IB History - Apartheid Vocab
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Khoisan
term used to describe the two earliest native populations of South Africa; they were pastoralists and hunter-gatherers who relied on cattle, sheep, and vast grazing lands for survival

Dutch East India Company
organization that was founded to establish a trading monopoly for the spice markets of East Asia; it also had the authority to establish colonies and trading outposts like the one at the Cape of Good Hope

Afrikaners
later name of the Boers; Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers first arriving in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries

Xhosa
a South African people traditionally living in the Eastern Cape Province; They form the second largest ethnic group in South Africa after the Zulus

Zulu
Largest ethnic group in South Africa; led by the warrior chieftain Shaka; they gradually expanded outwards from their homeland in Natal

Great Trek
The migration of thousands of Afrikaners to vast S African interior, away from British rule (trying to be independent) - Defining moment of Afrikaner identity, formed independent republics
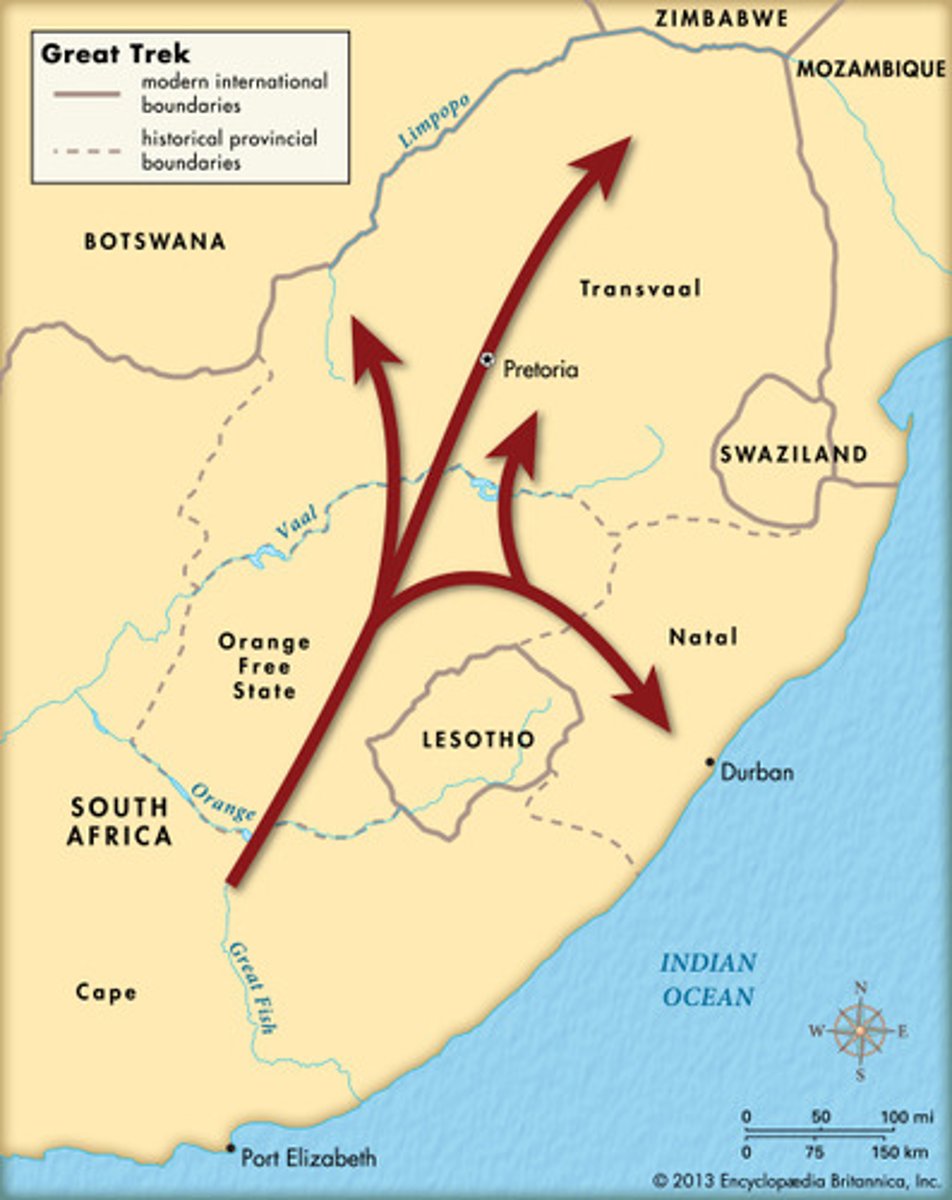
Orange Free State
One of two independent free states established by the Trekboers and their descendants; continued as an independent country with mainly Dutch speaking people until reconquered by the British in the late 1800's
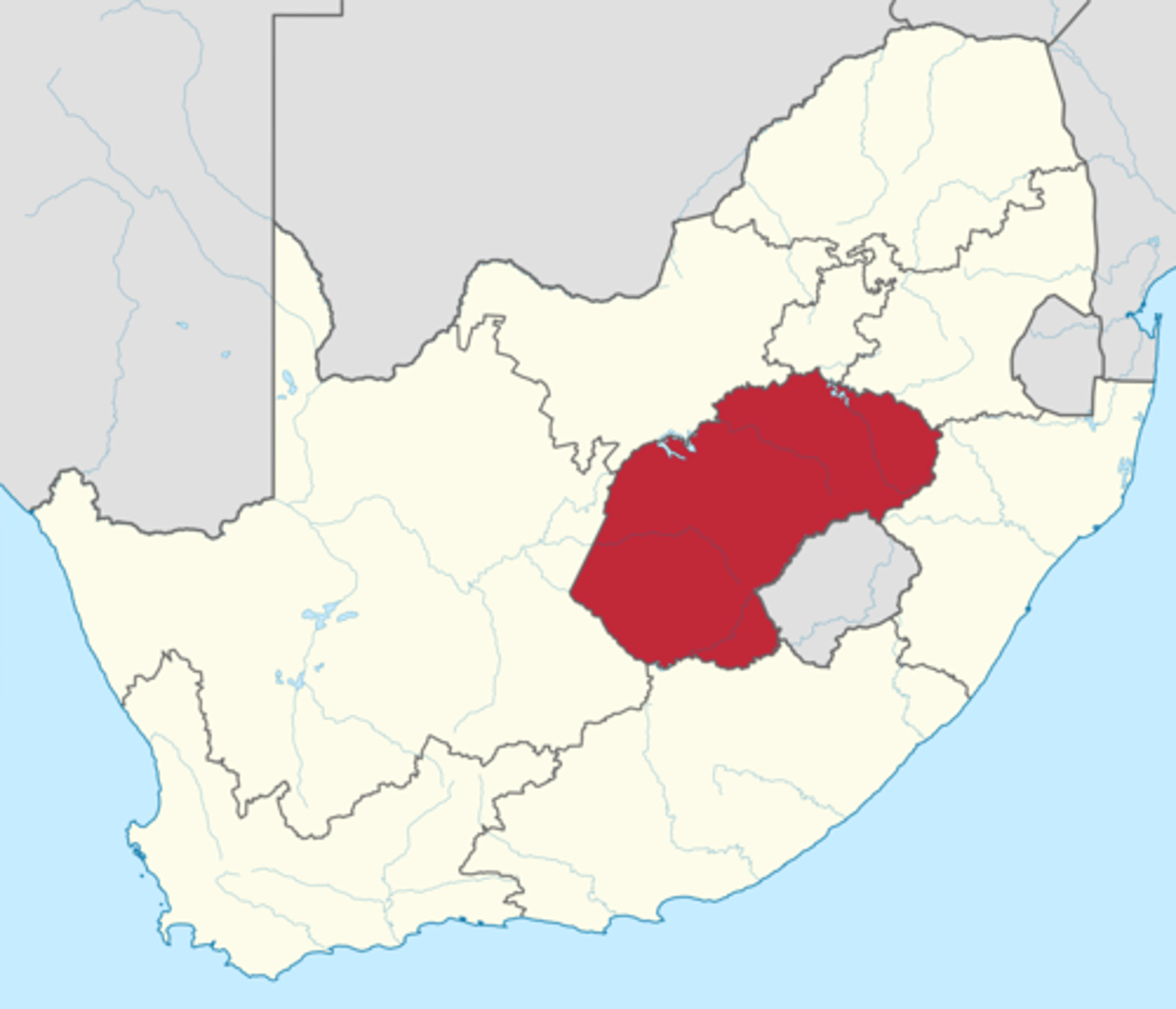
Transvaal
One of two independent free states established by the Trekboers and their descendants; continued as an independent country with mainly Dutch speaking people until reconquered by the British in the late 1800's
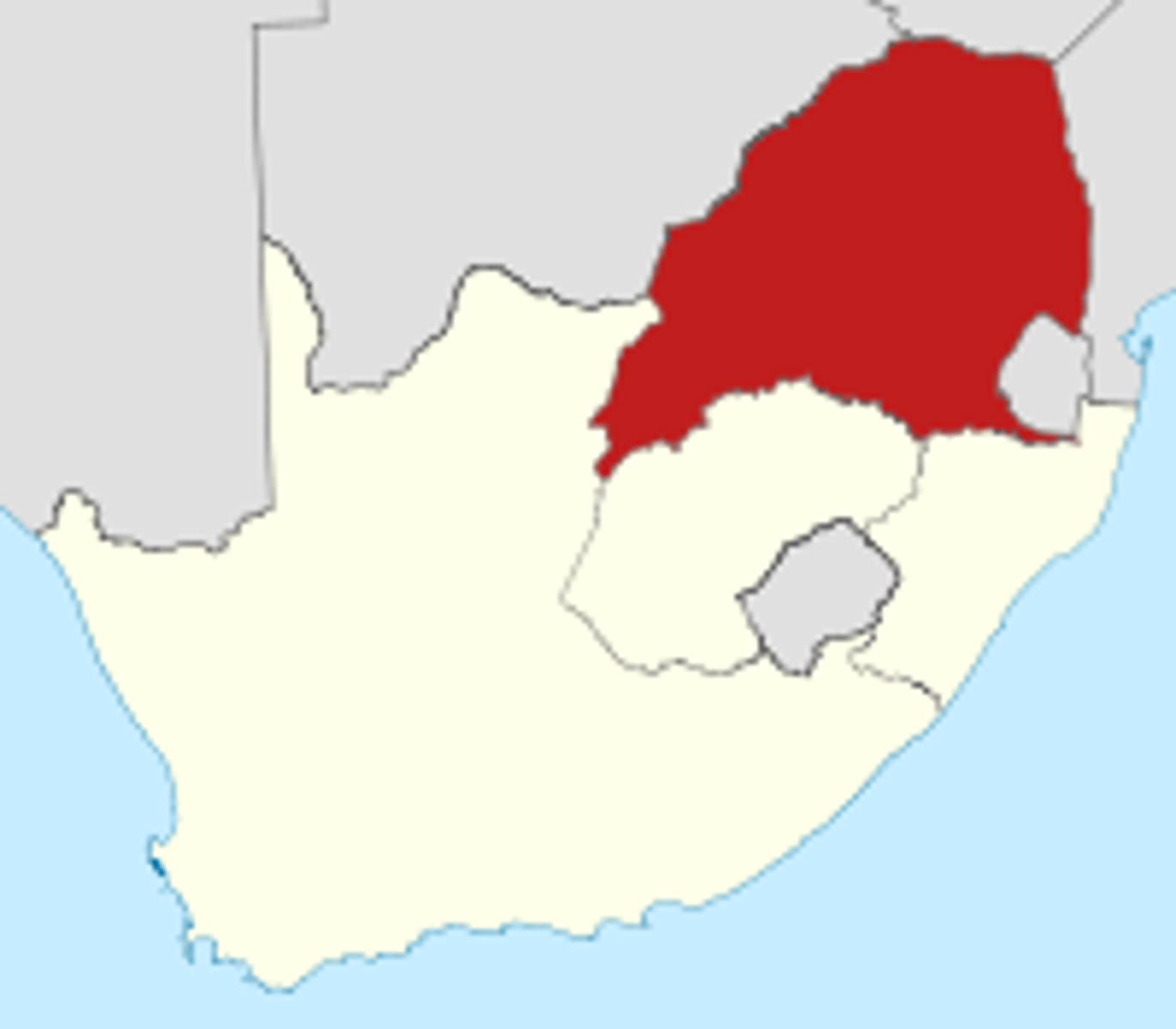
petty Apartheid
The first stage of the Apartheid era from 1948 - 1959; also called "baaskap" ("boss rule"); it's main purpose was. through a series of laws and actions, to ensure the complete domination of the white ethnic minority and the subjugation of the Black majority.

grand Apartheid
The second stage of the Apartheid era, beginning with the government of HF Verwoerd in 1959; its main goal was the complete territorial segregation of South Africa.
Social Darwinism
pseudo-scientific belief that "survival of the fittest" applied to human races and societies; used to justify the idea that some races were superior to others and to excuse racism and discrimination

township
underdeveloped urban living area, usually built on the periphery of towns and cities, that were reserved for non-white residents, namely black Africans, Coloureds and Indians
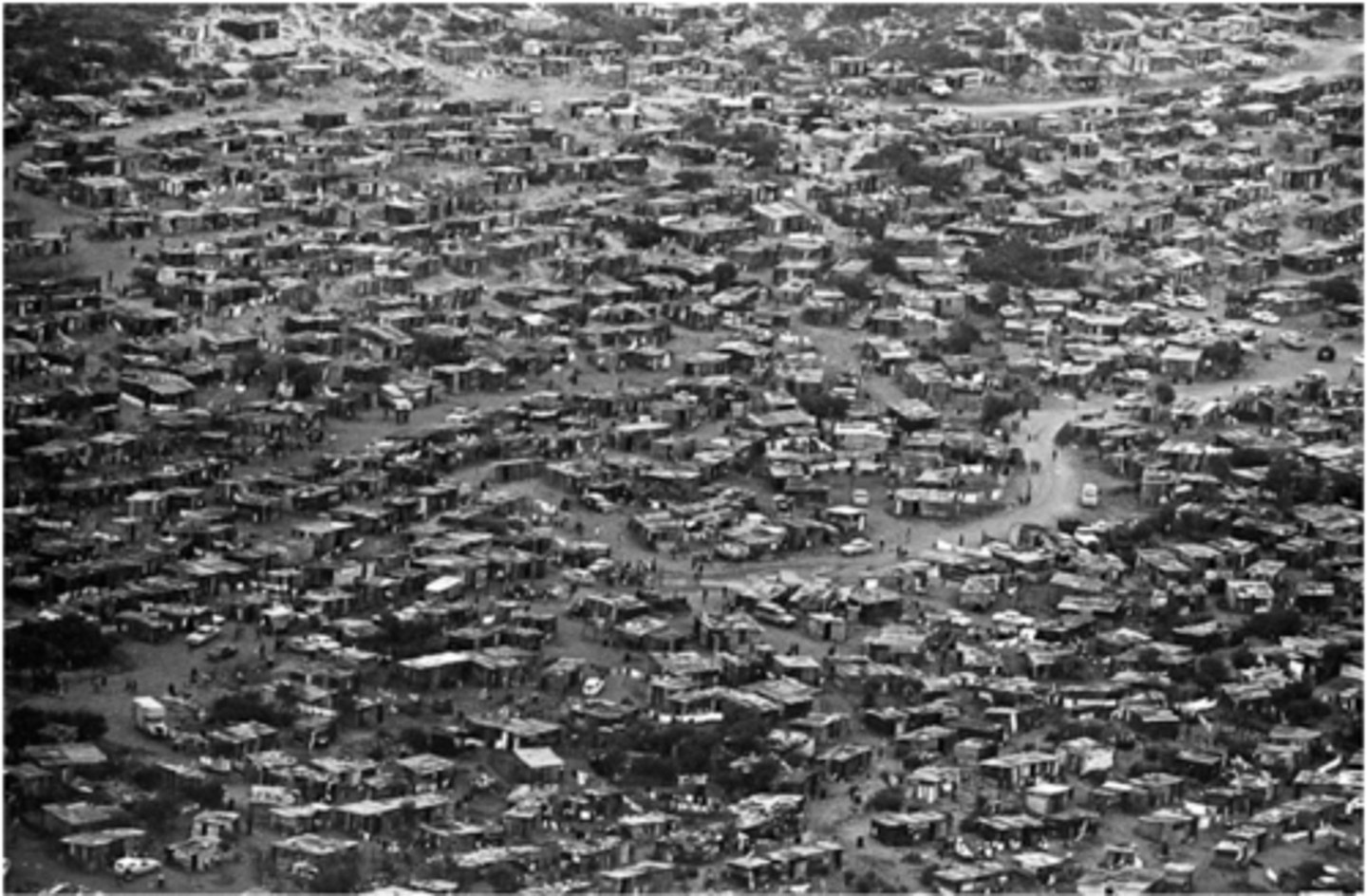

segregation
the enforced separation of different racial groups in a country, community, or establishment.

