Equine Industry
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These notes cover just about everything located on the ppt slides as well as some questions from Tophat.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
how does the horse industry differ?
management decisions are not always driven by profit
production goals
production components
industry diversity
Shared characteristics to other industries
marketing channels
consumer driven
Who leads the world in horse numbers?
the U.S
What are the horse numbers in the U.S?
peaked at 25 million in 1914, currently only 7 million
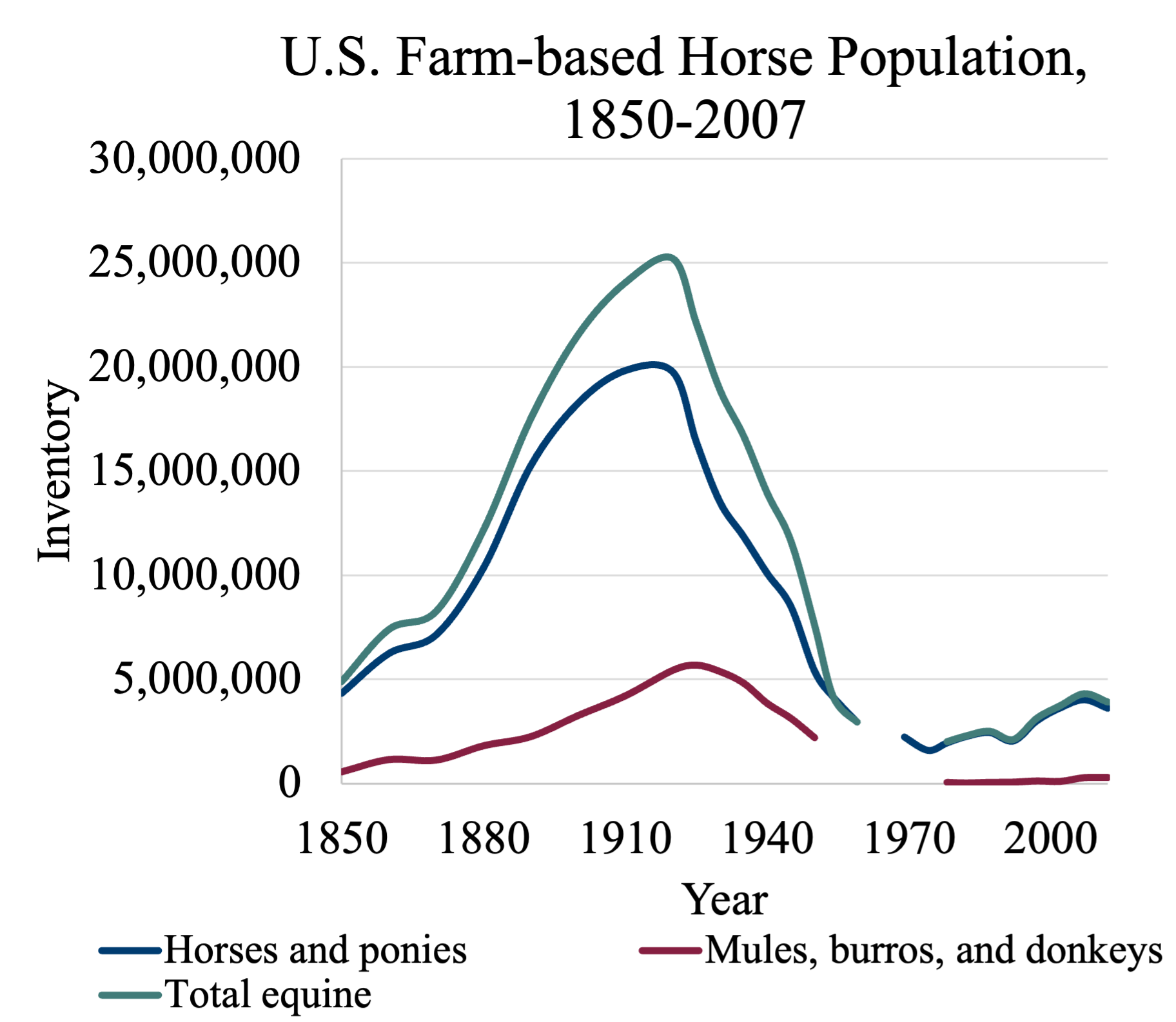
Which states are the most horses located?
Texas, California, and Kentucky
Virginia is 12th (1.2 billion industry)
Genus
Equus
Foal
young baby horse
filly foal
young female horse
colt foal
young male horse
mare
mature female horse
stallion
intact male horse
gelding
castrated male horse
foaling
act of giving birth for horses
herd
group of horses
English saddle
seat- girth- stirrup
western saddle
horn- seat- cinch- stirrup
other tack
bridle- bit- reins
Breed Types
draft horses, warmbloods, light horses, gaited horses, ponies
What is the unit of measurement used for horses, equivalent to 4 inches?
hand
Quarter Horses
United States
Race at ¼ mile distances
work cattle, pleasure
versatile, good temperament
most common
Which horse breed would be good for working cattle?
