AP Biology - Unit 3, AP Biology Unit 4, AP Biology Unit 2, AP Biology Unit 1
1/278
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
279 Terms
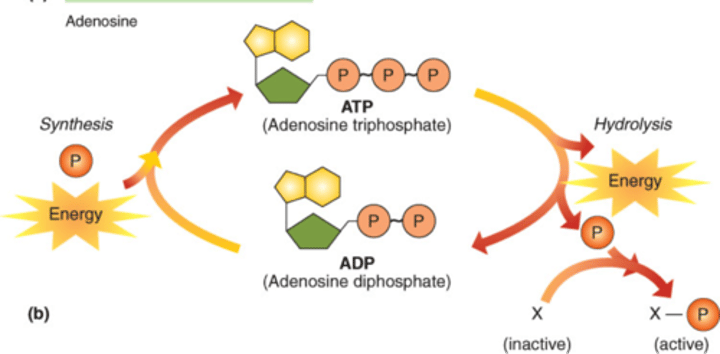
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
ADP
adenosine diphosphate; molecule that ATP becomes when it gives up one of its three phosphate groups
free energy
Chemical energy available to do work
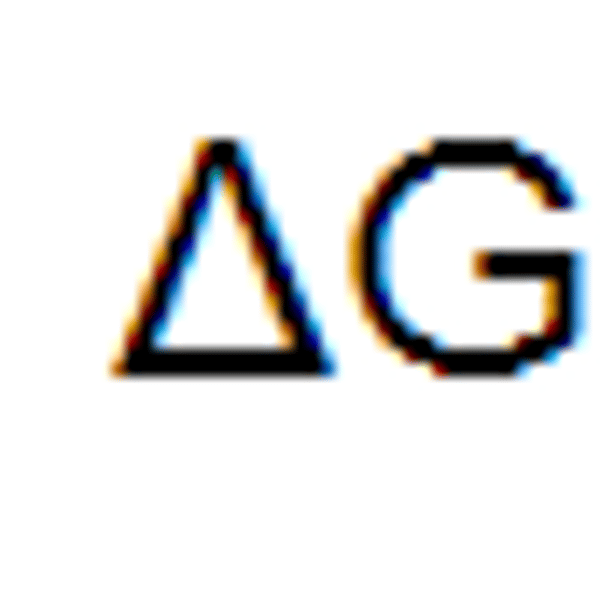
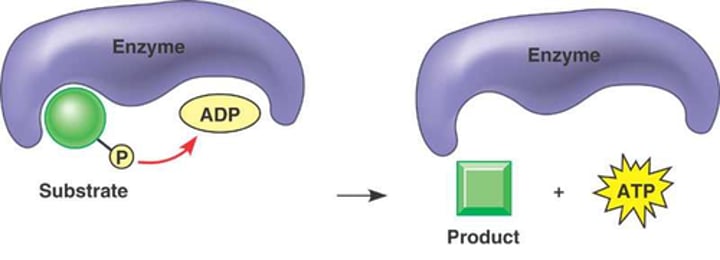
substrate level phosphorylation
the enzyme-mediated direct transfer of phosphate from another molecule (the substrate) to ADP
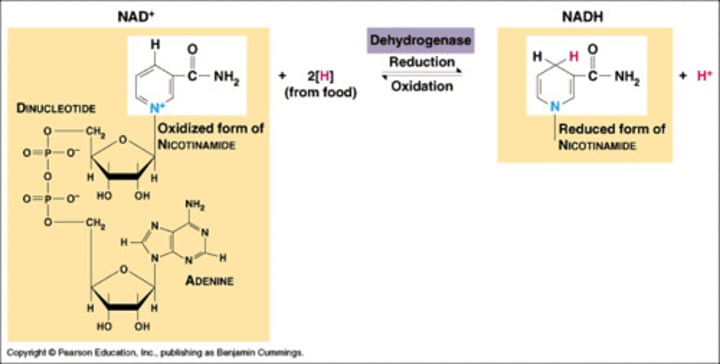
reduction
Gain of electrons by a chemical reactant; any reduction is accompanied by an oxidation.
oxidized
loses electrons
reduced
gains electrons
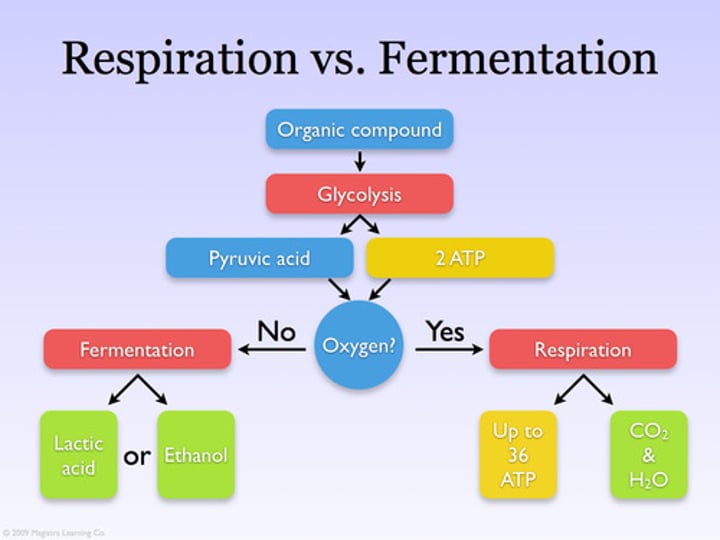
cellular respiration
The catabolic pathways by which electrons are removed from various molecules and passed through intermediate electron carriers to O2, generating H2O and releasing energy.

aerobic
Requiring molecular oxygen, O2
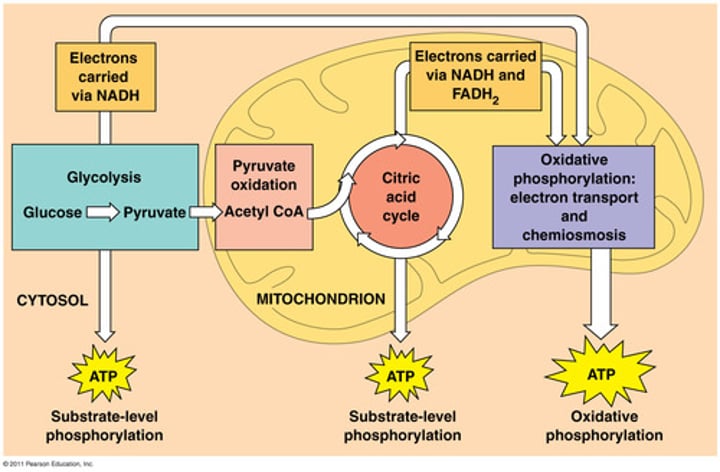
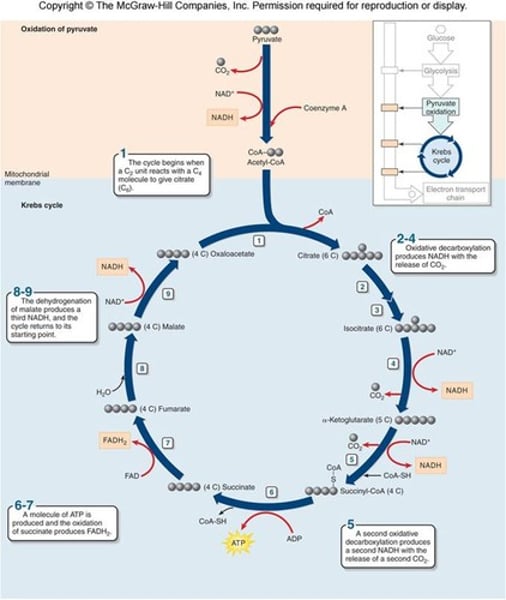
citric acid cycle
In cellular respiration, a set of chemical reactions whereby acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms are stored as NADH and FADH2. Also called the Krebs cycle.
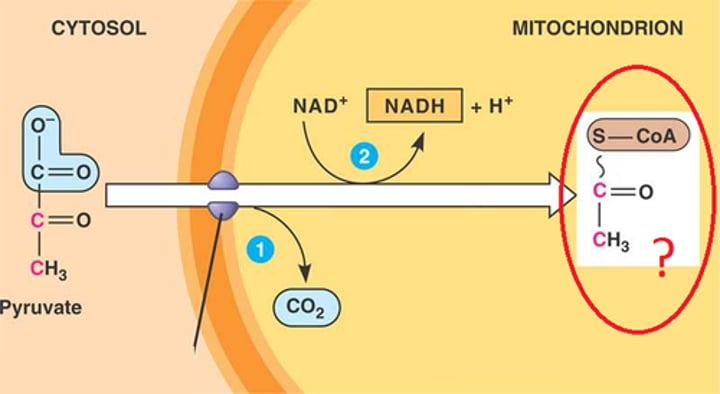
pyruvate
Three-carbon compound that forms as an end product of glycolysis.