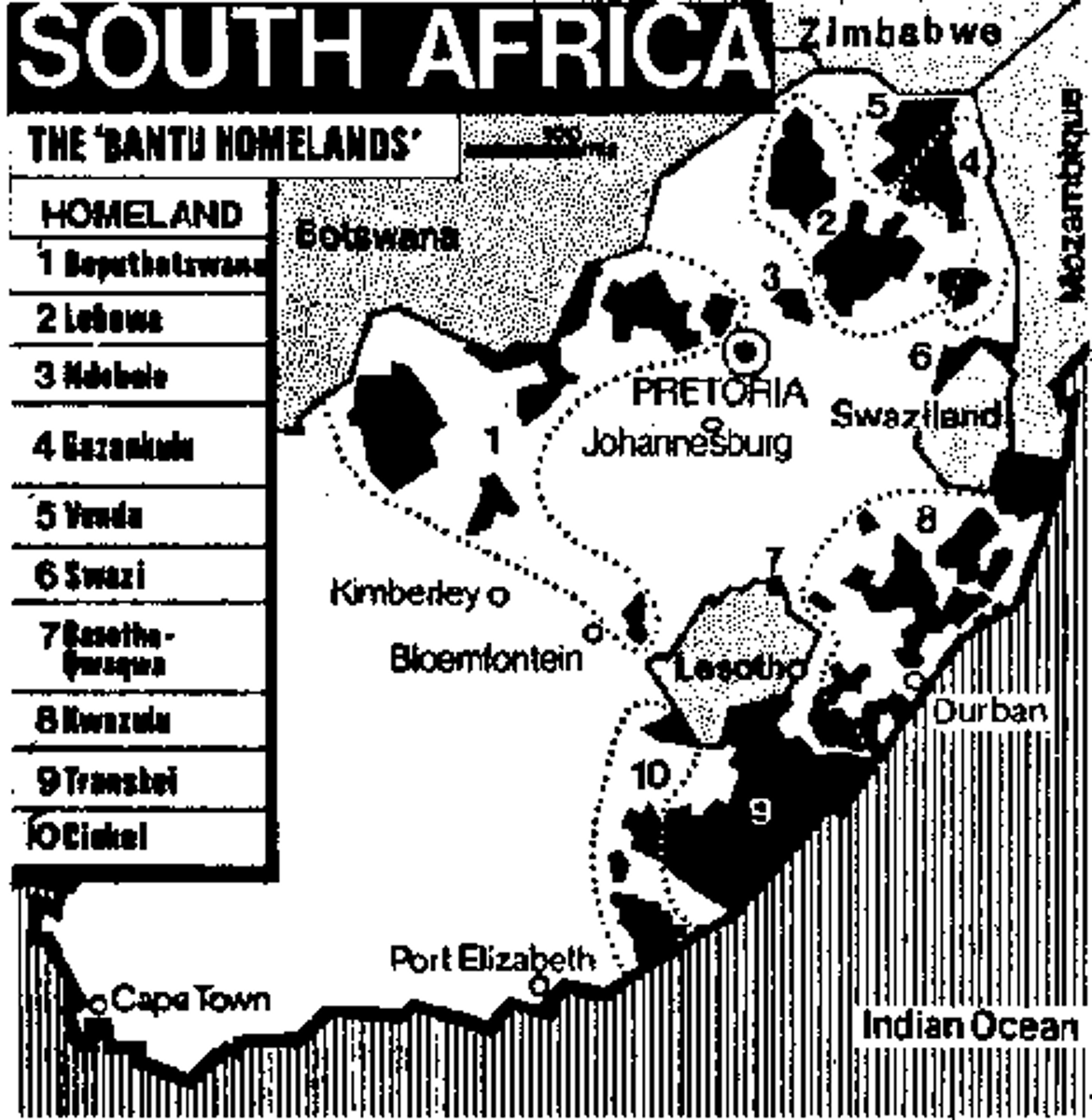
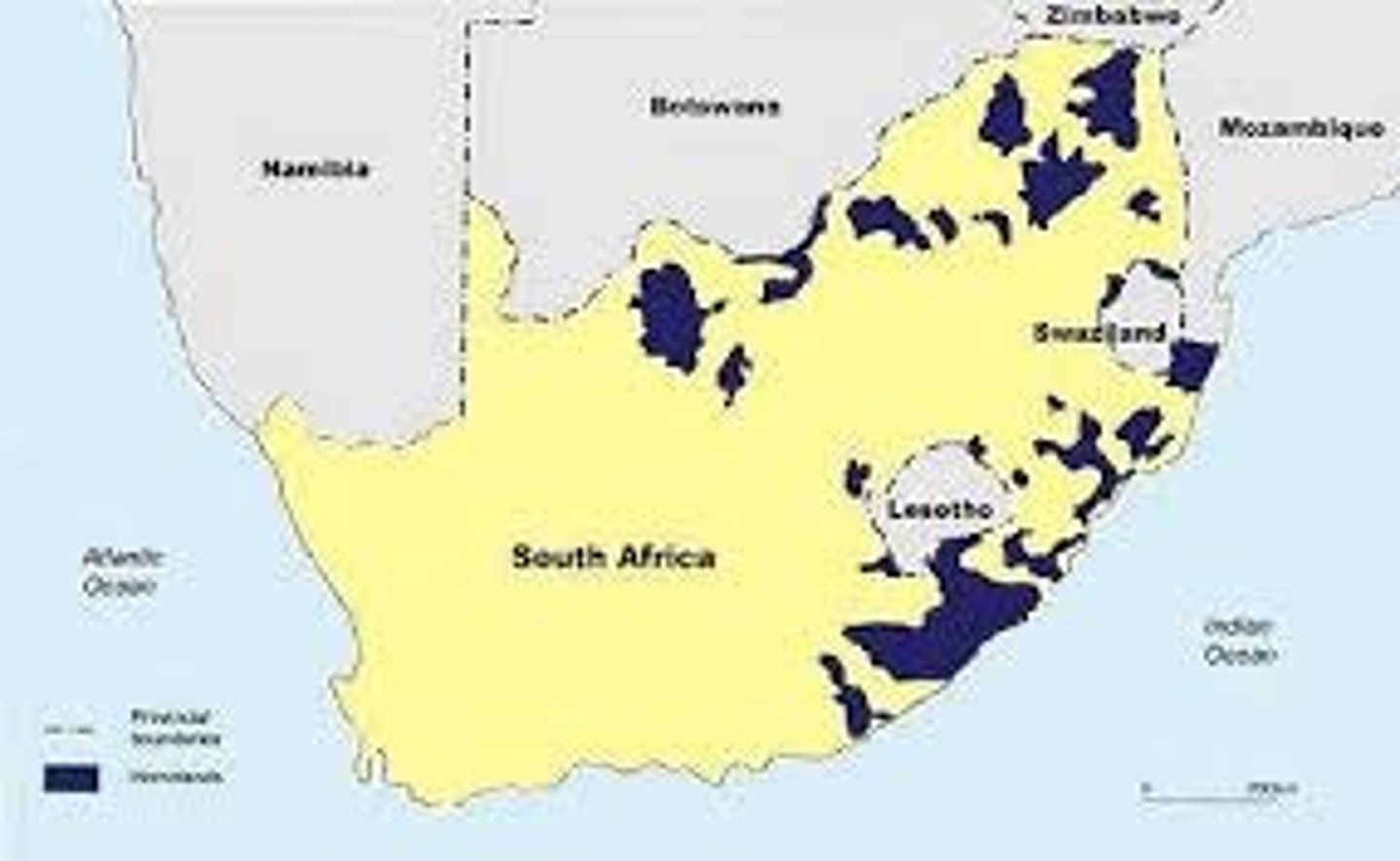
homeland
one of 10 tribal/ethnic areas created under the Promotion of Bantu Self-Government Act (1959); all Black Africans would be required to live in one of these designated areas which would be independent countries
civil disobedience
the strategy of protesting against unjust laws by deliberately breaking them, usually nonviolently; originated by Henry David Thoreau and used by Gandhi and Martin Luther King, Jr.

