Chemis
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
Elements, compounds and mixtures
All substances can be classified into one of these three types
Element
A substance made of atoms that all contain the same number of protons and cannot be split into anything simpler
There are 118 elements found in the Periodic Table
Compound
A pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined
There is an unlimited number of compounds
Compounds cannot be separated into their elements by physical means
E.g. copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), carbon dioxide (CO2)
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances (elements and/or compounds) that are not chemically combined
Mixtures can be separated by physical methods such as filtration or evaporation
E.g. sand and water, oil and water, sulfur powder and iron filings
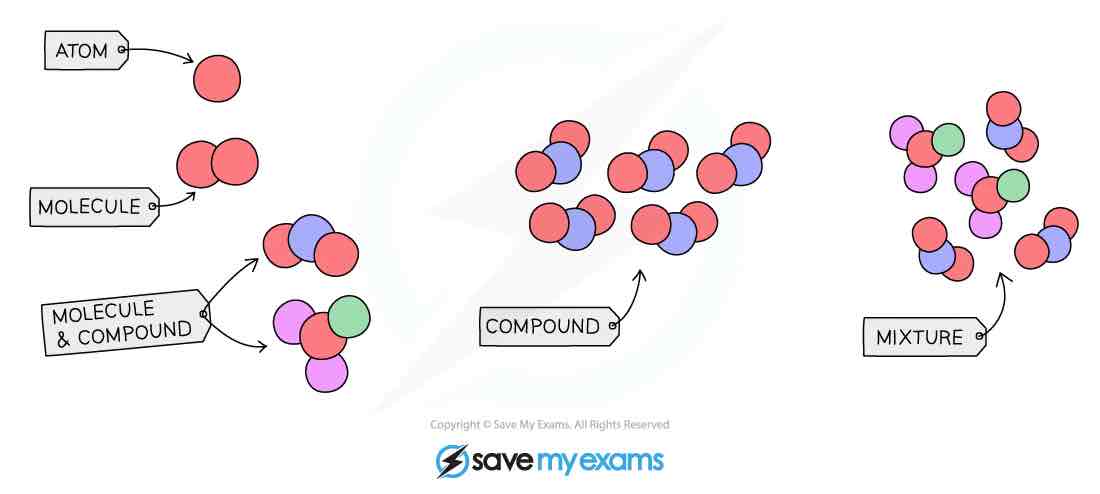
Particle diagram showing elements, compounds and mixtures
What is Atomic Structure?
All substances are made of tiny particles of matter called atoms which are the building blocks of all matter
Each atom is made of subatomic particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons
The protons and neutrons are located at the centre of the atom, which is called the nucleus
The electrons move very fast around the nucleus in orbital paths called shells
The mass of the electron is negligible, hence the mass of an atom is contained within the nucleus where the protons and neutrons are located
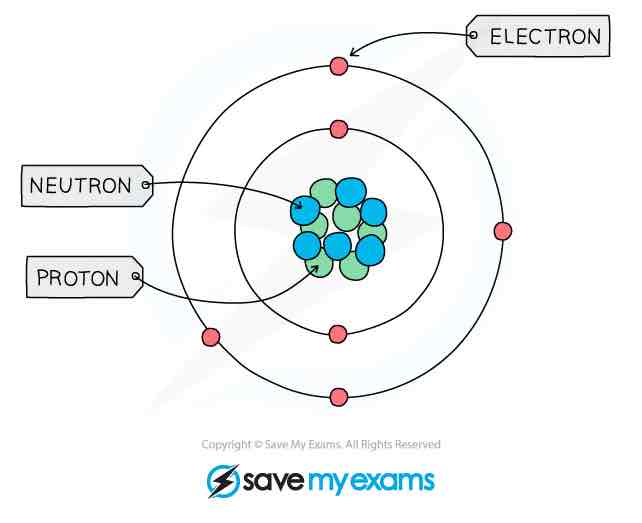
Protons, Neutrons & Electrons
The size of atoms is so tiny that we can't really compare their masses in conventional units such as kilograms or grams, so a unit called the relative atomic mass is used
One relative atomic mass unit is equal to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
All other elements are measured relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom, so relative atomic mass has no units
Hydrogen for example has a relative atomic mass of 1, meaning that 12 atoms of hydrogen would have exactly the same mass as 1 atom of carbon
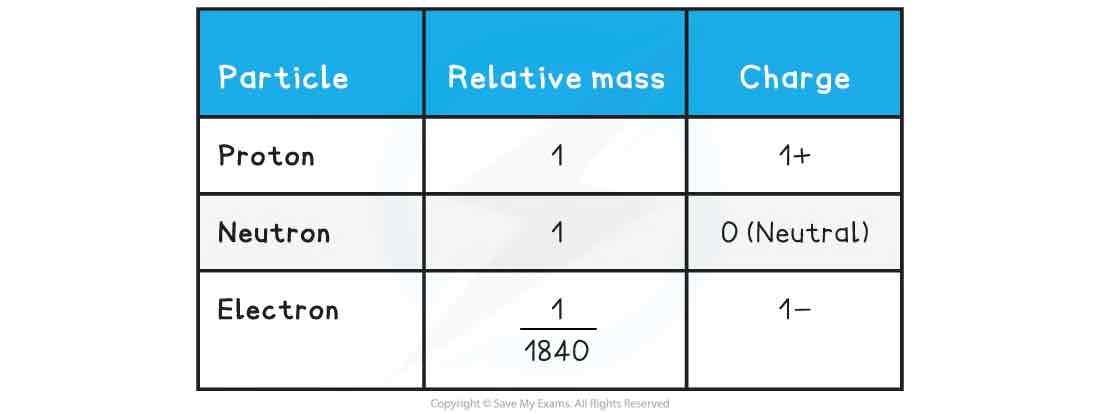
The relative mass and charge of the sub-atomic particles are shown below: