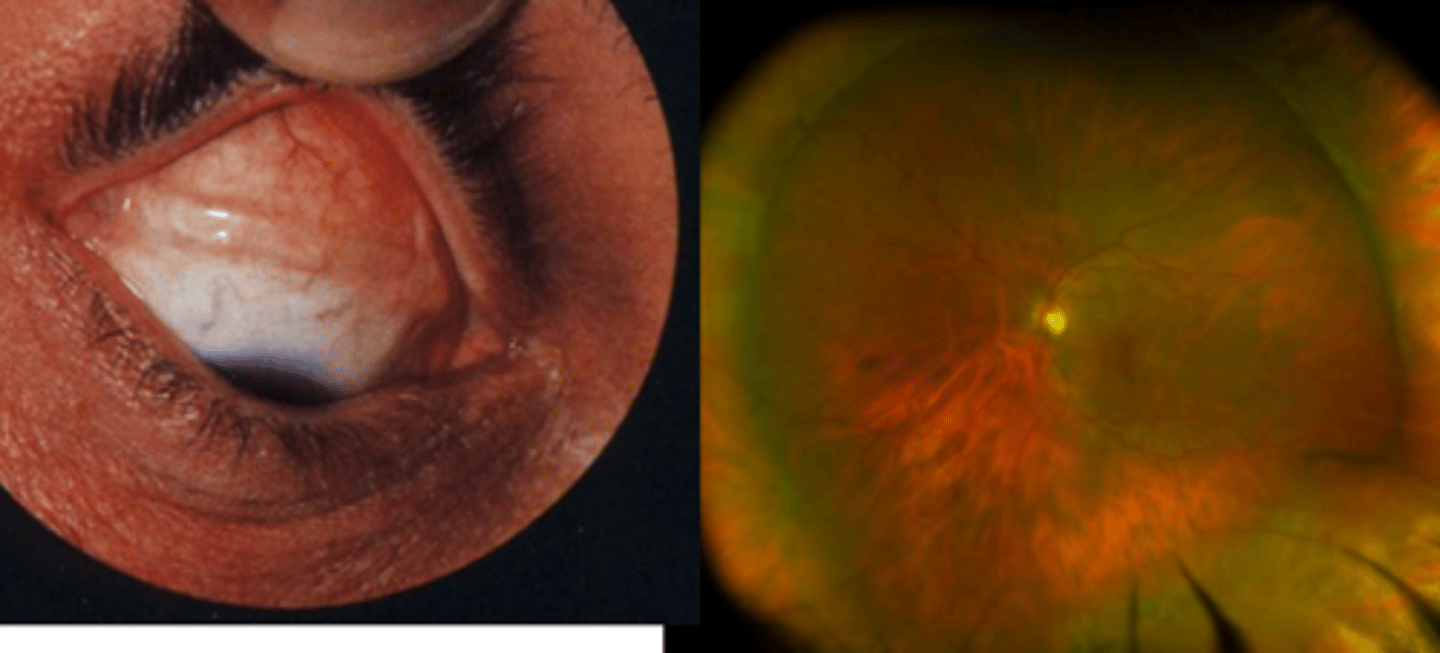
Peripheral Retina Pathology
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
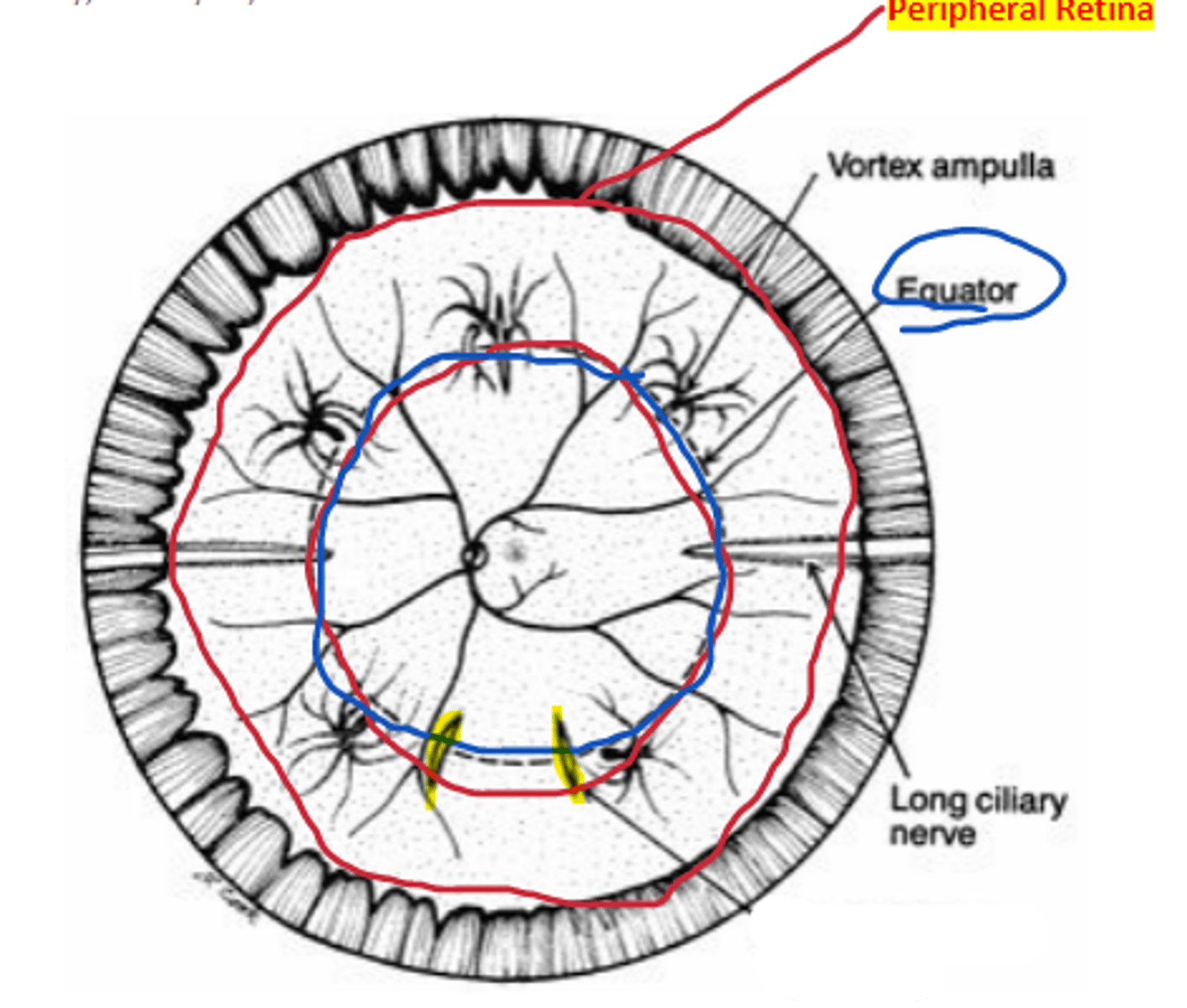
Equator
area of the retina that is an imaginary line drawn from the vortex ampullae in each retinal quadrant.
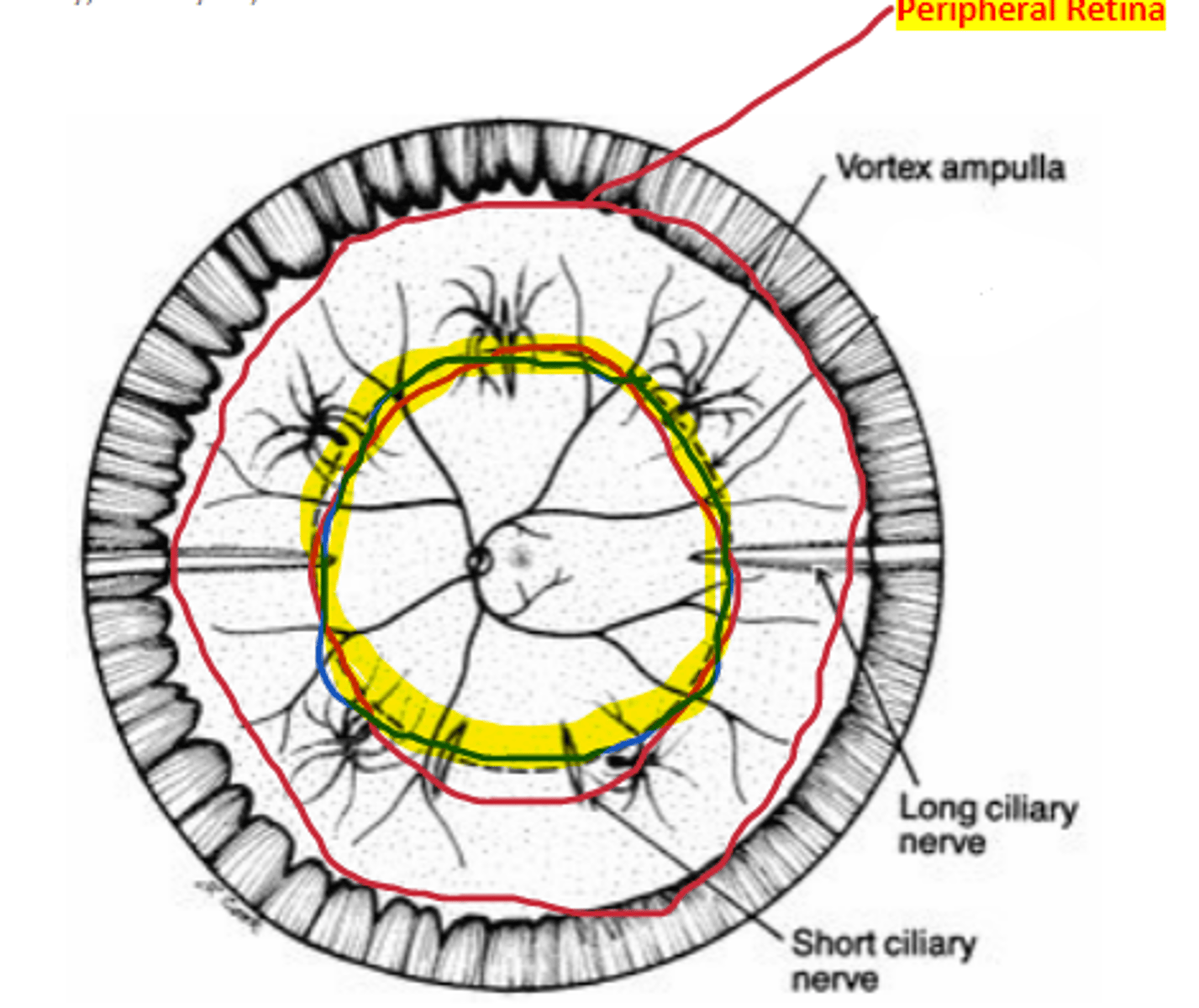
Peripheral retina
area of the retina anterior to the equator extending to the ora serrata, approximately 3 DD
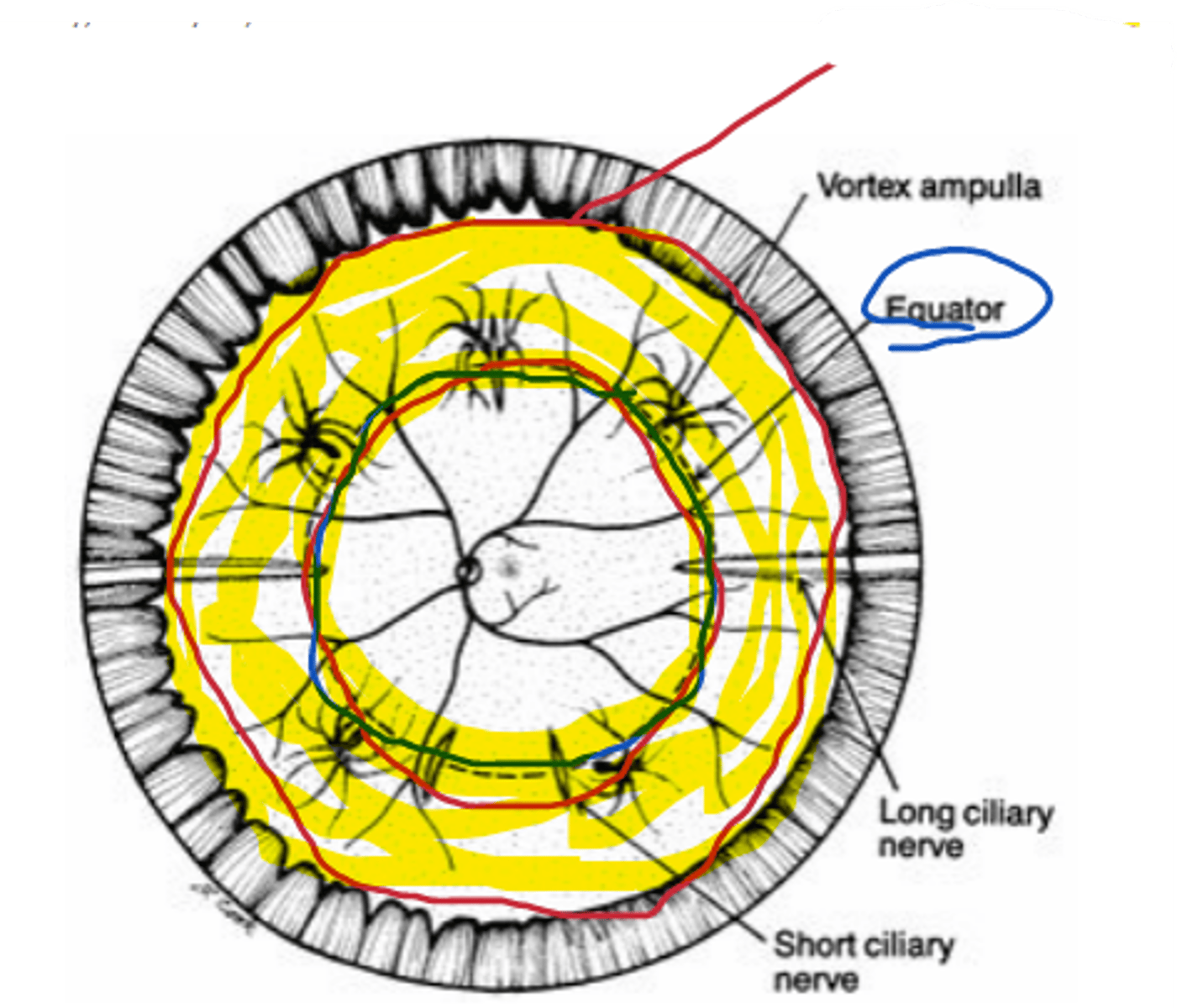
40%
percentage of ocular fundus encompassed by the peripheral retina
Long ciliary
nerve/artery complex located at the 3 and 9 o'clock positions separating inferior and superior retina.
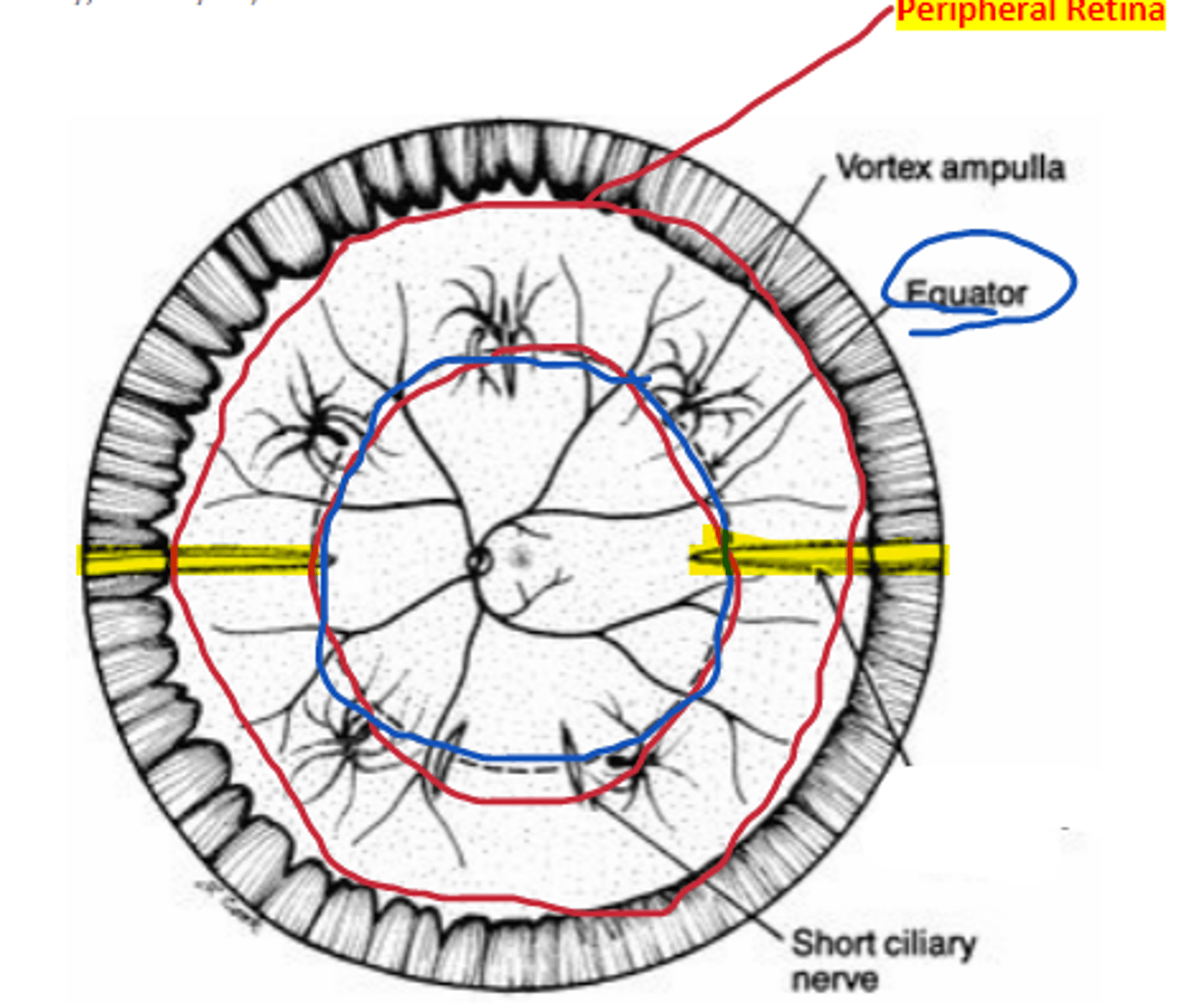
Short ciliary
nerve/artery complex located at the 12 and 6 o'clock positions separating nasal and temporal retina.
smaller
Retinal blood vessels become _____ in the periphery
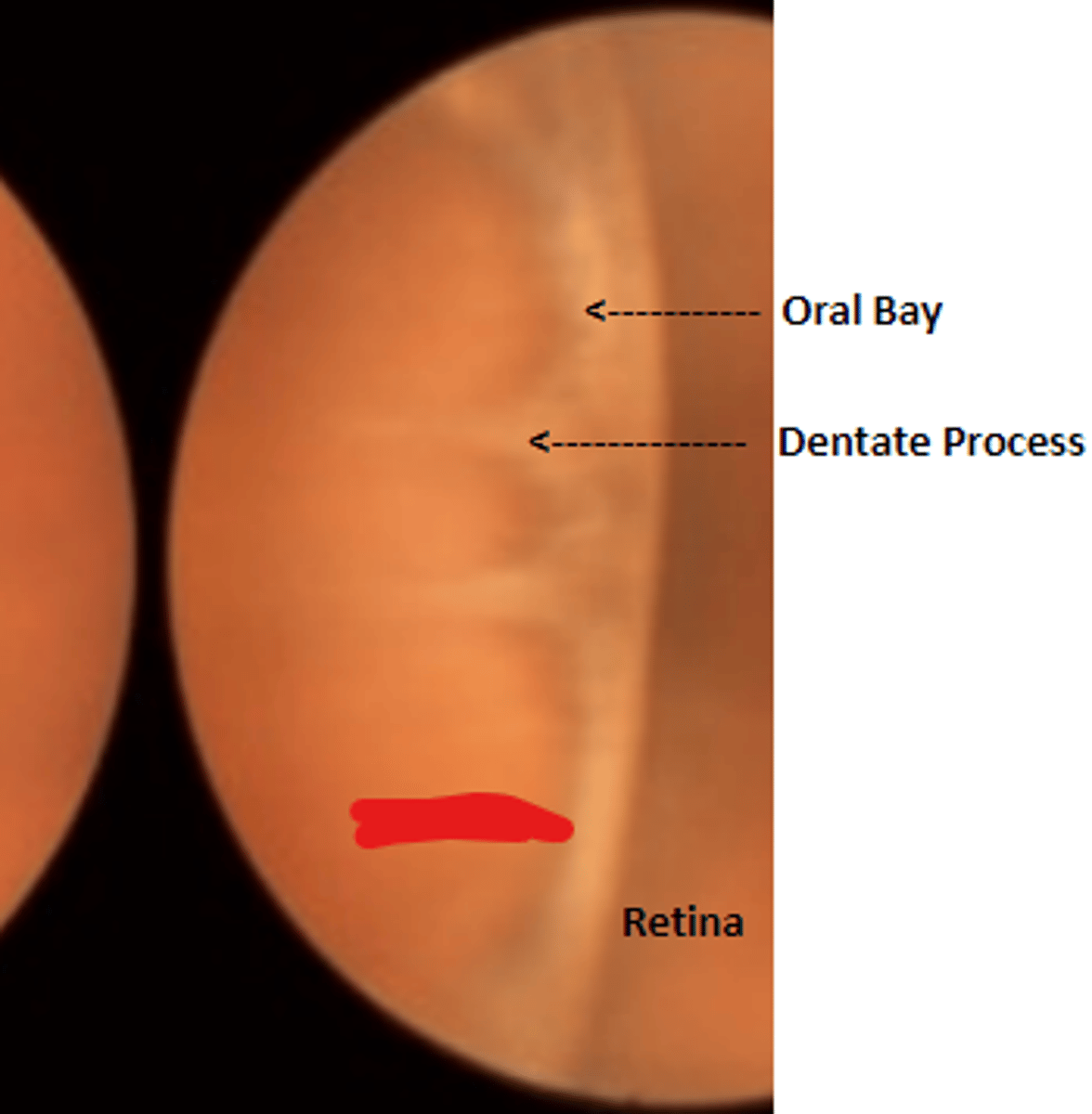
Ora serrata
the junction between the retina and ciliary body denoting the anterior limit of the retina. Retinal pigmentation decreases towards this area. Is more scalloped nasally.
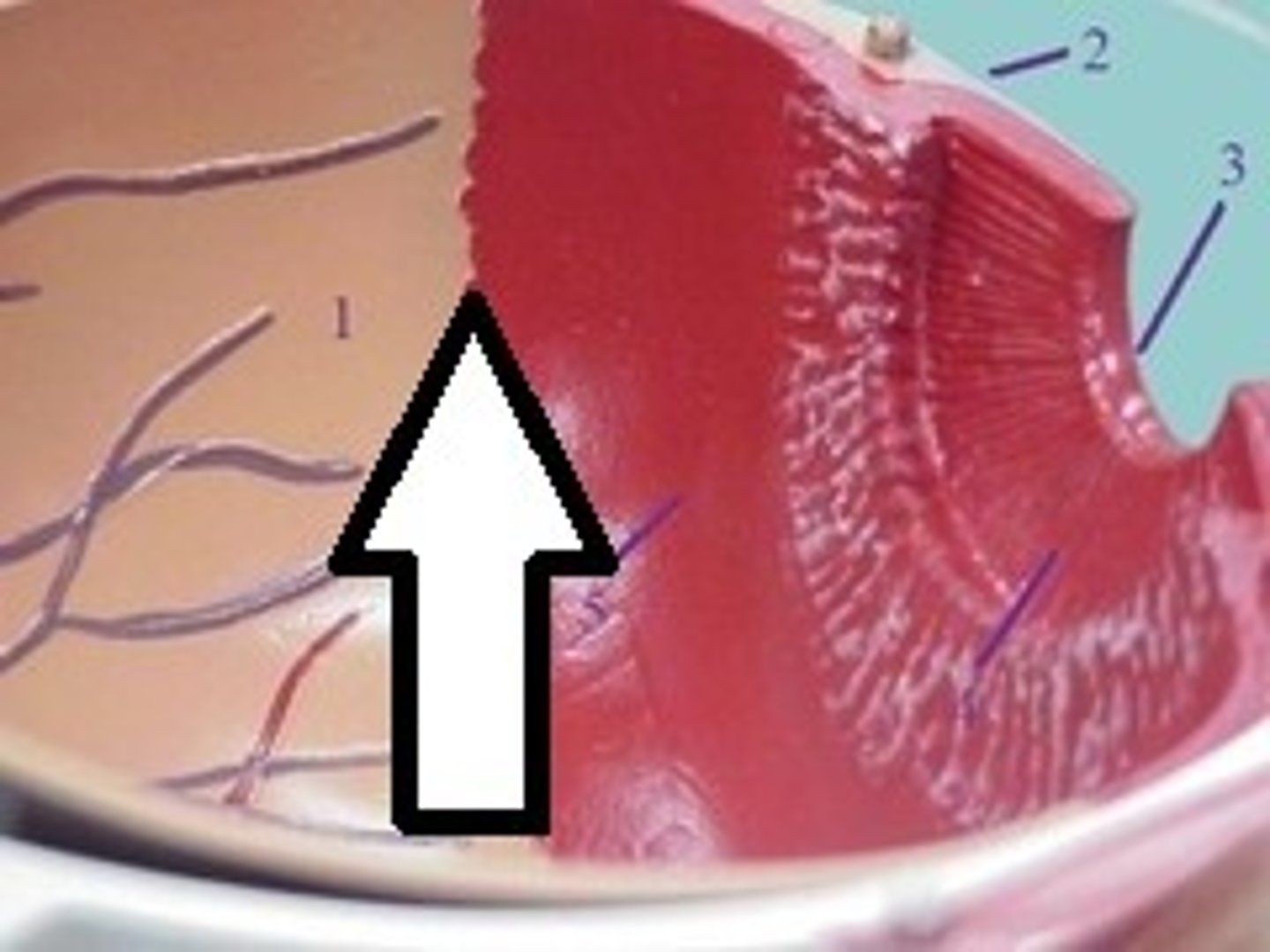
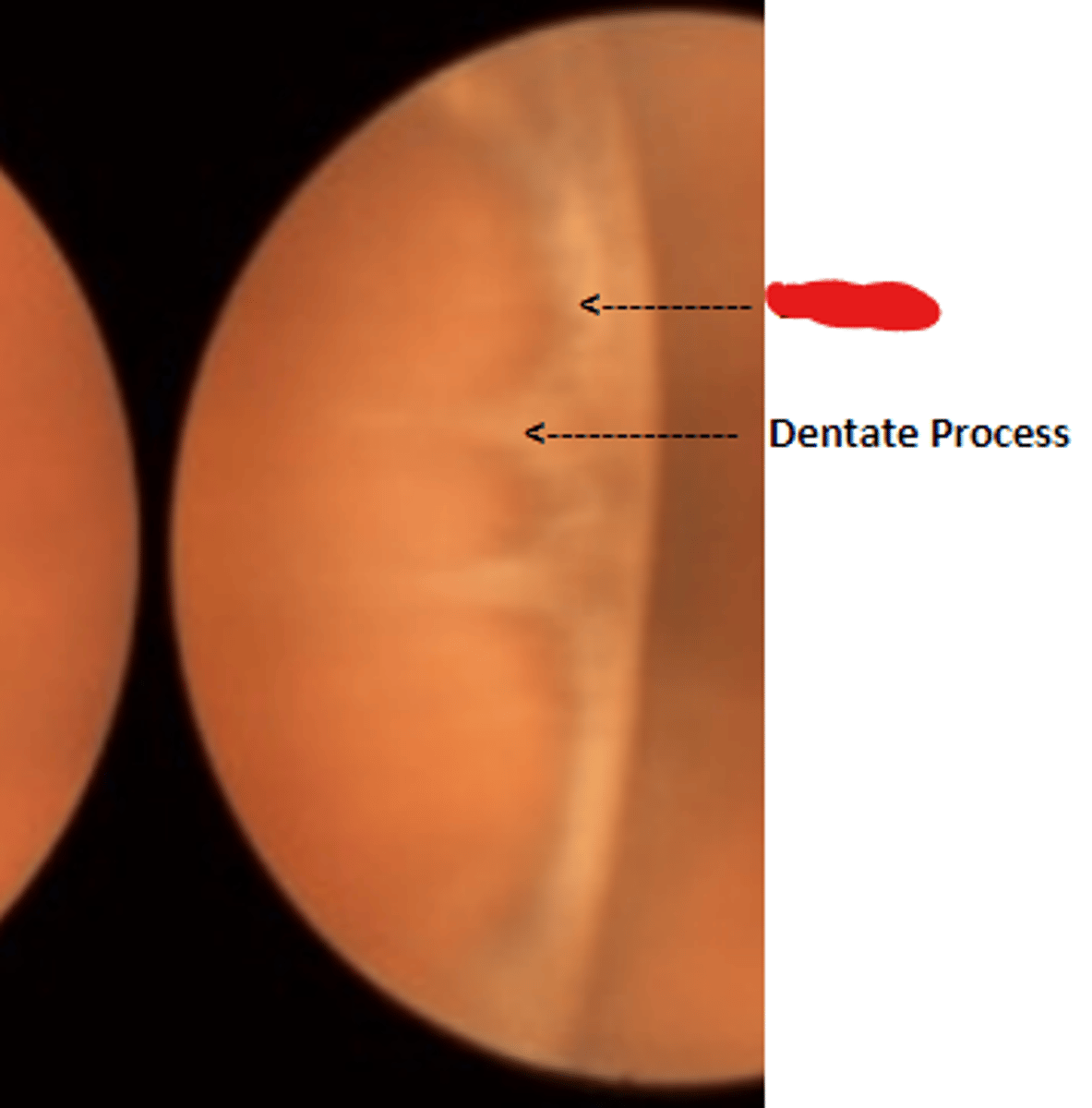
Dentate processes
white teeth like projections of the retina into the pars plana. Delineate oral bays.