Defiance Campaign
The first in a number of coordinated nationwide campaigns and protests organized by the ANC against the Apartheid system through breaking curfew, burning passports, boycotts;

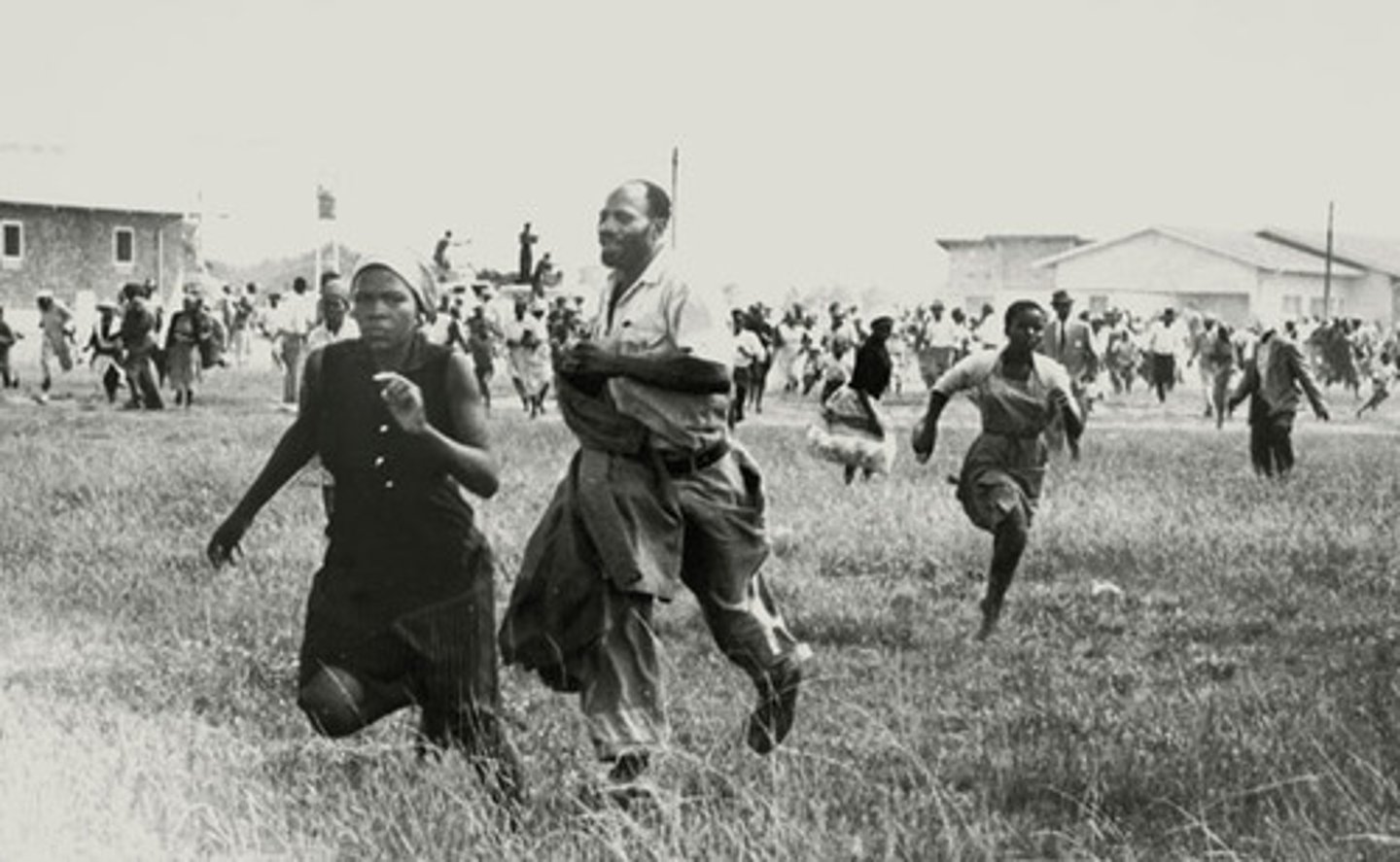
Sharpeville Massacre
21 March 1960, when White policemen opened fire on a crowd of demonstrators outside a police station. 69 unarmed people were killed (including 8 women and 10 children) and another 186 people injured. The primary effect was the decision of the ANC to change strategy from non-violent resistance to armed struggle.