NADH
reduced electron carrier molecule formed during CR
Krebs cycle
another name for the citric acid cycle
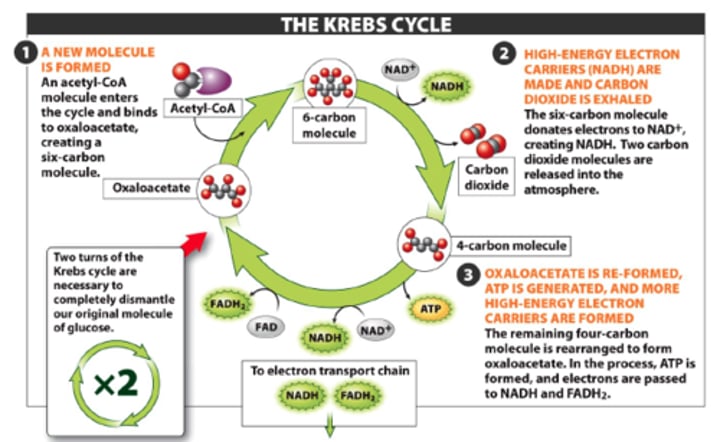
acetyl CoA
molecule formed from the oxidation of pyruvate (2C compound)
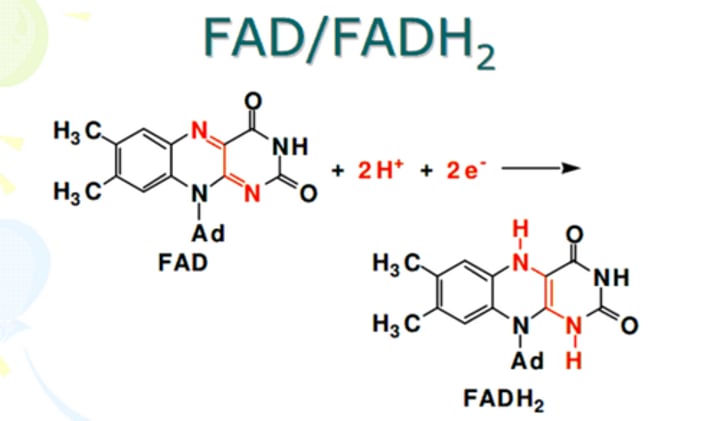
FADH2
a reduced coenzyme similar to NADH, an electron carrier
anaerobic
Occurring without the use of molecular oxygen, O2.
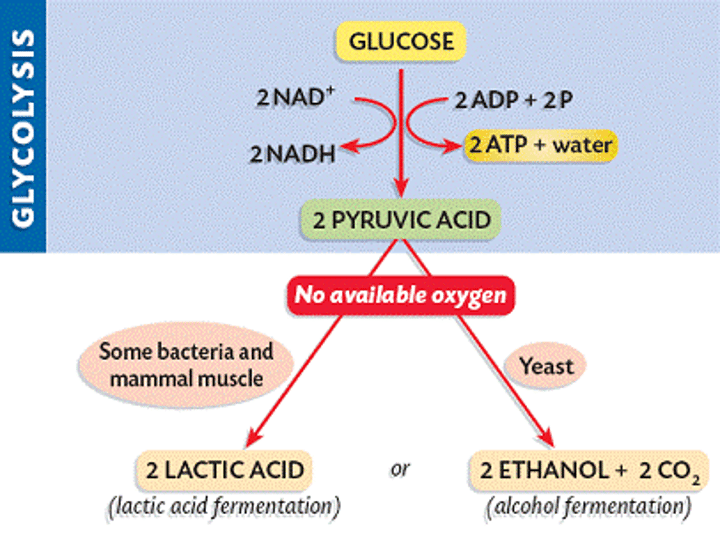
fermentation
Speaking specifically about energy metabolism, the anaerobic degradation of a substance such as glucose to smaller molecules such as lactic acid or alcohol with the extraction of energy. (2) Speaking generally, metabolic processes that occur in the absence of O2.
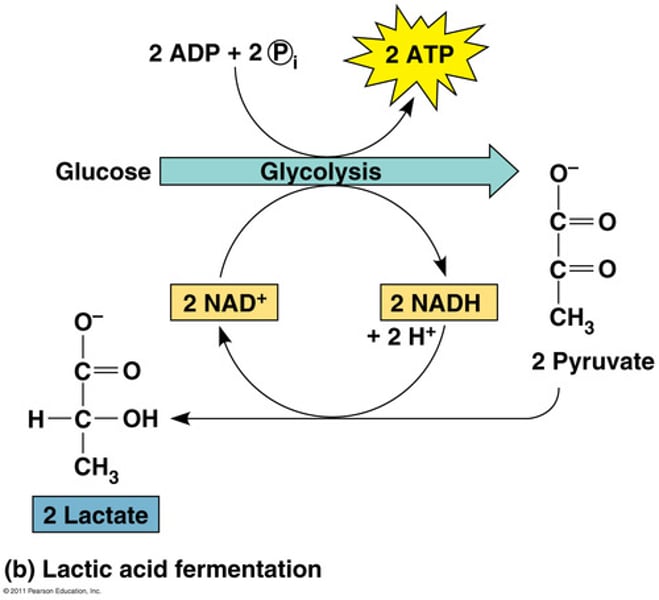
lactic acid fermentations
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to lactic acid, in some bacteria and animal cells.
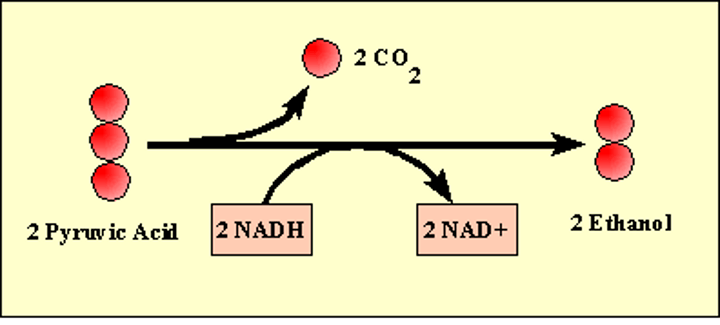
alcoholic fermentation
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide in some plants and yeast cells.
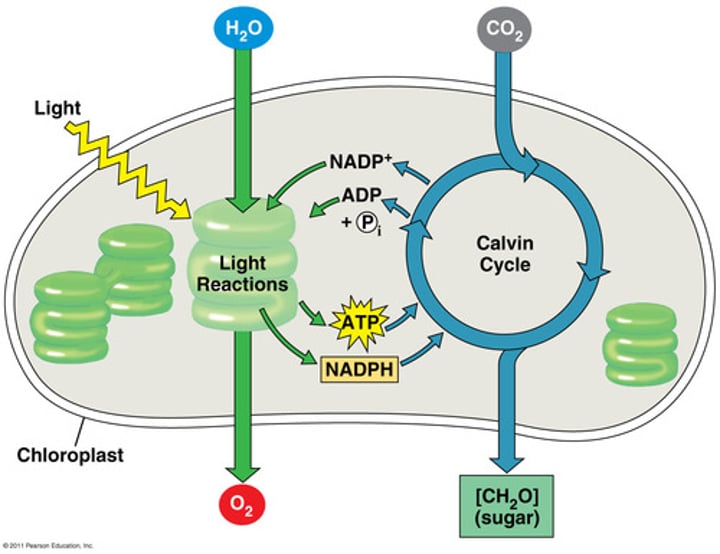
photosynthesis
photosynthesis: Metabolic processes carried out by green plants and cyanobacteria, by which visible light is trapped and the energy used to convert CO2 into organic compounds.
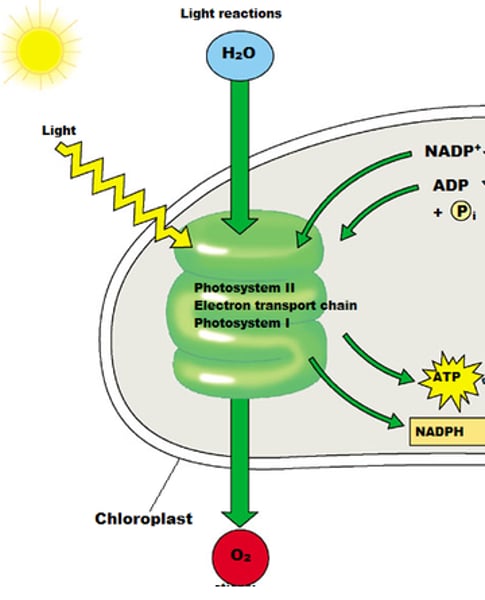
light reactions
The initial phase of photosynthesis, in which light energy is converted into chemical energy.
pigment
A substance that absorbs visible light.

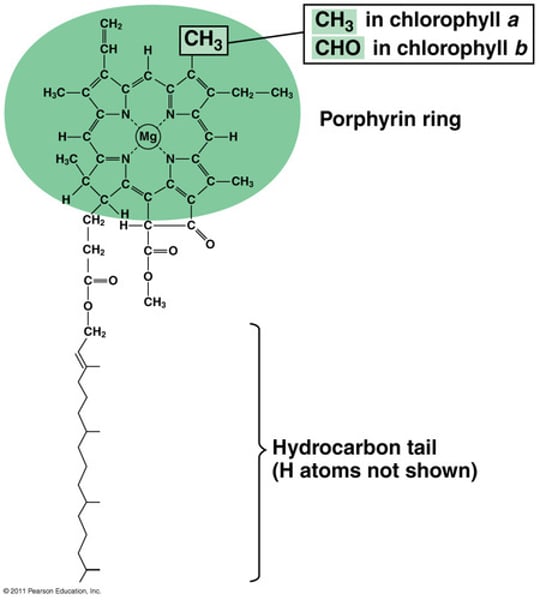
chlorophyll
Any of several green pigments associated with chloroplasts or with certain bacterial membranes; responsible for trapping light energy for photosynthesis.
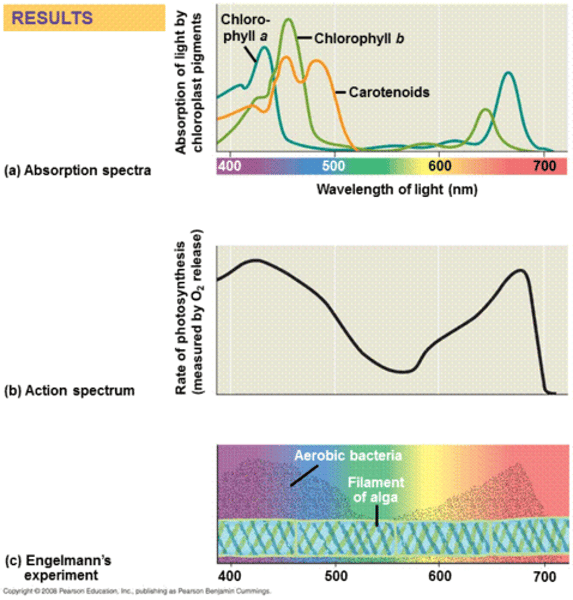
absorption spectrum
A graph of light absorption versus wavelength of light; shows how much light is absorbed at each wavelength.
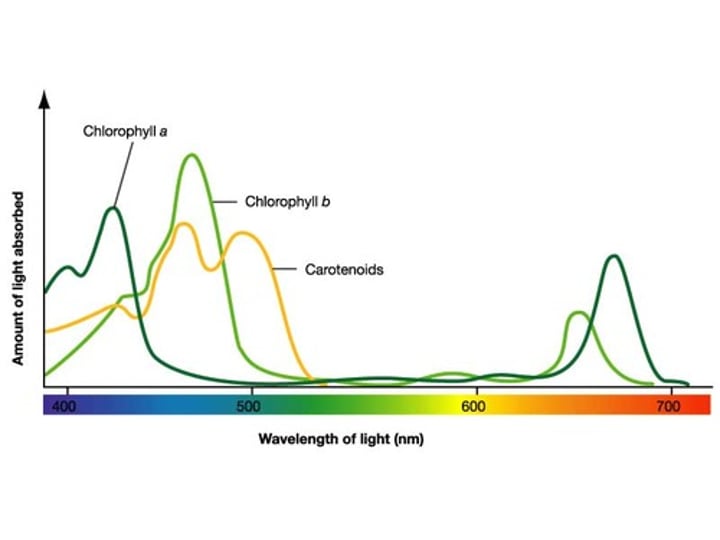
action spectrum
A graph of a biological process versus light wavelength; shows which wavelengths are involved in the process.
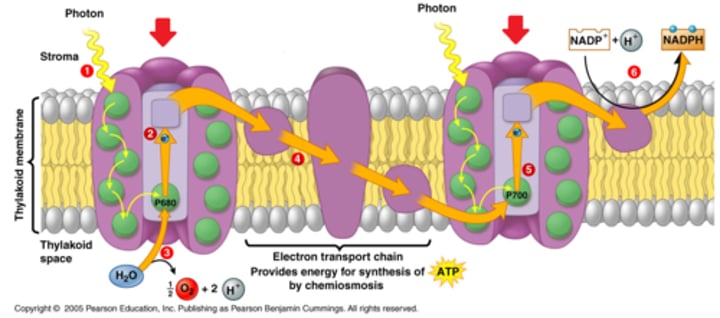
photosystem
A light-harvesting complex in the thylakoid composed of pigments and proteins.
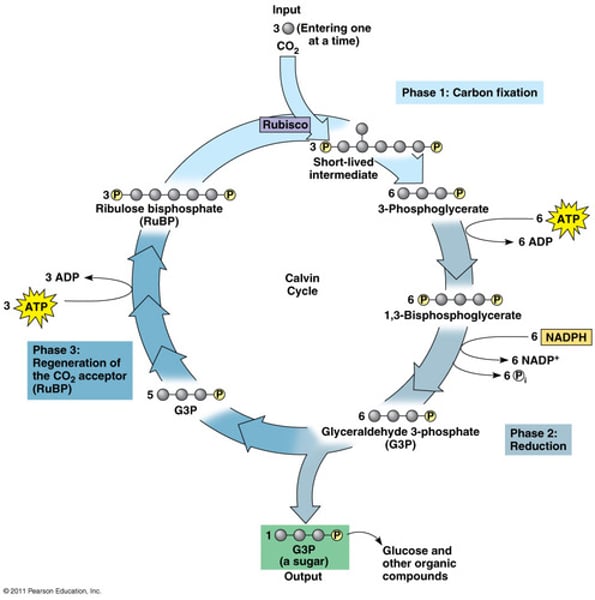
Calvin cycle
a series of enzyme-assisted chemical reactions that produces a three-carbon sugar from 3 CO2. Two 3C sugars will combine to form glucose
autotroph
An organism that is capable of living exclusively on inorganic materials, water, and an energy source other than the chemical bonds of organic compounds. Some autotrophs (photoautotrophs) use sunlight as their energy source. Others (chemoautotrophs) use oxidation of inorganic compounds.

heterotroph
An organism that requires preformed organic molecules as sources of energy and chemical building blocks.

kinetic energy
Energy associated with relative motion of objects.

thermal energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of molecules or atoms. (heat)

potential energy
Stored energy.

entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness. Tends to increase in the universe.

free energy
Measures the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell.
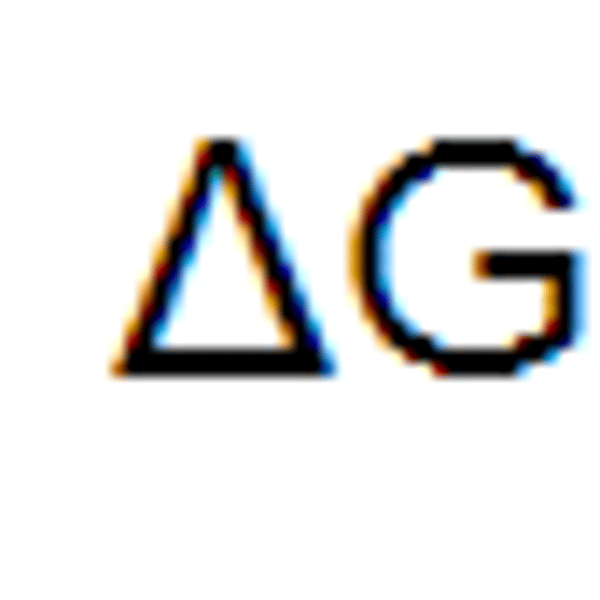
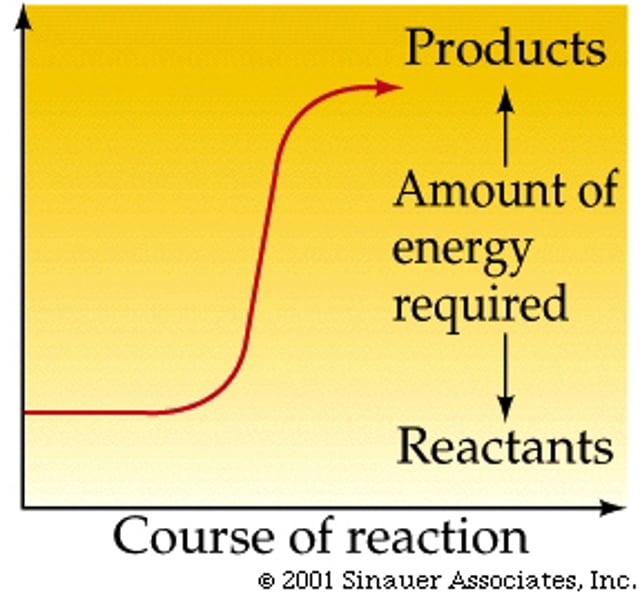
endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
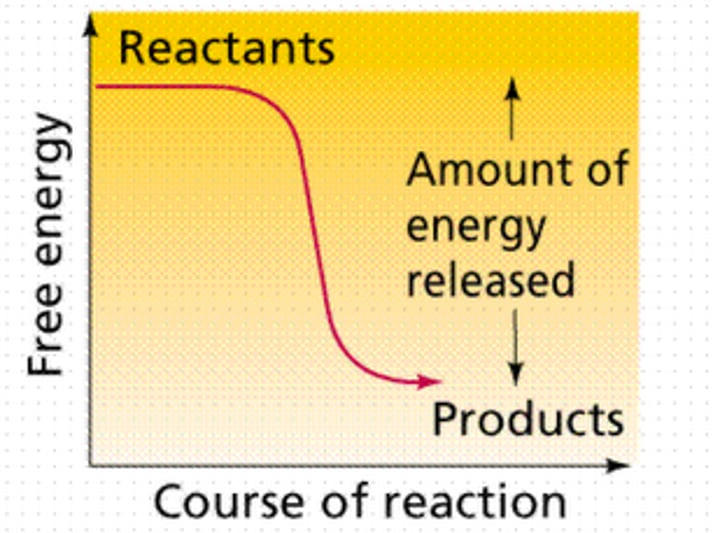
exergonic reaction
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy.
catalyst
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
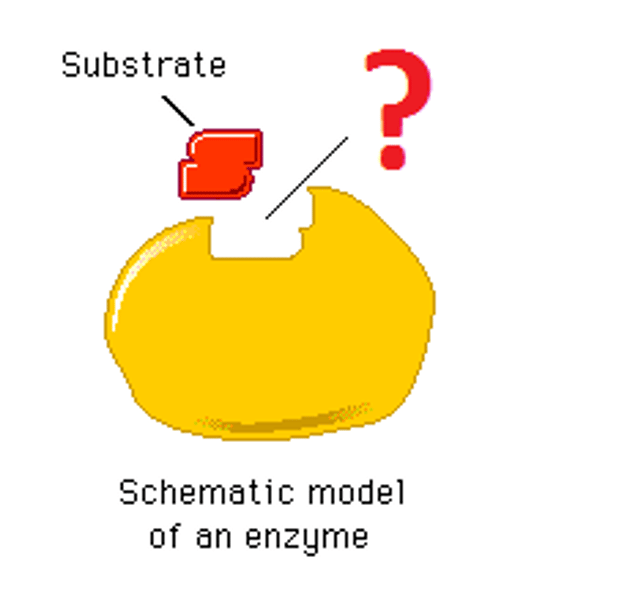
enzyme
Protein that speeds up reactions. Typically end in "ase" (ex. Peroxidase, Lipase)

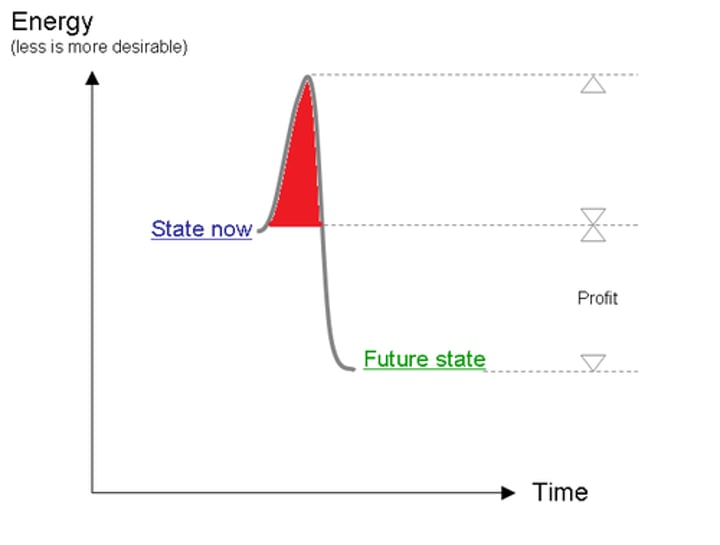
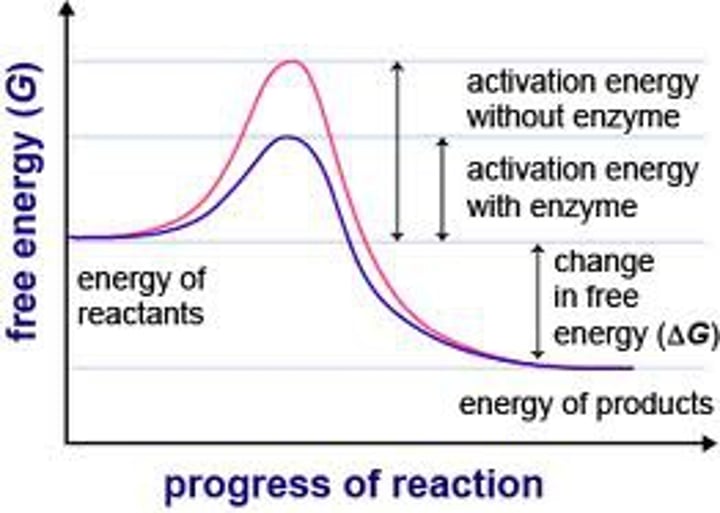
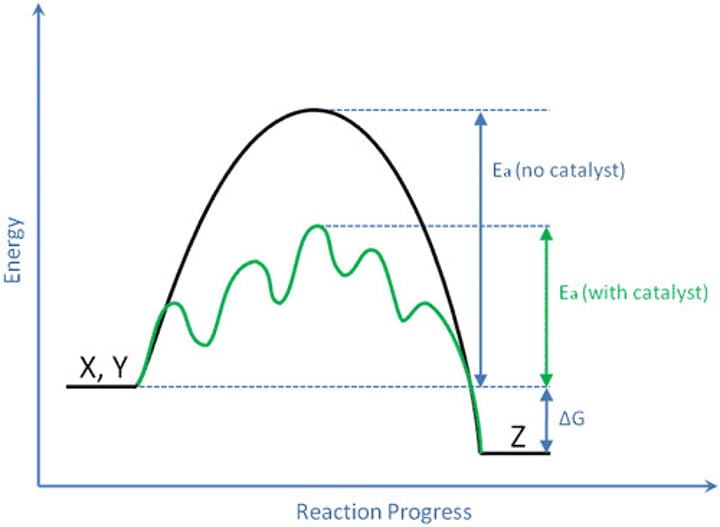
activation energy
The amount of energy needed to push the reactants over an energy barrier.