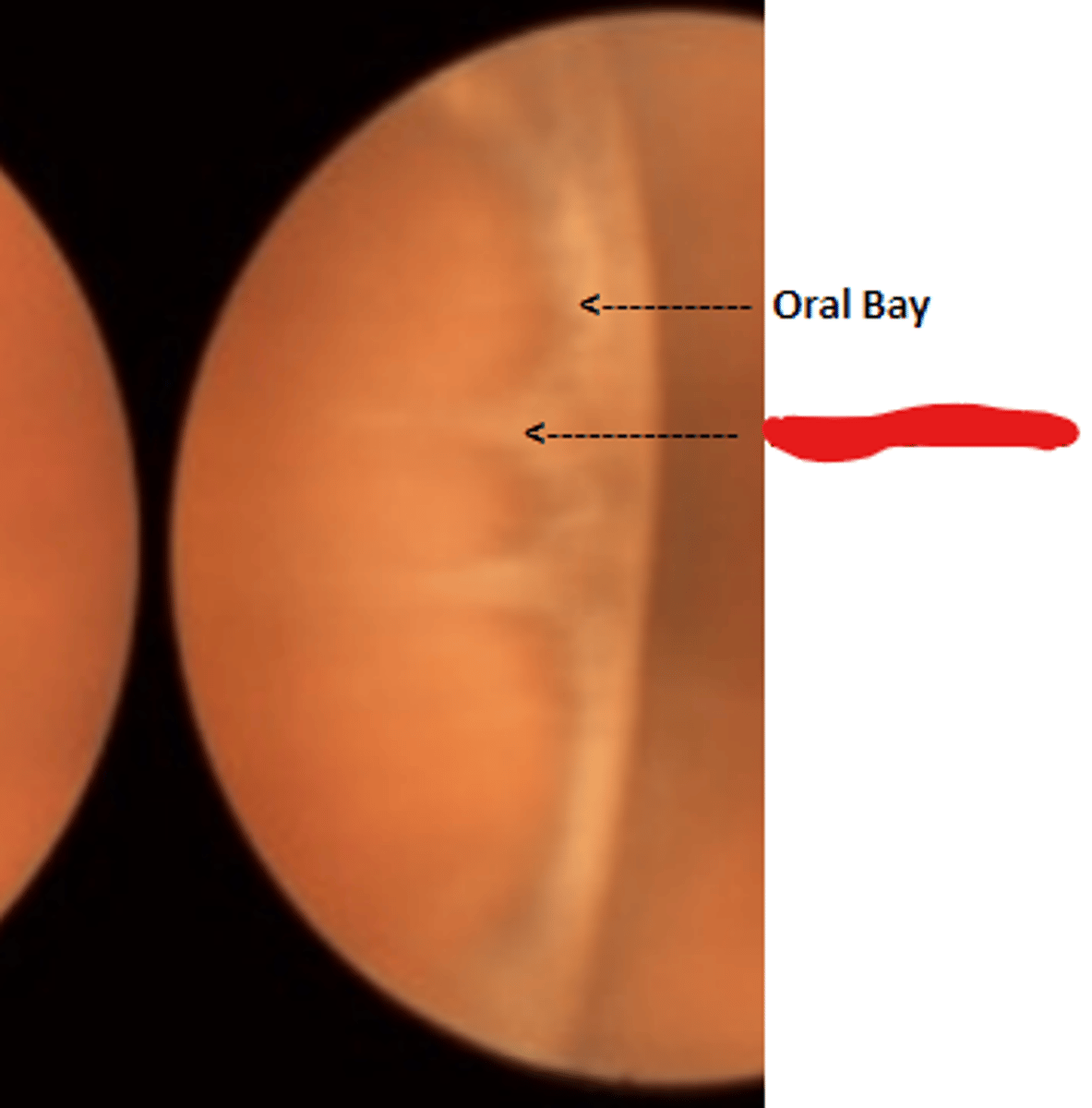
Oral bays
round extensions of the ora serrata and pars plana. Is enclosed by two adjacent dentate processes.
Pars plana
brown anatomical landmark extending from the ora serrata to the ciliary processes
Meridional fold
permanent folding of all retinal layers oriented perpendicular to the ora serrata. Is a developmental anomaly present in 25% of the population thought to be extensions of the dentate processes. Is usually bilateral in the superior nasal quadrant, more common in males.
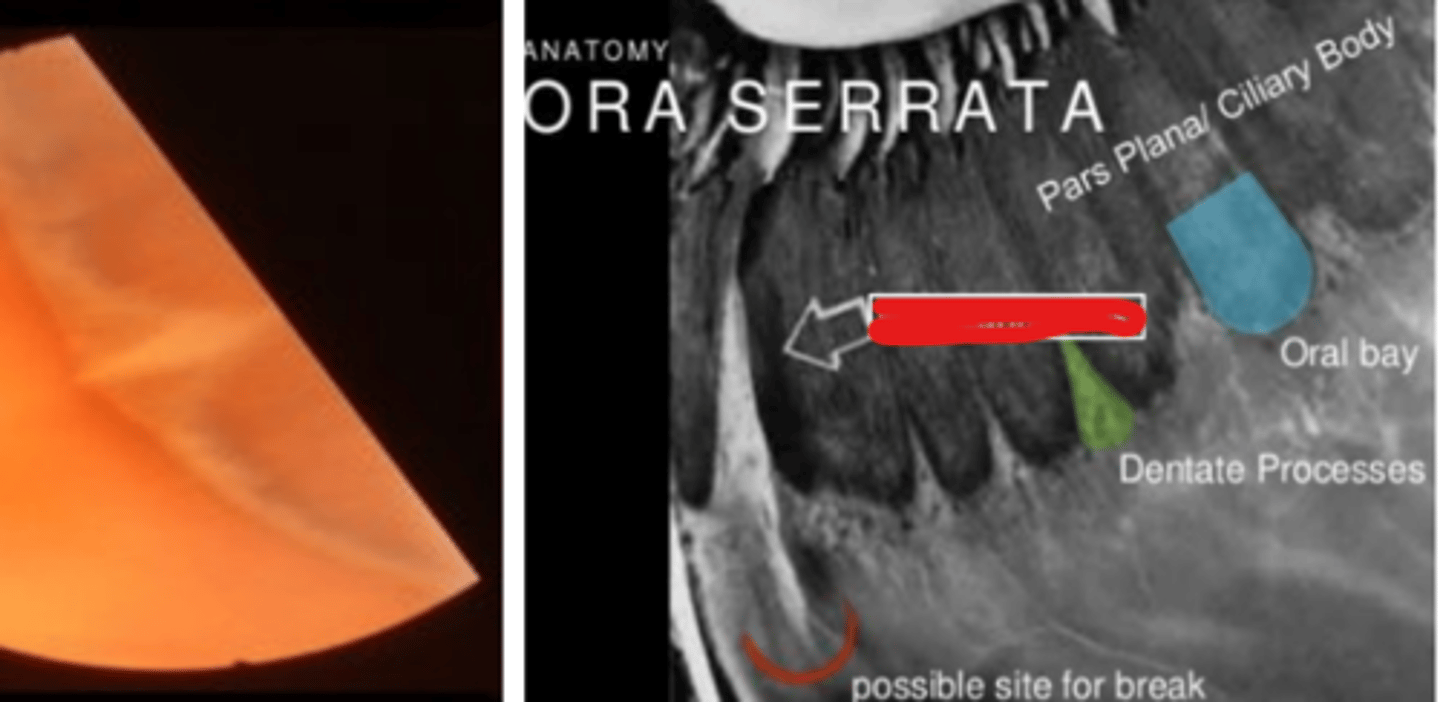
retinal break
The management of meridional fold is documentation and monitoring due to a slight increased risk in ____ (at the tip of the fold)
Peripheral (senile) pigmentary degeneration/reticular degeneration
peripheral RPE degeneration appearing as granular "bone spicule" piment between the ora and equator in 20% of the population over 40 yo. Is usually bilateral. Is benign with no associated risks indicating monitoring sufficient management.
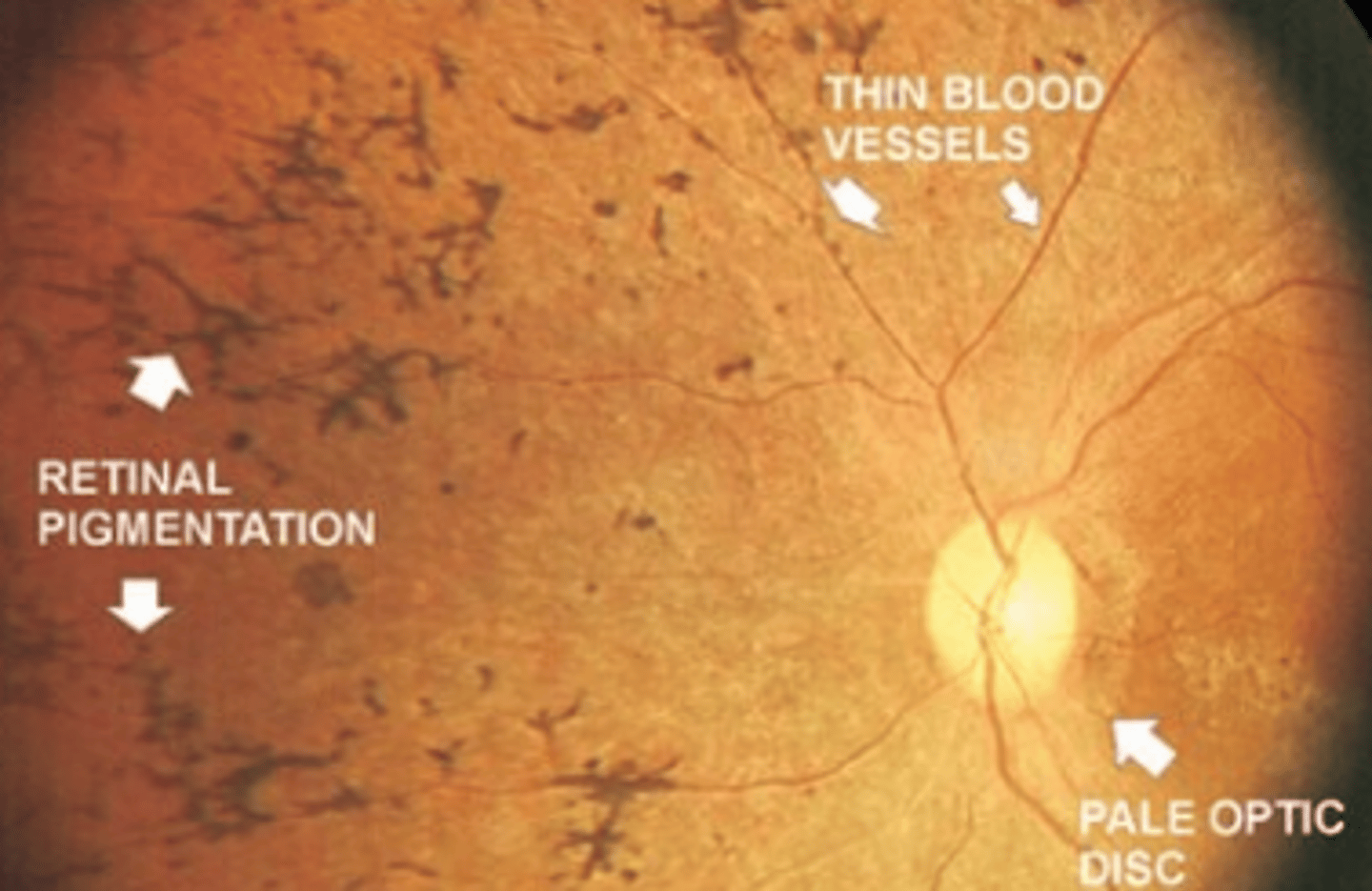
retinitis pigmentosa
RPE pigmentation which appears similar to reticular degeneration when seen in younger patients is suspicious of _____. The condition will occur with other retinal findings such as thinned blood vessels and a pale optic disc.
