Meat Science Exam 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Tissues are made up of ..?
Collagen
What color is collagen ?
White
Collagen will liquify at what temp?
160 degrees F
What conditions will collagen break down in?
Moist conditions
What is the 3 types of Connective tissue?
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
What do the Epimysium surrounds?
Muscle
What do the Perimysium surrounds?
Muscle bundle
What does the endomysium surrounds?
Muscle fibers
What color is elastin?
Yellow
Do elastin break down?
No
What are the 3 types of Fat?
saturated
Monounsaturated
Polyunsaturated
-Single bonds
-(harder)
-Higher melting point (more heat)
Saturated Fat
-2 double bonds
-softer ( lower melting point)
Monounsaturated
-Multiple double bonds
- softer (low melting point)
Polyunsaturated
Because of double bonds, the meat tends to..?
Oxidize quicker
What meat is most common with double bonds?
Pork
Red muscle fibers have __ Myoglobin?
High
Red muscle fibers have __ Contraction speed
Slow
Red muscle fibers have __ Metabolism Lipid Content.
High
White muscle fibers have __ Myoglobin.
Low
White muscle fibers have __ Contraction Speed
Fast
White muscle fibers have __ Glycolytic
High
White muscle fibers have __ Metabolism Lipid Content
Low
Red muscle fiber are usually in what part of cuts?
Thighs/ drums
White muscle fiber are usually in what part of cuts?
Breast
What are the 2 proteins of the Myofibril?
Actin
Myosin
Actin is __ percent of overall protein
20%
Myosin is __ percent of overall protein
45%
Sarcomeres are used for?
Muscle relaxation & contraction
ZIP stands for..?
Z- Zinc
I- Iron
P- Protein
What are the 3 types of muscle?
1- Skeletal
2- Cardiac
3- Smooth
What type of muscle is
- multi-nucleated
-striated
-voluntary- tells it what to do
skeletal
What type of muscle have 1-2 nuclei?
Cardiac
What type of muscle has
-single nuclei
-very pliable
-stretch/ expand
Smooth
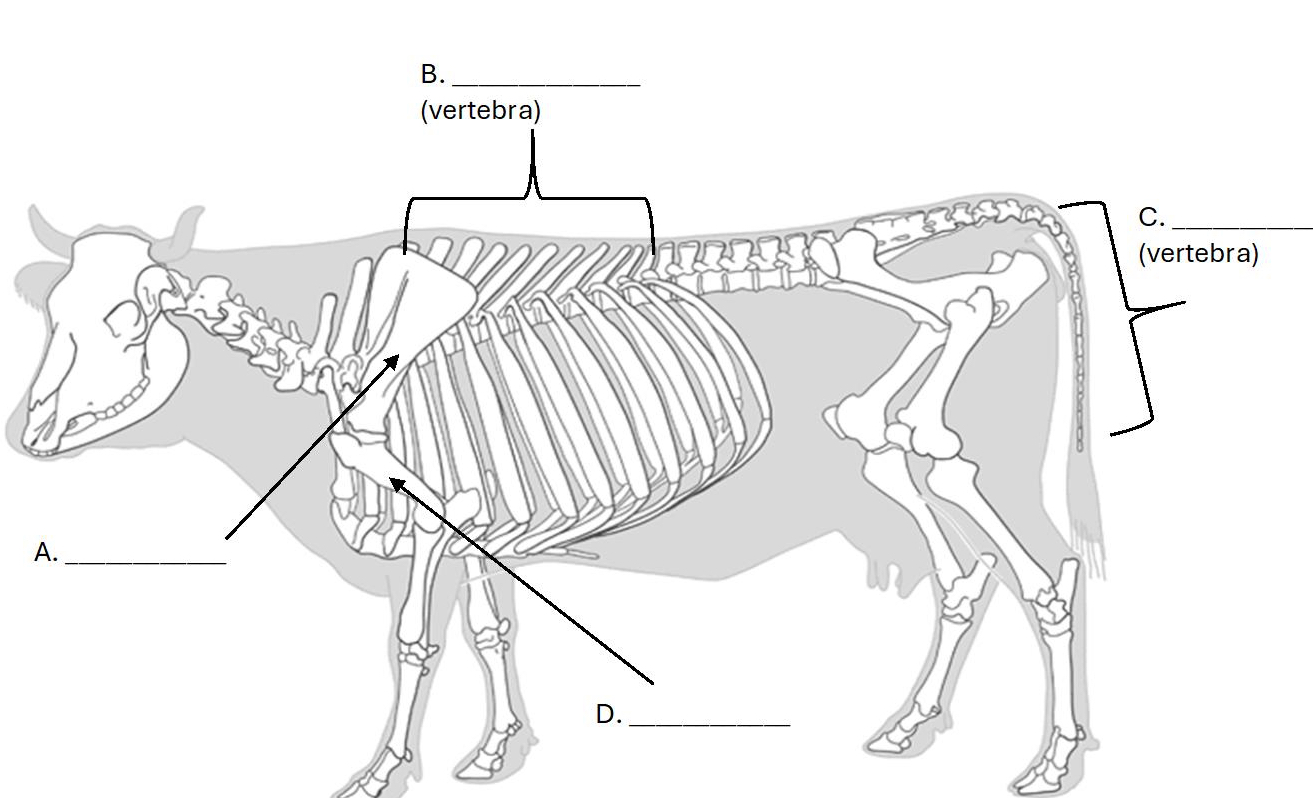
What bone is A. ?
Scapula
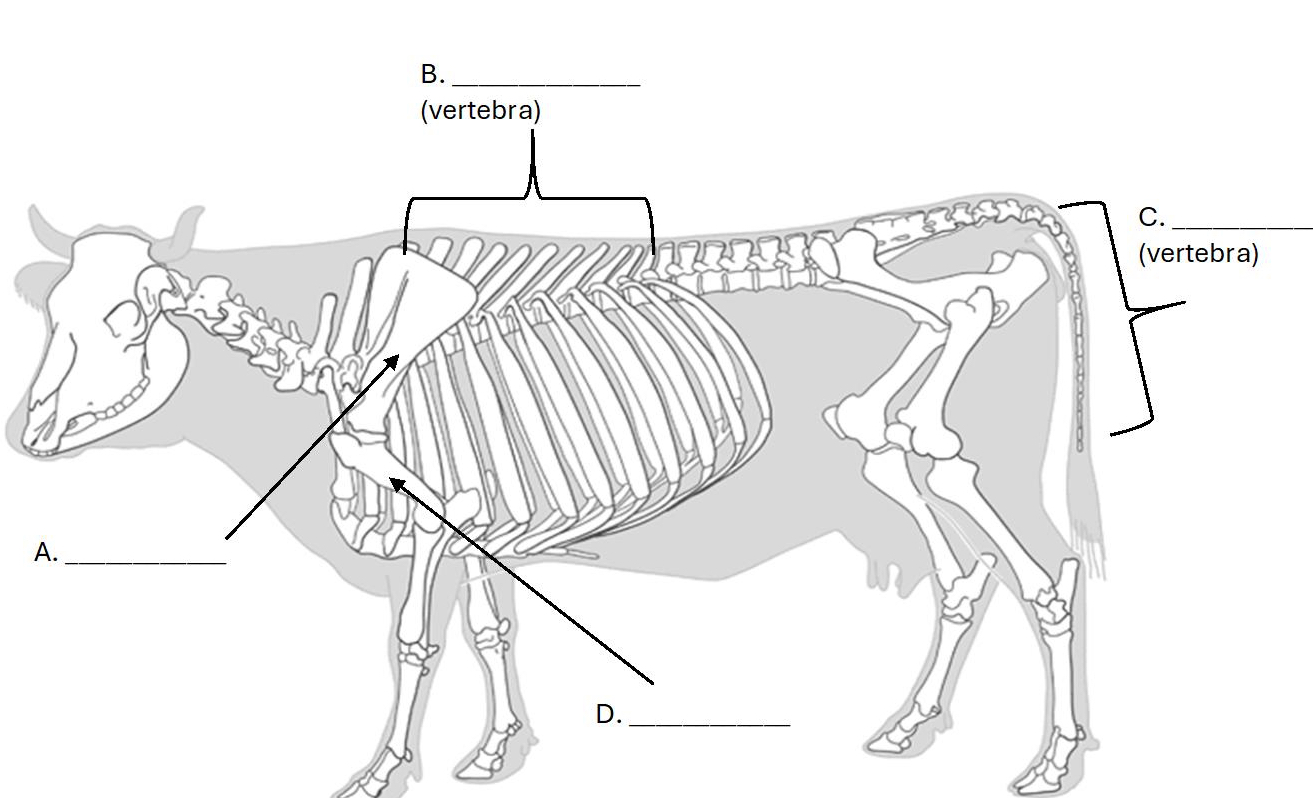
What bone is B.?
Thoracic
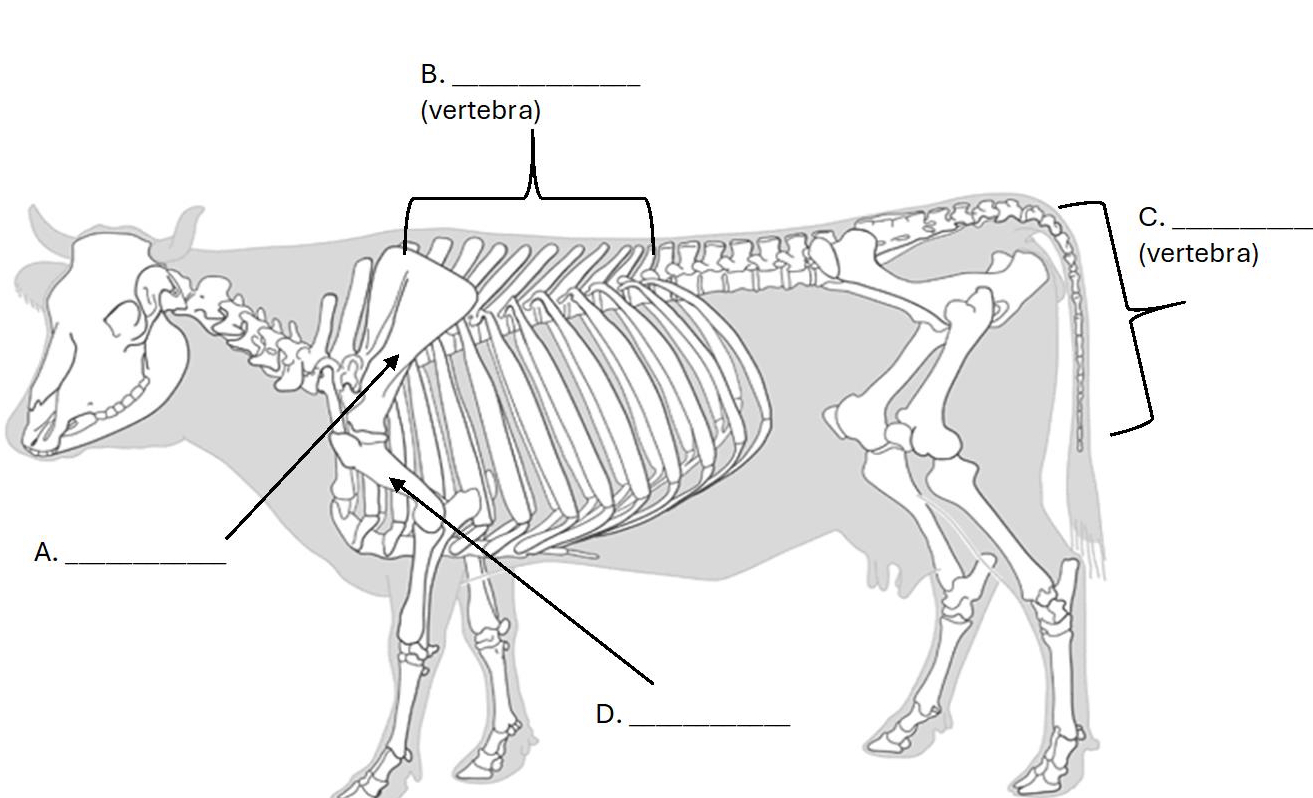
what bone is C. ?