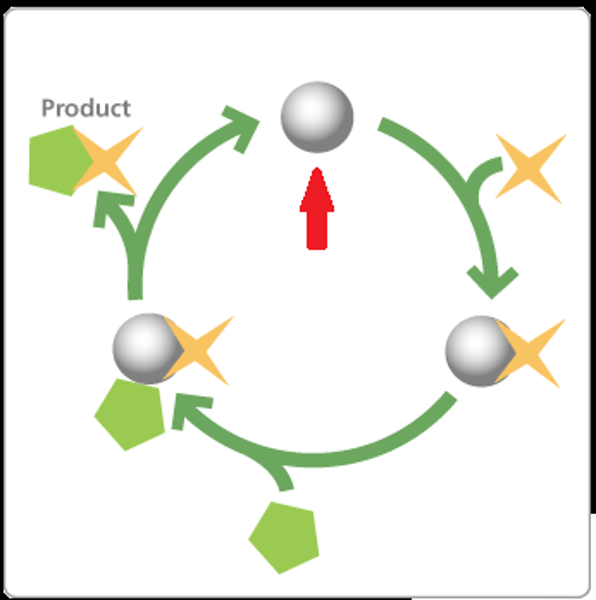
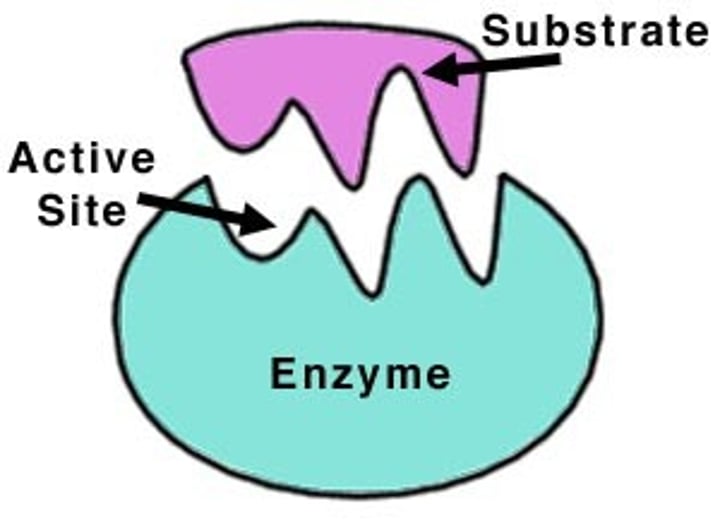
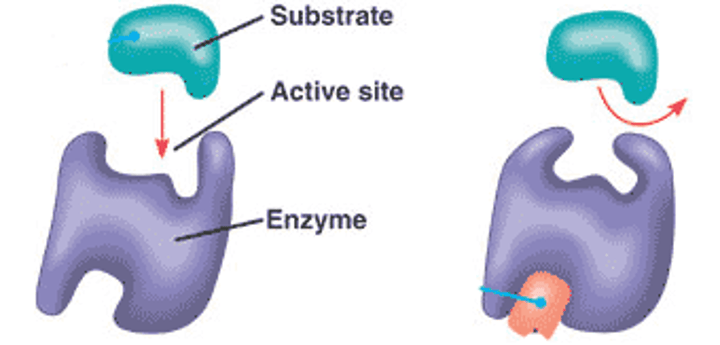
enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms:
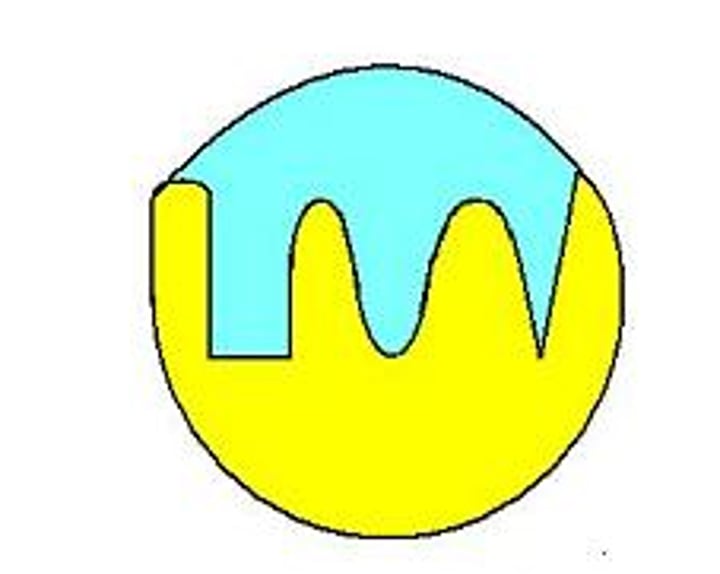

active site
A pocket or groove on the surface of the enzyme where a substrate can bind.
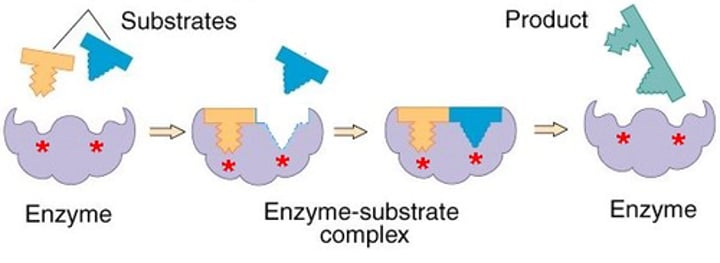
induced fit model
States that the enzyme and substrate undergo conformational changes to interact fully with one another (as opposed to "Lock & Key"
competitive inhibitors
Reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites.
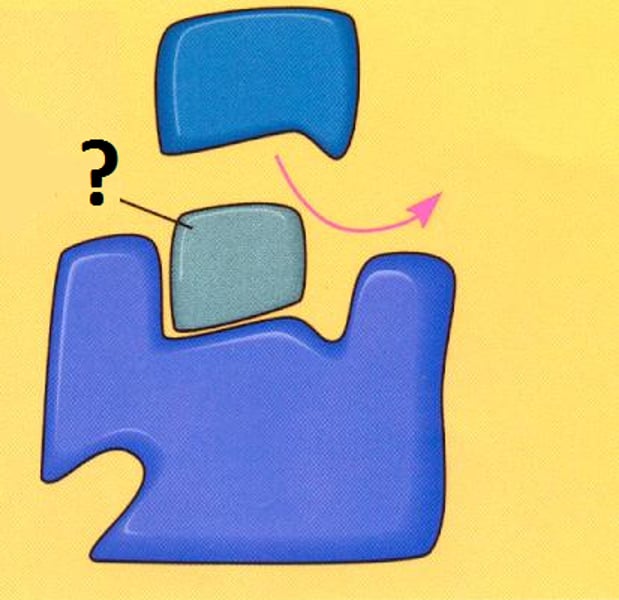
noncompetitive inhibitors
Impede enzymatic reactions by binding to another part of the enzyme (other than the active site).
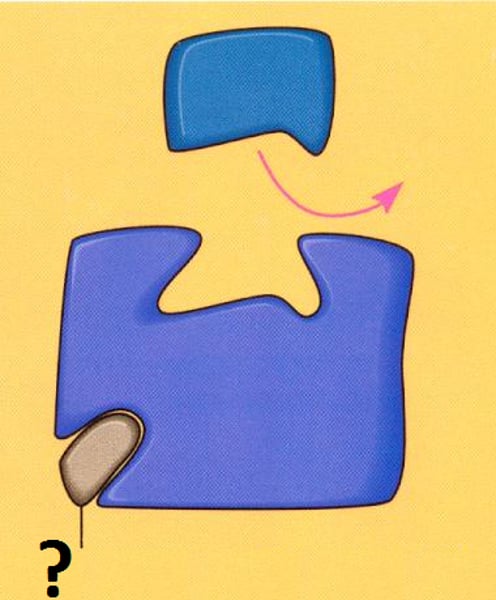
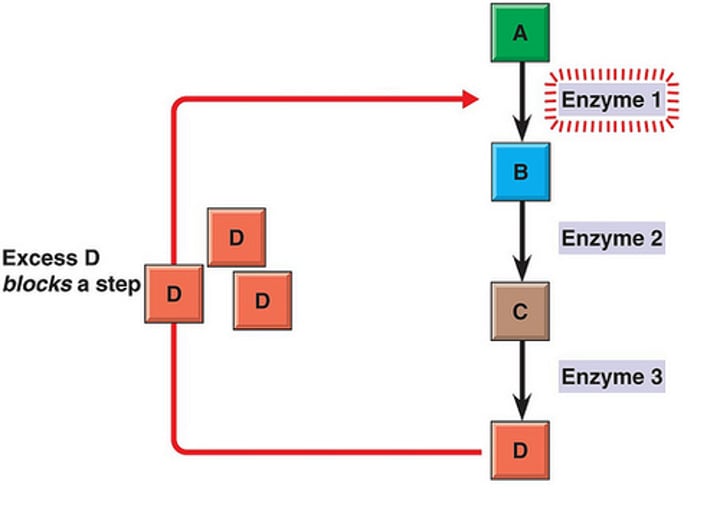
feedback inhibition/negative feedback
A metabolic pathway is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
Chemical Energy
Potential energy trapped in molecular bonds.

Spontaneous Reaction
When a reaction doesn't require energy to proceed it is said to be this - doesn't mean it will be FAST.
Competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
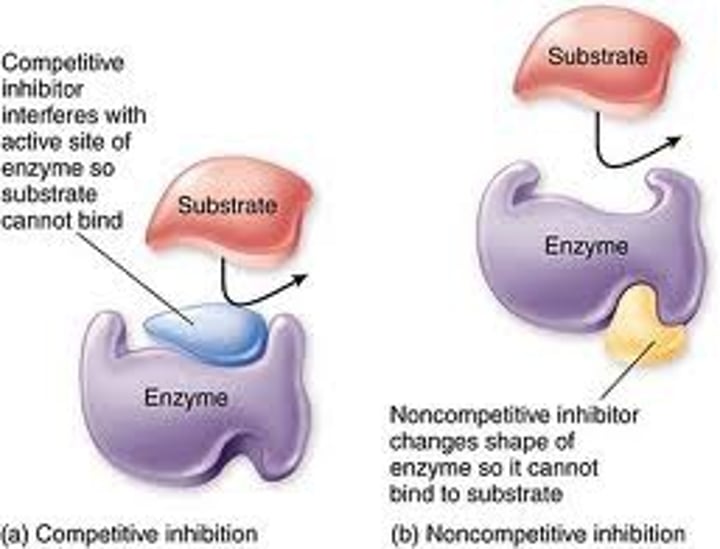
Noncompetitive inhibitor
a chemical that binds to an enzyme but not in the active site. This chemical will change the shape of the enzyme (reversible)
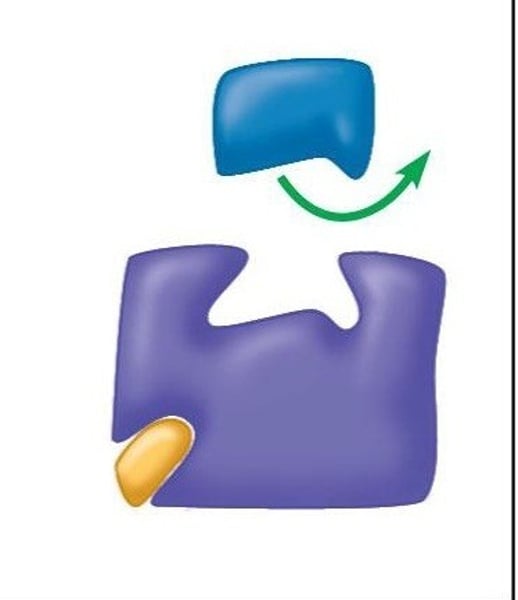

substrate
the substance an enzyme catalyzes, changes.
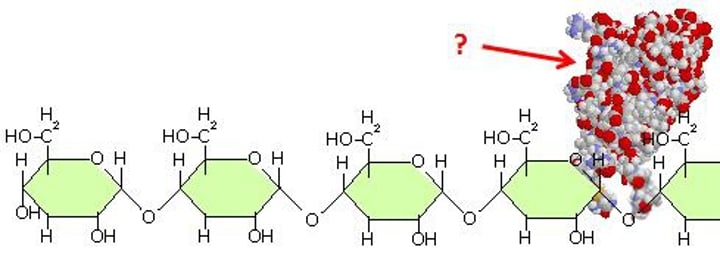
amylase
Enzyme that can break the bonds of starch to form the carbohydrate monomer, glucose.
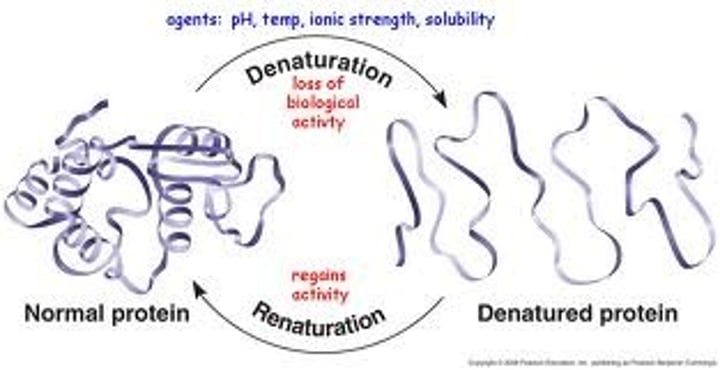
Denature
Characteristic of proteins; a change in shape that stops the protein from functioning.
Allosteric
__________ regulation of enzyme occurs when a molecule binds to an enzyme changing the protein's shape
Catalyst
______ an agent that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself being permanently altered
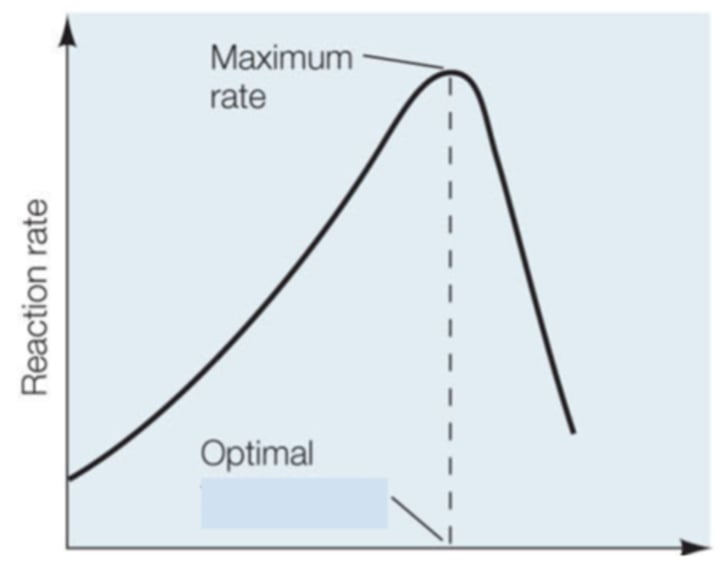
Temperature
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable:
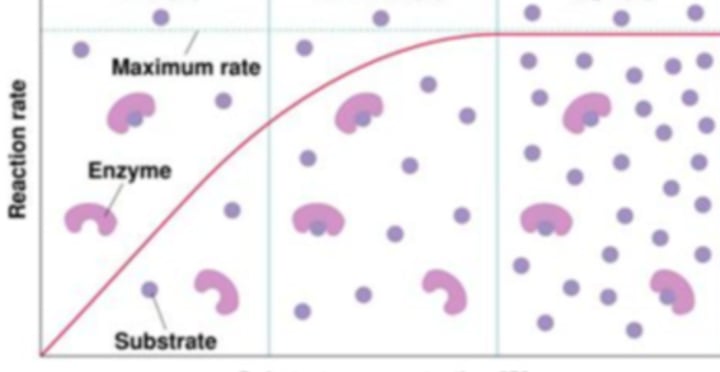
Substrate Concentration
After looking at the shape of graph the enzyme activity of this enzymes is being regulated by what variable:
Metabolism
The totality of an organism's chemical reaction
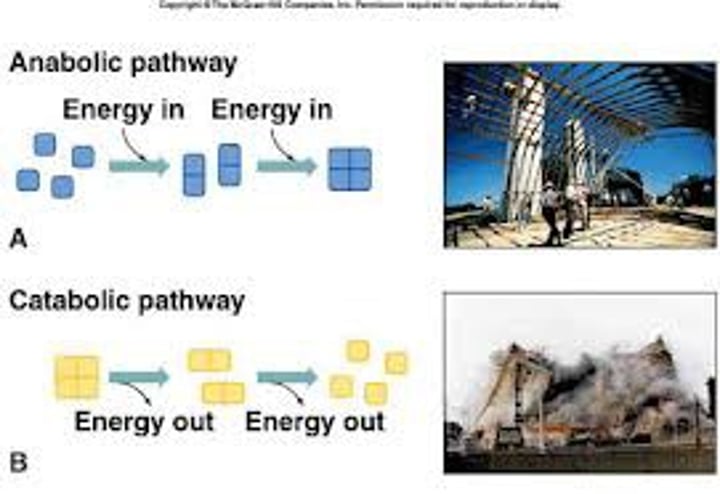
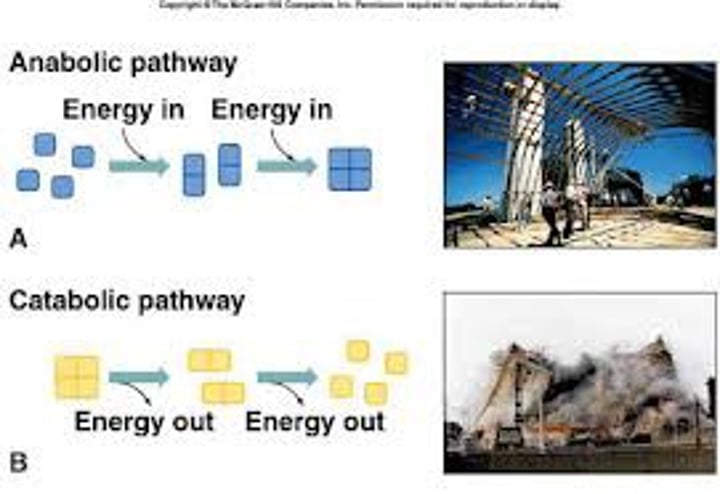
Catabolic pathway
Release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones i.e. Cellular respiration
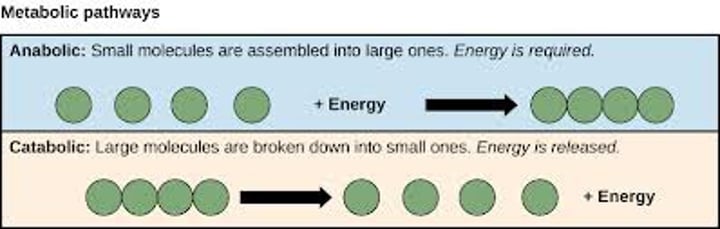
Anabolic pathways
Consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones i.e. Amino acids making up proteins
breaks down molecules, negative ΔG
Catabolic
Energy storing, Positive ΔG
Endergonic
builds larger products, Positive ΔG
Anabolic
symbol G
Free energy
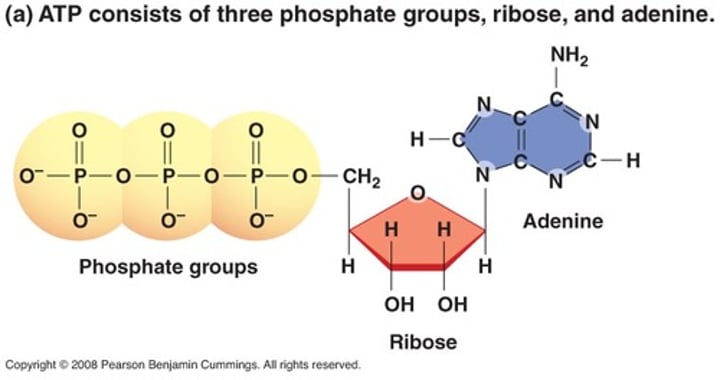
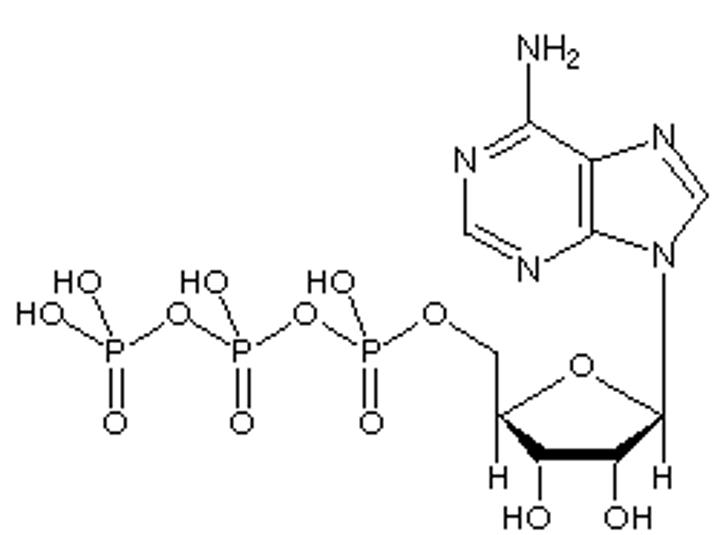
Adenine, ribose, phosphate group
ATP is composed of
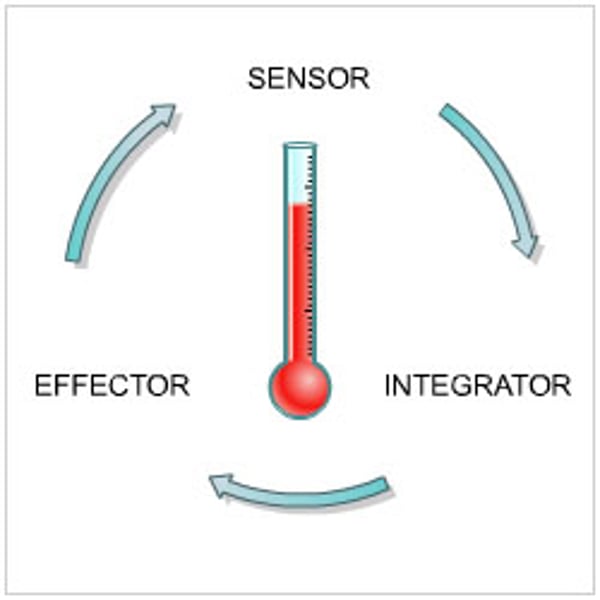
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Catalase
enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
chemiosmosis (oxidative phosphorylation)
the process of converting ADP to ATP by using the proton gradient to force protons (H+) through ATP synthase
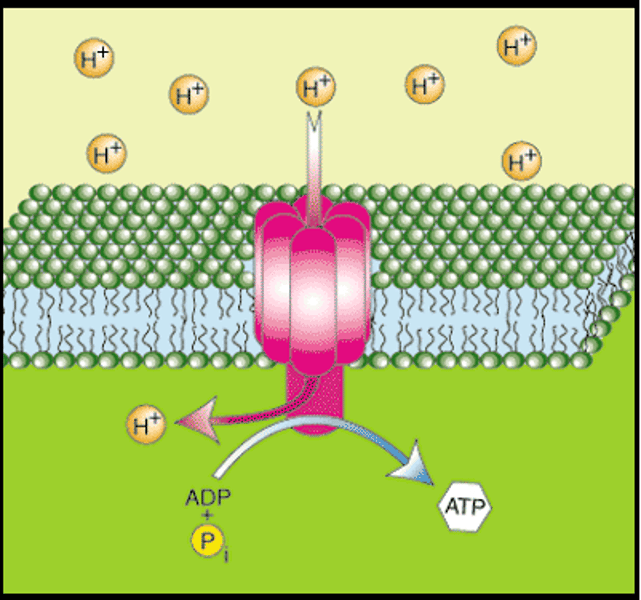
ATP synthase
enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that adds a high-energy phosphate group to ADP to form ATP
