Biology A2.3 - viruses (HL)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
outbreak
unexpected increase in number of people with a specific condition
epidemic
spreads over a large geographical area
pandemic
spreads globally and has exponential growth
phage
infect
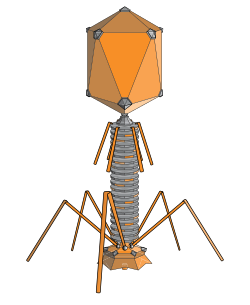
parts of a bacteriophage
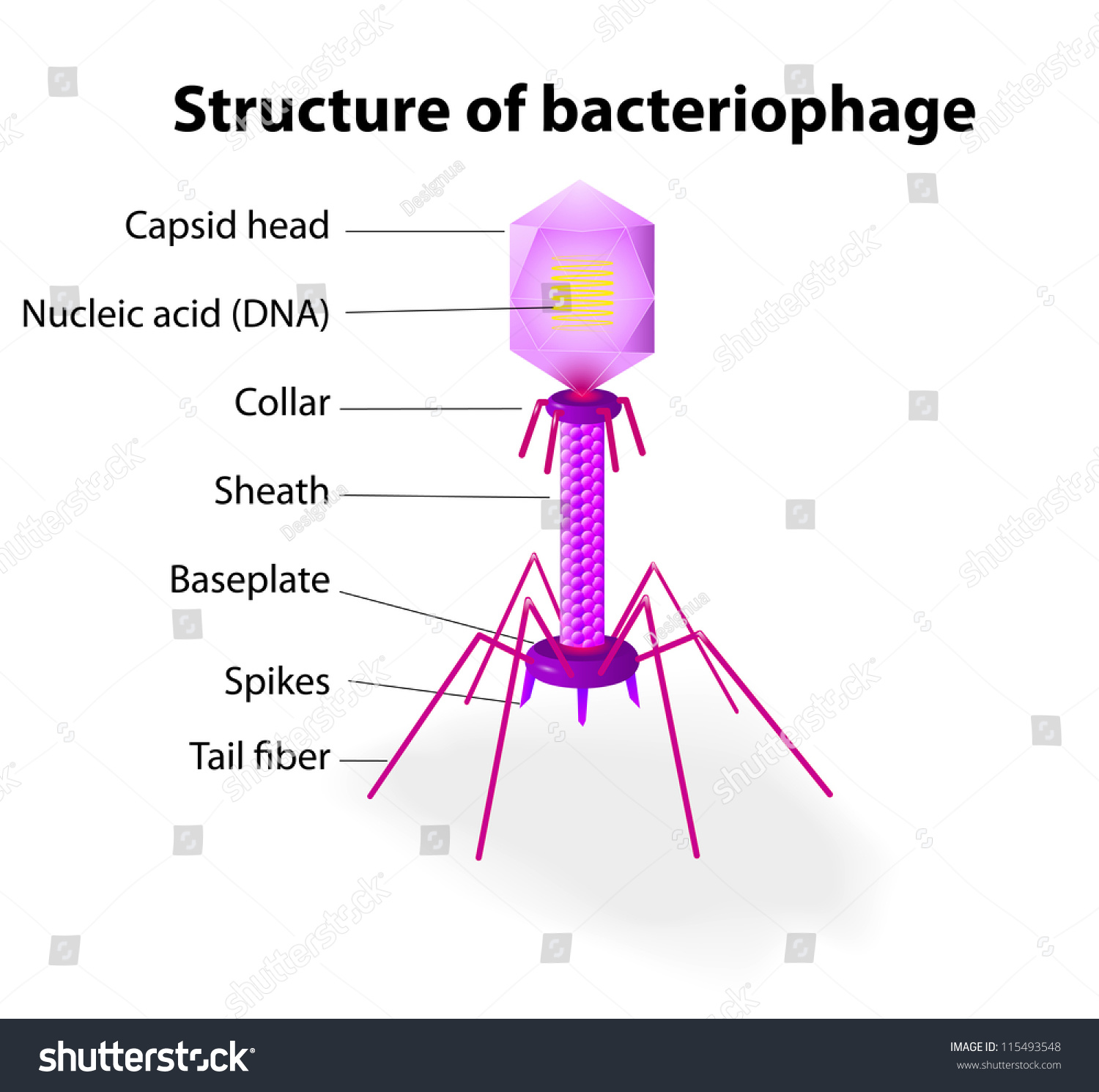
describe bacteriophage
small fixed shape
contain a nucleic acid and either DNA or RNA as genetic material
enclosed in a boundary - capsid
no cytoplasm in the capsid
some possess some enzymes
if they possess sing or double stranded, they possess very few genes
most contain less than 100 genes in their caspid
describe capsid
made up of proteins
protein shell
surrounded by DNA or RNA and protects it
helps with the attachment to host cells
delivers genetic material into the host cell
protects genetic material
all viruses have a capsid
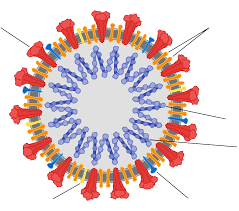
describe coronavirus
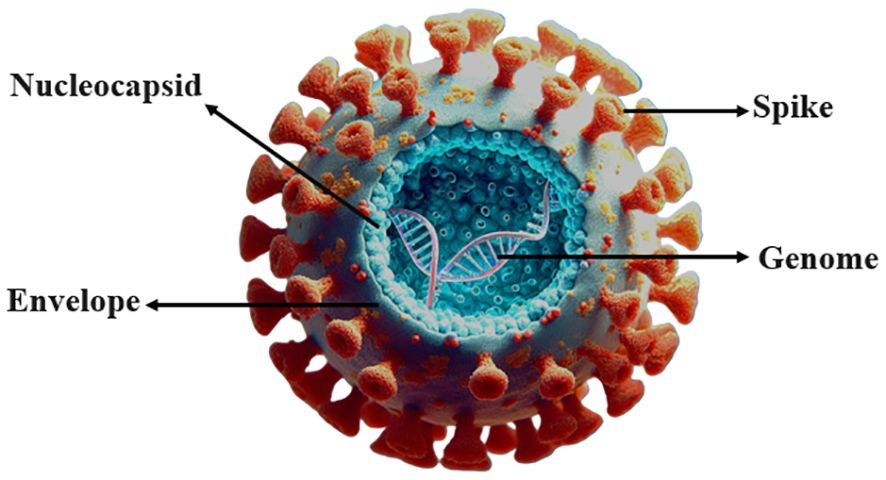
membrane envelope
outer layer surrounding some viruses
made of phospholipid bilayer
helps the virus enter host cell receptors
enables entry into the hosts cell
protects the capsid
not all viruses have this
non enveloped virus
no membrane envelope
made of DNA or RNA and a capsid
enters the host cell via endocytosis or injection
adenovirus
enveloped virus
has a membrane envelope surrounding the capsid
membrane envelope is the outer layer of the cell
enters the host cell via endocytosis or membrane function
lentivirus
bacteriophage lambda
affects the bacteria
attaches to specific regions on the bacterium
bacterium lambda key features
infects E coli
double stranded DNA genome
switch between 2 life cycles (lytic and lysogenic)
uses different sites to infect the host at different locations
regular genes that control which pathway it chooses
important model organism in biology
key features in a corona virus
spherical shape
single stranded RNA as its genetic material
envelope outside capsid
projections of spike proteins at the envelope
examples of past pandemics
black death
flu pandemic
spanish flu
asian flu
AIDS
what all viruses must do to reproduce
attach to a site on a specific host cell
incorporate their genetic material into the cytoplasm of the host cell
use the host cell’s proccesses to produce components of themselves
assemble the viral components into new functioning virus particles
