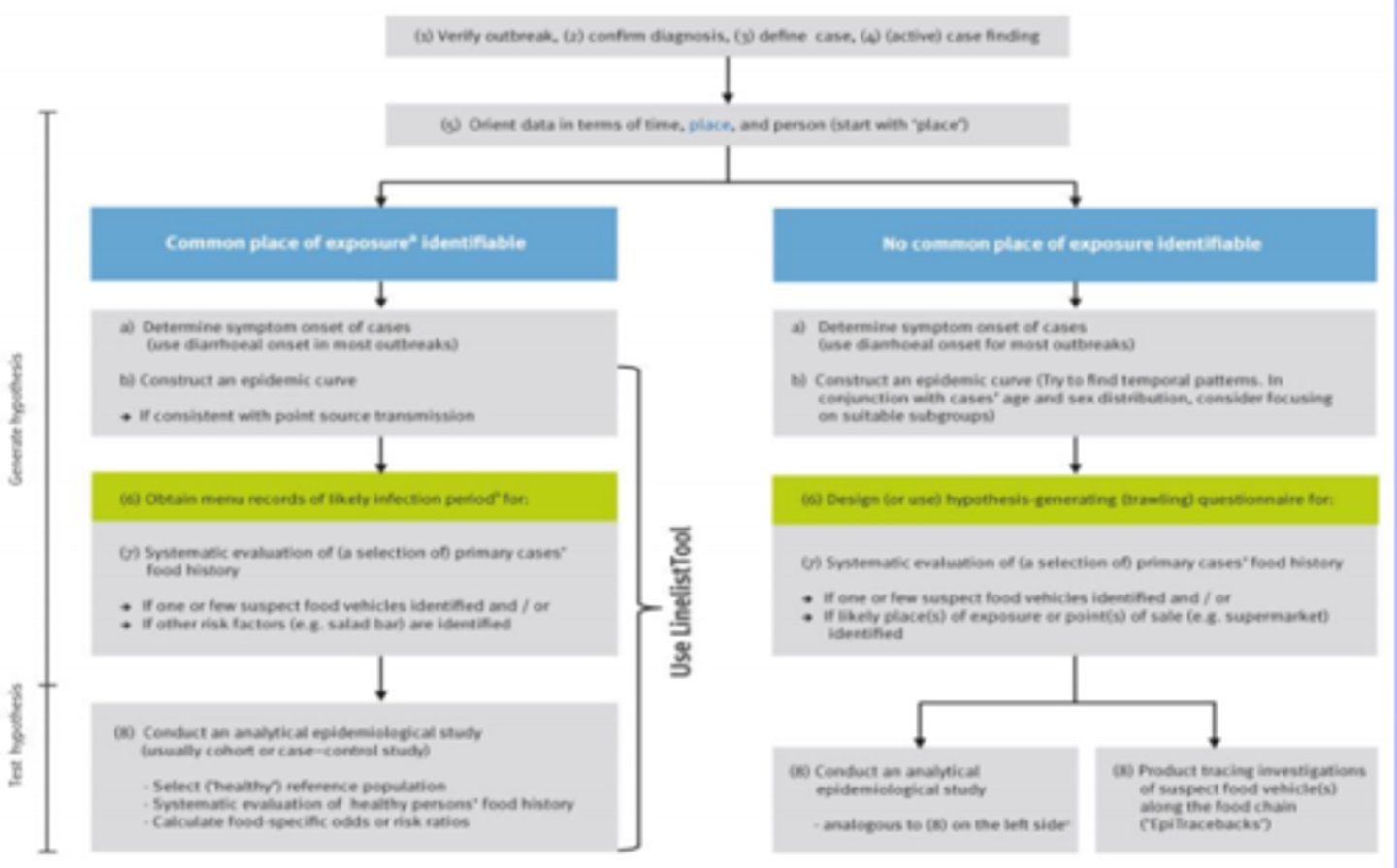
7. What are the major steps in foodborne disease outbreak investigation?
a. ?
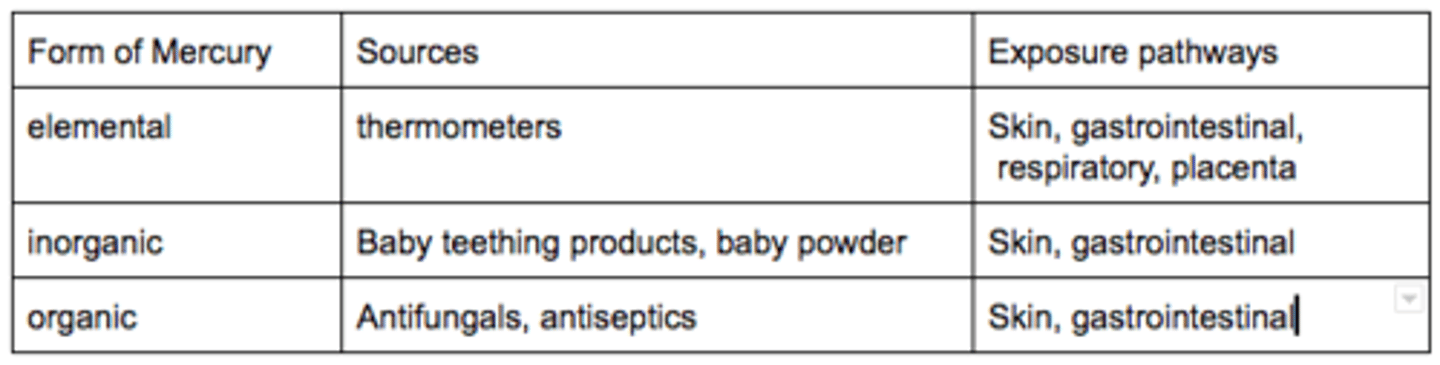
8. What are the three forms of mercury? What are the major sources and major exposure pathways of the three forms of mercury?
a. Elemental mercury
i. Heavy, silver-grey, metal; liquid at room temperature
ii. Conducts electricity & mixes easily with other metals
iii. Elemental mercury exposure pathways
1. Respiratory: easily absorbed into bloodstream & crosses blood-brain barrier