NADPH
electron carrier that provides high-energy electrons for photosynthesis
purpose of light reactions
convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH
Purpose of Calvin Cycle
To make glucose from carbon dioxide using the enzyme Rubisco.
Purpose of the Krebs Cycle
Make energy carriers (NADH, FADH2)
purpose of glycolysis
break down of glucose into pyruvate
purpose of Fermentation
to regenerate NAD+ so glycolysis can continue
mitochondrial matrix
The compartment of the mitochondrion enclosed by the inner membrane and containing enzymes and substrates for the Krebs cycle.
Stroma (chloroplast structure)
fluid inside chloroplast where Calvin cycle occurs.
Endocrine system
Secretes hormones into blood from ductless glands that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses
Paracrine
Signals act on cells near the secreting cell
Local regulators
Chemical signals that travel over short distances due to diffusion
Autocrine
Signals act on the secreting cell itself (usually for apoptosis)
Pheromones
Chemical signals that are released from the body and are used to communicate with other individuals
Type I diabetes mellitus
An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells (usually develops while you're young)
Type II diabetes mellitus
Involves insulin deficiency or reduced response of target cells due to change in insulin receptors (due to being overweight and not exercising)
Hormone
A regulatory substance produced in an organism and transported in tissue fluids such as blood or sap to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action.
Negative Feedback
The diminution or counteraction of an effect by its own influence on the process giving rise to it, as when a high level of a particular hormone in the blood may inhibit further secretion of that hormone, or where the result of a certain action may inhibit further performance of that action.
Plant growth regulator
Organic compounds other than nutrients (like hormones that affect plant growth.
tropism
A growth response that results in the curvature of whole plant organs toward or away from stimuli owing to differential rates of cell elongation.
phototropism
Growth of a plant shoot toward or away from light.