Alzheimer's disease and chronic kidney disease
Drusen of the peripheral retina can be seen with or without AMD associated with aging. Recent studies consider a potential association with these two conditions. However, this information is not diagnostically significant. Referral to PCP is indicated.
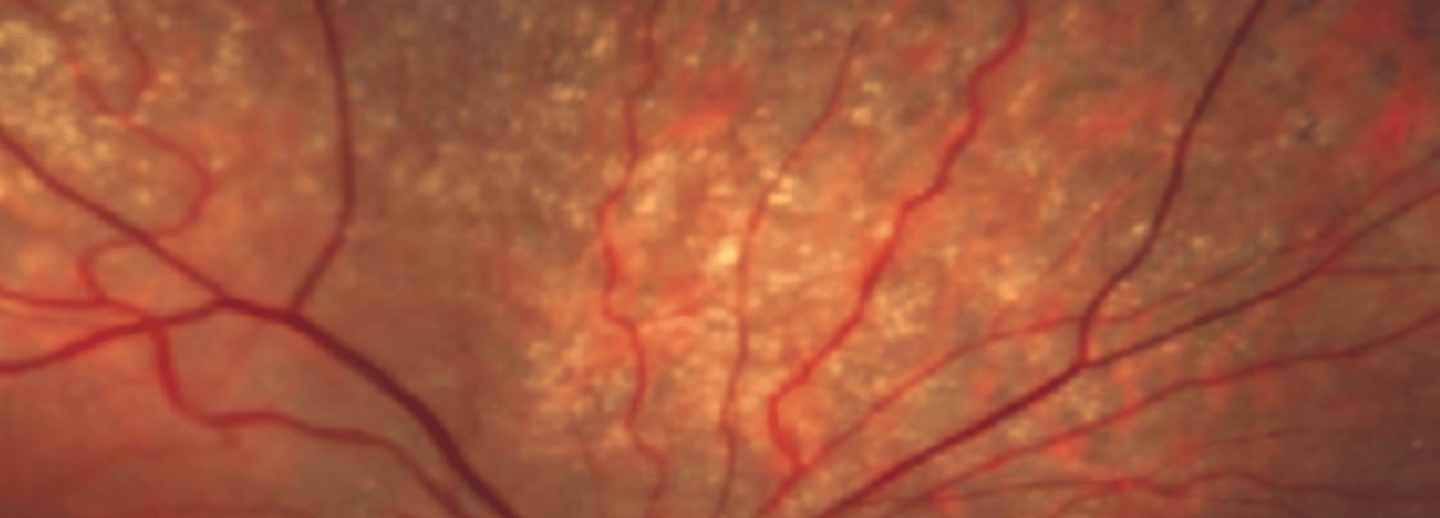
AMD
reticular degeneration has a strong association with this other retinal condition. Patients with peripheral drusen should also be screen for this condition using a macular OCT.
Pavingstone degeneration/cobblestone degeneration
outer retina and chorioretinal degeneration resulting from occlusion of compartments of the choriocapillaris. Is usually bilateral, asymmetrical, and inferior occurring between the equator and ora. Is associated with increasing age (above 40) and is generally benign with no increased risk of retinal breaks.
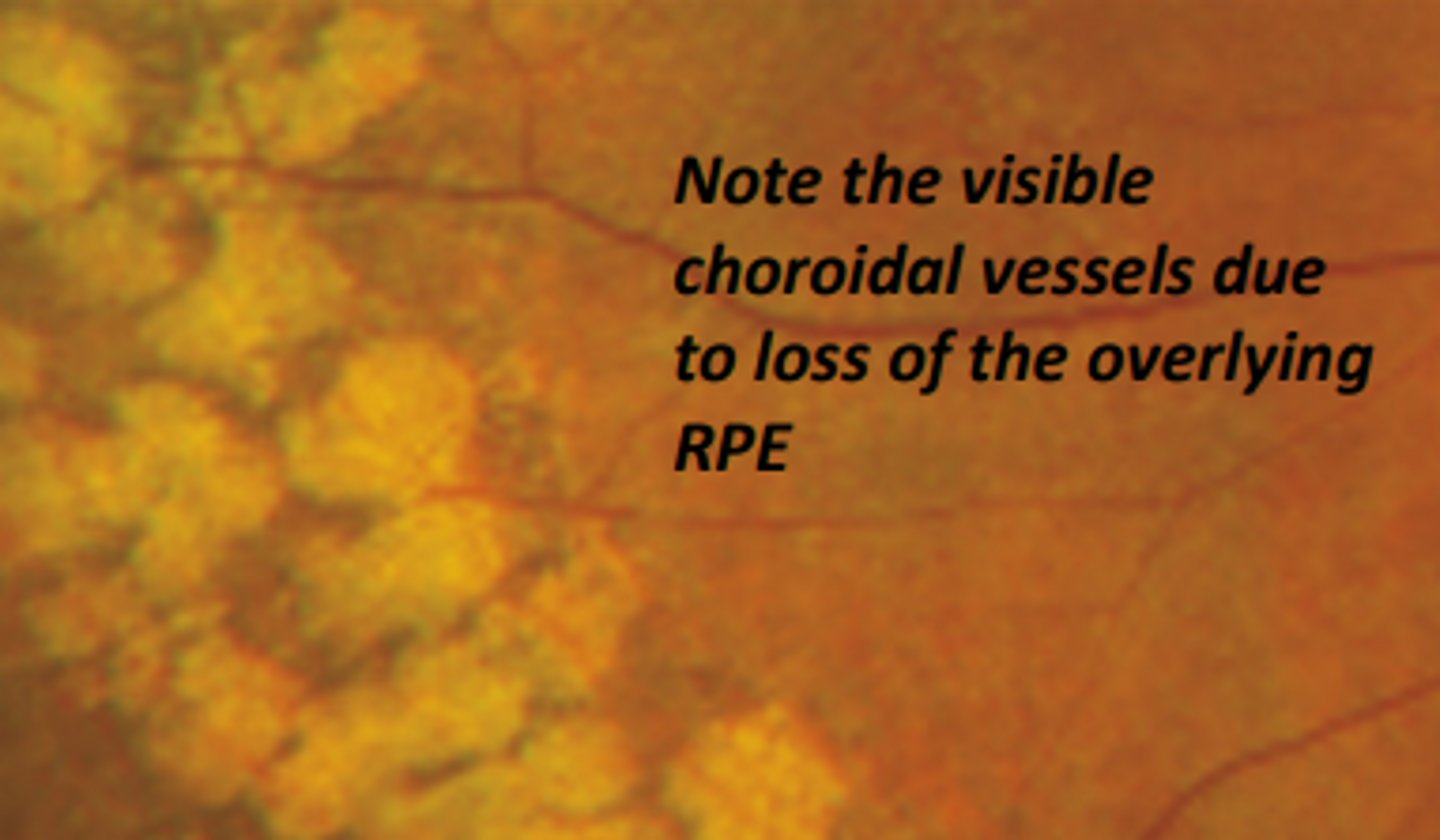
-Larger affected area
-inner retina remains intact
-no history of ocular trauma
three characteristics of pavingstone degeneration that can help differentiate this diagnosis from a chorioretinal scar.
Peripheral cystoid degeneration
the most common** intra-retinal degeneration involving cystoid like changes of the INL/OPL which can extend to the sensory retina. Is generally benign, but can cause splitting of the sensory retina (retinoschisis) if they coalesce to form large cystic spaces. Potential for retinal hole and detachment.
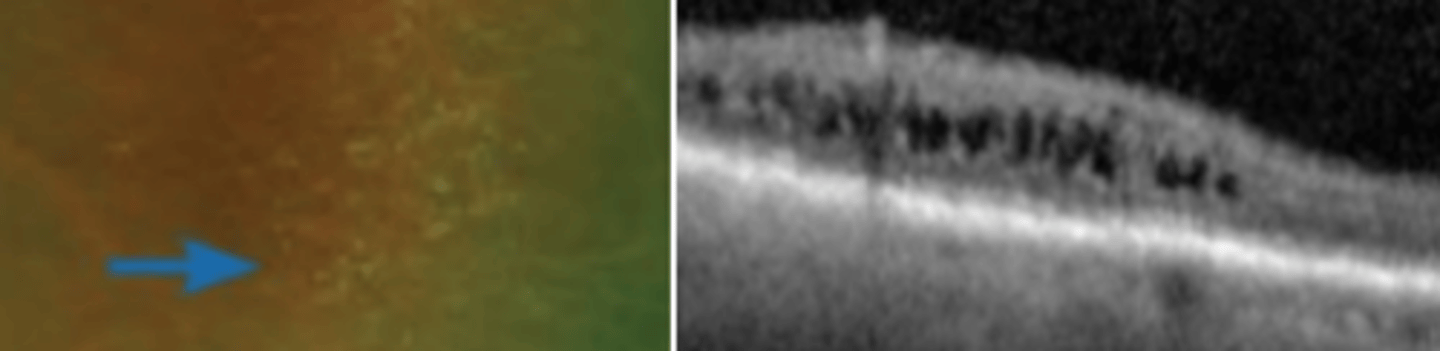
Retinoschisis
splitting of the sensory retina commonly caused by the coalescing of peripheral cystoid degeneration. Occurs in less that 20% of patients having peripheral cystoid degeneration, so there is generally a low risk.
White with pressure (WWP)
white appearance of the peripheral retinal observed in 32% of patients upon scleral depression. Does not indicate the presence of retinal disease.
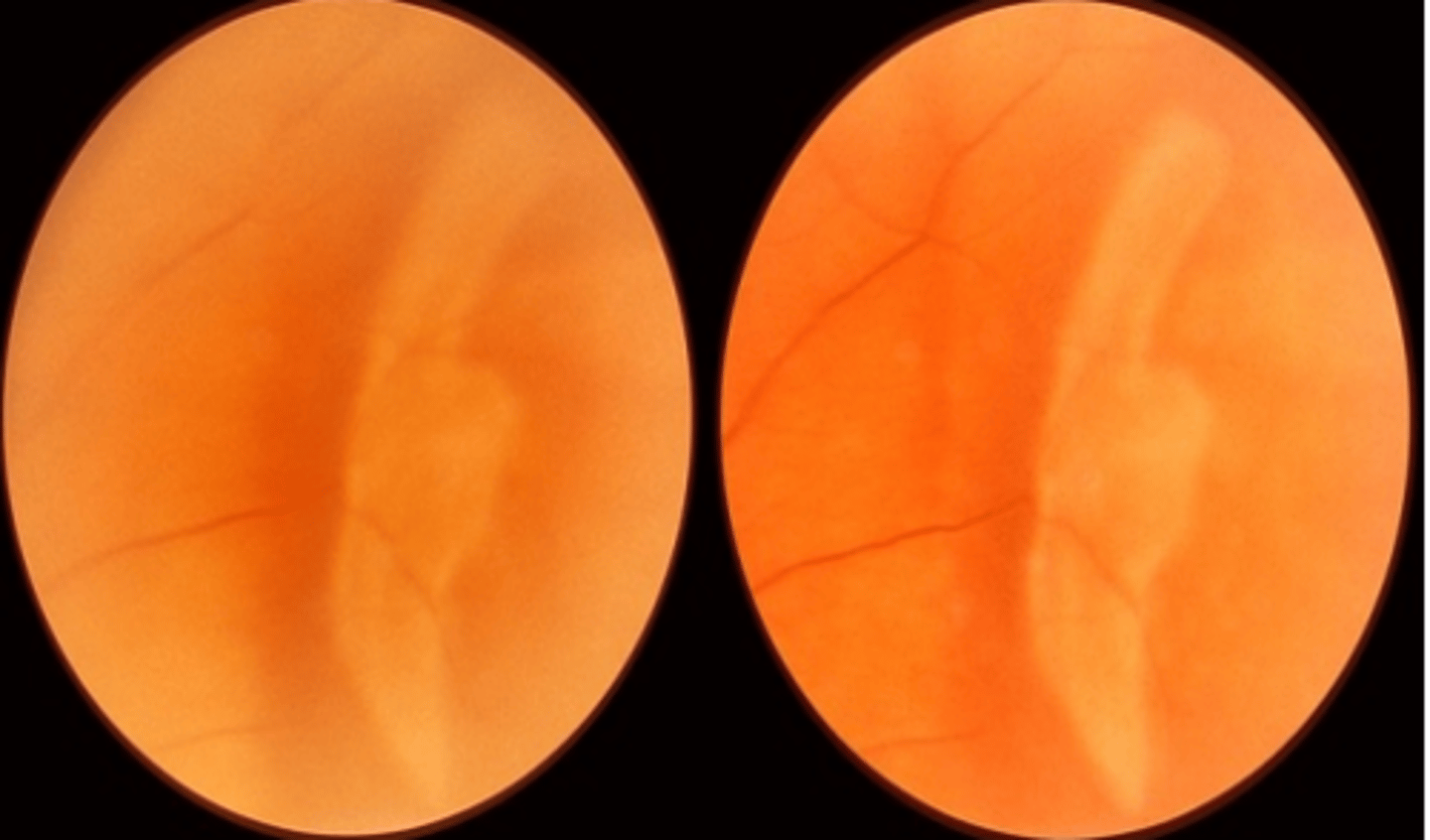
White without pressure (WWOP)
white appearance of the peripheral retina visible without scleral depression. Is thought to be caused by an abnormal vitreo-retinal relationship resulting in disorganization of the NFL. Could also be caused by thickening ellipsoid zone. Is more common in dark fundi and myopes. Is usually temporal and bilateral.