Caudal
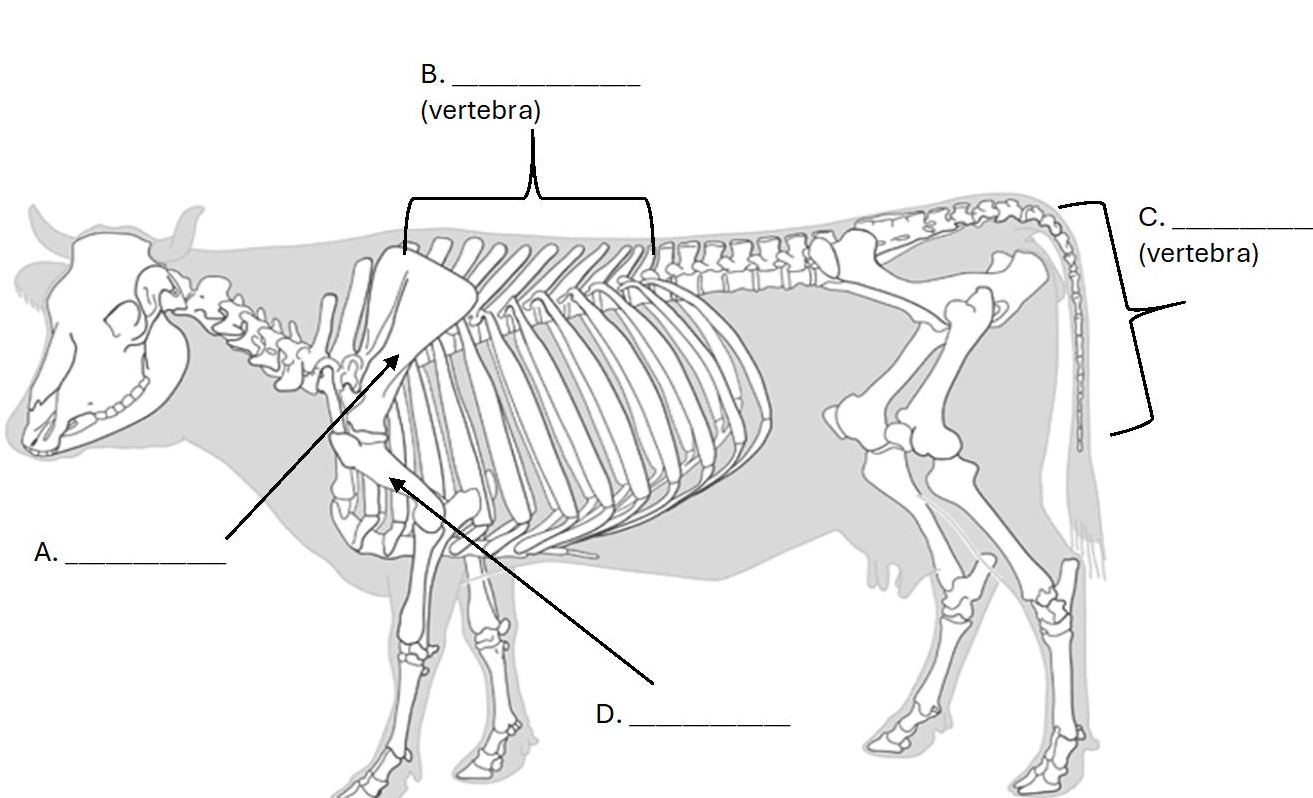
What bone is D. ?
Humerus
What type of muscle is 1?
Biceps
What type of muscle is 2?
Longissimus Dorsi
What type of muscle is 3?
Supra Spinatus
What type of bone is 4?
Scapula
What cross- breed goats are most common?
Boer X Spanish
Qualities of the Kiko goat
grow fast
Strong parasite resistance
Qualities of the Spanish goat
smaller frame
Good mothering skills
Highly adaptable
Qualities of the Boar Goat
South African
Heavily muscled
What is development?
Changes in form resulting in different growth of muscle, fat, & bone
What is growth?
Increase of mass over time
What are the 4 types of deposits of fat?
Mesenteric- internal fat
Inter muscular- seam fat ( between)
Subcutaneous- external fat
Intramuscular- marbling
Poor nutrition consequences
Stunted growth
Malformed
Disease/ parasites
Reproductive performance
Parasites take __ away from the animal
Nutrients
The effects parasites have on the animal
Decreased appetite
Bad digestive functions
Stunted cellular growth
Physically sick
Death
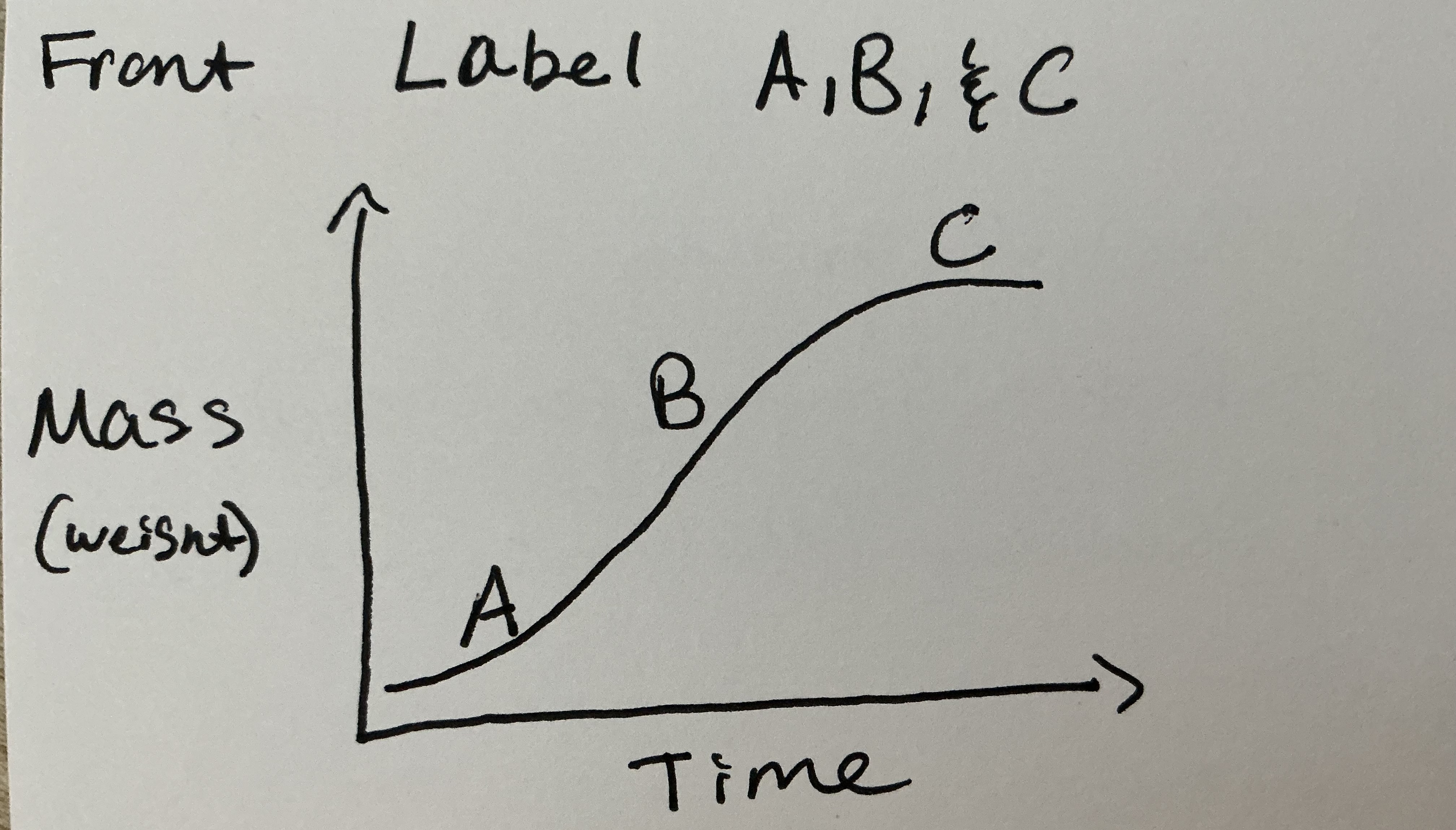
Label A, B, & C
A- small growth
B- rapid growth (teen years)
C- slow down ( Mature size/ ages)
Anterior
Head
Posterior
Tail
Functions of Skeletal System
Support
Protect- internal organ
Mineral reserve
What is bone made of?
water
Mineral
Fats
Protein
What percent of water is in the bone?
50%
What percent of mineral is in the bone?
26%
What percent of Fats is in the bone?
4
What percent of Protein is in the bone?
20%
Bone Types
Femur/ Humerus- long bone
Ribs- Flat
Vertebra- irregular
Parts of the Axial skeleton
skull
Sternum
Ribs
pats of the Vertebra/ Colum
cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccygeal
Parts of the Appendicular Skeleton- Thoracic/ Forelimb
Shoulder
Humerus
Radius
Parts of the Appendicular Skeleton- Hind limb
pelvic girdle
Femur
Tibia
What is the definition of hypertrophy?
Enlargement of existing cells
What is the hormone estrogen responsible for during animal growth?
Deposition of fat
Based on the nutritional makeup of muscle, which component is found as the highest percentage?
water 75-80%
Define an indicator.
Point to or show
True or False. Goats are a great complement to cattle because they do not compete for the same forages?
True
What breed of goat is highly adaptable with good maternal instincts
Spanish
Which contractile protein burns ATP to utilize that energy during contraction and relaxation?
Myosin
What ion is critical for muscle contraction and attaches to troponin?
calcium
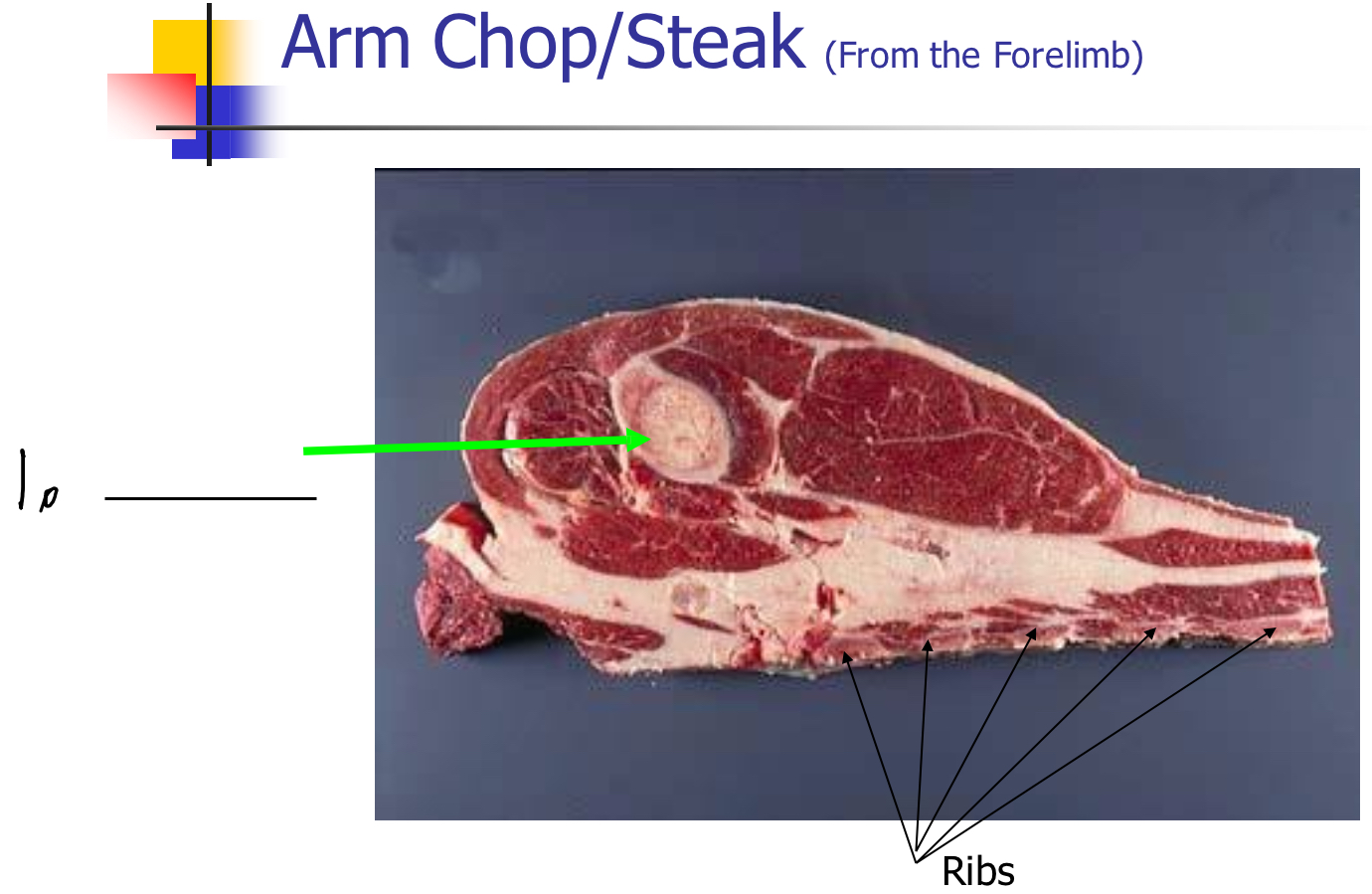
Label 1-
Humerus
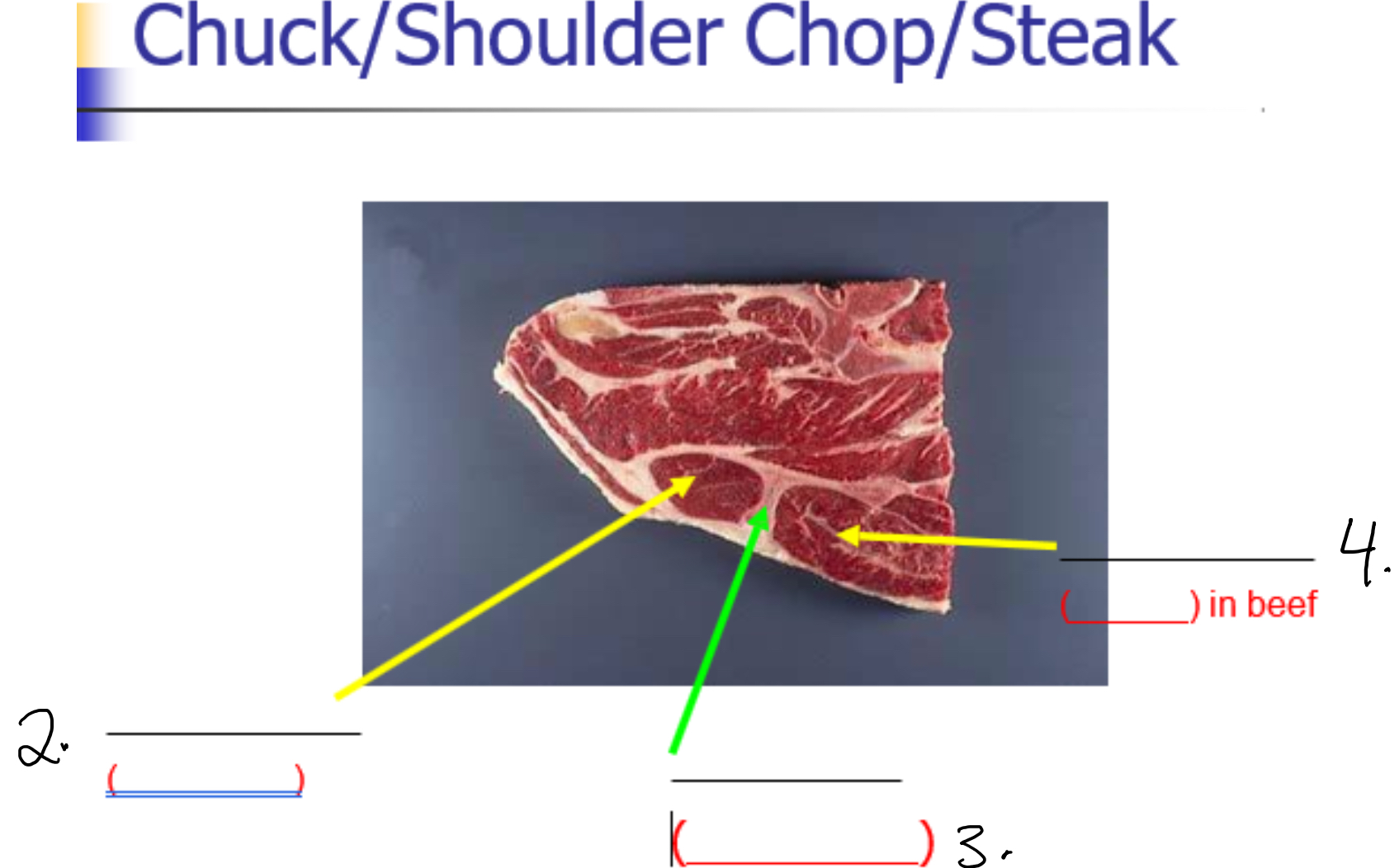
Label 2-
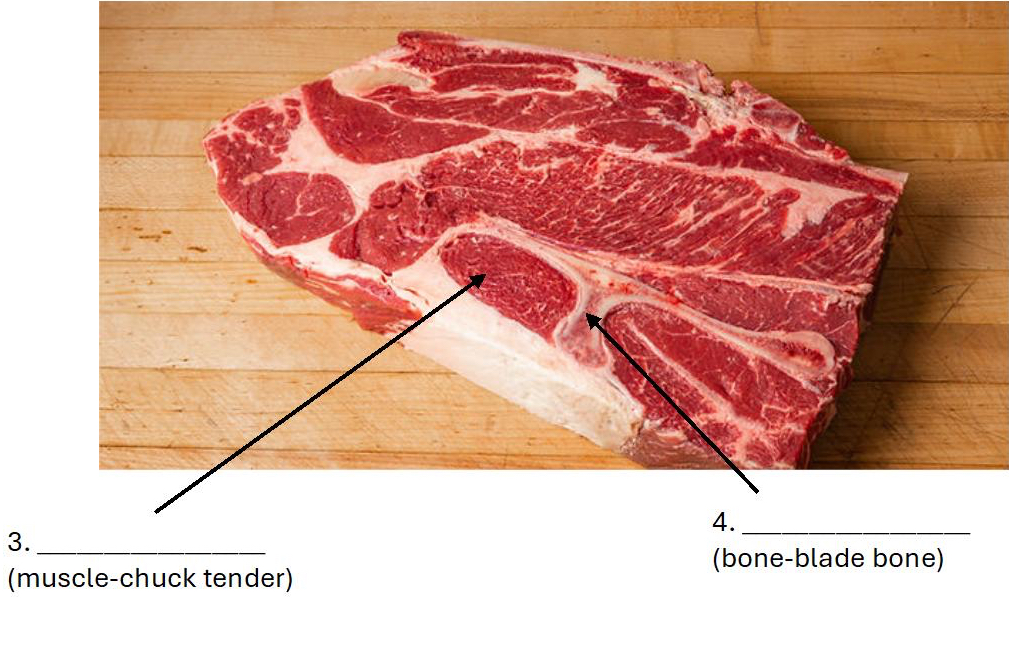