b. Inorganic mercury
i. Mercurous, Hg1+ or mercuric, Hg2+
ii. Oxidized mercury that combine with other chemical elements to create salt forms.
iii. Inorganic mercury exposure pathways
1. Gastrointestinal
2. Skin: poor systemic absorption unless exposed to large amounts
c. Organic mercury
i. Methylmercury (crop)
ii. Ethmercury (antifungal, vaccine preservative)
iii. Phenulmerrcry (preservative in paints and disinfectant
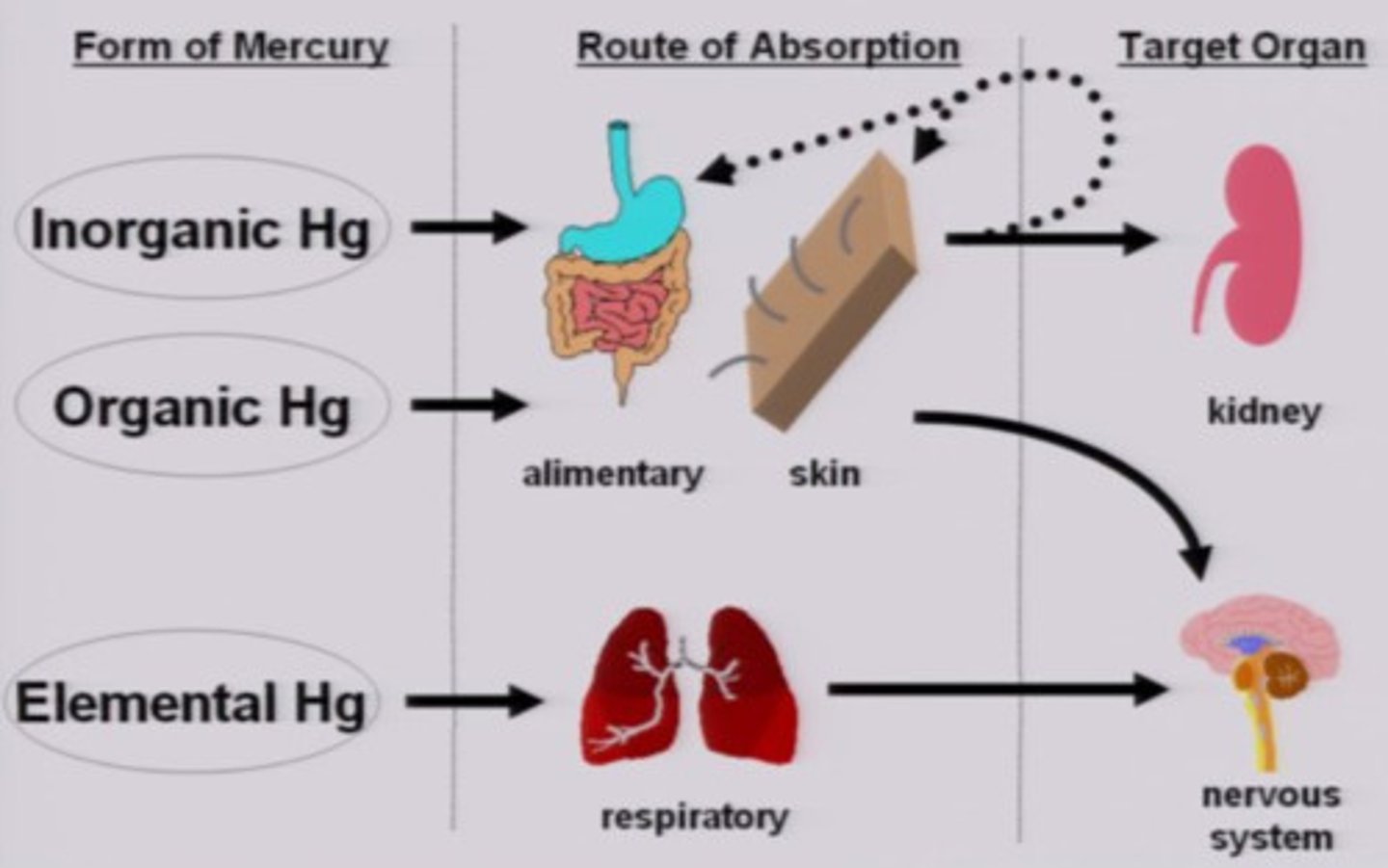
9. What is the cause of the "pink disease"?
a. Exposure to mercury (powder)