Rivonia Trial
Court proceeding that took place in South Africa between 1963 and 1964, in which ten leaders of the African National Congress were tried for 221 acts of sabotage designed to overthrow the apartheid system

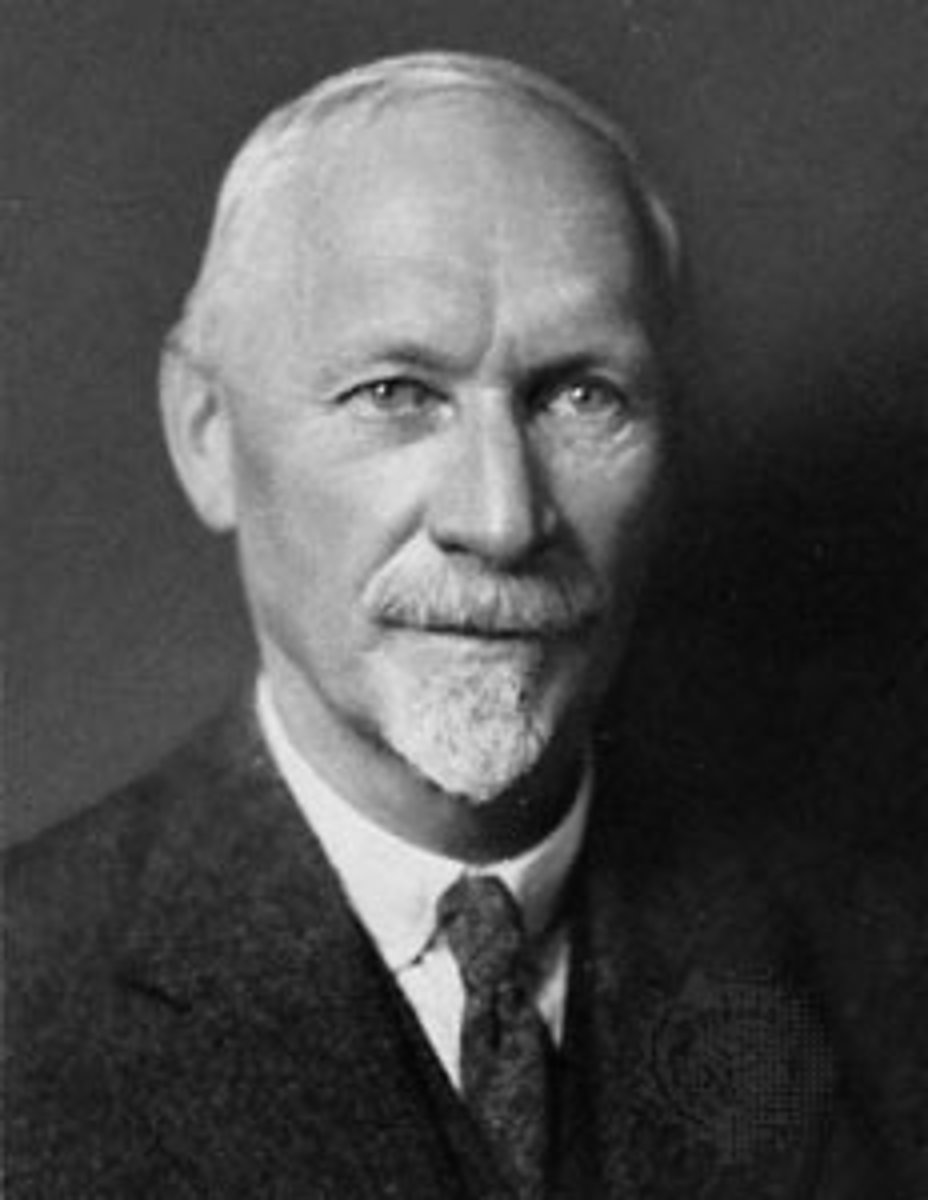
Jan Smuts
the second Prime Minister of South Africa; served in office from 1939 to 1948; the principal architect of the system of segregation, he was also planning to dismantle some of its more discriminatory laws before the National Party won the election of 1948