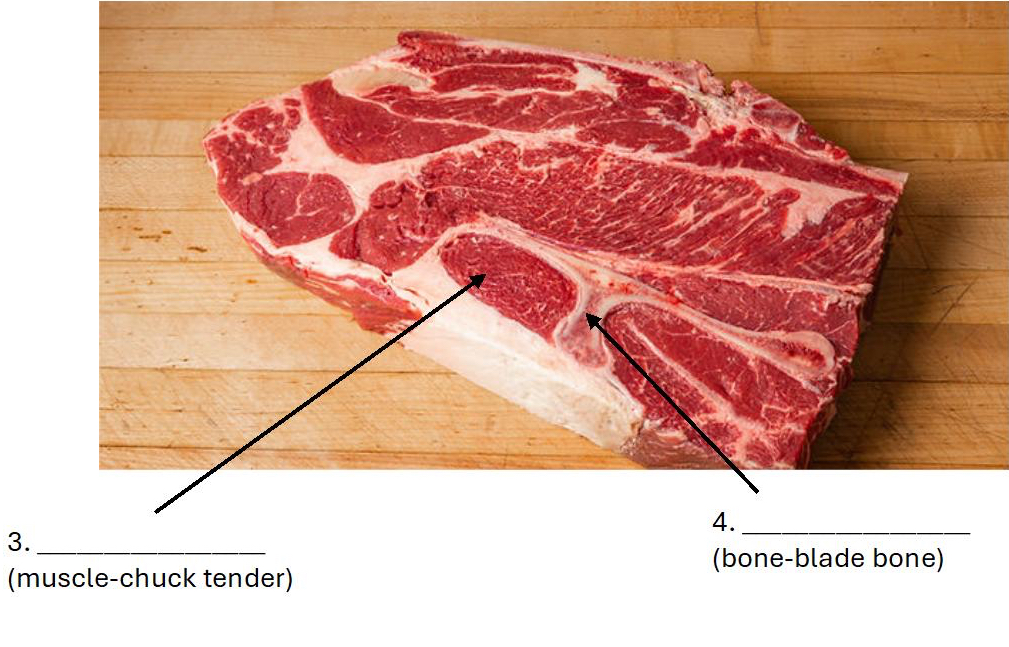
Supraspinatus (Chuck tender)
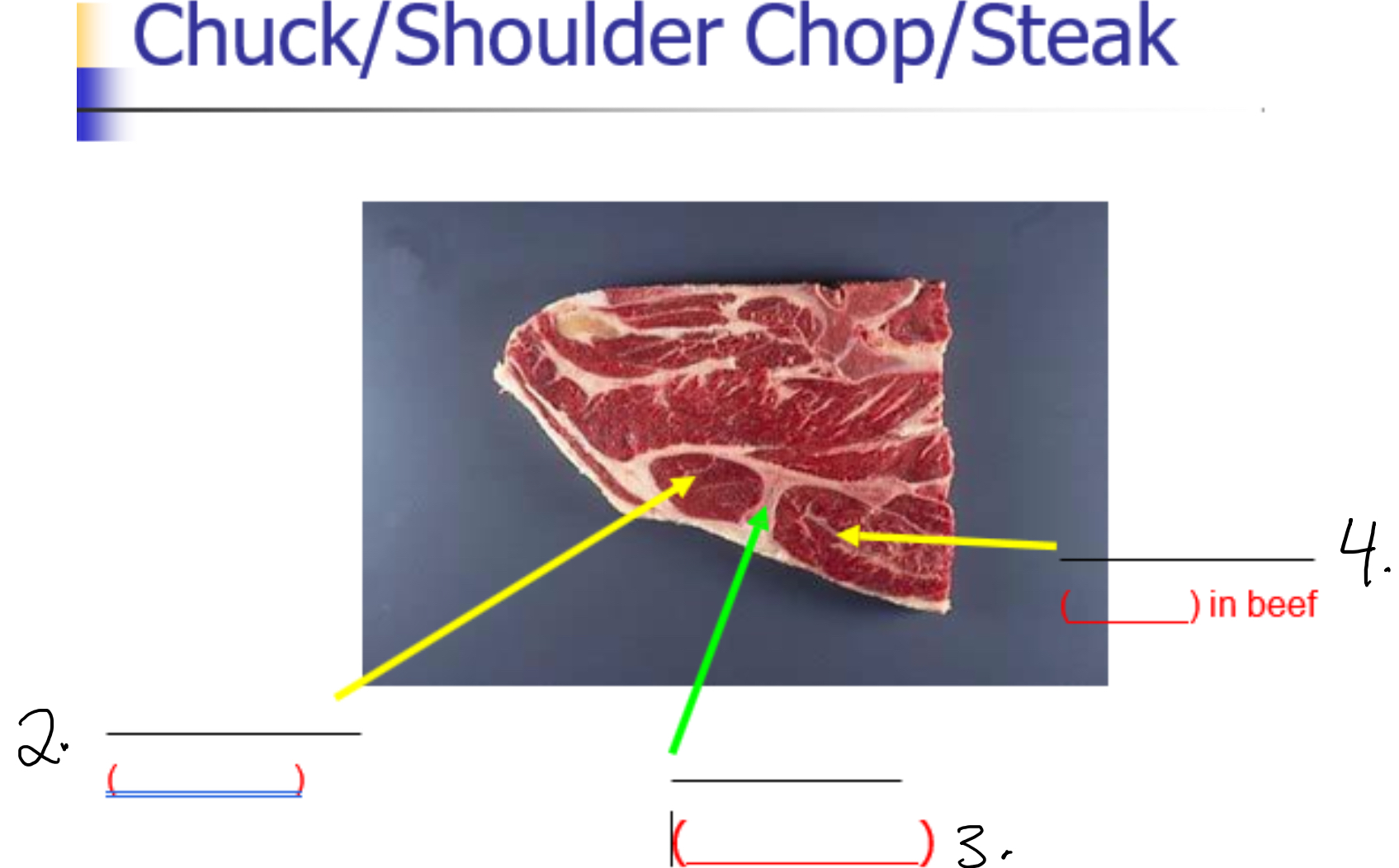
Label 3-
Scapula (Blade bone)
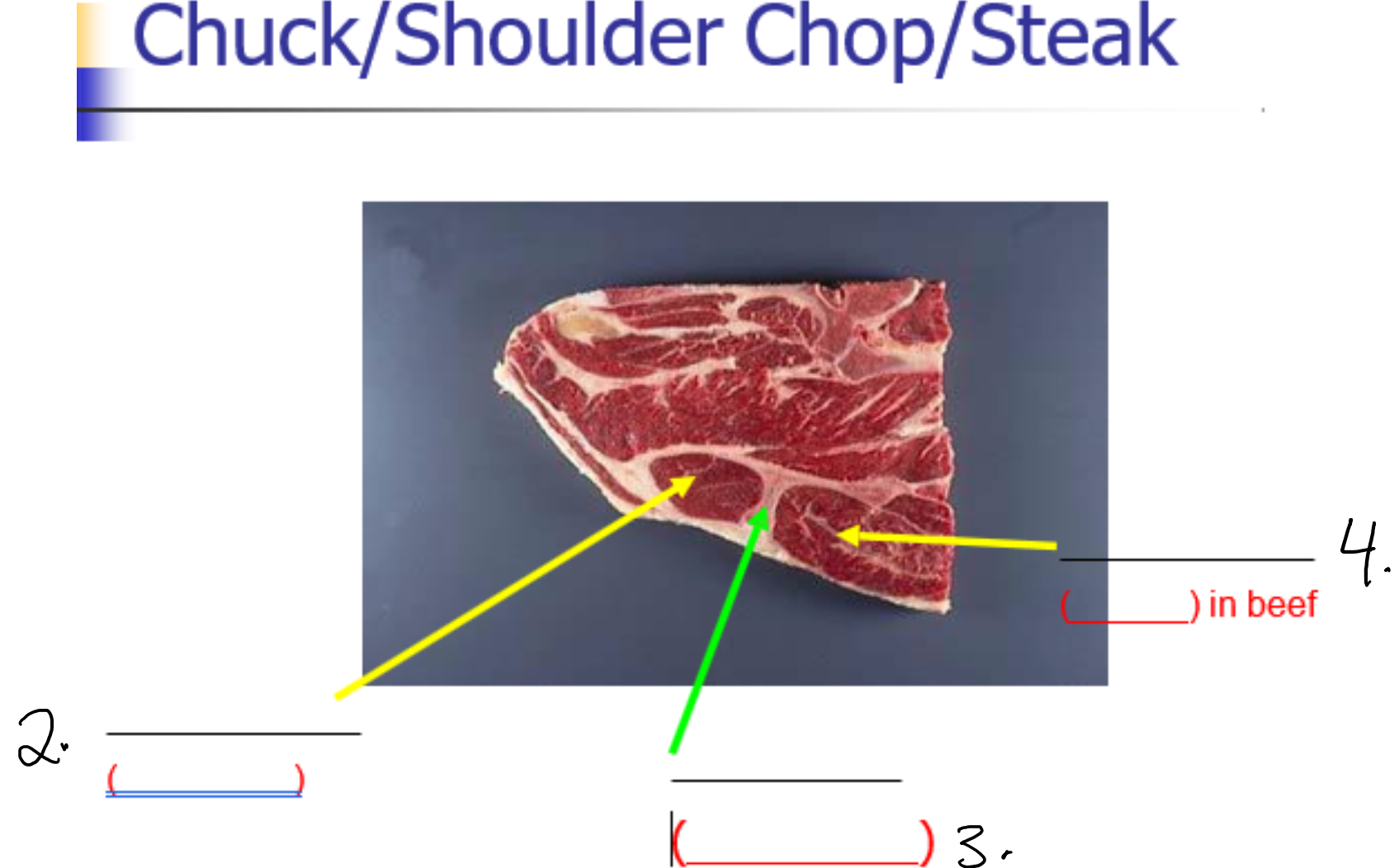
Label 4-
Infraspinatus (flat) in beef

Label 5