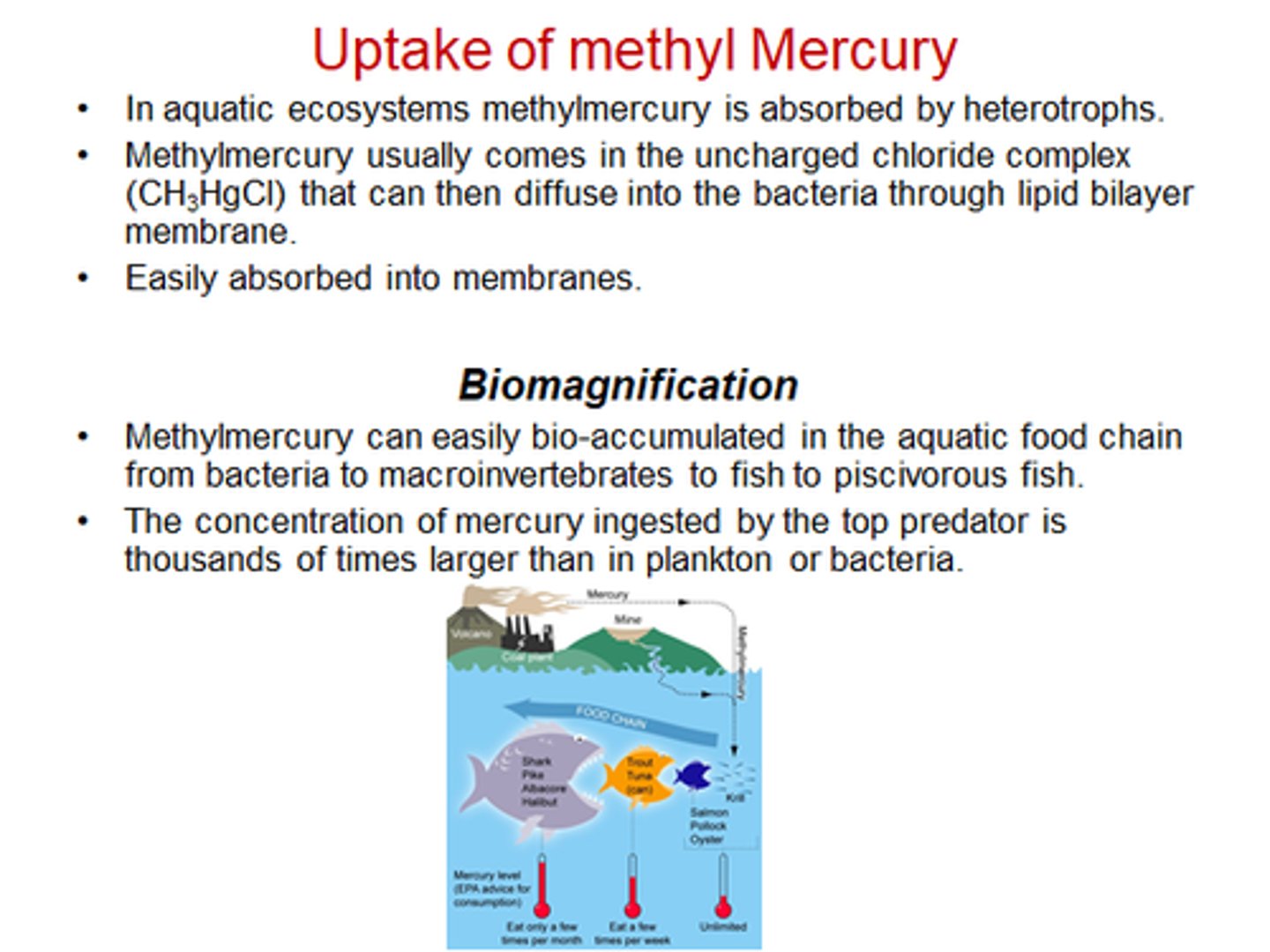
10. How is methyl mercury accumulated in the fish?
a. Methymercury is in water from air -> biotransformated by bacteria -> build up to high levels in predatory fish
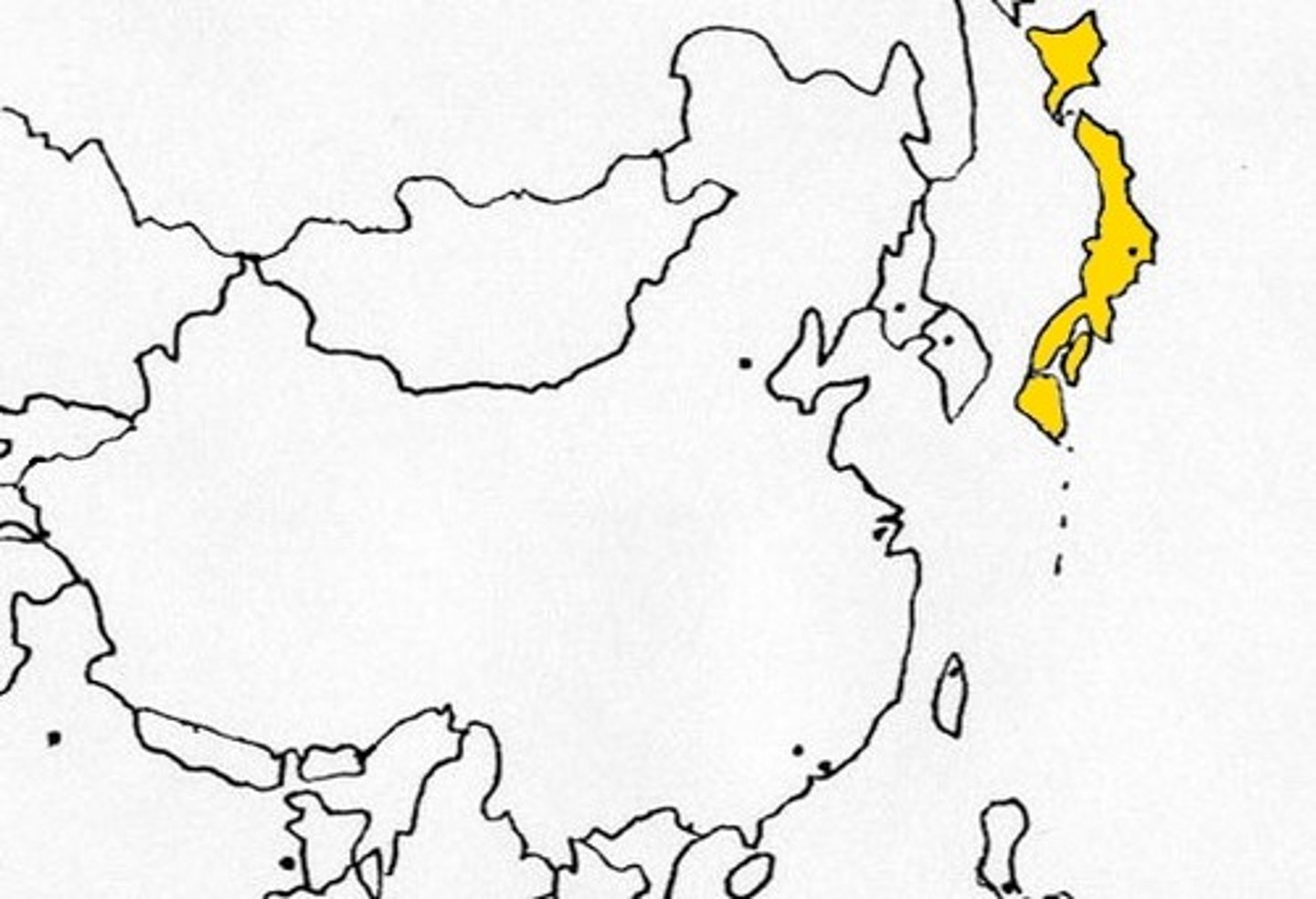
11. Please list the major health effects of methyl mercury. Please describe the two largest mercury poisoning events in 1900s, one in Minamata, Japan and the other in Iraq.
a. Kids: Cerebral palsy, abnormal reflexes, mental retardation, developmental delays
b. Adults: parethesisa, cerevellar, constriction of senses, insomnia, speech disorder, cognitive impairment
c. Japan: seafood from bay was polluted with mercury from industrial source; causes of neurotoxcity from seafood consumption (fetal brain toxicity from cerebral palsy in children
d. Iraq: mercury as antifungal in seed grains; CNS damage
12. Is vaccine (ethyl mercury) associated with autism? Why?
a. No
13. Which type of fish contains the highest level of mercury and which contain the lowest level of mercury?
a. Large predatory marine fish, freashwater fish

14. Please describe the reasons and changes in recommended mercury consumption from seafood by the government over time.
a. As more research came about, consumption of seafood was found to be safe at a certain extent
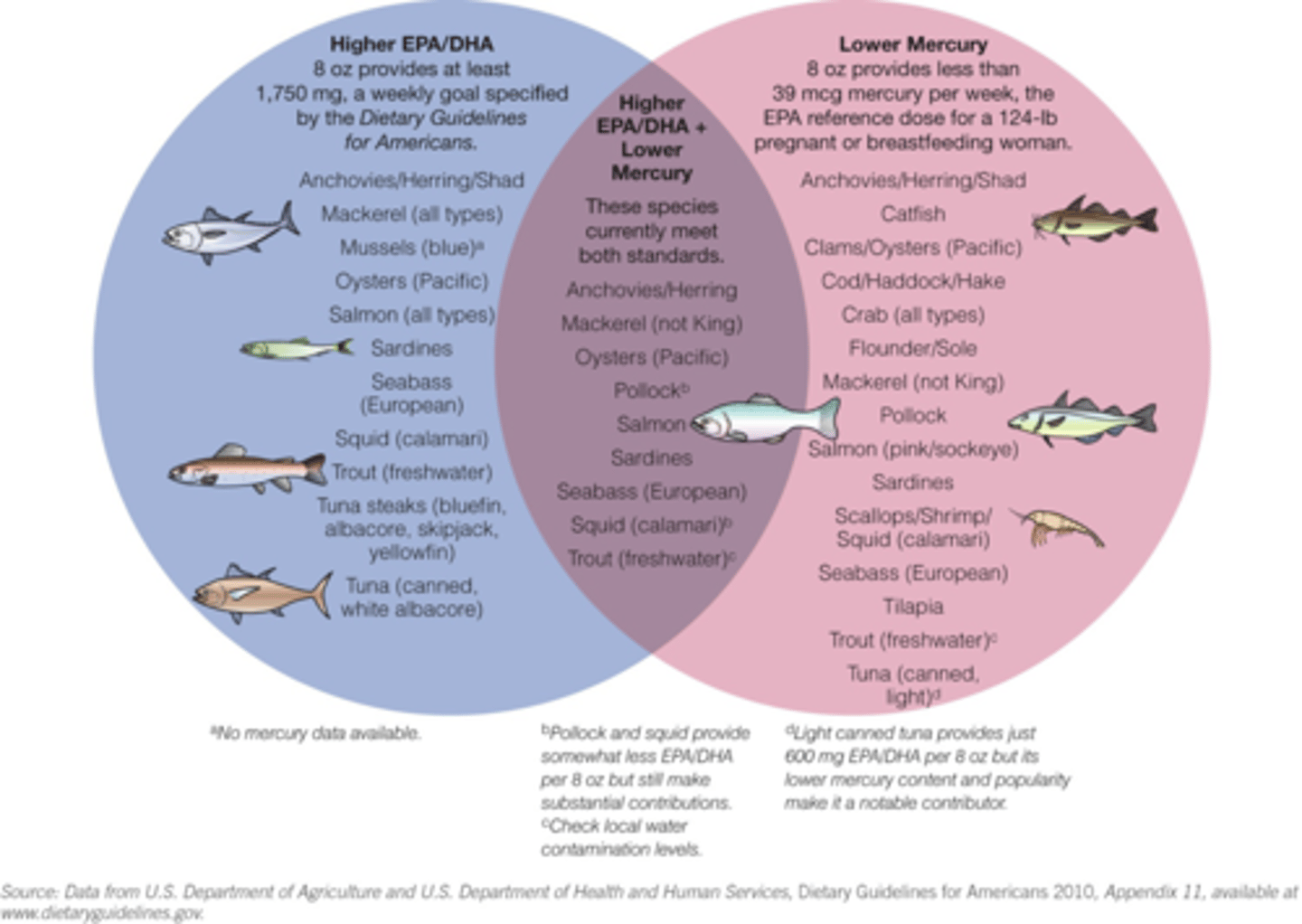
15. What are the main sources of lead exposure historically and at present?
a. Historically: paint in older buildings
b. Present: soil, dust, drinking water, renovation/removal