action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
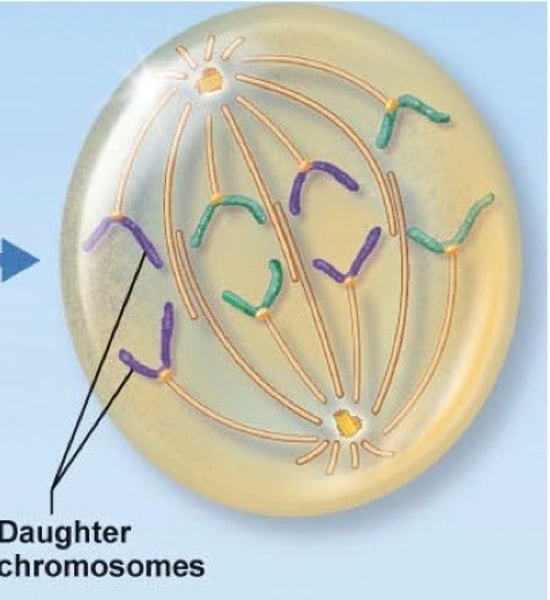
anaphase
fourth stage of mitosis, in which the chromatids of each chromosome have separated and the daughter chromosomes are moving to the poles of the cell
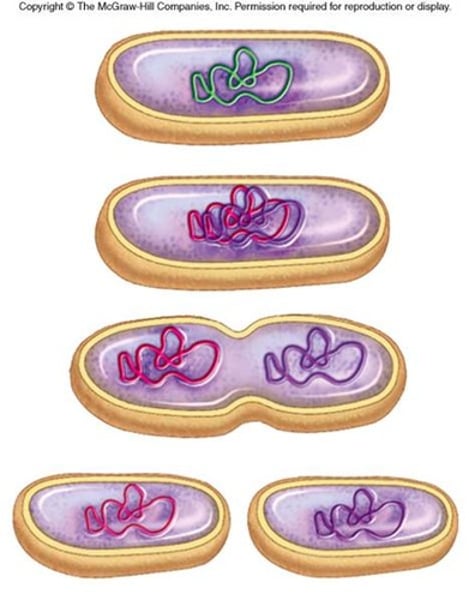
binary fission
the type of cell division by which prokaryotes reproduce; each dividing daughter cell receives a copy of the single parental chromosome
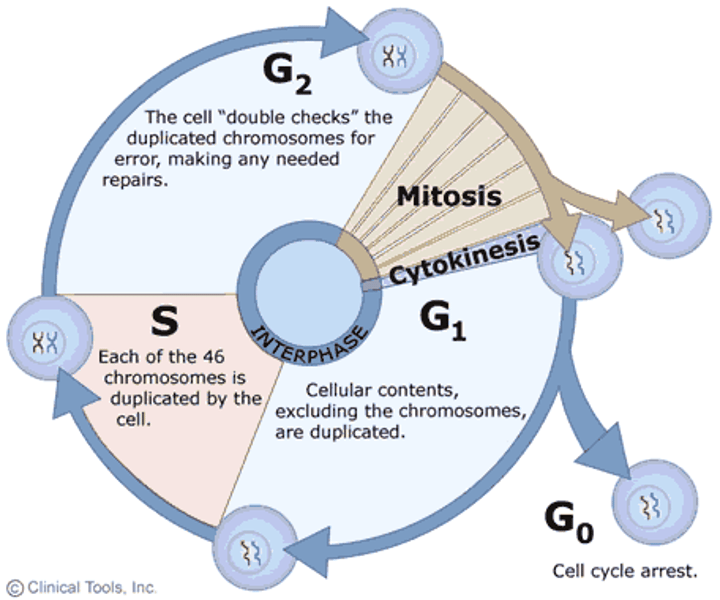
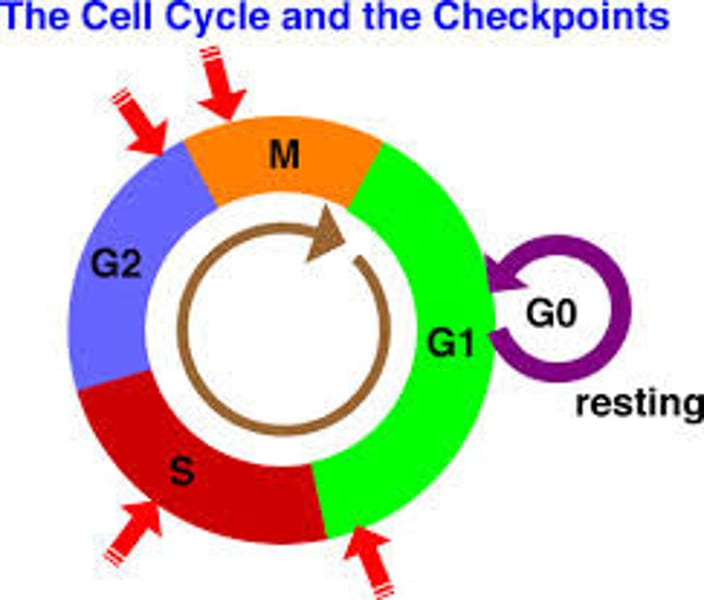
cell cycle
an ordered sequence of events in the life of a eukaryotic cell, from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two; composed of M, G1, S, G2
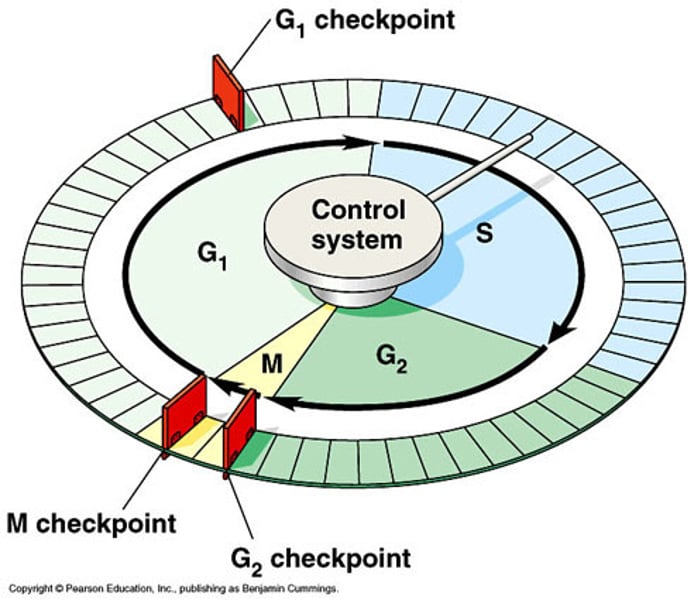
cell cycle control system
a cyclically operating set of molecules in the cell that triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle
cell division
reproduction of a cell
cell plate
a double membrane across the midline of a dividing plant cell, between which the new cell wall form during cytokinesis
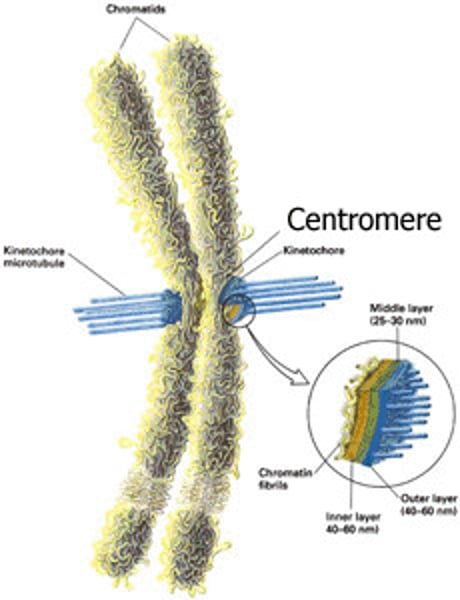
centromere
the centralized region joining two chromatids
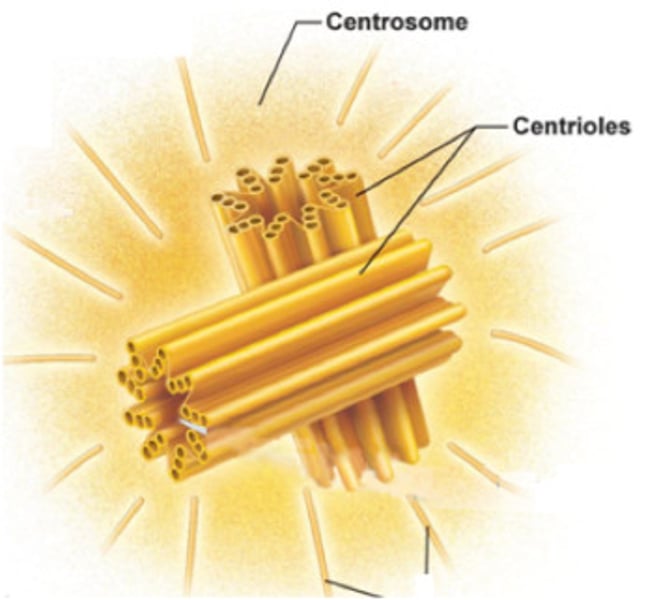
centrosome
material present in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells, important during cell division; the microtubule organizing center
checkpoint
a critical control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals regulate the cycle
chromatin
complex of DNA and proteins that makes up a eukaryotic chromosome; when a cell is not diving it exists as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope
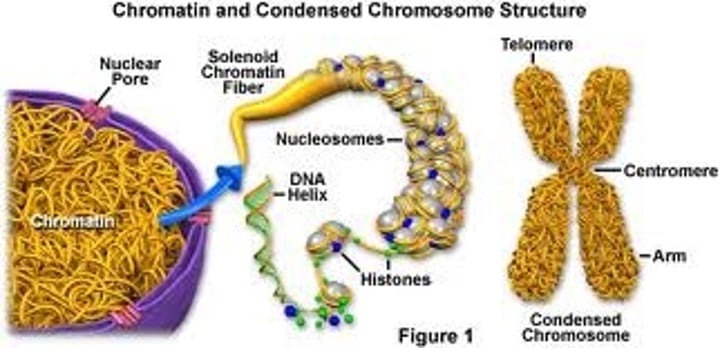
chromosome
a threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus; each consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins, more condensed and coiled than chromatin