Longissimus dorsi (ribeye)

Label 6-
Spinalis Dorsi (ribeye cap)
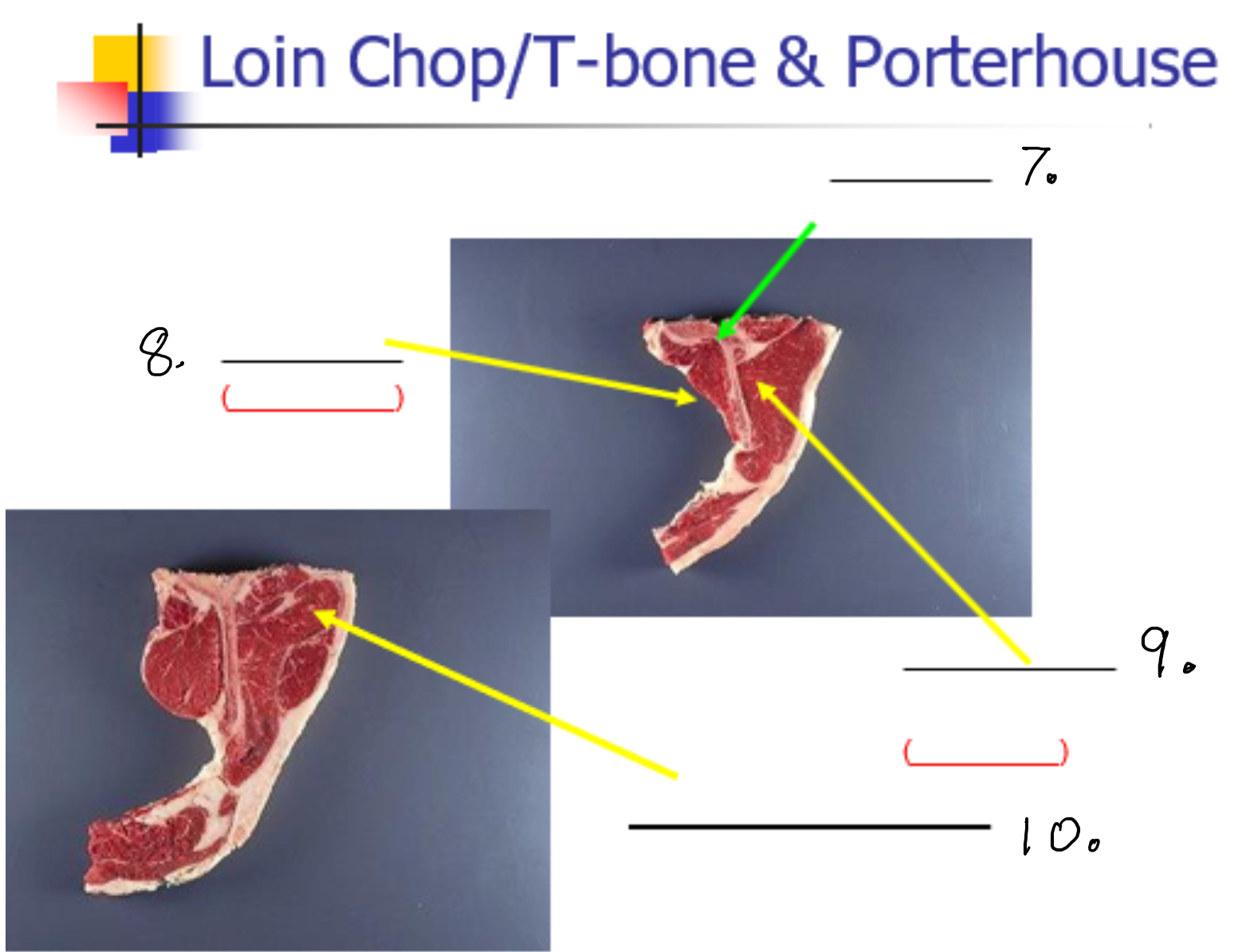
Label 7-
Lumbar vertebrate
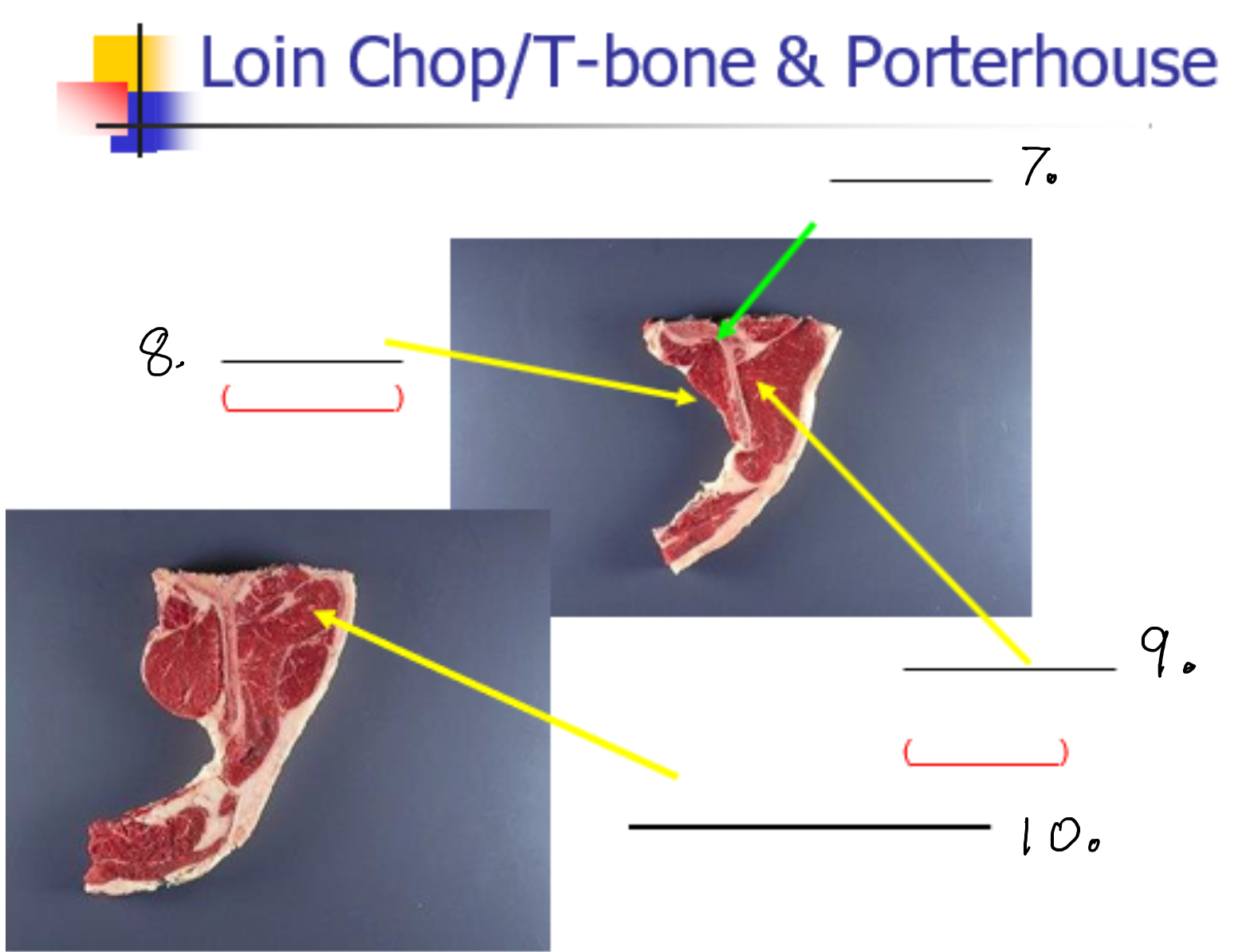
Label 8
Psoas Major (Tender loin)
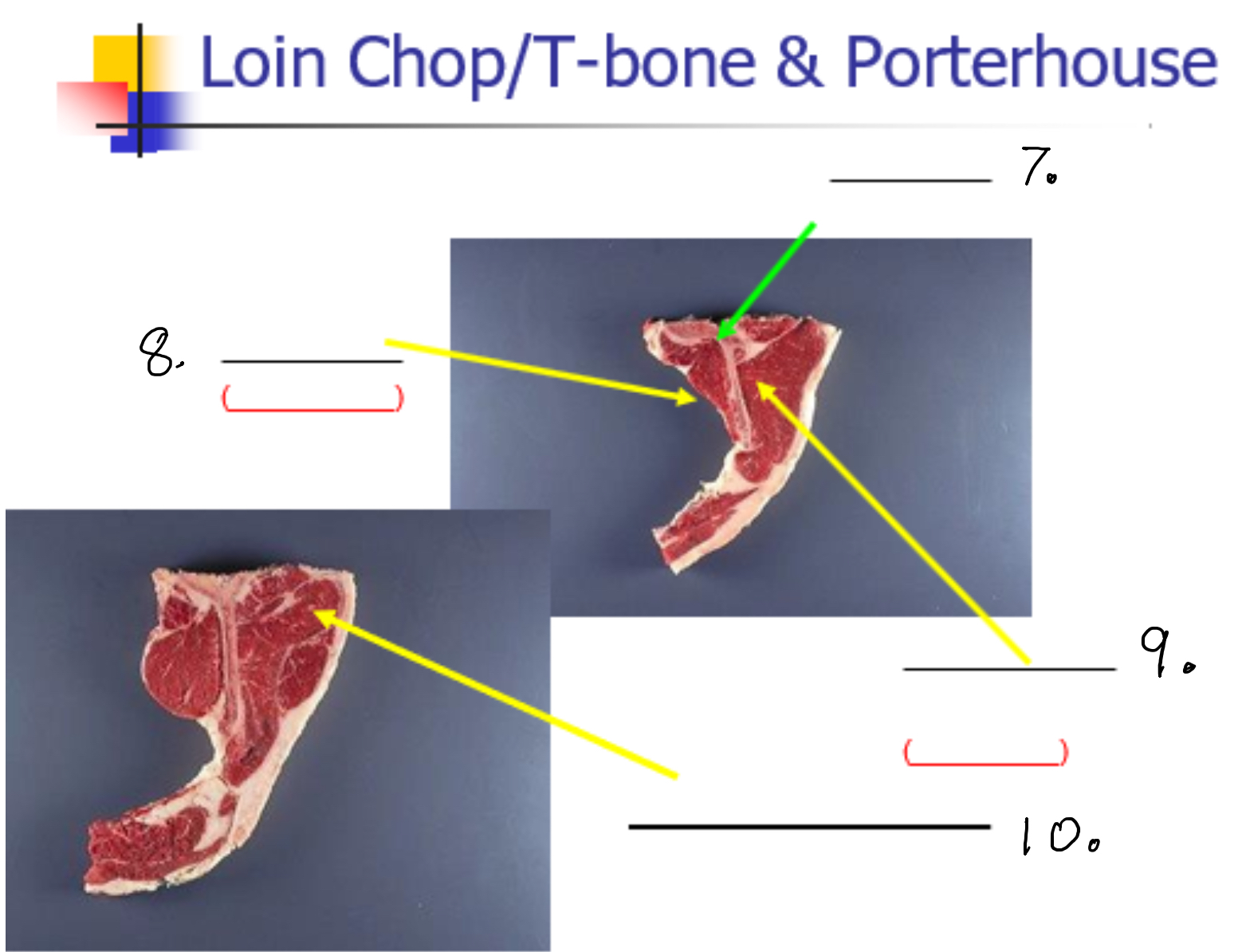