16. How does lead get into the environment? Which is the most significant source of lead source of lead exposure: water, air, food, or dust/soil?
a. Soil
b. Deterioration of lead containing materials

17. Understand the lead metabolism and movement in the human body.
a. Goes through long bones (95%), brain, liver kidneys (4%), blood (1%)
18. Which population sub-groups on average have higher blood lead concentrations and why?
a. Children (black)
b. Pregnant women
c. Adult male (occupation)
d. Women at post-menopausal peak
19. What are the main health effects of lead?
a. Adverse developmental outcomes on a variety neurological, neurophysiological, cognitive, and behavioral endpoints
i. Neuromotor function
ii. Academic achievement and reading or math skills
iii. Delinquent or antisocial behavior
iv. Attention and executive function
v. Auditory function
vi. Visual function
vii. Likely ADHD (insufficient to infer causality)

20. Why does a few points IQ loss from lead exposure have a significant societal impact?
a. 57% increase in mentally retarded population

21. Is there a threshold of lead toxicity? Why?
a. No; at its lowest, there are bad effects such as low-birth weight, miscarriages, etc.

22. Please describe the environmental justice issues in children's lead exposure and its health impact.
a. Black children who live in the city are more likely to experience lead exposure; any children who lives in older homes or houses that are being renovated are at risk

23. Please describe regulations taken by the U.S. government to reduce lead exposure since 1970s, and the descending "upper limit' of lead poisoning diagnosis.
a. 1971: lead-based paint poisoning prevention act
b. 1978: ban on residential lead paint (blood level with lead high)
c. 1988: lead contamination control act (significantly lower)
d. 199: lead safe housing rule (lower)
e. 2001: lead dust soil hazard standards (lower)
f. Upper limit lead poisoning diagnosis has lowered over time (5 ug/DL)

24. What is noise pollution? What are the major health effects from noise pollution?
a. Unwanted sound
b. Effects: hearing loss (wears out hair cells)

25. How can you determine noise-induce hearing loss from an audiogram? What is the difference of the audiogram for hearing loss due to excessive exposure to noise and from normal aging?
a. 500 Hz = normal speech
b. Higher dB = hearing capability not good
c. Normal aging: gradual loss vs. steep loss for those with NHL
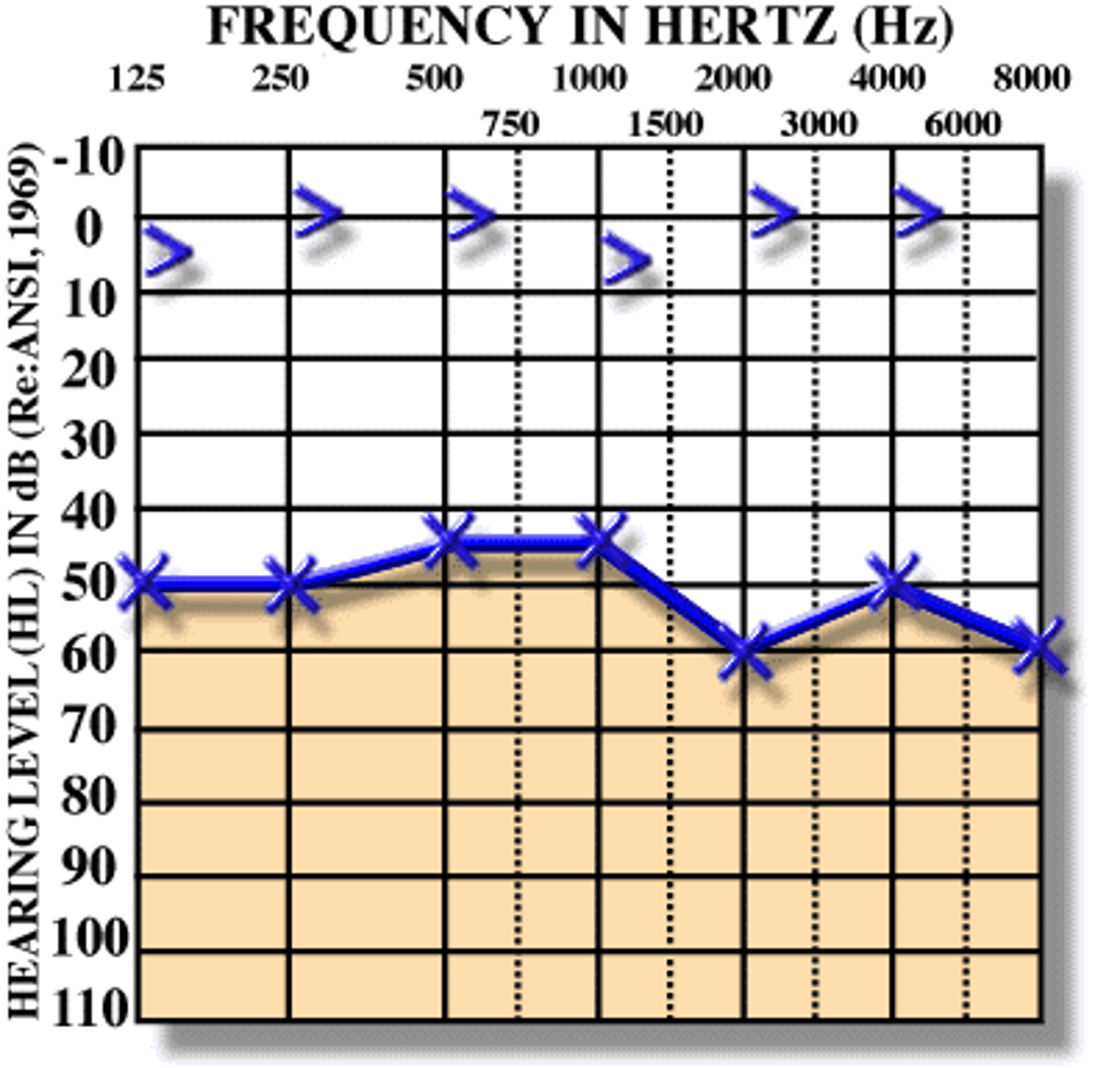
26. What are the key variables affecting noise levels?
a. Distance: further = less noise
b. Topography: elevation that is higher = not as nosiy
c. Atmosphere effect: sound wave affected by atmosphere; higher temp and lower humility = atmosphere absorb more sound energy = hearing less noise; stable atmosphere = hear more sound
27. Understand the federal regulations on noise exposure and the differences of three exposure metrics of noise (Leq, Ldn, CNEL).
a. Equivalent sound levels - Leq: intermittent sounds/sudden sounds; constant noise measure over periods of time
b. Day-night average sound level Ldn: nighttime noise is more annoying; accounted effect by adding 10 dBA between 10pm-7am
c. Community noise equivalent level - CNEL: similar to above, but a 5 penalty dBA for evening time and the nighttime live above
d. Federal Noise Control Act of 1972: all federal agencies must administer programs to promote an environment free of noise that jeopardizes public health/welfare
e. EPA
i. Outdoor Ldn limits of 55 dB
ii. Indoor Ldn limits of 45 dB as desirable for residential, educational, and healthcare areas
iii. 24-hour Leq of 70 dB in commercial and industrial areas (both outdoors and indoors)