Quarter Horses
Thoroughbred
England
Racing, polo, hunters
2nd most popular
Which horse breeds discussed in class would be best categorized as a draft breed?
Clydesdale and Belgian

Which saddle is pictured?
English Saddle

Which saddle is pictured?
Western saddle
Arabian
Egypt or Libya
Oldest horse breed
smart
stamina/heat tolerance
Tennessee walking horse
Tennessee
Gaited Horse
4 beat “running walk”
Pleasure riding, show horse
Belgian
Belgium
Draft
Heaviest
Most popular draft horse
Clydesdale
Scotland
Draft Horse
Popular show horse
Breeds originating from color patterns:
Paint and Appaloosa
Black coat color classification
no brown hairs around muzzle or flank
Bay coat color classification
brown (many shades) coat with black points
Chestnut coat color classification
brown/red, mane and tail same color as body, no black points
Sorrel coat color classification
light red, similar/lighter mane and tail
Gray coat color classification
white and any other color, white hair with age
Lightened colors of coats come from …
dilution genes
What are examples of dilution genes in coat colors?
Buckshin, champagne, cremello, dun, palomino, etc.
What are some white patterns that can show in a horses coat?
leopard complex (spotting)
pinto
roaning
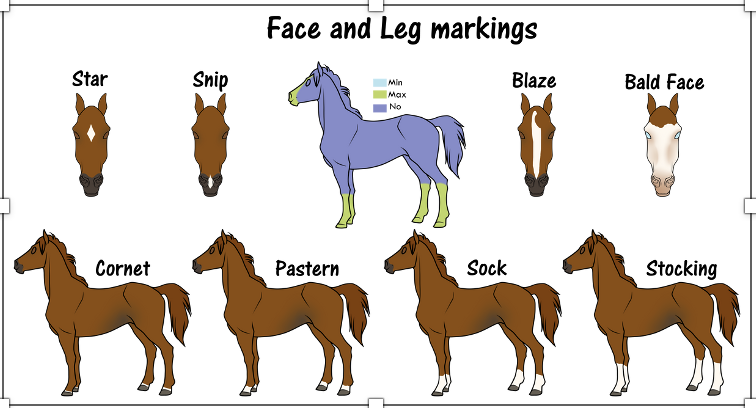
markings (face and legs)
What are some face and leg markings on a horse?
stars
snip
blaze
bald face
cornet
pastern
sock
stocking
What are some examples of industry structures?
racing
recreation
showing
working
wild horses
Horse racing types
flat
steeplechase
harness
endurance
What is an example of a horse that would be popular in endurance racing?
Arabians
Working horses
Ranch
work with cattle
stamina
navigate rough terrain
Police
equine assisted therapy
transportation
farming/draft
What is an example of a horse breed that would be good working cattle?
Quarter horses
Showing horses
dressage
show jumping
eventing
hunter
English or Western pleasure
cutting
team penning
Recreational Horses use:
Pleasure riding
possible companion animals
Wild horses
Federal land out west
BLM
Adoption Program
Colorado, Nevada, etc
What percentage of the horse industry is racing?
9%
What percentage of the horse industry is recreation?
42%
What percentage of the horse industry is showing?
30%
What percentage of the horse industry is working horses?
8%
At what age are horses typically weaned?
5 months
When does a female horse typically hit puberty?
13 months
When would be a good time for breeding a female horse?
When she is about 3-5 years old
allows for full growth to happen
What is the gestation length of horses?
336 days or about 11 months
What are some options for housing?
Barn or Pasture
Barn housing
Individual stall
at least 10×10 ft
size depends
weather protection
more labor input
vices
Pasture housing
fence must be easy to see, materials matter
shelter should be provided
What gastric type do horses have?
hindgut fermenter
What type of nutrition is important?
forage-based nutrition, high-quality roughages
What are some routine care for horses?
dental care- annual, usually in older horses
hoof care- trimmed every 6-8 weeks, type varies on horse
internal parasite control
vaccines
What are some common problems in horses?