Label 9
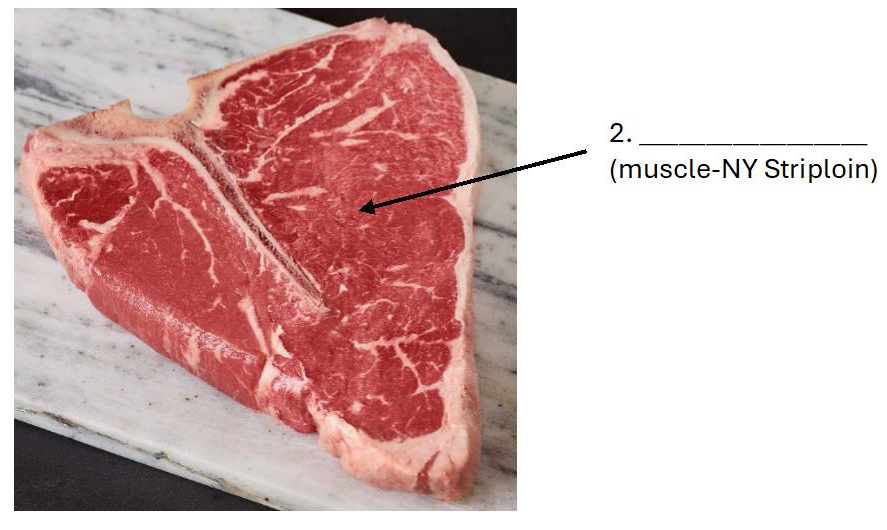
Longissimus dorsi (New York strip)
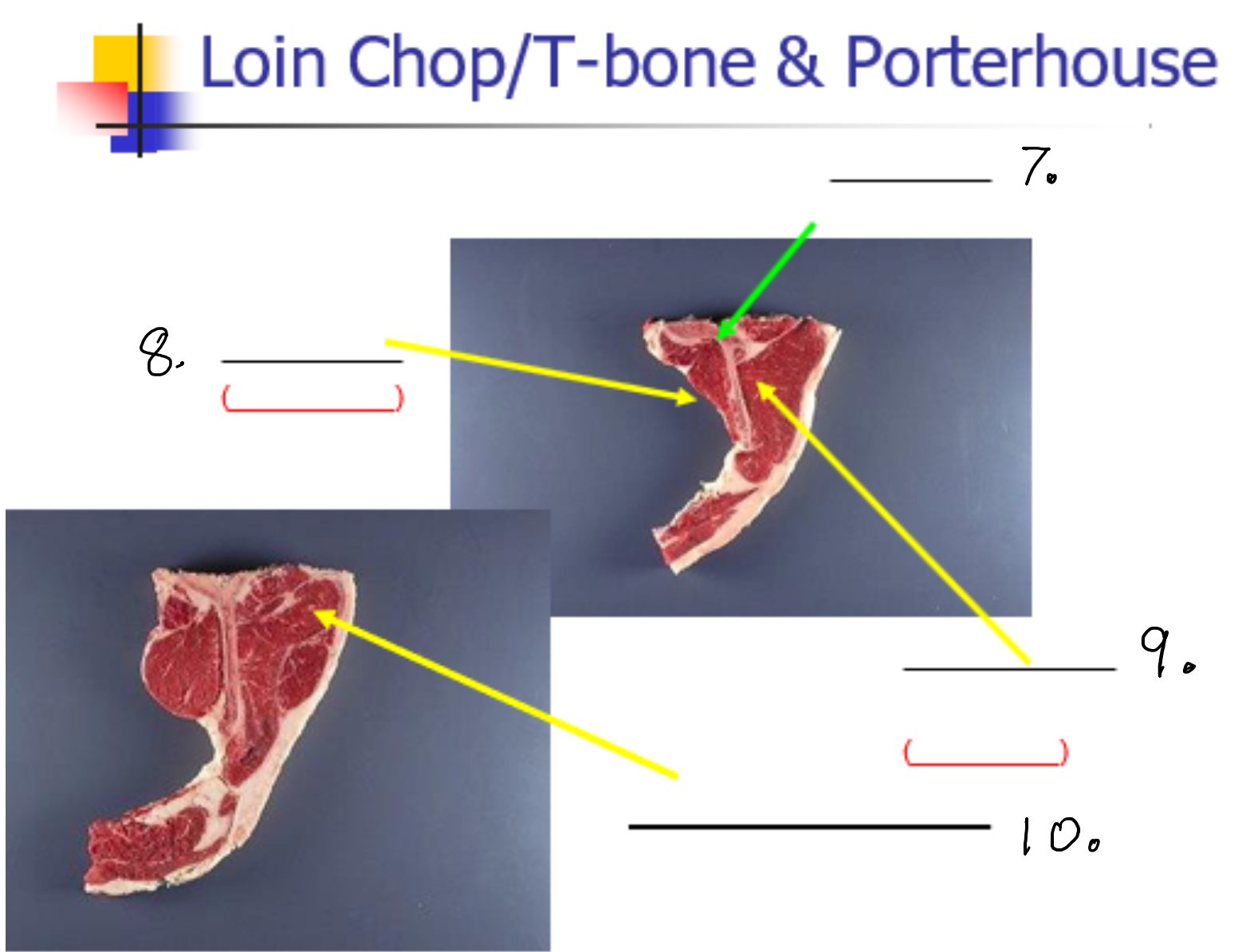
Label 10
Label 11
Bicep femoris (Picanha)
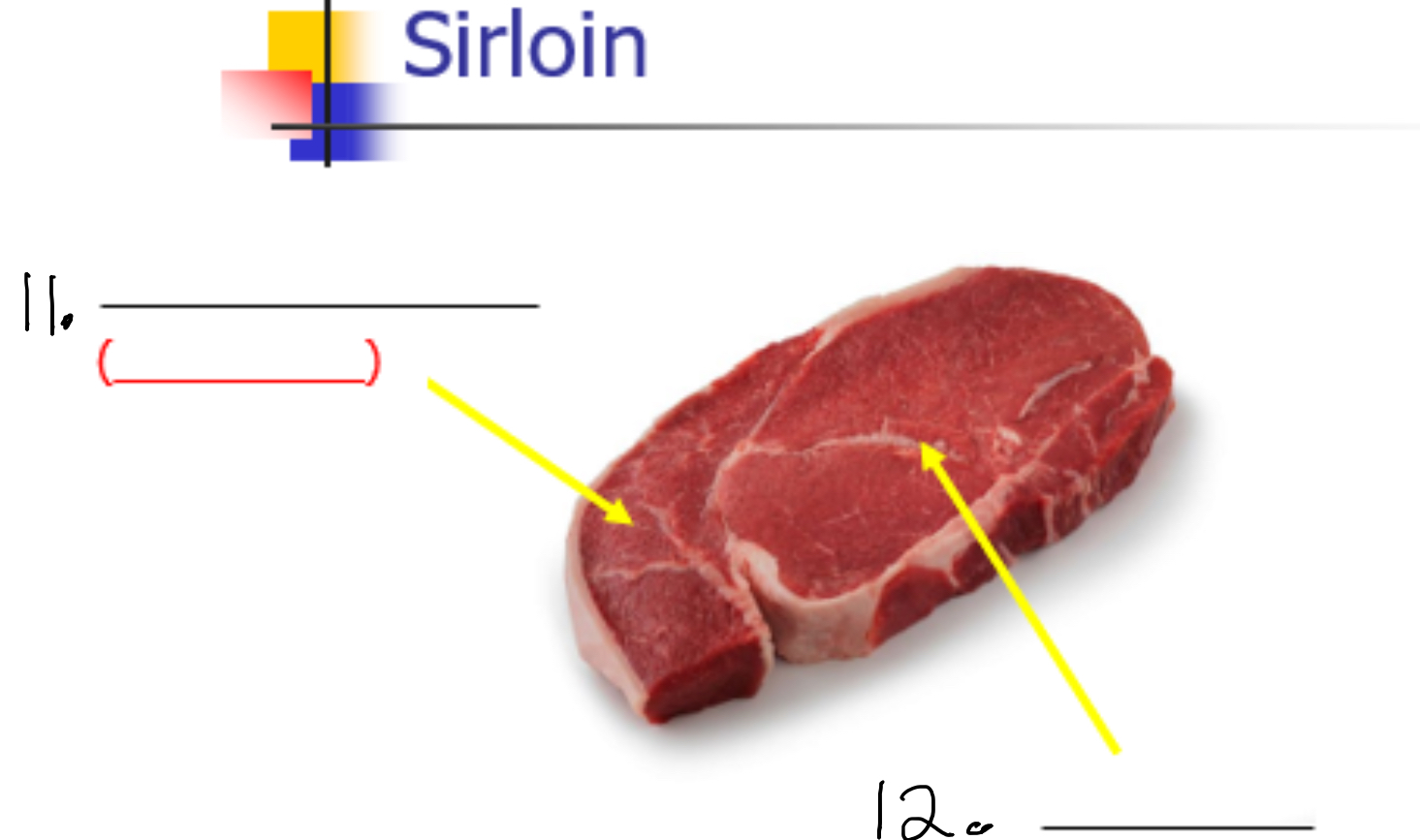
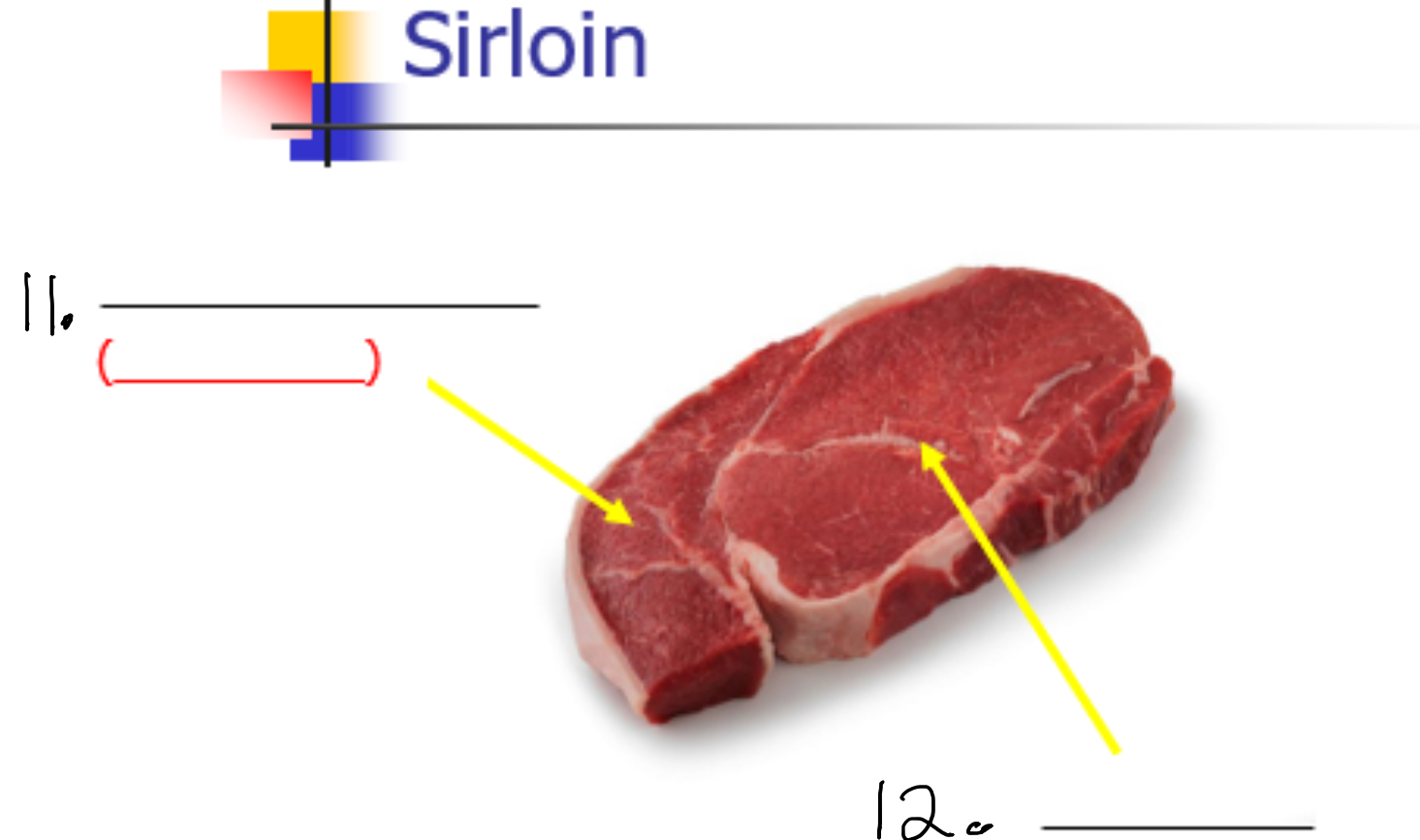