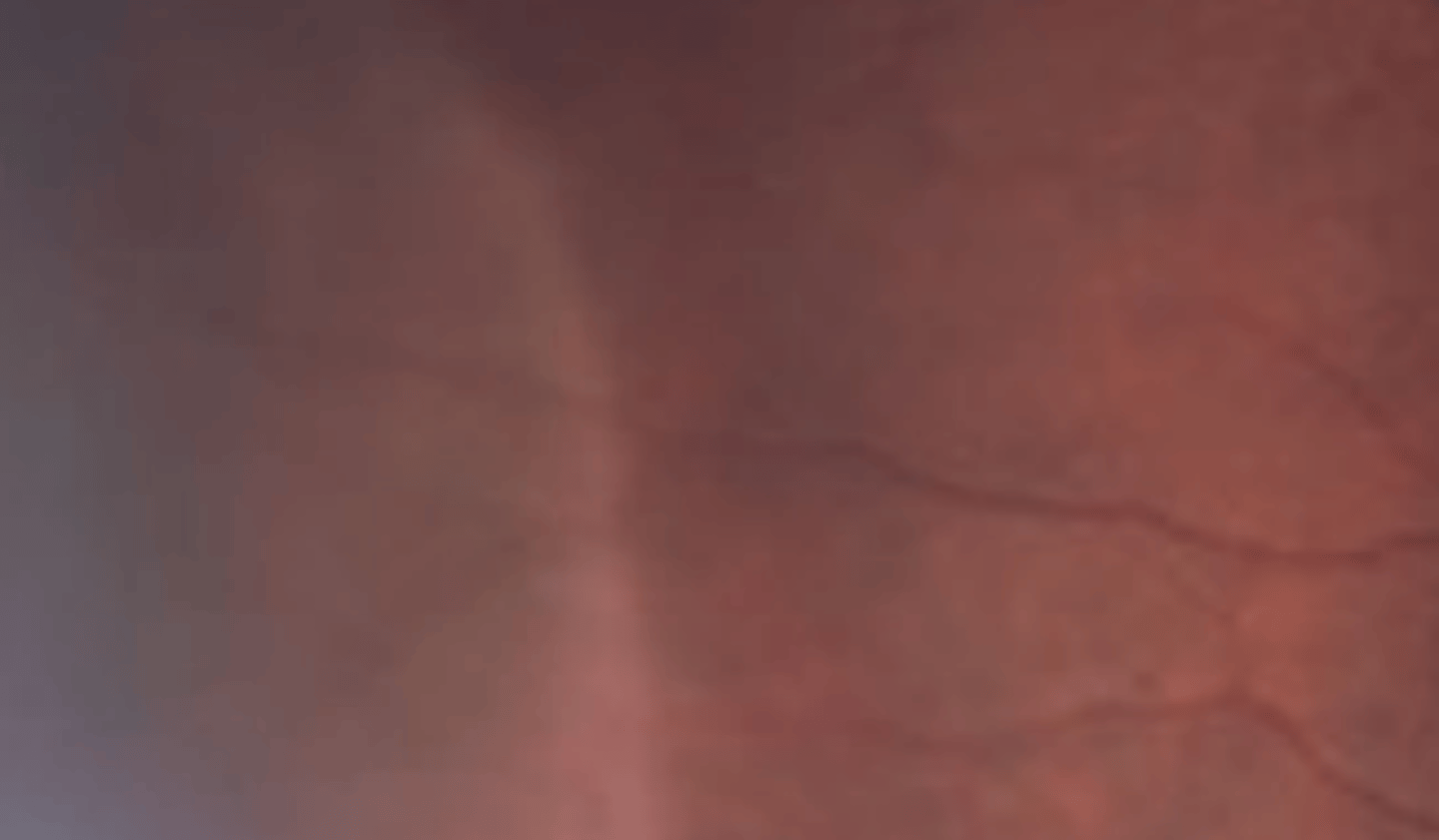
Dark without pressure
patches of darkened retina associated with changes in the outer retina. Occurs in the central to mid peripheral zone. Generally benign and can be transient, but may have an association with sickle cell disease
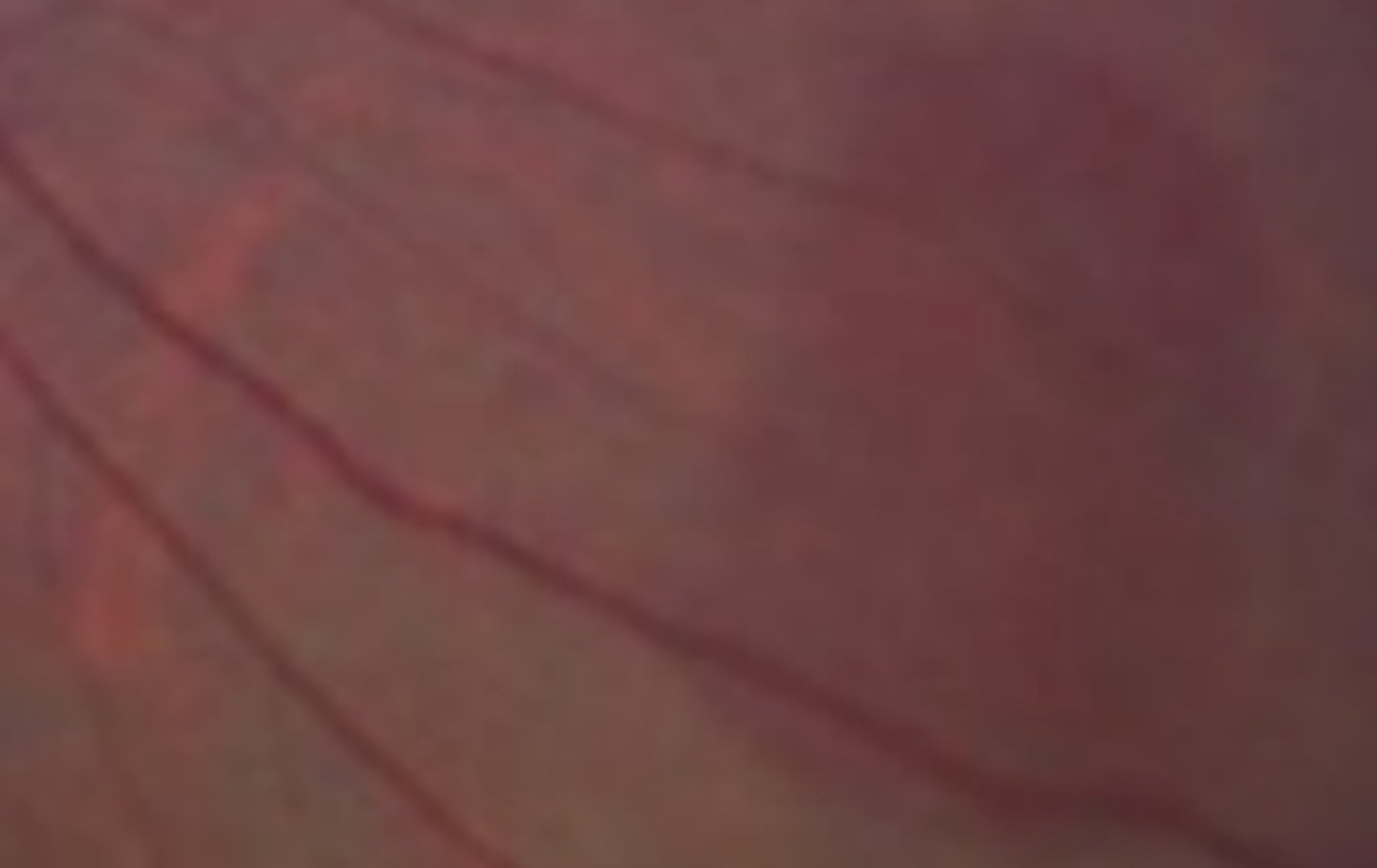

Less reflectivity of EZ, may occur in the central retina
two characteristics of dark without pressure that differs from white without pressure.
Atrophic retinal holes
full thickness breaks in the retina caused by retinal thinning thought to be secondary to underlying vascular insufficiency. Is not associated with vitreoretinal traction and patients are usually asymptomatic having low risk for retinal detachment or tears. Common in myopes. Can occur independently or through patches of lattice degeneration.
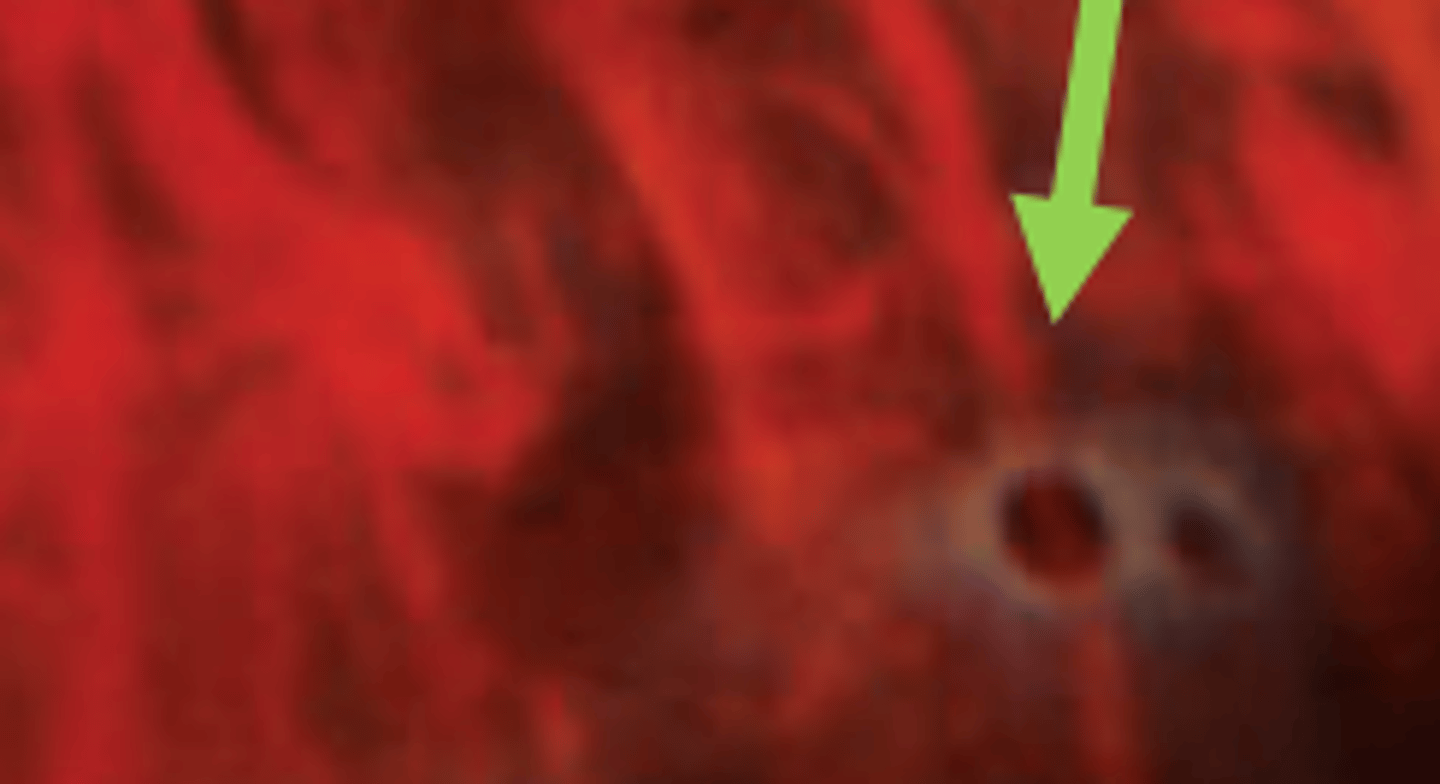
Sensory retinal detachment
fluid accumulation between the sensory retina and RPE may cause this type of retinal detachment in 10% of patients having atrophic retinal holes. Can be clinically observed as a cuff of edema surrounding the lesion
3
Pigment surrounding an atrophic retinal hole is good because it indicates that the hole has been present for at least ___ months and that it is making an attempt at repair
monitor annually
what is the management for an atrophic retinal hole with pigment?
monitor annually
what is the treatment for an atrophic retinal hole that is asymptomatic with no edema?
monitor DFE 3-6 months, co-manage with retina under certain circumstances
what is the treatment for an atrophic retinal hole that is asymptomatic with edema <1 DD?
refer to retina
what is the treatment for an atrophic retinal hole that is asymptomatic with edema >1 DD?
