Animal Cell Biology - Exam 4
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
what are the four main mechanisms of cellular communication via chemical messengers
autocrine signaling
paracrine signalling
endocrine signalling
signaling molecules not secreted (gap junctions or protein junctions)
what happens in autocrine signalling?
the cell that secretes the signal also receives the signal
what happens in paracrine signalling
1 cell produces a ligand, the ligand travels a short distance and attaches to a receptor - ligand and receptor are both proteins
what happens in endocrine signalling?
ligands circulate in the blood stream, then reach target cell some distance away. they can reach anywhere in the body
what happens in contact dependent signalling?
signalling molecule travels directly from one cell to the other - can be contact dependent (gap junctions) or juxtacrine (protein juction)
***how do organ systems, tissues, and cells communicate with one another?
cell signaling pathways/signal transduction pathways
what are the ways the next molecule in a cell signaling pathway can be activated?
phosphorylation → conformational change, enzymatic exchange (GTP ←→ GTP, ion binding
what are some of the “cellular responses” of cell signaling pathways?
affect gene expression (turn gene on or off) - regulate cell cycle; cell growth; cell survival
open/close ion channels on cell membrane
regulate metabolic pathways to synthesize biomolecules
***what are the characteristics of signaling molecules that can pennetrate the cell membrane? give three examples
small, non-ionic, hydrophobic molecules
examples: Nitric Oxide (N=O), steroid hormones, thyroid hormones
***where are receptors for signaling molecules that are small, non-ionic, and hyrdophobic?
not at the cell surface (membrane) → cytoplasmic or nuclear
***what are the traits of signaling molecules cannot penetrate the cell membrane? what are some examples?
hydrophilic (charged) or large molecules,
examples - proteins, peptides, amino acid derivatives
acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can elicit different cellular effects on its target cell. how can this be?
acetylcholine interacts with more than one specific type of receptor - those receptors function as different ion channels to increase membrane potential to specific ions
***where are the receptors for signaling molecules that are charged or large?
at the cell surface (membrane)
what are some examples of chemical messenger receptors that are on the cell membrane?
ion linked channel receptors
G-protein linked receptors
receptor tyrosine kinase (enzyme linked receptors)
cell contact dependent signaling
***what is nitric oxide?
gas with a free electron that can freely diffuse through the cell membrane
where is nitric oxide (NO) synthesized?
from arginine on demand
how does nitric oxide (NO) work as a signaling molecule?
there is no specific receptor for NO, but it alters the activity of intracellular target enzymes
what is one significant pathway that nitric oxide (NO) is involved in?
controlling blood pressure
how do blood vessels contract and dilate?
there is a layer of smooth muscle in the wall of blood vessels, when the smooth muscle is relaxed the blood vessel is dilated (more open), when the smooth muscle is contracted (shortens lengthwise) the blood vessel constricts (narrower)
smooth muscle contraction requires what ion?
Ca++
how does nitric oxide (NO) control blood pressure?
to reduce blood pressure, the parasympathetic nervous symptom releases acetylcholine (ACh), which binds to and stimulates endothelial cells of blood vessels
NO is synthesized in endothelial cells upon ACh stimulation
NO diffuses into smooth muscle cells
NO helps exchange GTP for cGMP
cGMP activates the Protein Kinase G (PKG) that inhibits Ca++ to influx to cytosol
intracellular [Ca++] decreases → smooth muscle relaxes → blood vessel dilates → blood pressure is decreased → blood flow is increased
!! cGMP must be degraded to allow smooth muscle to contract and regulate blood pressure/blood flow
what kind of chemical messenger are thyroxine, cortisol, aldosterone, estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone?
hormones (steroid and thyroid hormones)
what kind of effect do hormones have on organs?
slow and long lasting
what kind of receptors do steroid and thyroid hormones bind to?
intracellular receptors - penetrate the plasma membrane to bind
what kind of receptors so non-steroid hormones bind to?
membrane localalized
are steroid derivatives hydrophobic or hydrophillic?
steroid derivatives are hydrophobic
where are sex steroids secreted from?
gonads
where are corticosteroids secreted from?
adrenal glands
how is the estradiol ligand made?
cholesterol → progesterone → testosterone → estradiol
is thyroid hormone hydrophilic or hydrophobic
hydrophobic
why is thyroid hormone’s solubility special?
its an amino acid derrivative, which are typically hydrophillic, but thyroid hormone is hydrophobic
how does thyroid hormone cross the plasma membrane?