release the new virus entities into the host cell’s environment
why cant viruses produce their own energy
they do not have a mitochondria and only rarely have enzymes
lytic cycle
attachment- phage attaches to the surface of the host'
penetration- DNA enters the host cell
biosynthesis - phage DNA replicates and phage proteins are made
maturation - new phage particles are assembled
lysis - the cell lyses which releases the newly made phages
lysogenic cycle
the phage infects the cell
the DNA becomes incorporated into the hosts genome
the cell divides and the prophage DNA is passed onto daughter cells
DNA is made from bacterial chromosomes and enters the lytic cycle
DNA replicates and phage proteins are made
new phage particles are assembled
the cell splits which releases newly made phages
difference between the two cycles
lysogenic cycle:
host cell remains alive
virus remains dormant
DNA integrated into the host’s DNA
no viruses produced until activated
cell does not split
lytic cycle:
host cell is destroyed
virus immediately takes over
replicated immediately
viruses produced quickly
cell splits
evidence on the origin of the first viruses
first virus hypothesis: originated before cells
regressive hypothesis: viruses were once small cells that became parasites of larger cells
escape hypothesis: parts of genetic material escaped from larger organisms and became surrounded by an outer boundary
convergent evoloution
when different species develop similar features because they live in similar environments. this helps them survive and do the same job, but they evolved independently
features that suggest evidence of convergent evoloution in viruses
are obligate parasites, none can replicate or carry out the functions of life inidividually
have a protein outer boundary - the capsid with no cytoplasm
have genetic material inside the capsid and the code is shared between viruses
rapid evoloution examples
influenza
HIV
antigenic drift
small and slow
small gradual changes in a virus antigens
caused by random mutations during replication
happens continuously over time
common in influenza viruses
results in slightly different strains which is why flu vaccines need updating
antigenic shift
big and sudden
sudden major change in a virus’s antigens
caused by mixing of genetic material between different virus strains
happens quickly
may lead to pandemics because people have little or no immunity
can create a new virus strain