Operculated retinal holes
holes in the retina caused by abnormal vitreo-retinal adhesion which may be preceded by a retinal tuft. A portion of sensory retina detaches from the RPE (operculum) and remains attached to the vitreous. If the operculum does not completely detach, refer to retina is indicated due to slight increased chance of retinal detachment. Treatment is the same as for an atrophic hole.
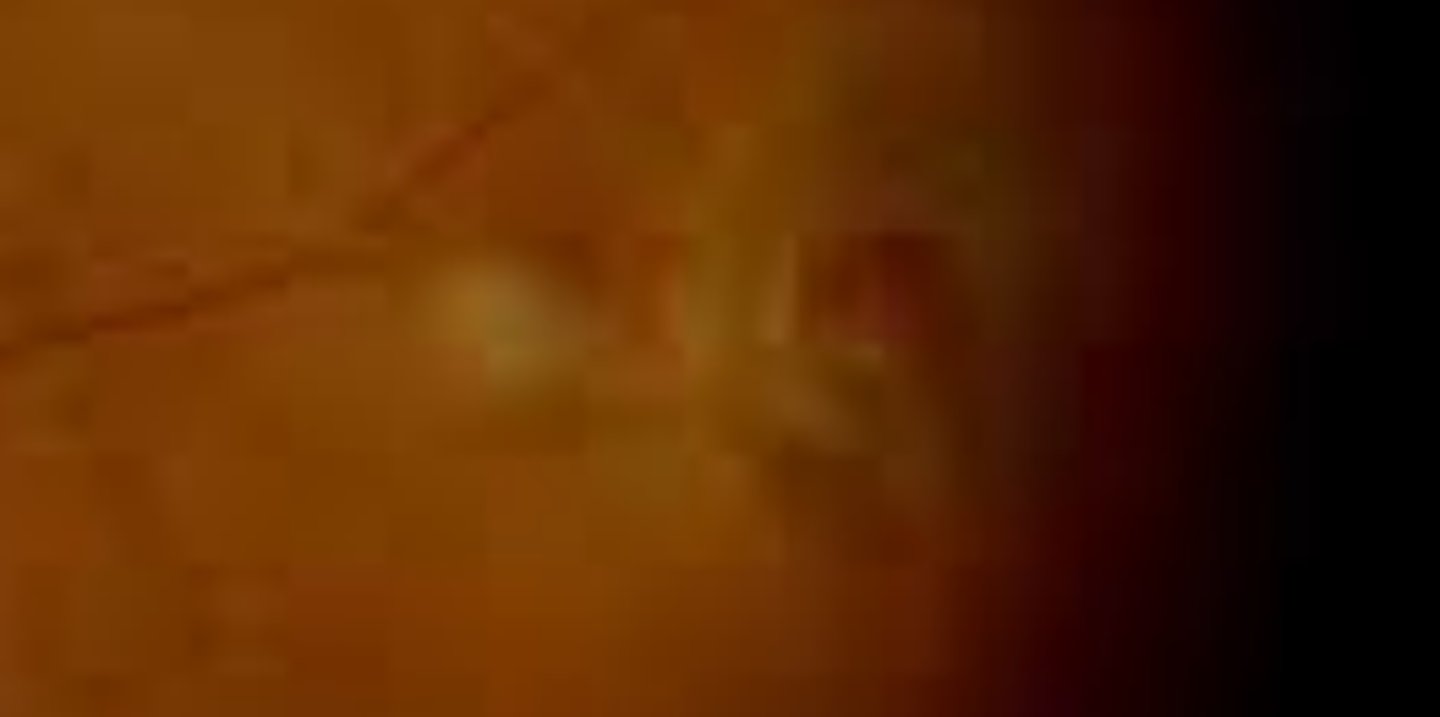

Horseshoe (flap) tear
a full thickness sensory retina break that can be caused by vitreo-retinal adhesions or trauma. The base of the tear remains attached to the RPE whereas the free end remains attached to the vitreous being pulled and being a large risk for retinal detachment.
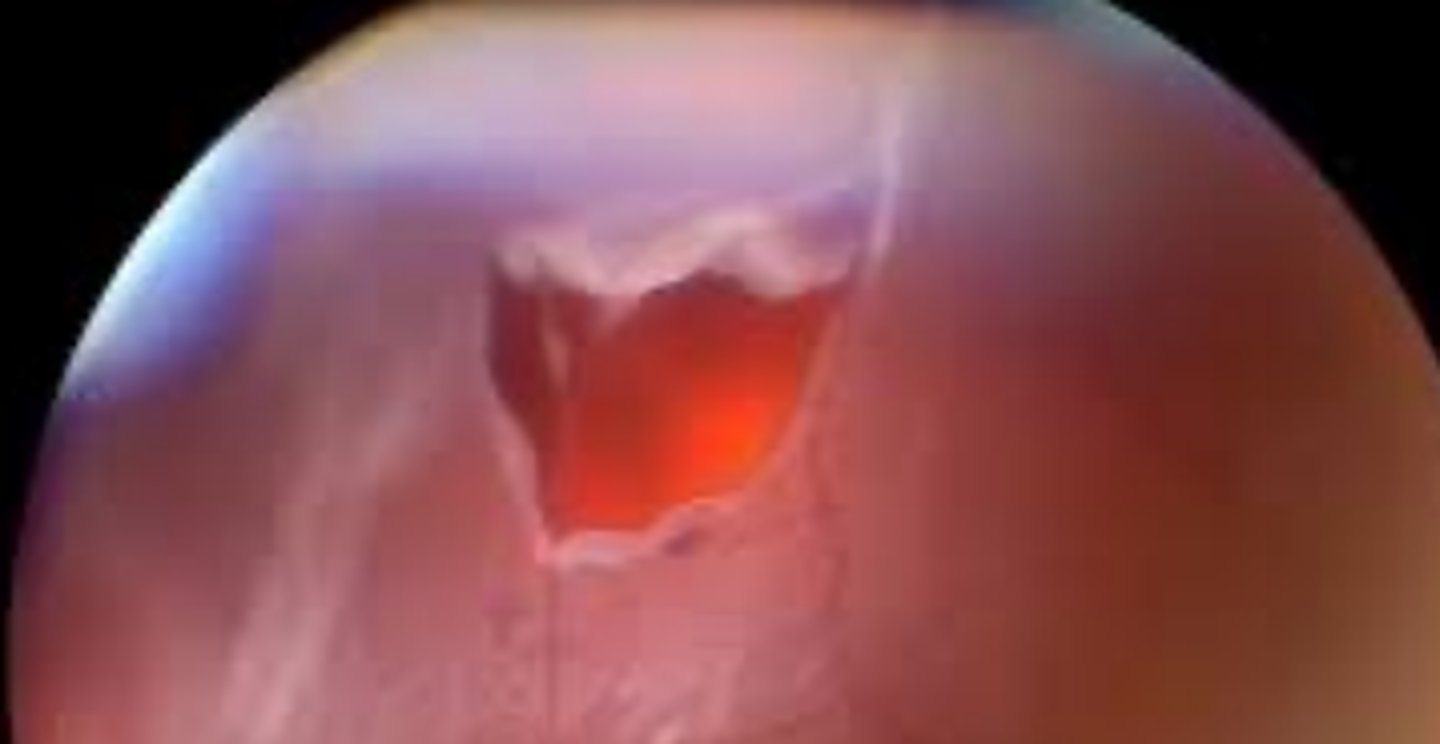
Age
trauma
high myopia
lattice degeneration
four risk factors for a horseshoe retinal tear
symptomatic, trauma
Treatment is recommended when a retinal hole, tear, or break is ____ or caused by ____
vitreoretinal traction
A retinal tear is considered more concerning than a retinal hole due to the presence of...
Laser photocoagulation (laser retinopexy)
prophylactic procedure where 3 rows of laser burns are used to create scarring that seals the retina down preventing a detachment. Patient may experience a small amount of pain. Scar will form in about 2 weeks.
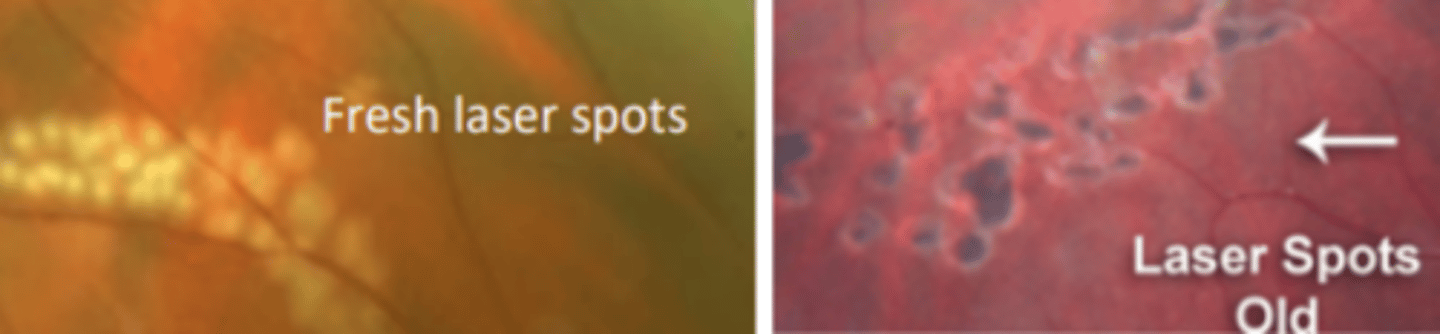
Cryotherapy (cryopexy)
prophylactic procedure where cold is applied to the sclera in order to create a scar and seal the retina preventing a detachment. Is performed in areas where laser photocoagulation is difficult to perform, but is usually not preferred over photocoagulation because it is not as precise and is more painful for the patient.
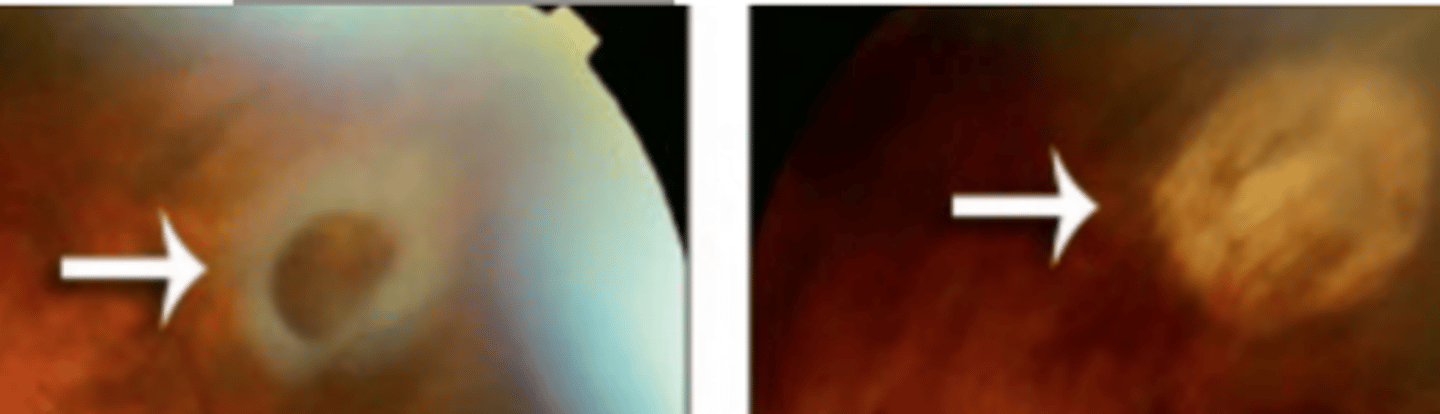
Lattice degeneration
elliptical area of retinal thinning located between the equator and posterior border of the vitreous base running parallel to the ora serrata more commonly superiorly and inferiorly. Is usually bilateral. Is commonly seen in the population (8%) especially in high myopes. May result in holes or tears due to extreme thinning in this region.