Label 12-
Gluteus medius
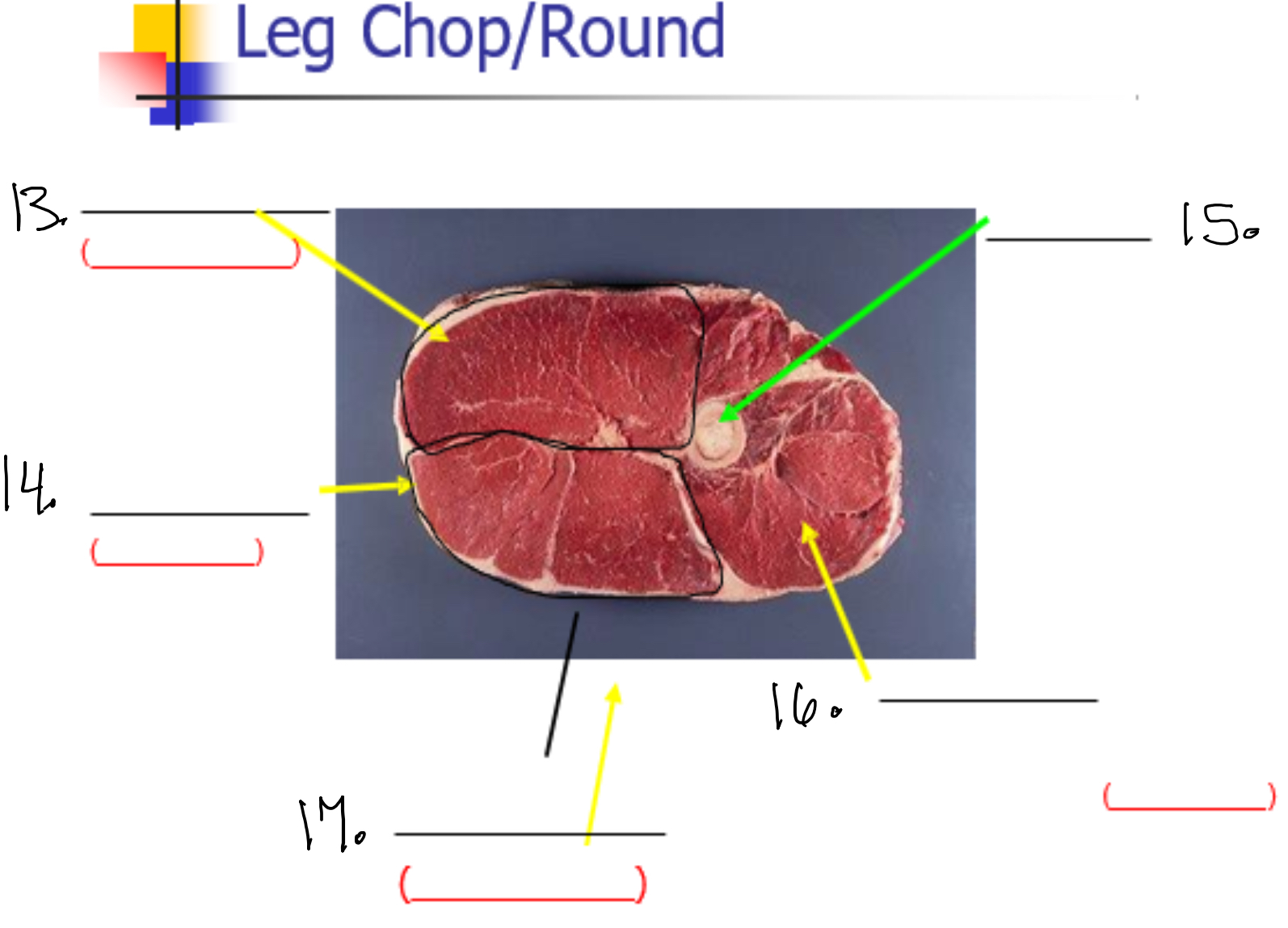
Label 13
Semi membaneos (Inside round)
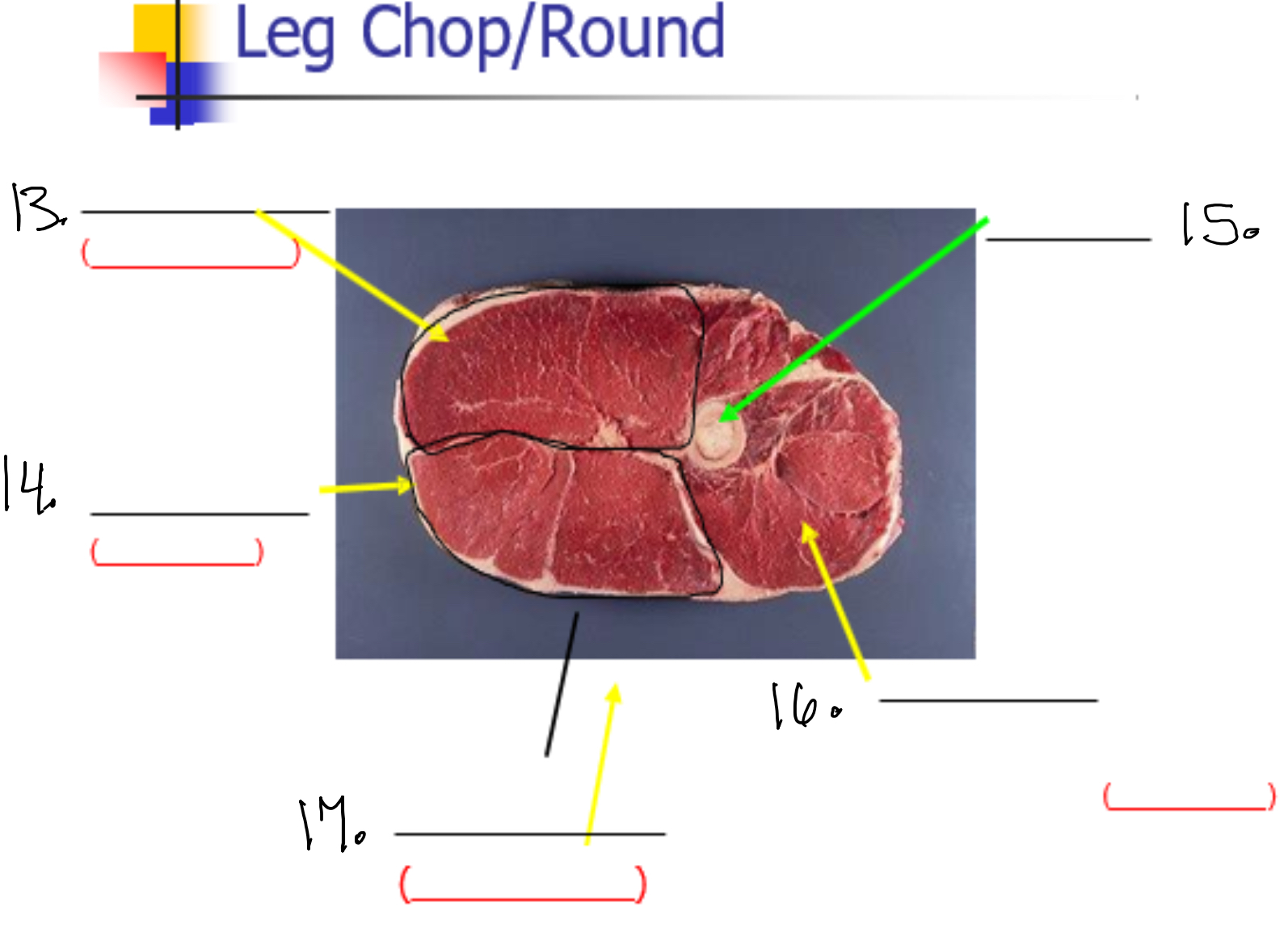
Label 14
Semi tendinasous (eye of round)
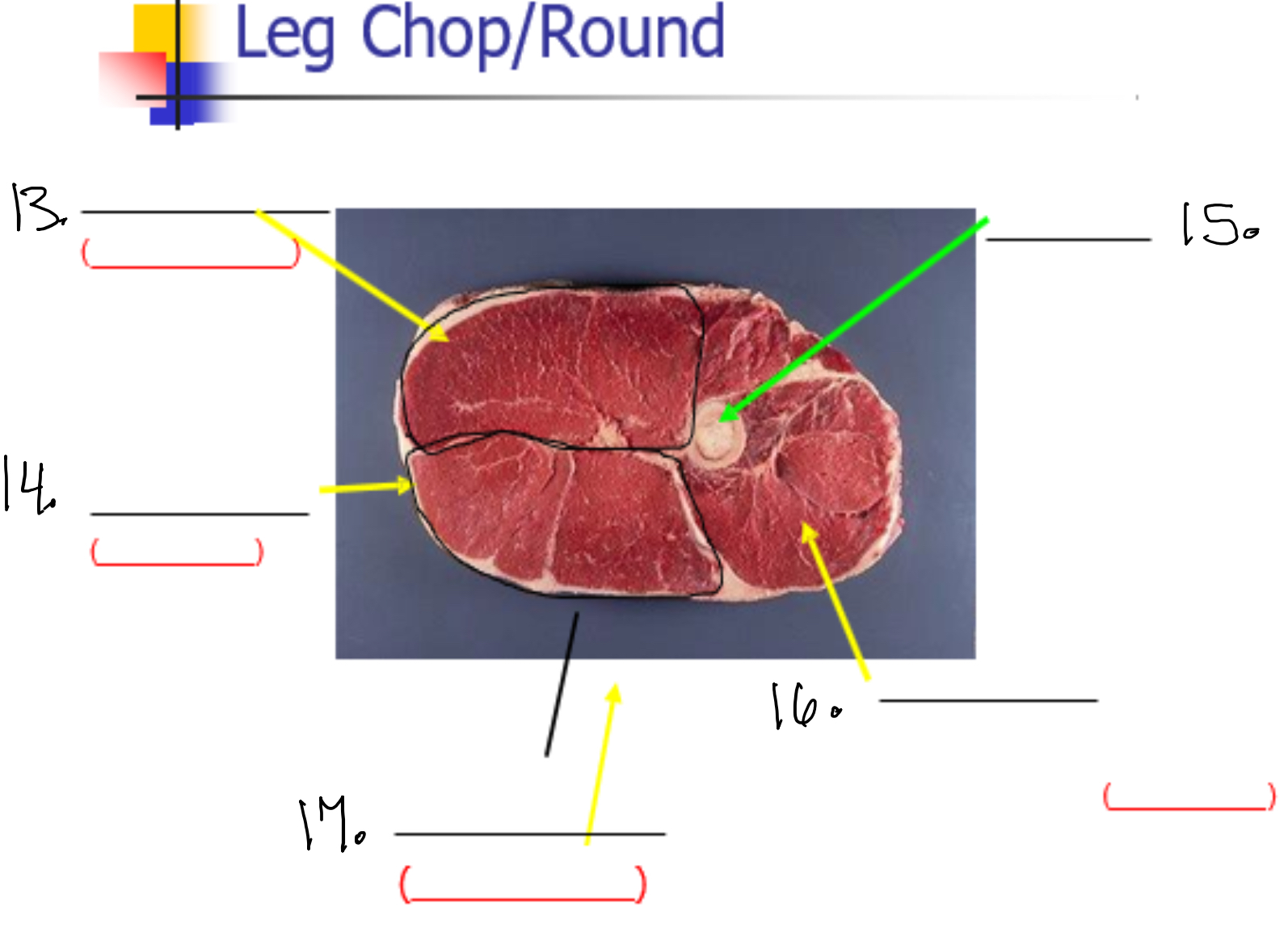
