Amino Acid Metabolism and Urea Cycle Overview
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Amino acids are not stored in the body
There is no “storage” protein in the body whose sole function is to maintain a supply of amino acids
Glucose is stored as glycogen
Fats are stored as triacylglycerols (TAG)
Amino acids have to be obtained from
The ____
Synthesized _____
Produced from ______
diet, de novo, protein degradation
Catabolism of amino acids involves the removal of nitrogen which is released as: ____, ____, and _____
ammonia, urea, uric acid
Protein digestion
In the stomach
HCl denatures the protein
HCl activates _____ to form _____, which breaks complex proteins to polypeptides
pepsinogen, pepsin
Protein digestion
In the pancreas
The protease enzymes _____, ______, _______, and _______ break down polypeptides to oligopeptides
trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypeptidase
Protein digestion
In the small intestine
_______ cleave oligopeptides to small peptides and free amino acids which are taken into the liver
Aminopeptidases
Catabolism of amino acids: Transamination
Reaction(s) involving the removal of nitrogen from amino acids
Removal of α-amino group
Reaction involves the transfer of the α-amino group to α-ketoglutarate to form ______ and an _____
glutamate, a-ketoacid
Catabolism of amino acids: Transamination
Reaction(s) involving the removal of nitrogen from amino acids
Removal of α-amino group
Reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme (______) along with a prosthetic group (_______)
aminotransferase, pyridoxal phosphate
Catabolism of amino acids: Transamination
Two aminotransferases are
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Catabolism of amino acids: Transamination
______ (prosthetic group) transfers the amino group
Pyridoxal phosphate
Catabolism of amino acids: Transamination
_________ are all α-keto acids
They have a –C=O group on the carbon adjacent to the –COOH group
Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate
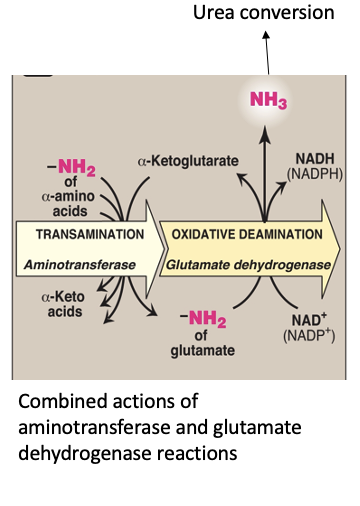
Catabolism of Amino Acids
Oxidative deamination results in removal of the amino group as free ammonia
Enzyme: _______
Uses NAD+ or NADP+
glutamate dehydrogenase
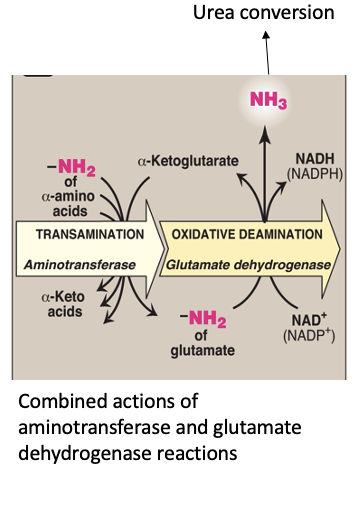
Catabolism of Amino Acids
Occurs in the liver and kidney
Products are ________ and ______
Ammonia is toxic, and is converted to urea in the liver
a-ketoacids, ammonia (NH3)
______ is the major disposal form of amino groups from amino acids
Derived from ammonia, aspartate and carbon dioxide
90% of the nitrogenous components of urine
Urea
Synthesis and elimination of Urea
Urea is produced in the _____, transported in the blood to the _____, and excreted in _______
liver, kidneys, urine
Synthesis and elimination of Urea
Some urea is cleaved by ______ in the intestine into ammonia which is removed in the feces
In kidney failure, high levels of urea are found in the blood
bacterial urease
Nitrogen elimination
Removal of α-amino group of AA
_____ and ______
NH3 is toxic
Converted to urea in the liver
Eliminated in the urine
Transamination, oxidative deamination
Amino acids that we have to get from our diet are ______ amino acids
essential
Amino acids that our cells can synthesize are______ amino acids
have biosynthetic precursors in the carbohydrate and lipid biosynthetic pathways
nonessential
Type of amino acid: Glucogenic amino acids
Their catabolism yields ______ or intermediates of the TCA cycle
These are substrates for gluconeogenesis
pyruvate
Type of amino acid: Ketogenic amino acids
Their catabolism yields ______ or its precursors, acetyl CoA and/or acetoacetyl CoA
These are substrates for ketogenesis
They do not give rise to the net formation of glucose
acetoacetate
List the ketogenic essential amino acids
Leucine (Leu,L), Lysine (Lys,K)
List the Glucogenic and Ketogenic essential amino acids
Isoleucine (Ile, I), Phenylalanine (Phe, F), Tryptophan (Trp, W)
List the Glucogenic essential amino acids
Histidine (His, H), Methionine (Met, M), Threonine (Thr, T), Valine (Val, V)
Amino acid biosynthesis can be divided into six families of pathways
Glutamate, aspartate, serine, alanine, aromatic AA, histidine
What is the source of Glutamate
a-ketoglurarate
What is the source of Aspartate
oxaloacetate (OAA)
What is the source of Serine
3-phosphoglycerate
What is the source of Alanine
pyruvate
What is the source of Aromatic Amino Acids
phsophoenolpyruvate, erythrose 4-phosphate
What is the source of Histidine
ribose 5-phosphate