28. What are the personal protection equipment and procedures to protect people from excessive noise exposure? Under what circumstances you should adopt noise protection? How should you do to protect yourself from noise exposure?
a. Control at source, control noise path, protect the receiver (ear plugs)
b. When to control:
i. Steady state noise measured at 85 dBA or greater
ii. Impulse noise measured at 140 dBA or greater
iii. Rule Of Thumb: If you have to raise your voice to be heard by someone less than 3 feet away, then you need hearing protection.
29. What is light pollution and what are the major types of light pollution?
a. presence of anthropogenic and artificial light in the night environment
b. 3 types: glare, light trespass, skyglow

30. Will light reduce crime rate? Why?
a. No, can't reduce crime itself (mixed) because light made viewing more visual for the crimer... no consensus; reduce fear of crime/makes you feel safe

31. Why is light pollution a public health concern? What are the effect of light pollution on our environment and human health?
a. Mixed increase crime findings
b. Neighborhood tension
c. Not safe if it reduces visual perception due to glare, over lighting, and length recovery time
d. Environmental:
i. 30% light wasted
ii. 66% electrical power produced by fossil fuel
iii. Ecological effects on animals (change patterns in growth of pets) and plants (vulnerable to air pollution)
e. Human
i. Air pollution related problems
ii. Sleep disruption
1. Disrupts circadian rhythms which are essential for good health
iii. Melatonin suppression (from NOT having no light)
1. Lack of melatonin production promotes growth breast tumors in women and may similarly effect other cancers, including prostate cancer.
2. Suspected in rise in childhood leukemia.

32. How to reduce the light pollution problem?
a. Education and better policies
b. Use right color of light: blue light should be minimized
c. Dim the light
d. Shield the light where it shines it only needed space

33. What is built environment?
a. Human made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity

34. How can built environment affect obesity and other health outcomes?
a. Affect physical activity level, access to healthy foods, natural environments
35. What built environment factors affect physical activity levels and how to promote physical activity by improving built environment factors?
a. Not built: Technology reduced physical activity in jobs, daily living, schools; Sedentary lifestyle associated with obesity, etc.
b. Walkable, mixed-use communities, short distance to park, using public transit increases physical activity levels
c. Improve conditions and access

36. What are food desert and its adverse influence on health?
a. parts of the country vapid of fresh fruit, vegetables, and other healthful whole foods, usually found in impoverished areas
b. AKA limited access to affordable and nutritious food
c. Effects: poor diet, higher levels of obesity and other diet-related diseases (ex. diabetes)

37. Understand the argument of the paper "The Geography of Poverty and Nutrition: Food Deserts and Food Choices Across the United States" on food deserts vs. food choices and the implications in promoting healthy food consumption.
a. High price (same as high-income) does not explain difference in health index
b. Store nutrients (same as high-income) explain 10% of the difference
c. Nutrient preference (same as high-income) explains a lot
d. Product group preference (same as high-income) explains a lot
e. Years in education and nutrition knowledge explains demand in heathier food

38. What are the beneficial health effects of the natural environment?
a. Restorative effect on cognition
b. Decrease stress
c. Green space = social interactions, increase social cohesion
d. Physical activity
e. Buffer exposure to air polluants
f. Reduce noise and alleviate thermal discomfort from heat
g. Increased physical activity
h. Lower obesity
i. Improved mental health
j. Reduced aggressive behavior in adolescents
k. Higher birth weights
l. Lower cardiovascular disease risk
m. Lower overall mortality

39. What is the current condition of the parks in Los Angeles?
a. Park poor
i. One park for every 10,000 kids in LA County
ii. 2 in 3 kids do not live within walking distance (1/4 mile) of a park
b. Park disparity: fewer parks in the most environmentally burdened communities.
c. Over 35% of parks in LA County are within 500 m of a freeway

40. What does the case study on green space and pregnancy outcomes show?
a. More green space = less LBW

What are the major criteria air pollutants regulated by the U.S. EPA in the Clean Air Act?
CO, NOx, particulate matter, O3, Pb, and SO2

Ozone occurs in the troposphere because:
NOx and hydrocarbons react in sunlight

Which of the following is true about the Earth Day?
It marked the beginning of the modern environmental movement.

