Consciousness - Attention and Sleep (Exam 2)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Attention
ocusing consciousness on specificstimuli or aspect of stimuli
Selective attention
focusing on specific information while ignoring other information
Inattentional blindness
failing to detect available stimuli due to selective attention
Change blindness
failing to detect changes instimuli due to selective attention
What controls our sleep-wake cycle?
Our sleep-wake cycle is controlled by two main systems: the brain's internal "circadian clock" and the body's "sleep drive".The circadian clock, a part of the hypothalamus called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), is a 24-hour internal clock that is reset by light signals from the eyes, while the sleep drive builds the longer you are awake. These two systems work together to regulate when you feel awake and when you feel tired.
What are our brains and bodies doing during different sleep stages?
During non-REM sleep, the body slows down for physical restoration, with heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing decreasing. During REM sleep, the body becomes more active, with increased heart rate and blood pressure, while the brain becomes highly active, leading to dreaming and temporary muscle paralysis.
Why do we sleep?
We sleep so our bodies and brains can repair, rest, and recharge, which is essential for overall health. During sleep, the brain processes information and consolidates memories, while the body repairs cells, conserves energy, and releases necessary hormones.
Why do we dream?
Freud - dreams stem from unconscious thoughts
Manifest content
the actual images in the dream
Latent content
the unconscious thoughts, feelings, andwishes behind the manifest content
Activation synthesis
brain's internally generated signalsform dreams
Information processing
memories of events form dreams
Preserving neural pathways
purpose of dreaming is toprovide brain stimulation
Circadian rhythm
biological clock (controlled by hypothalamus)-
- Provides approximate schedule for physical processes
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
in hypothalamus -sensitive to changes in light• Controls pineal gland- Pineal gland - secretes melatonin• Melatonin - hormone that causes sleepiness
- controls the pineal gland
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
Melatonin
hormone that causes sleepiness
Circadian Rhythms
darkness & light
Darkness
SCN directs pineal gland to secrete melatonin
Light
SCN directs pineal gland to stop secretingmelatonin
Artificial lighting
interferes with circadian rhythm
types of sleep
1. Non-rapid eye movement (N-REM) - 3 stages
2. Rapid eye movement (REM) - brain waves resemble wakefulness
Sleep Stages
90-minute cycles of sleep stages
1. Non-rapid eye movement (N-REM) - 3 stages
N1
N2
N3
N1
light sleep- Hypnic or hypnagogic jerk- Hypnagogic hallucinations
N2
true sleep• Brain activity slows• Reductions in heart rate and muscle tension
N3
deep sleep• Further slowing of brain activity• Hard to awaken, disoriented when awakened• Growth hormones released from pituitary
Rapid eye movement (REM)
Eyes move back and forth- Heart rate, blood pressure, breathing - rapid or irregular- Sleep paralysis- "Paradoxical sleep"- Dreams
Sleep Cycle
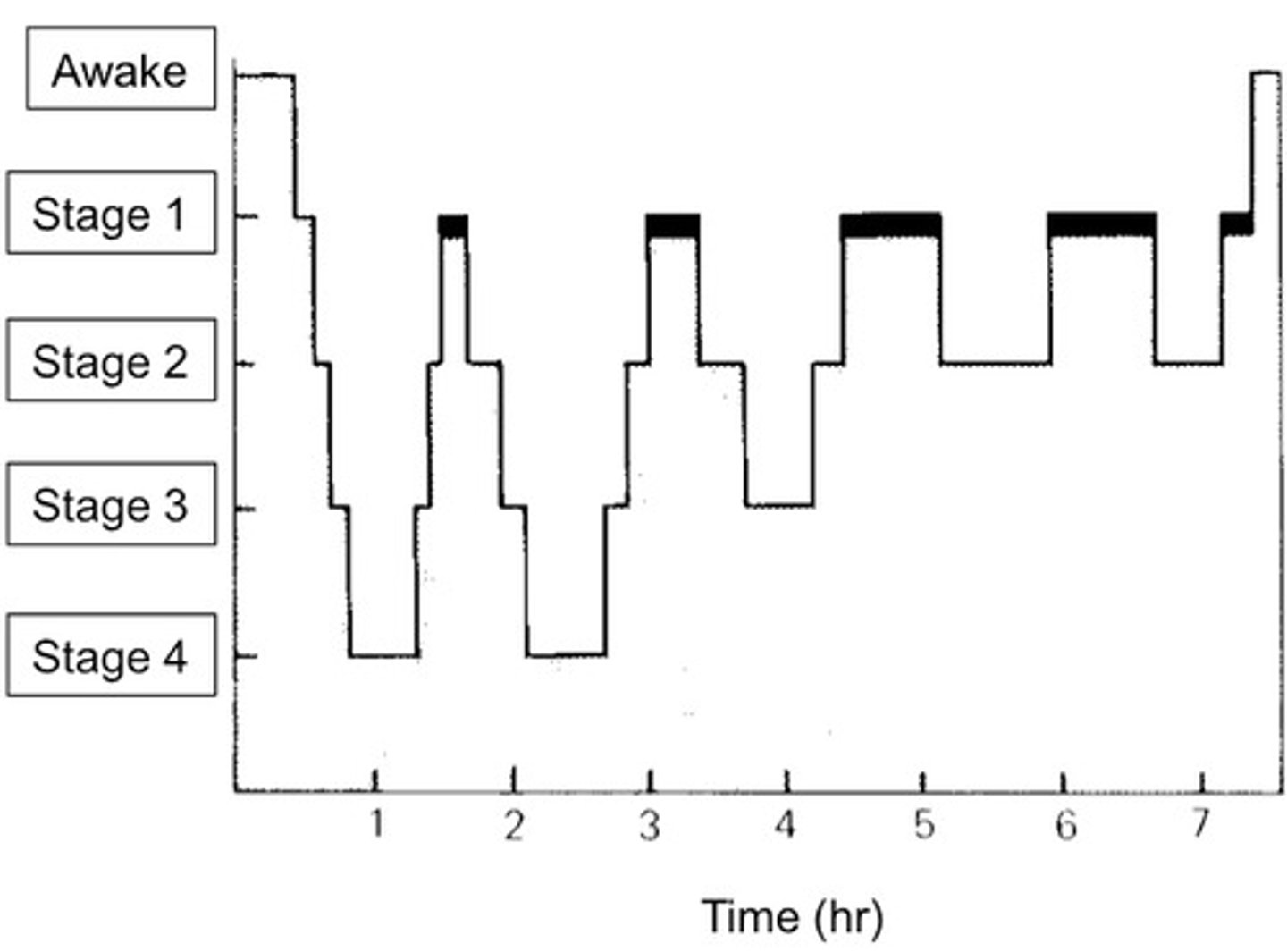
Evolutionary/adaptive theory
protection - not outand vulnerable to predators in the dark
Restorative theory
sleep supports growth and healing- Production of growth hormone- Supports immune functioning
Sleep deprivation
slower healing, reduced immune system activity
impairment of memory formation
Information processing theory
sleep supports cognitive processes- Supports learning- Restores and rebuilds memories, Supports creative thinking
Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Irritability, mood disruption• Increased risk of depression• Increased risk of obesity