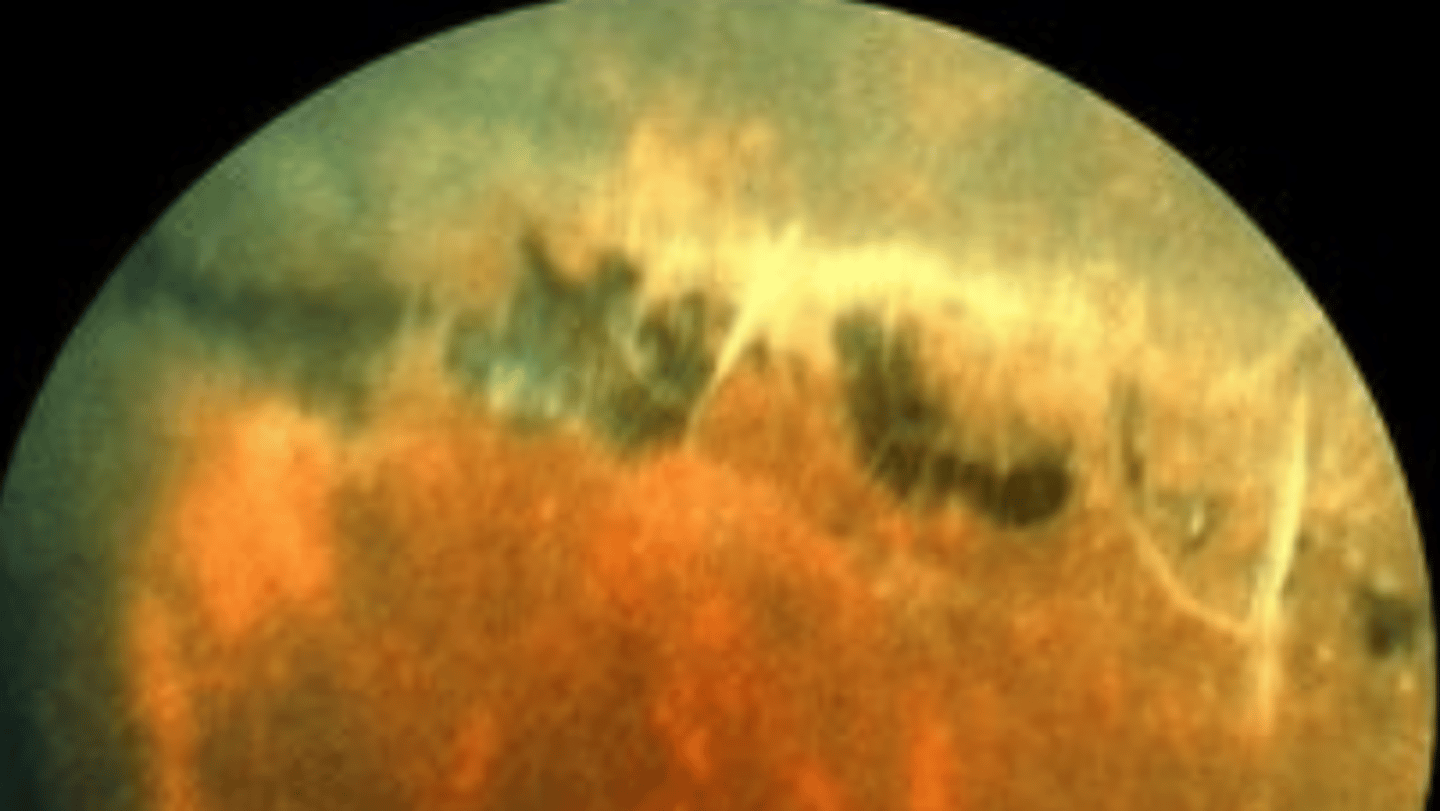
sclerosed retinal vessels
White lines seen in lattice degeneration represent...
education and yearly monitoring
what is the management of lattice degeneration with no holes, breaks, or tears?
6 month follow up
what is the management of ASYMPTOMATIC lattice degeneration with holes or breaks?
refer to retina
what is the management of SYMPTOMATIC lattice degeneration with holes, breaks, or tears?
Snail tracking degeneration
retinal finding that is the same as lattice degeneration, but with no pigment or sclerosed vessels. Is a precursor to lattice degeneration and its management is the same.

Acquired retinoschisis
a splitting of the sensory retina (NOT A RETINAL DETACHMENT). Is usually bilateral (useful for differentiating from RD) occurring in the inferior temporal quadrant. Is usually asymptomatic, but causes an absolute VF defect. Holes of the inner and outer retina may occur, posing a small risk for retinal detachment.
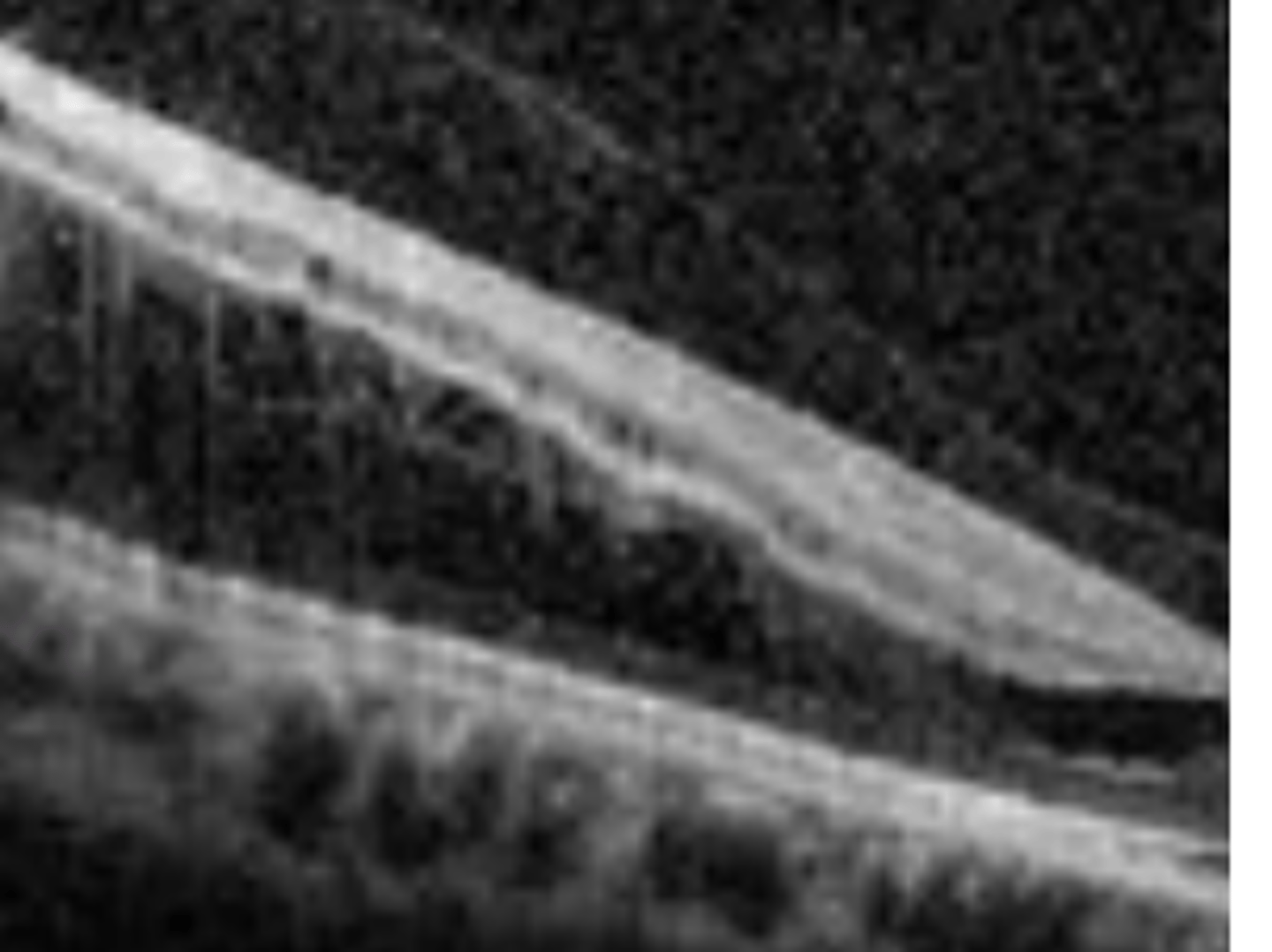
Bilateral, asymptomatic, absolute VF defect
two characteristics of acquired retinoschisis differentiating it from retinal detachment.
Flat retinoschisis
retinoschisis that is more common and believed to be caused by advanced cystoid degeneration. Remains anterior to the equator, has a deep split into the retina versus bullous retinoschisis, and is usually not associated with retinal holes.
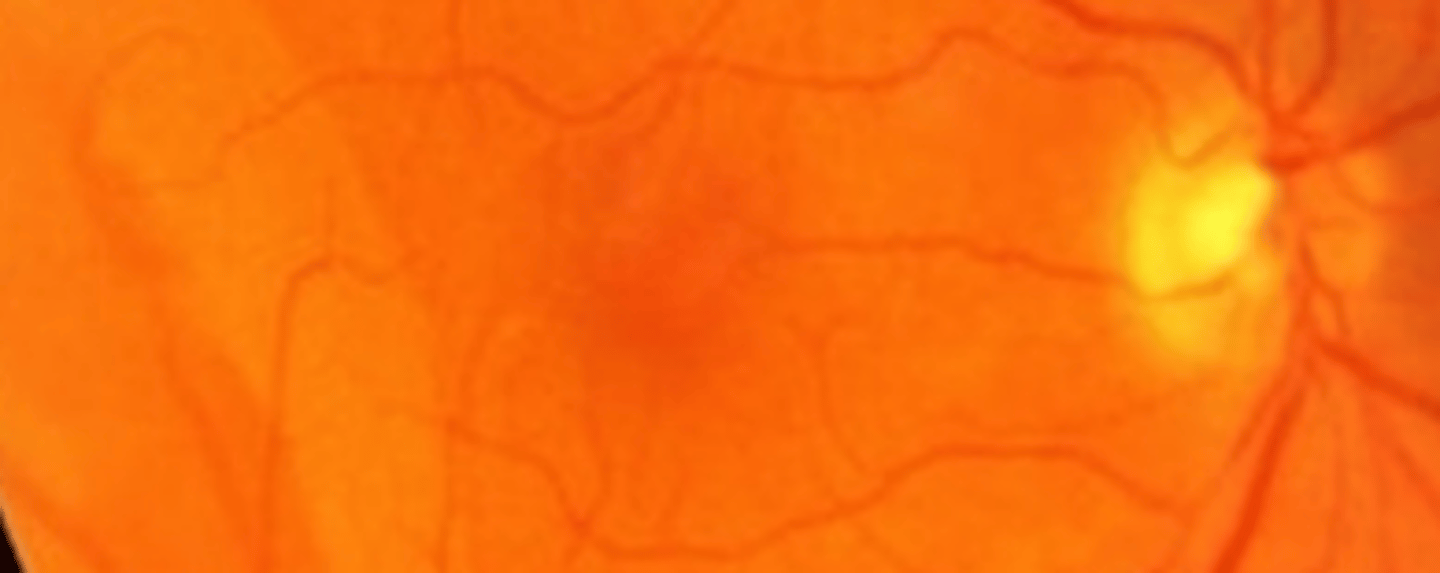

Bullous retinoschisis
retinoschisis that appears as a thin, transparent, ballooning of the retina filled with hyaluronic acid and not moving with eye movement. Has a small association with retinal detachment.
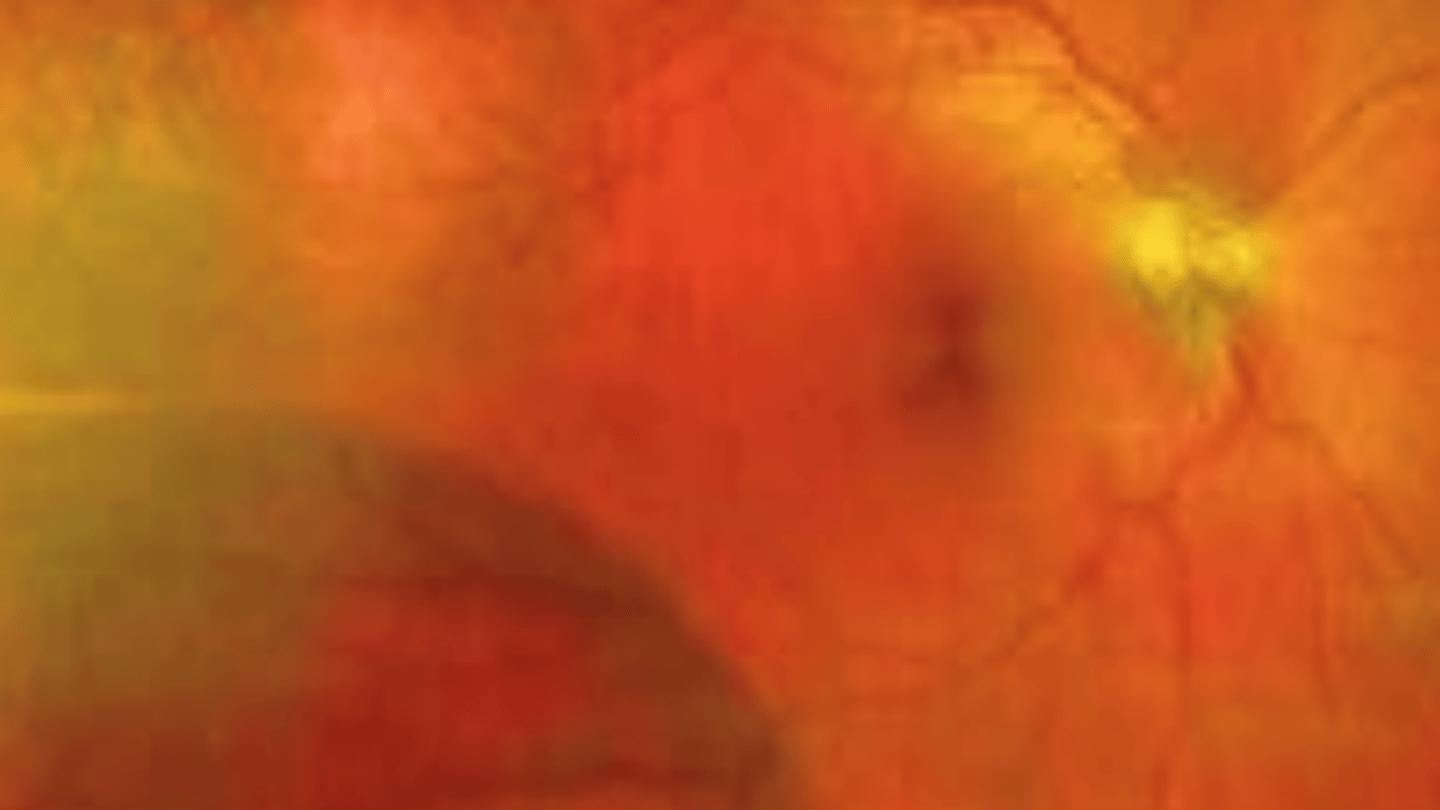
inner
Holes of the _____ retina associated with bullous retinoschisis are typically clear and oval in shape. Should be monitored annually
outer
Holes of the ____ retina associated with bullous retinoschisis are pink and large will rolled edges. Have a larger risk of retinal detachment because they can separate the RPE from the sensory retina
Transparent, does not move with eye movement, no edge of pigment
three characteristics of bullous retinoschisis that differentiate it from retinal detachment
Rhegmatogenous
the most common form of retinal detachment which is caused by a retinal break. I.e.) vitreo-retinal traction, high myopia, retinal dialysis, holes. Patient will be symptomatic. APD may be present if it is extensive Produces a relative VF defect.