Larger particle is more toxic because they can carry more air toxics than ultrafine particle
false
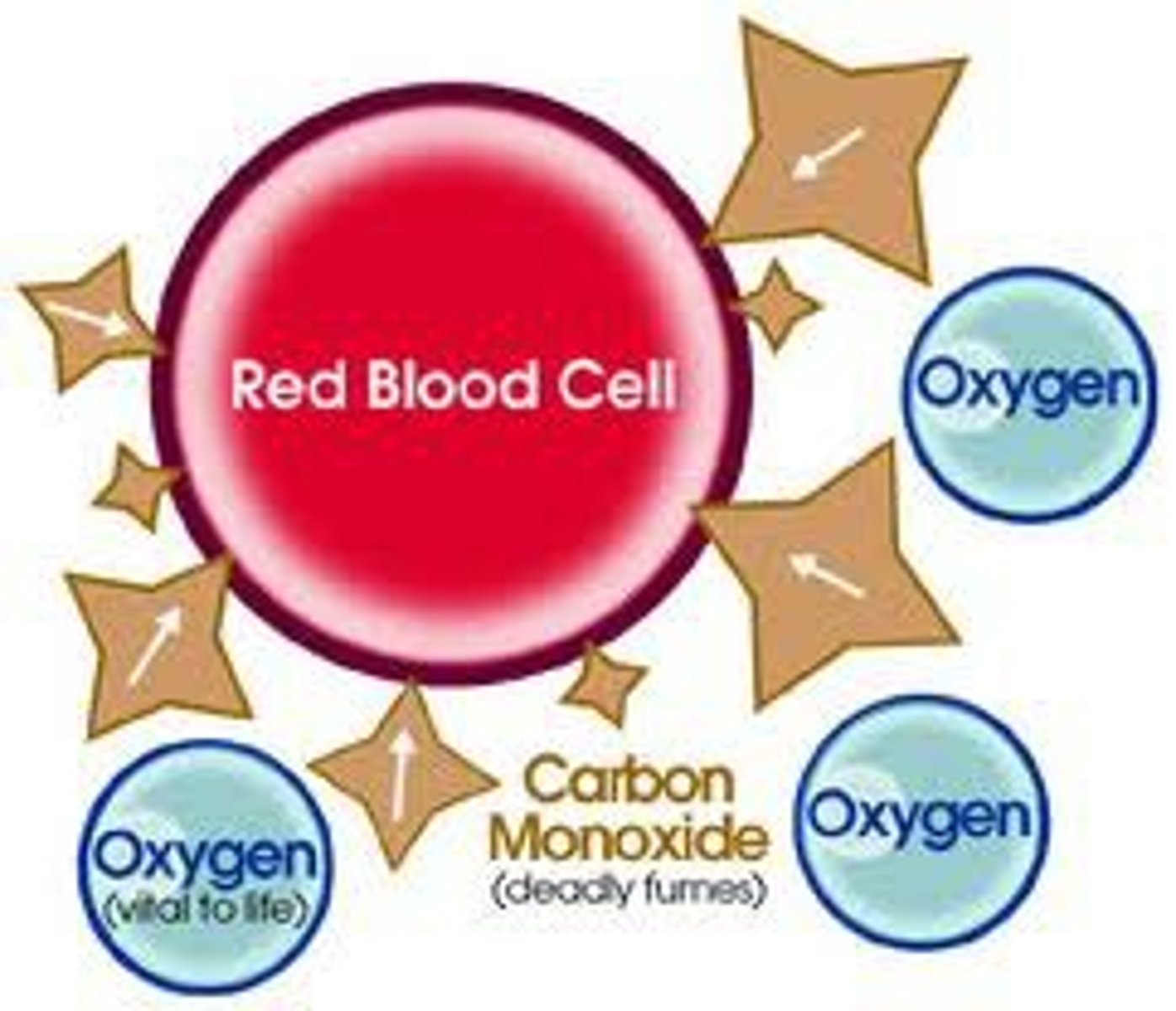
Carbon monoxide is a human health concern because it:
replaces oxygen in the hemoglobin of the blood
Globally the burden of mortality due to air pollution is still high because
Air pollution affects many vulnerable people, e.g. children and elderly

New particle-board furniture contains a major indoor air pollutant called:
formaldehyde

The most important pathway of radon exposure is through:
air
The best way to control for the growth of biological agents indoors is
controlling for humidity and temperature

Which of the following is true about asbestos?
Its exposure can cause asbestosis and lung cancer
Pesticide exposure is a concern only among agriculture workers
rather than residential exposure.
false

PBDE, used as fire retardant in indoor future, is harmful for health
mainly because it is a strong carcinogen.
false

Which of the following is usually the most effective method in improving indoor air quality?
increase air ventilation

Which of the following is NOT true about minimizing COVID-19
infection risk indoors where there are potentially people who carry the
virus?
Use ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the most cost-effective in reducing the
potential risk in any indoor environment
Clean Water Act is the main federal law that ensures the quality of
Americans' drinking water.
false; clean water act = wastewater; safe drinking water act = drinking water