Label 15
Femur
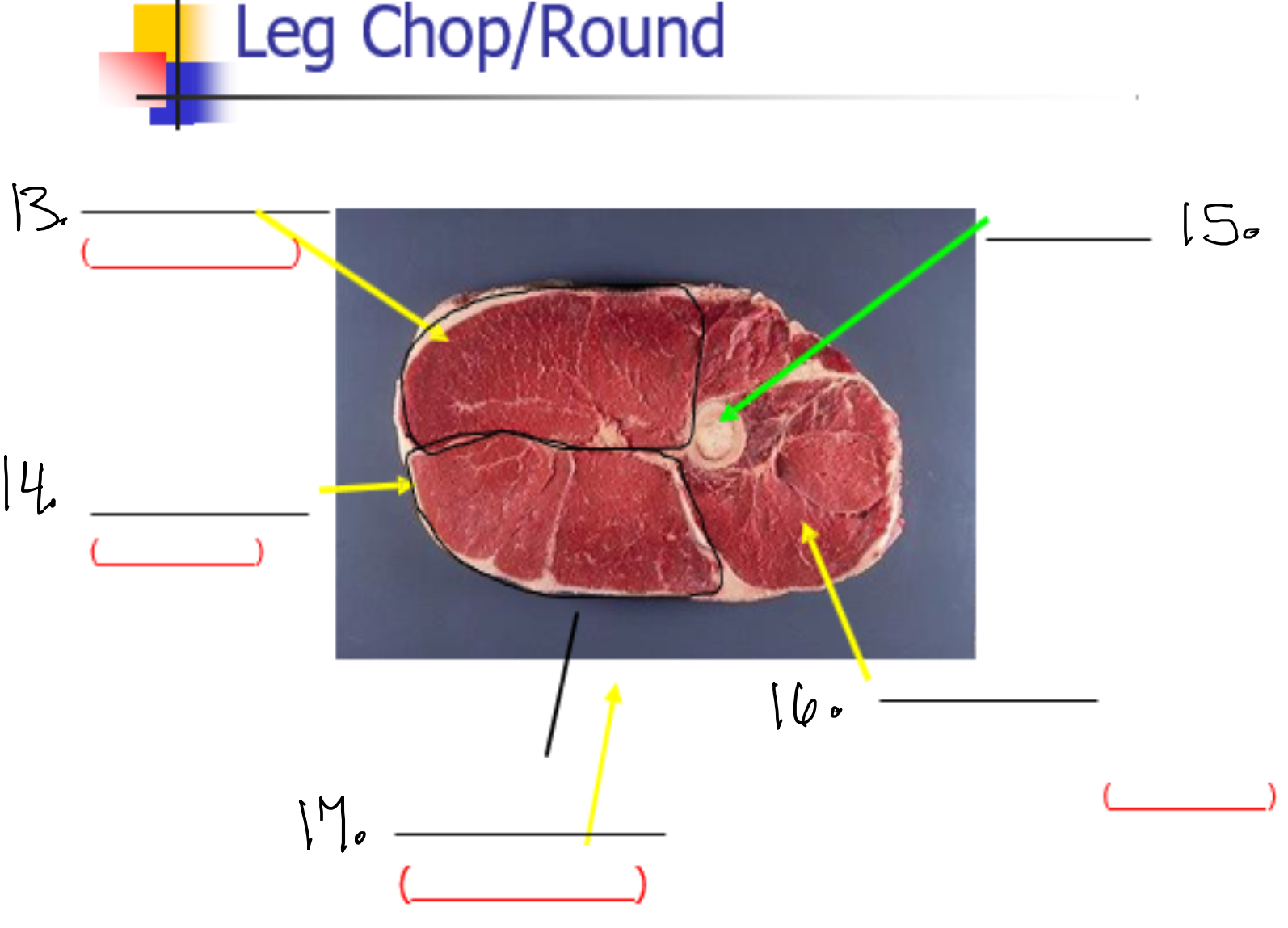
Label 16
vastus lateralis (sirloin tip or knuckle)
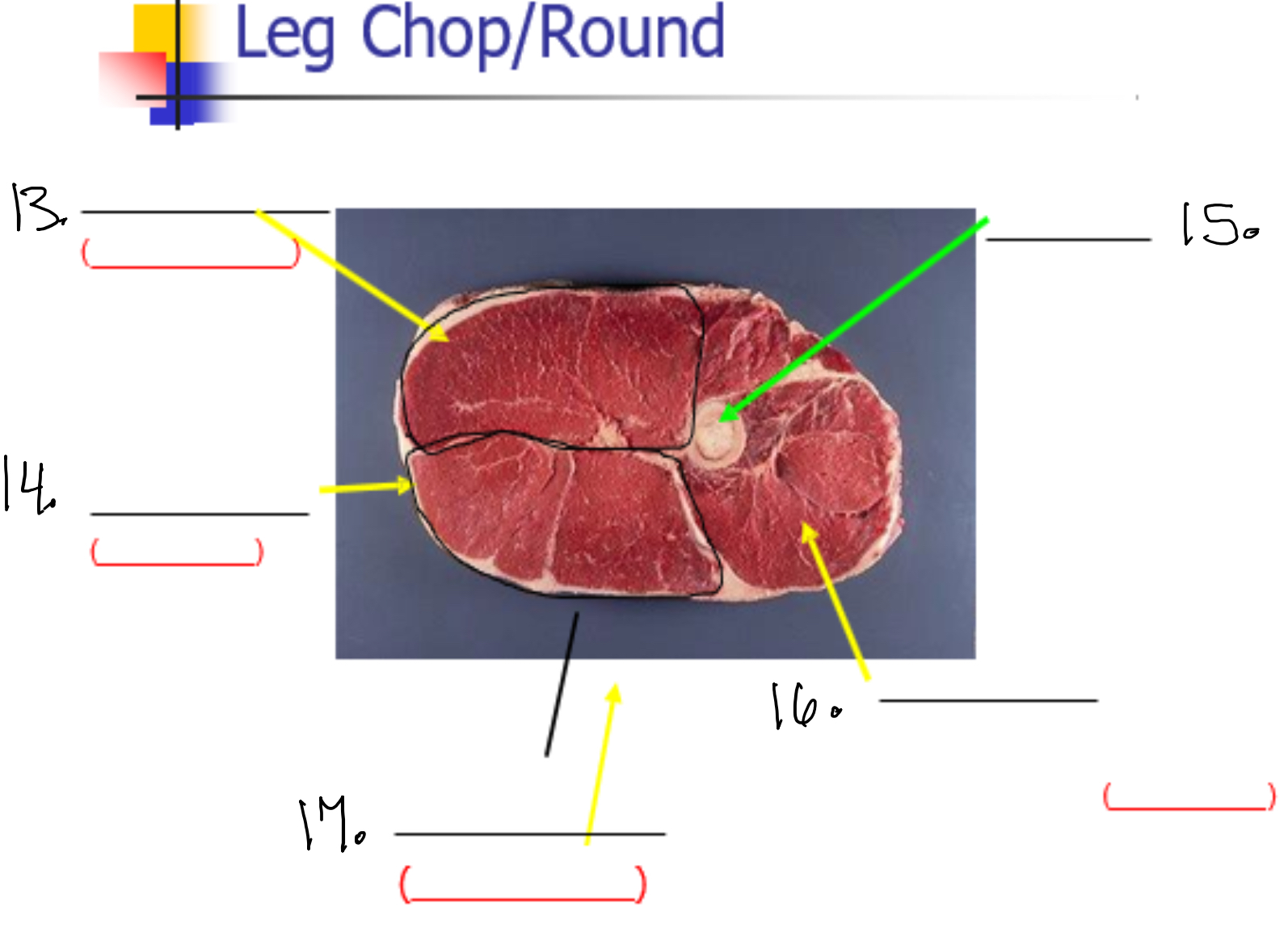
Label 17
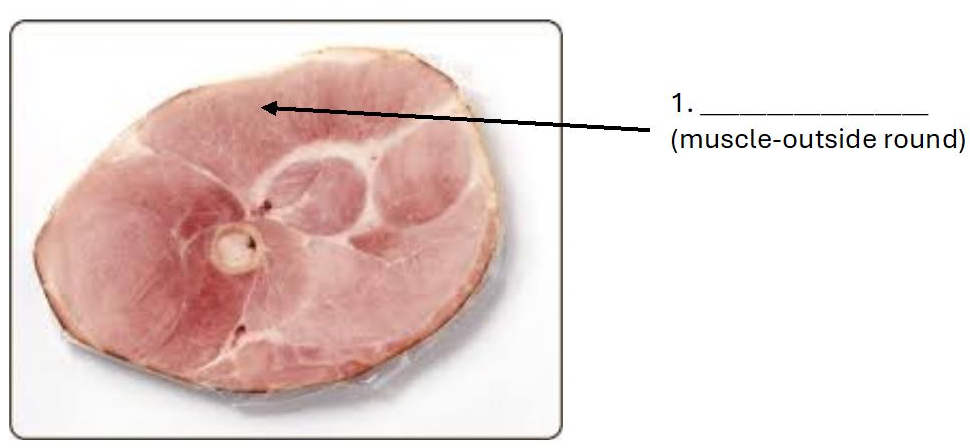
Bicep femoris (outside round)