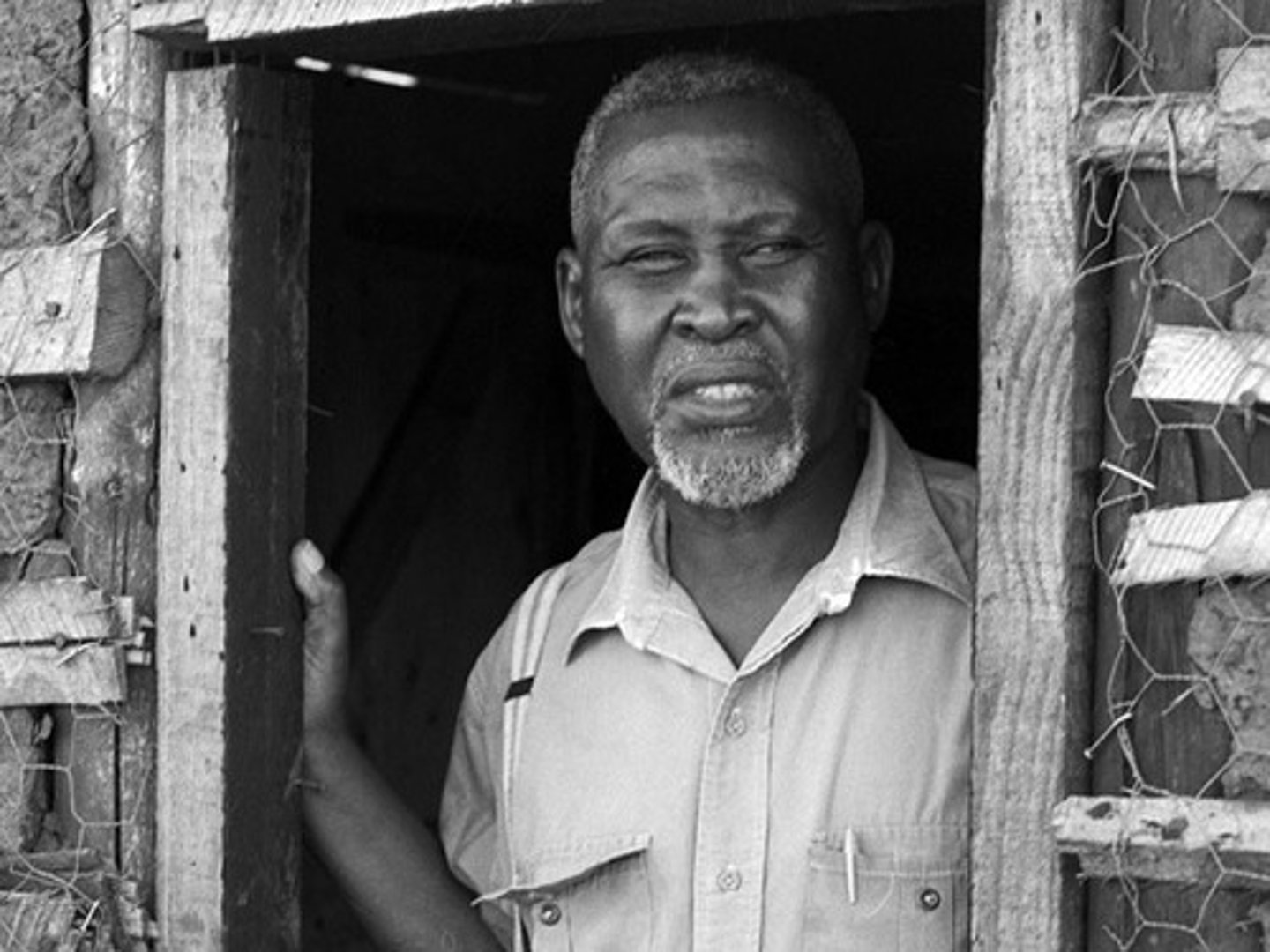
Albert Luthuli
Zulu chief who became the president of the ANC in 1952 known for his commitment to non-violence. Repeatedly banned by the South African government, he opposed the adoption of armed struggle and was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1960.

