Genetics Key Terms 2: Ploidy, Chromosomes, Division
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Ploidy
The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
Haploid
A cell/organism that has 1 set of chromosomes
Diploid
A cell/organism that has 2 sets of chromosomes
Polyploid
A cell/organism that has more than 2 sets of chromosomes
What does the variable n equal?
The number of chromosomes in a full set depending on the cell or organism and its state
What is the n value of a human?
n = 23, 2n = 46
Homologous Chromosomes
A chromosome pair that has the same genes in the same order, only with slight variations
Chromosome
A thread of DNA wrapped around proteins at a nucleus that carries genetic info
Chromatin
The material that composes chromosomes, roughly 40% DNA and 60% histone proteins
Histone Proteins
Proteins found in the center of eukaryotic cells; helps make up chromatin
Centromere
This is where the sister chromatids meet to create a long and short area of a chromosome; spindle fibers attach to this using the kinetochore during mitosis
Telomere
Protein and DNA structures found at the end of chromosomes that protect the DNA ends
(Sister) Chromatid
An identical copy of a chromosome that has not yet been separated after duplication
Chromosome Arms
The sections of a chromosome, split specifically by the centromere
Cohesin Protein
Protein complex that mediates sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination, and DNA looping.
Karyotype
A visual representation of someone’s full chromosome set, including names, sizes, and shapes
Autosomes
One of the numbered chromosomes besides those defining biological sex (humans have 22 sets)
Sex Chromosome
The 23rd set of chromosomes that helps to determine biological sets using X and Y genotypes
Genome
The total amount of all genetic info within an organism; helps to code genetic information
Somatic Cells
All cells in the body that are not related to reproduction
Meiocyte
Cells that produce gametes (reproductive cells) through the process of meiosis
Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)
Used during the interphase stage, these structures organize microtubular parts; creates the spindle apparatus to help divide cells
Microtubule
A thin, hollow tube structure located in the cytoplasm; helps notably with cell support and shape
Kinetochore
A complex of proteins related to the centromere of a chromosome; The microtubules attach to this area
Synapsis
The fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis
Synaptonemal Complex
A protein that forms in between and connects homologous chromosomes during meiosis
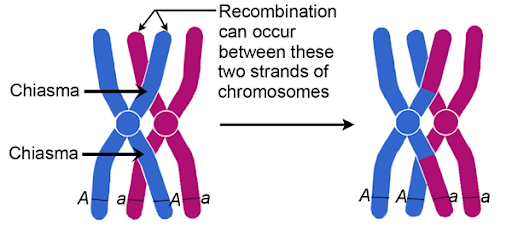
Chiasma (s.)
A point along the chromosome where non-sister chromatids entangle and swap bits of chromosomal material during meiosis
Chiasmata (pl.)
The area in which homologous chromosomes switch genetic material by crossing over during meiosis
Tetrad
2 pairs of homologous chromosomes next to each other during meiosis
Crossing Over
When genetic material is switched between paired homologous chromosomes, resulting in new genetic offspring