with a carrier protein
what does the structure of vitamin D3 and retinoic acid resemble
chemical structure resembles steroid molecules
***what must the ligand do if the receptor is in the nucleus?
the ligand penetrate the plasma membrane and nuclear envelope to bind to receptor → conformational change activates receptor → activated ligand receptor-complex binds to DNA
nucleus ligand receptors in cell signaling can also work as ______
transcriptional regulators
receptors in the nucleus that also work as transcriptional regulators have a ________ binding domain and a _______binding domain
DNA, ligand
how does a transcriptional regulator ligand receptor work?
ligand penetrates plasma membrane and nuclear envelope to bind to receptor → conformational change activates receptor → activated ligand-receptor complex binds to DNA → influences gene expression by activating transcription! — Lag time to metabolic effect (metabolism just means chemical reactions in the cell)
what is the process of a steroid hormone initiating a certain cell response?
diffusion through membrane lipids
hormone enters nuclease and binds receptor
binding of hormone-receptor complex to DNA
gene activation
transcription and mRNA production
translation and protein synthesis
Target Cell Response
what effect do Heat Shock Proteins (Hsp) have on cytosolic receptors?
ligand-free receptor is bound to Hsp90, which keeps the receptor tethered outside the nucleus
upon ligand-binding, Hsp90 dissociates from the receptor allowing ligand-receptor complex to enter nucleus
receptor binds specific DNA sequence and recruits a transcriptional coactivator (ex: histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
in regards to heat shock proteins, when the hsitone is not acetylated, what happens to transcription?
transcription is repressed
in regards to heat shock protein, when histones are acetylated what happens to transcription?
transcription occurs
what is the primary response to the binding of a steroid hormone? what is the secondary response?
hormone-receptor complexes activate primary response genes
if the primary response protein activates a secondary response gene, secondary response proteins are synthesized
why are steroid hormones so powerful?
they can directly regulate gene expression and have widespread effects (many genes and target cells)
individual amino acids form a chain called a _________, which gets folded into structures called _______
peptide, protein
are neurotransmitters hydrophobic or hydrophillic?
neurotransmitters are hydrophillic
peptides and glycoproteins are _______, which are [HYDROPHILLIC / HYDROPHOBIC] ligands
hormones, hydrophillic
what is the most known inhibitory neurotransmitter?
GABA
when an amino acid looses it’s carboxyl group, it becomes a ________
neurotransmitter
what is the process of cell signaling via surface cell receptors
ligand binds receptor at outside surface of cell → ligand-receptor binding sets off chain of intracellular signaling events → cellular/metabolic effects
some acetylcholine receptors are also _______________
ligand gated ion channels
neurotransmitters with receptors that also act as ion channels - opening ion channels is ________
direct
neurotransmitters that cause depolarization of a post synaptic cell are ___________________
excitatory synapses
neurotransmitters that cause depolarization of a post synaptic cell are ____________________
inhibitory synapse
neurotransmission can be ________ or _________
direct, indirect
receptors can use different types of signal transmission because they have __________
diversity
is neurotransmission through G-protein-coupled receptors direct or indirect?
indirect
in indirect transmission, the receptor is NOT an ion channel, but a ______________________
transmembrane protein associated with a G protein
are peptide hormones hydrophobic or hydrophillic?
peptide hormones are hydrophillic
can peptide hormones enter the target cell?
no they cannot
what is the process of signaling through G-protein-coupled receptors & the second messenger system?
hormone binds to receptor to form the hormone receptor complex → the G-protein activates and leaves the G-protein → G protein activates adenylate cyclase → adenylate cyclase cycles ATP into cAMP → cAMP activates kinase → kinase alters enzyme activity; opens ion channels → open ion activate target cell resposne
activated enzymes catalyze ______________
metabolic reactions
GDP + Pi → GTP via _________
GEFs
GTP → GDP + Pi via __________
GAPs
a G-protein with GDP binded is [ACTIVE / INACTIVE]
inactive
a G-protein with GTP bound is [ACTIVE / INACTIVE]
active
What part of the G protein leaves the complex?
the ɑ subunit
when a ligand binds a receptor on a G-protein coupled receptor, what happens?
GEF activity activates G-protein
what does GEF stand for?
guanine exchange factor
what does GAP stand for?
GTPase activating protein
what receptor does epinepherine bind to?
G-protein coupled receptor
what is the process of epinephrine signaling through its G-protein coupled receptor?
epinephrine binds to the G-protein coupled receptor, the activated receptor kicks off the ɑ subunit of the G protein, which binds to and activated adenylyl cyclase
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into cAMP
cAMP binds to protein kinase A, phosphorylating and activating the kinase
Protein kinase A’s C subunis leaves and gets ATP exchanged with ADP, then the phosphate binds to a phosphorylase kinase, activating it
activated phosphorylase kinase activates glycogen phosphorylase, which catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate, glucose is ready for glycolysis and the cell can produce ATP for energy
what is the net effect of epinepherine on a cell?
epinephrine signaling → frees glucose to enter the blood stream for delivery to/uptake by cells that need energy → “fight or flight”
signal amplification***
relative speed = fast (compared to hydrophobic ligand signaling)
why is singal amplification so important?
even if ligand levels are low, can activate many enzyme molecules and produce very large effects
1 receptor-hormone complex → 3 activated G proteins → 10 activated adenylyl cyclase → 21 cAMP → 36 activated protein kinase enzymes is an example of?
signal amplification / reaction cascade
what is the most widely used second messenger?
cAMP
epinephrine adrenaline is a ____________, which is an amino acid derivative, produced/secreted by adrenal medulla
catecholamine
how can signaling through G-protein coupled receptors affect gene expression?
activated protein kinase A catalytic subunits can enter the nucleus and phosphorylate (activate) a a transcription factor called CREB (CRE-binding protein)
activated CREP binds a specific regulatory (DNA) sequence (called the CRE, cAMP response element) of target genes
regulate transcription of target genes →
effect on target cell: regulate cell division, cell survival, cell differentiation
cAMP acts as a “messenger” to relay a message from ________ the cell to ______ the cell
outside, inside
what are the first and second messengers in the second messenger system? where are they in relation to the cell?
1st messenger = the original cell messenger, outside the cell
2nd messenger = cAMP and effector molecules that will ultimately bring about the desired response within the cell
***can a hydrophobic ligand (NO, steroids, thyroid hormone) pass through the plasma membrane?
no, they cannot cross the plasma membrane
how is a hydrophobic ligand (NO, steroids, thyroid hormone) secreted from it’s cell of origin
simple diffusion/facilitated diffusion
how is a hydrophobic ligand (NO, steroids, thyroid hormone) transported in the blood stream
bound to a protein carrier (not soluble in aqueous solution)
***how does a hydrophobic ligand (NO, steroids, thyroid hormone) interact with the target cell?
crosses the cell membrane and binds to receptor in the nucleus or cytosol
***can a hydrophillic ligand (amino acid derivatives/peptides) cross the plasma membrane?
no, they cannot cross the plasma membrane
how is a hydrophillic ligand (amino acid derivatives/peptides) secreted from its cell of origin?
exocytosis → vessicles
how is a hydrophillic ligand (amino acid derivatives/peptides) transported in the blood stream?
as dissolved particles
***how does a hydrophillic ligand (amino acid derivatives/peptides) interact with its target cell?
binds to a receptor on the cell membrane
***what does a kinase do?
adds a phosphate group = phosphorylates
***what does a phosphatase do?
removes a phosphate group = dephosphoylates
the enzyme with the opposite function of a kinase is a ________
phosphotase
the enzyme with the opposite function of a phosphatase is a __________
kinase
true or false: phosphorylation always activates a protein
false: some (like Bad in the cell death pathway) are inhibited when binded to phosphate
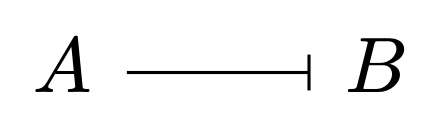
what does a blunt arrow represent in a cell signaling pathway?
A inhibits B
in the following, increased expression of A would have what effect on B? what effect on C?
A → B → C
increased activation of B, increased activation of C
in the following, increased expression of A would have what effect on B? what effect on C?
A → B -| C
increased expression of B, decreased expression of C
in the following, increased expression of A would have what effect on B? what effect on C?
A -| B -| C
decreased expression of B, increased expression of C
in the following, increased expression of A would have what effect on B? what effect on C?
A -| B → C
decreased expression of B, decreased expression of C
what happens to a protein when a phosphate group binds? (not activation/inactivation, what happens to the protein itself)
the protein changes conformation
***some cell surface receptors act as intracellular ________
enzymes
is a cell surface receptor is not acting as an intracellular enzyme, it is ___________ to an intracellular enzyme
directly linked