bacterial/viral infections (vaccines critical)
Biosecurity is nearly impossible due to travel and mingling
quarantining new animals from others (about 30-60 days)
Equine Infectious Anemia (EIA)- horses get it for life and can’t be around others
colic
abdominal pain
can be fatal
prevention is critical
can be treated
Founder
bone breaks away from laminae tissue
laminitis- infection
can be caused by excessive weight or high-grain diet/lush pasture
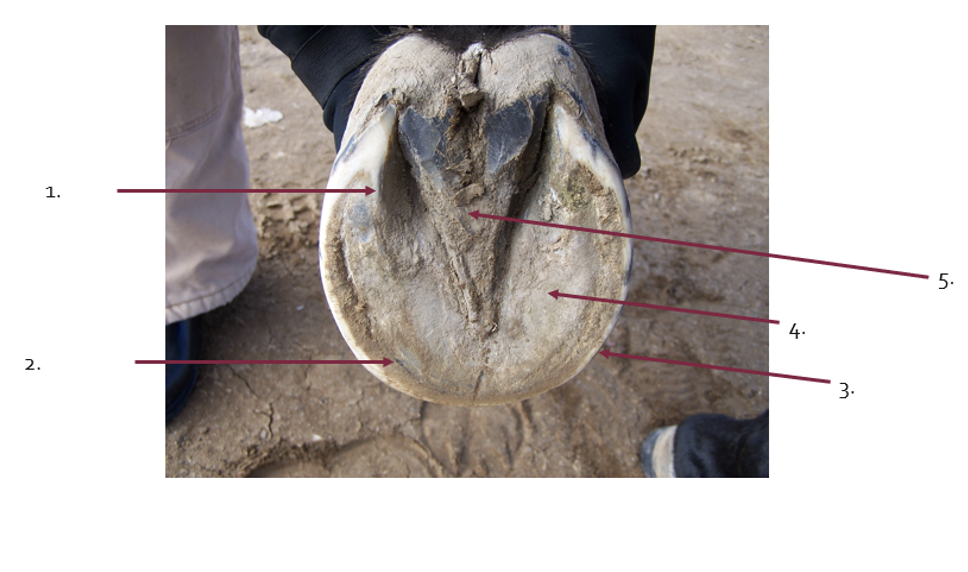
What is the term for 1?
bars
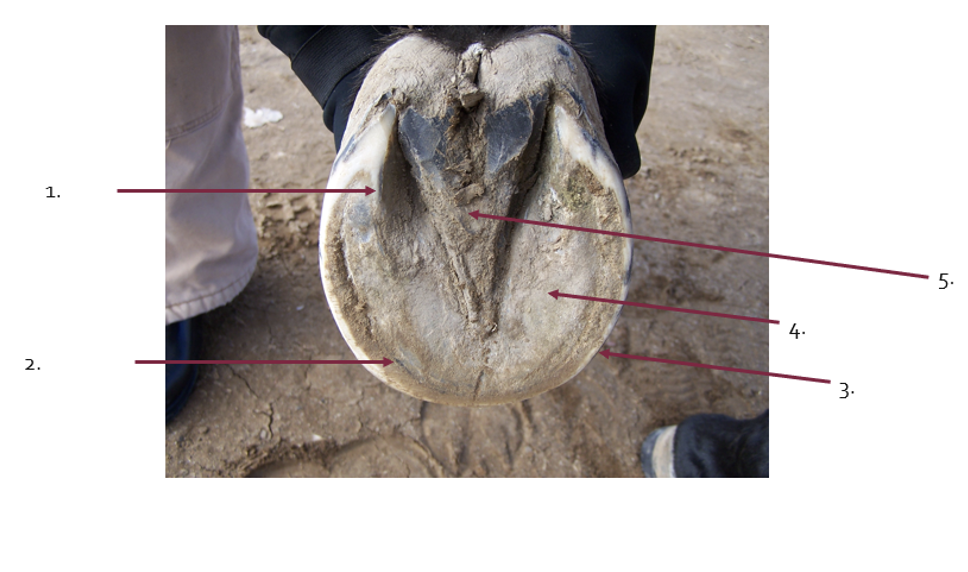
What is the term for 2?
White line
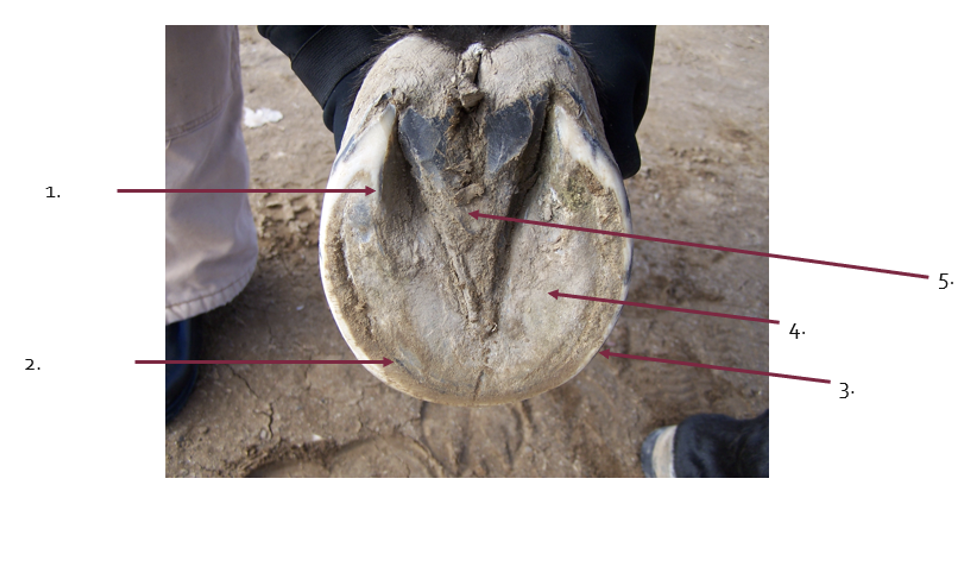
What is the term for 3?
Walls
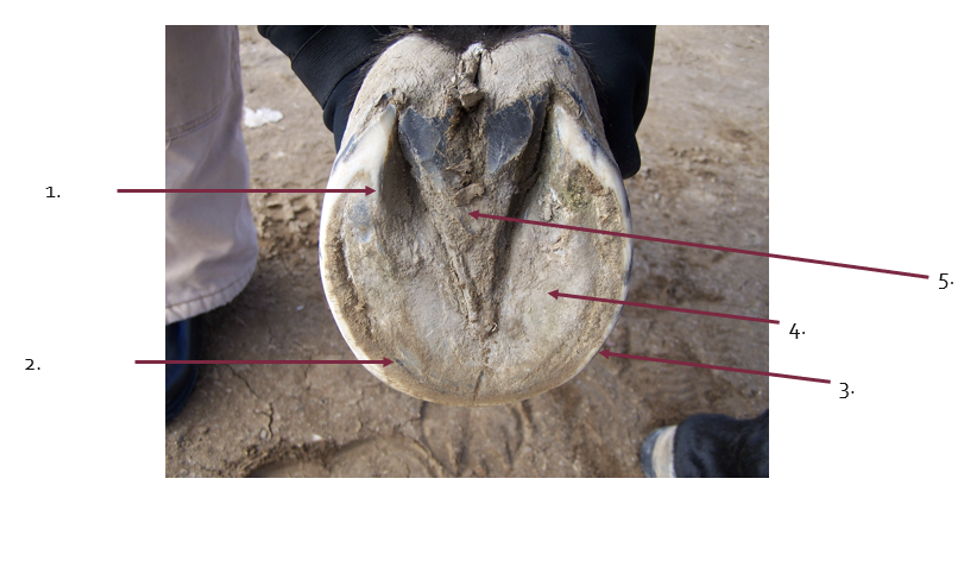
What is the term for 4?
sole
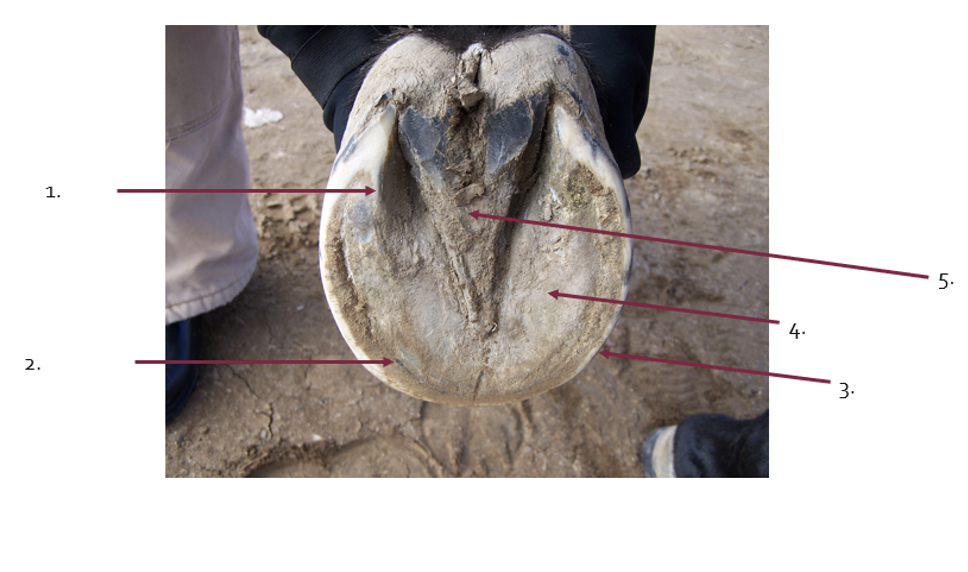
What is the term for 5?
Frog