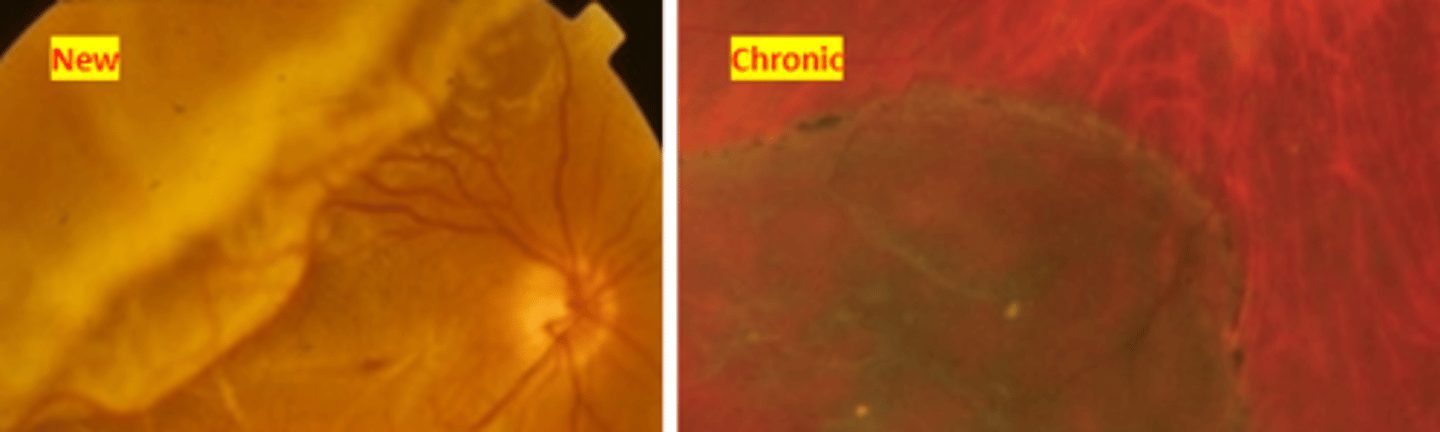
Exudative (Non-rhegmatogenous)
retinal detachment that is not caused by a retinal tear, but is most often caused by a space occupying lesion such as a tumor** (assume until proven otherwise) where fluid accumulation occurs due to a break down in the inner or outer blood retinal barriers. Photopsia will not occur because there is no vitreoretinal traction.
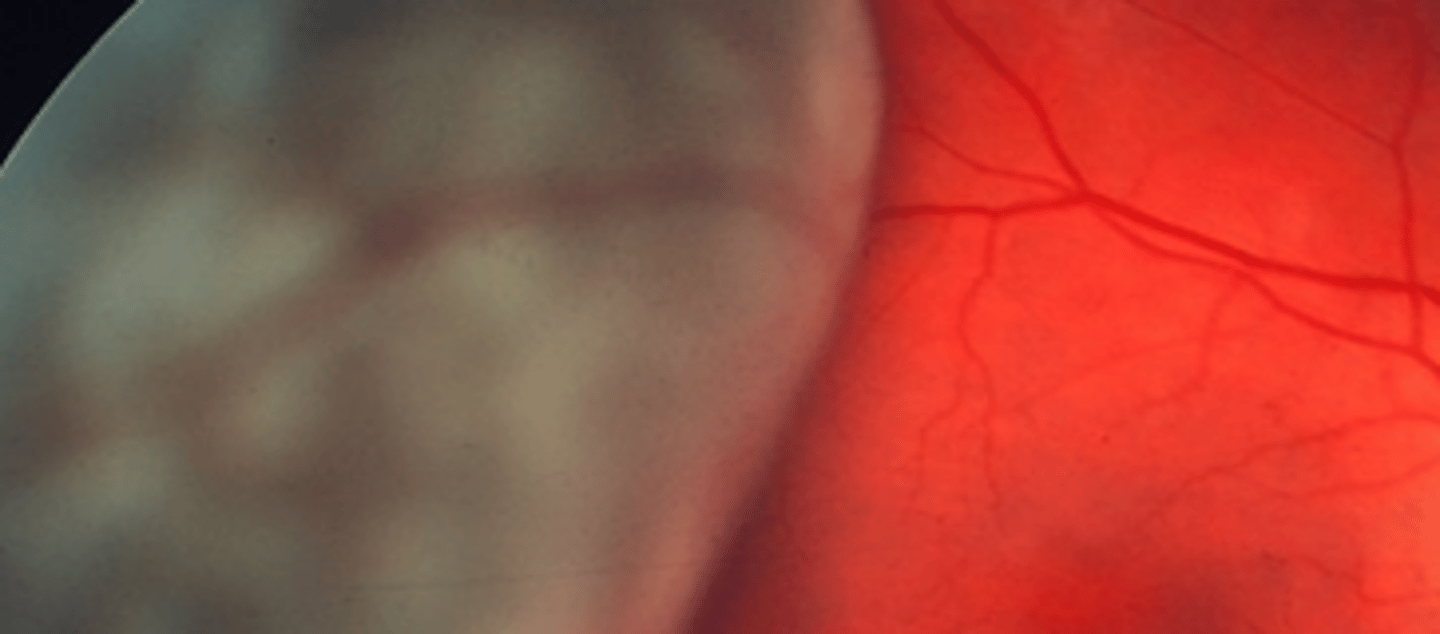
Tractional
retinal detachment that involves some form of vitreous membrane exerting traction on the retina. Patient may be asymptomatic. A mild APD may be present if a large amount of the retina is involved. Is very common in conditions causing neovascularization**
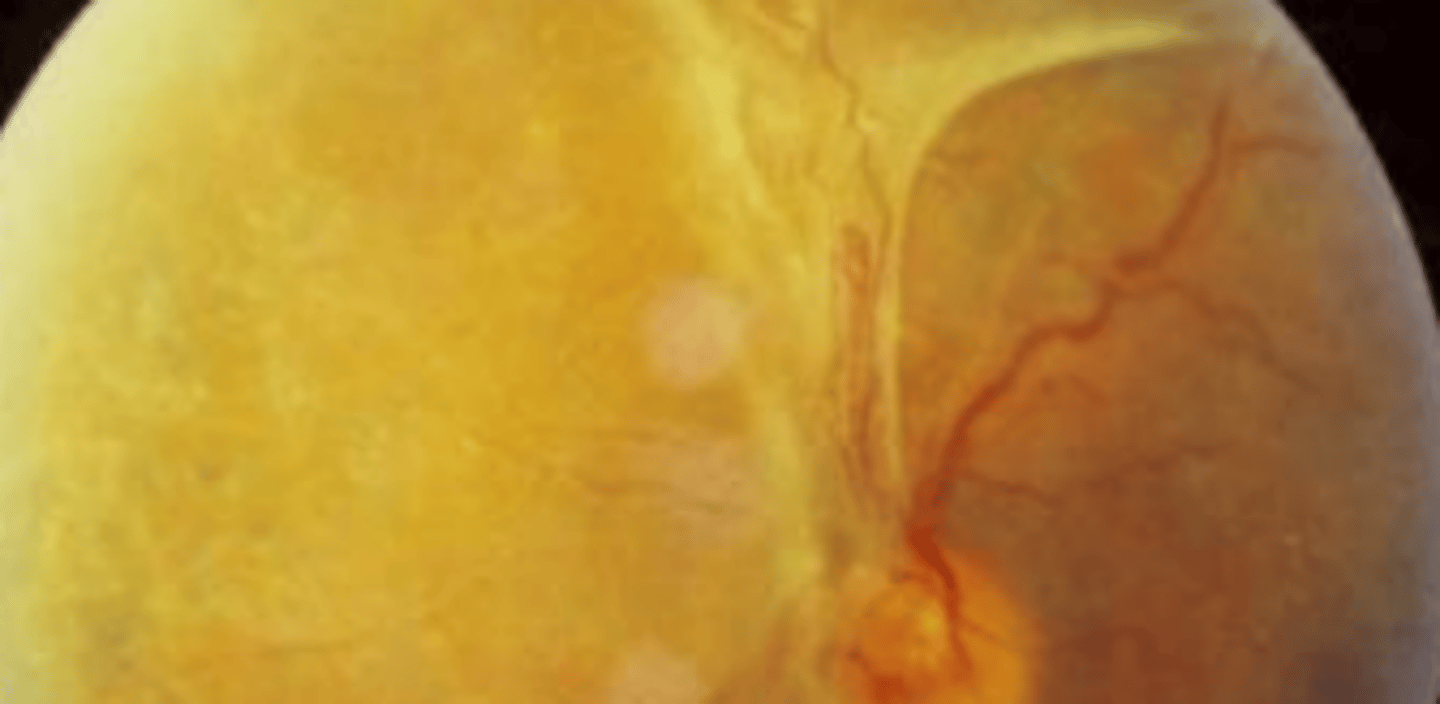
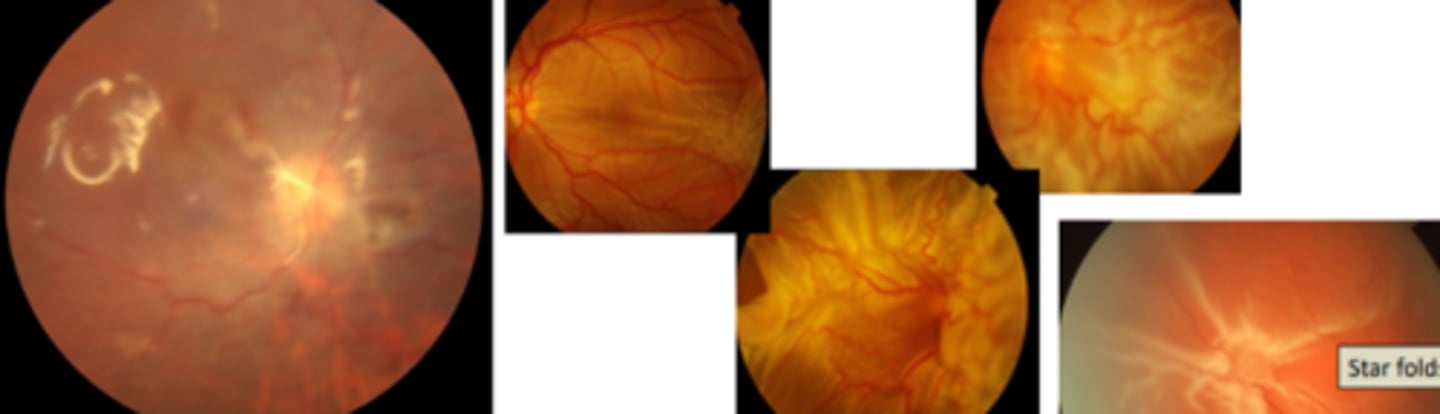
Proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR)
epiretinal and subretinal membrane formation from proliferation of sheets of ectopic cells in the vitreous and/or periretinal and intraretinal areas. Contraction of these tissues then causes folding of the retina. Is an abnormal wound healing process thought to be mediated by inflammaation. Most often occurs when there is failure surgery for retinal detachment repair** or when there is chronic retinal detachment with no treatment. Is also common in patients having other underlying retinal complications. Very poor prognosis even with surgery.
referral within 24 hours
what is the management for retinal detachment that is threatening the fovea?
referral within a few days
what is the management for retinal detachment that is macula off but not chronic?
referral within a week
what is the management of chronic macular off retinal detachment?
exudative retinal detachment
For management of ___, treatment of the underlying condition should resolve the retinal detachment
Pneumatic retinopexy (outpatient)
retinal detachment surgery where a small amount of aqueous is removed and a gas bubble is inserted. This bubble pushes against the retinal detachment and the retina is adhered back using cryotherapy. The bubble dissolves on its own within a few weeks.
Pars plana vitrectomy (inpatient)
retinal detachment surgery where the vitreous is removed (besides the base) in order to eliminate vitreoretinal traction. Either cryo or laser therapy is then used to repair the retina. Gas will also be administer to help keep the retina in place.
Scleral buckle (inpatient)
retinal detachment surgery where a silacon ring is placed around the sclera in order to close retinal tears by apposing the RPE to the sensory retina, reducing vitreoretinal traction. Laser of cryotherapy may also be used in conjunction. Causes a significant MYOPIC shift in refractive error. May uncommonly become infected causing discomfort for the patient.