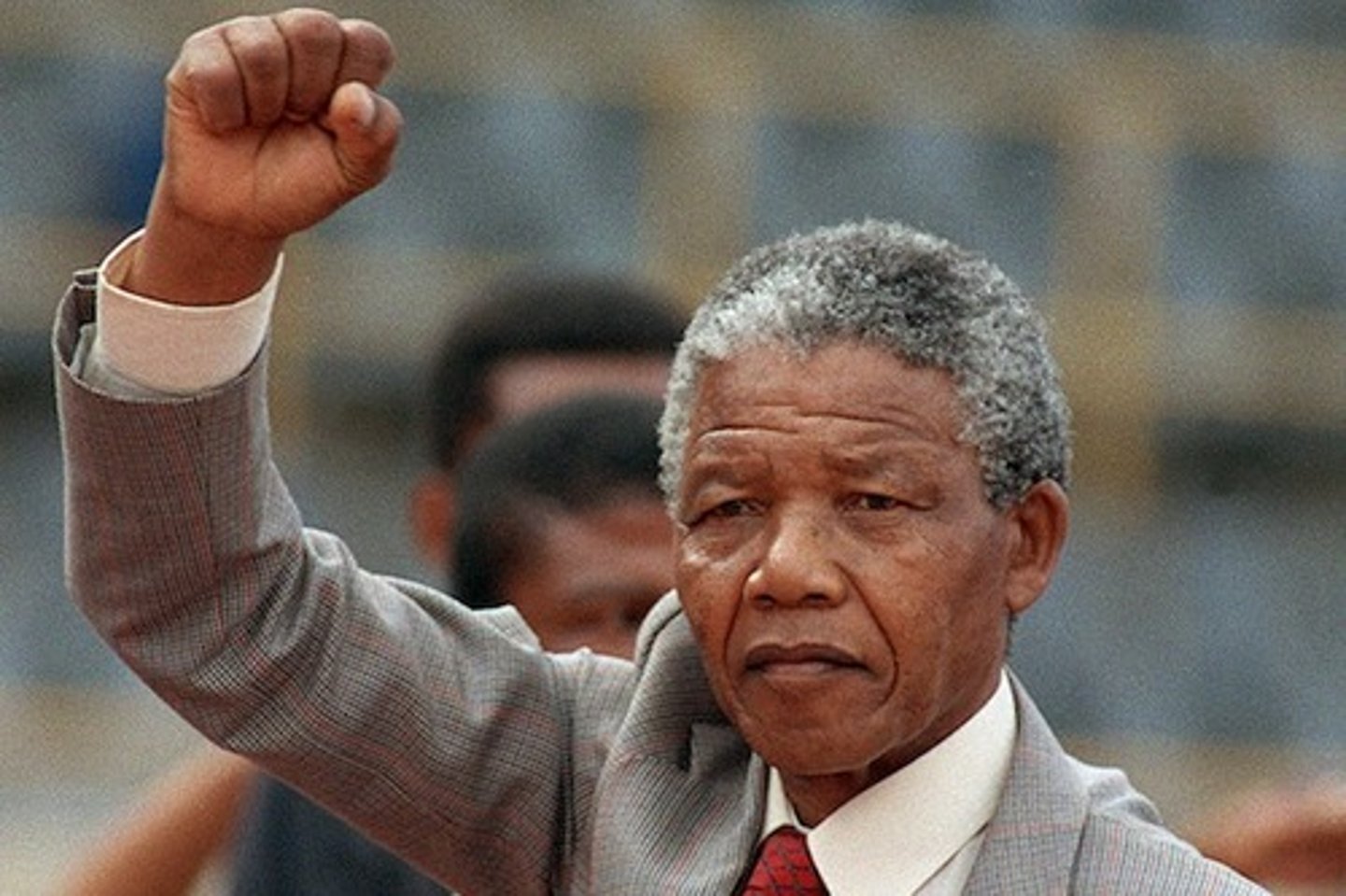
Nelson Mandela
iconic leader of the anti-Apartheid movement who founded the ANC Youth League in 1944. He generally believed that non-violence as a means of protest against the government was naive.

African National Congress
the dominant nationalist opposition organisation against the Apartheid system in South Africa between 1948 and 1964. It organised major campaigns like the Defiance Campaign, bus boycotts, stay-at-home strike and passbook protests.

South African Communist Party (SACP)
Marxist organisation closely tied to the ANC; the organised workers' strikes in an effort to pressure the Apartheid government and were accused of treason by the South African government after socialist principles were included in the Freedom Charter.

Hendrik Verwoerd
Architect of apartheid; Minister of native affairs who fought for Afrikaners and wanted to "protect" blacks
National Party (NP)
Afrikaners who wanted to prevent African domination of South Africa
Pan African Congress (PAN)
Black African organization that broke away from the ANC to set up an agenda, in which S. African govt should comprise only black Africans
Umkhonto we Sizwe (MK)
Armed wing of the ANC ("Spear of the Nation")
Robben Island
Prison where Nelson Mandela served 18 of his 27 years behind bars
Group Areas Act 1950
Required registration of all land ownership, and authorized govt to designate area for one group alone to occupy and evict members of other groups
Pass Laws
Laws that prohibited the free movement of African people out of the reserves; failure to carry a pass would result in prison sentence
Freedom Charter
1955 - A statement of democratic principles that became the basis of ANC policies; called for social, economic, and poltical equality for all
apartheid
African word meaning 'separate' or 'apartness' --
Law in S Africa from 1948-1990 that implemented a system of racial segregation
Boers
'farmer,' their rugged farming lifestyle formed the basis of the new Dutch settler, and later Afrikaner, identity
Anglo-Boer War
British vs Dutch conflict in 1899-1902, over gold, diamonds, independence from British rule; Afrikaner (Dutch) nationalism grew
Union of South Africa
1910 -- British colonies and Afrikaner Republics joined together under this designation
Bantu
African people who speak a common group of languages -- white minority used this word to refer to indigenous Africans (often in a derogatory way)
Pass Books
Documents used to restrict the movement of Africans - Non whites did not have to possess them
Homelands (reserves)
Areas laid aside for Africans to live in according to their tribal groups
'Black Spots'
Areas outside the land officially designated for settlement by native Africans where they nevertheless managed to acquire land
1913 Natives Land Act
Restricted African ownership of land to 7% of S Africa (and they received the land of poorest quality) -- Africans were forced to work for white farmers or in mines/cities
influx control
methods used to control African migration into urban areas (such as the pass laws)
Shanty towns
areas made up for temporary, often inadequate accommodation and lacking proper facilities such as sanitation or fresh water
1910 Constitution
document which set how S Africa was to be governed and what powers it possessed as a dominion within the British Empire
Dutch Reformed Church
Afrikaner religious organization that supported apartheid
pastoral environment
rural life based on small scale agriculture or animal husbandry --- whites felt that this lifestyle best suited the blacks
JBM Hertzog
merged the National Party with Smut's South African Party (opposed Smuts)
National Party
Afrikaner (white) party. for apartheid. wanted things to be separate between all the races.