Intro & Biochem
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Macromolecules
large complex biomolecules
Monomers
smallest molecules that act as building blocks for polymers
Dehydration synthesis
a simple way of joining monomers to make polymers
end product is H2O
Carbohydrates
energy storage, receptors, food, structural role in plants, fungal cell walls, exoskeletons of insects
Lipids
Energy storage, membrane structure, insulation, hormones, pigments
Nucleic acids
Storage and transfer of genetic information
Proteins
Enzymes, structure, receptors, transport, structural role in the cytoskeleton of a cell and the extracellular matrix
Sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides
four main building blocks of small organic molecules in cells
polysaccharides/glycogen/starch (plants), fats and membrane lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
four main building blocks of large organic molecules in cells
Carbohydrates
most abundant biomolecule on Earth
Carbohydrates (saccharides)
Functions:
food source
store and transmit genetic information (DNA & RNA)
basis of biological polymers such as cellulose and chitin (cell wall)primary source of energy storage in forms of starch and glycogen
Monosaccharide
Simplest form or basic building blocks of carbohydrates
Monomers for the synthesis of complex polymers
C=O
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides join to form this
Mostly sweet and water soluble
Dehydration principle (H2O as a product)
e.g.,
monosaccharide-O-monosaccharide
glycosidic bond
The covalent bond that attaches disaccharides/polysaccharides together is called a….
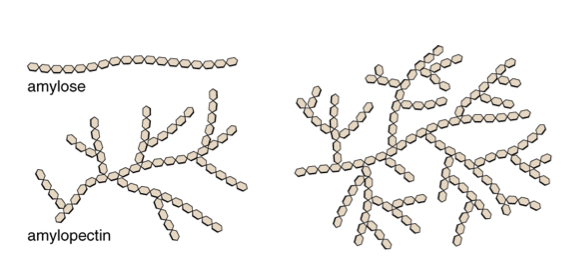
Polysaccharides
Larger than disaccharides
Composed of hundreds (or thousands) of monosaccharides
NOT sweet
NOT soluble
linked together by glycosidic bonds
polysaccharides
Which carbohydrate is NOT sweet and NOT water-soluble?
Starch and Glycogen
Which example of polysaccharides?
Branched
Primary energy-storage in animals
Bacteria and plants
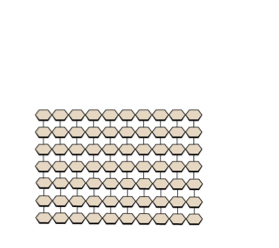
Cellulose(fiber)
Which example of polysaccharides?
Linear chains
Cell wall of plants and other organisms
Lipids
Roles:
Source of nutrients
Storage form for carbon
Energy-storage molecules
Structural component of membrane and hormones
Composed of:
C & H primarily
Also, O, N, S, and P
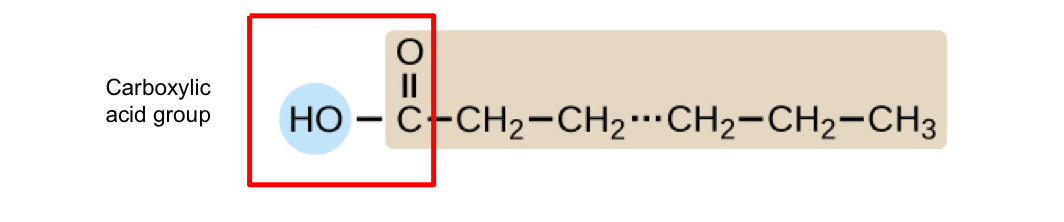
Fatty acids
lipids that contain long-chain hydrocarbons terminated with a carboxylic acid functional group
can be saturated or unsaturated
Saturated
Saturated or Unsaturated?
Linear with most amount of H
Unsaturated
Saturated or Unsaturated?
Slightly bent with fewer H
Triglycerides
form when three fatty acids are chemically linked to a glycerol molecule
by Dehydration Synthesis
found in adipose (body fat) tissue
Used as energy-storage molecules
glycerol; fatty
Triglycerides are simple molecules of two types of compounds: ________ & _______ acids.
hydrophobic
Complex lipids such as phospholipids contain:
a _________ tail
hydrophilic
Complex lipids such as phospholipids contain:
a _________ head
Amino Acid
Organic molecule
H group, carboxyl (-COOH) group, and amine group (-NH2) all bonded to the same carbon atom (alpha carbon)
protein
When many polypeptides come together, the macromolecule formed is called a ________.
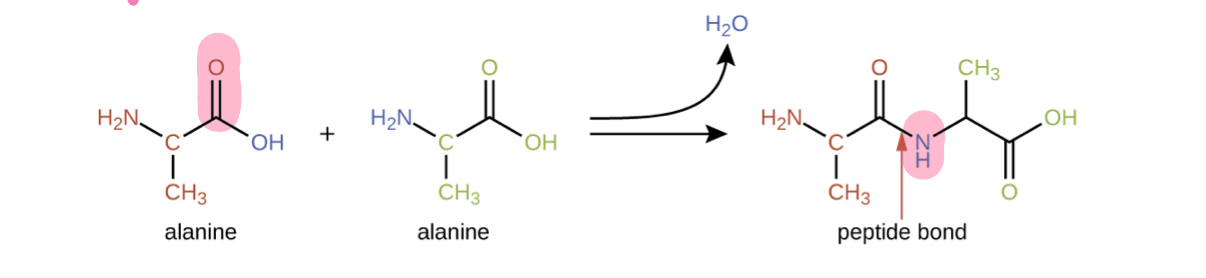
Peptide bond
Reaction between the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid with the amine group of another
also an example of dehydration synthesis
nucleotides
Nucleic acids are composed of monomers called…..
DNA
Nucleotides for DNA or RNA?
Five carbon sugar called deoxyribose
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
A → T
C → G
Hydrogen bonds
Which type of bonds form between the bases of each DNA strand?
Water
The most abundant molecule in the cell is: