Kin 311: Lecture 2 Pre Screening and Risk Assessment
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms related to fitness and health assessment as discussed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Pre-Screening
The process of identifying individuals at risk for cardiovascular events or injuries before beginning an exercise program.
ACSM
American College of Sports Medicine, which provides guidelines for exercise testing and prescription.
Cardiac Rehab
A supervised program that helps improve the health and fitness of people with heart problems.
Moderate Intensity Exercise
Physical activity that raises your heart rate to a level where you can talk, but not sing, while doing the activity.
Vigorous Intensity Exercise
Physical activity that causes a large increase in heart rate and breathing. You cannot say more than a few words without pausing for breath.
CVD Risk Factors
Attributes or conditions that increase the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease, such as physical inactivity or high blood pressure.
Sudden Cardiac Death
An unexpected death caused by loss of heart function, often related to underlying cardiac conditions.
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath that can occur at rest or with exertion and may indicate underlying health issues.
Angina
Chest pain or discomfort resulting from reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, often provoked by stress or exertion.
Medical Clearance
A recommendation from a healthcare provider that a patient may safely engage in exercise based on their medical history.
Intermittent Claudication
Pain in the legs or buttocks that occurs during exercise due to inadequate blood flow, typically relieved by rest.
Risk Assessment
The process of evaluating individuals' health status based on personal and family medical history to determine exercise safety.
Exercise Paradox
The concept that while exercise can pose risks, it also offers profound health benefits for most individuals.
Orthopnea
Shortness of breath that occurs when lying flat but is relieved by sitting or standing.
Edema
Swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues, particularly noticeable in the legs or abdomen.
Arrhythmias
Irregular heartbeats that may be benign or indicative of underlying heart disease.
The Exercise Paradox
Refers to the phenomenon where physical activity increases the risk of acute cardiovascular events in individuals with cardiovascular disease, despite the well-established health benefits of regular exercise.
Why Pre Screen
Asses Safety, ID those who may need medical clearance or supervision, choose appropriate assessment, minimize risk, provide effective exercise program
What does a proper risk assessment require
A prediction of how things could go wrong and what you will do to mitigate those risks
How can we decide who needs medical clearance
Using the ACSM guidelines for exercise testing Pre- Participation screening
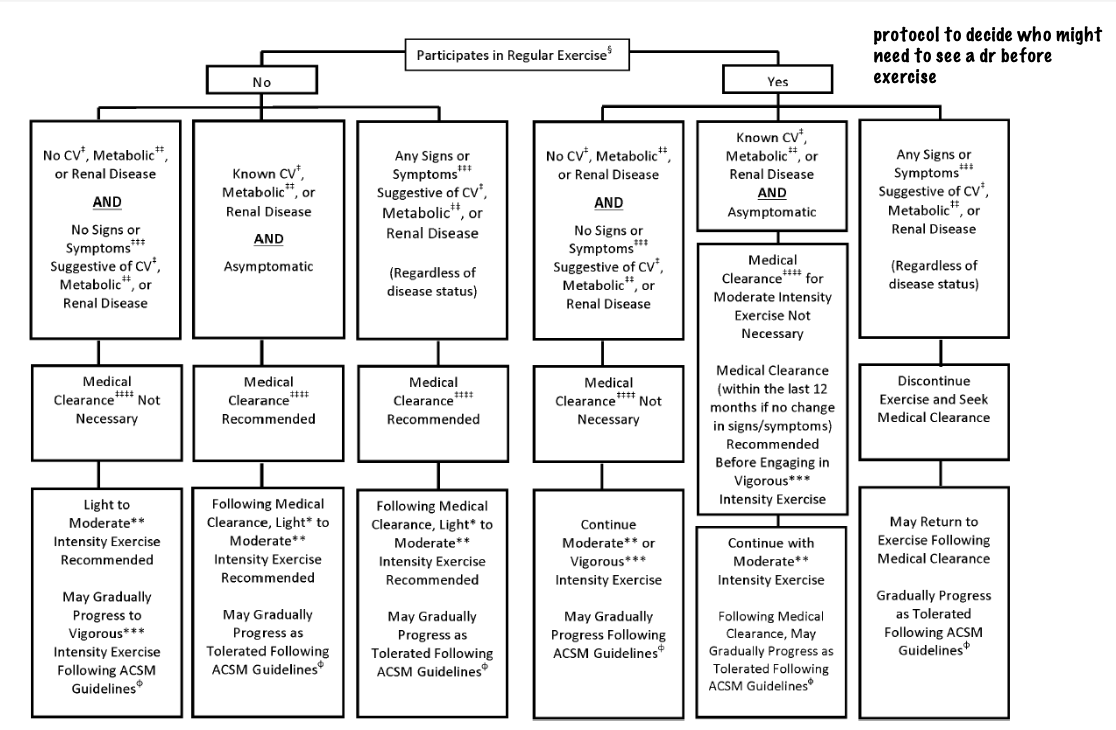
What are the two things that are asked about in the ACSM Pre- Participation screening
Individual's current level of exercise/physical activity and Presence of signs or symptoms and/or known disease cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, renal disease
Examples of Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Cardiac disease, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease
Examples of metabolic disease
Diabetes (type 1 & 2)
Thyroid disorders
Renal or liver disease
Examples of Pulmonary Disease
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, interstitial lung disease, cystic fibrosis
What are the 9 major symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
Angina (chest discomfort), dyspnea, unusual fatigue, dizziness or syncope, edema, orthopnea or proximal nocturnal dyspnea, arrhythmias, intermittent claudication, known heart murmur
Angina
mismatch between supply and demand of blood in the heart which results in oxygen deficit
Characteristics of Angina
•Constricting
•Squeezing
•Burning
•“Heaviness”
•“Heavy Feeling”
•Broad and general
•Dull
•“knife like”
•Sharp
•Stabbing
•“Jabs” aggravated by respiration
Provoking factors of angina
Exercise or activity
•Excitement
•Other forms of stress
•Cold weather
•Occurs after meals
•Is provoked by a specific position
•Comes on after completion of exercise
common pain locations related to angina
•Substernal
•Across mid thorax, anteriorly
•In on or both arms, shoulders
•Neck
•Cheeks, teeth
•Interscapular region
•One side sub mammary
•One side of the chest / thorax
When to send someone to the hospital for suspected angina
when it is Accompanied by
•Dyspnea
•Fast Irregular Heartbeat
•Sweating / pale / ashen in colour
•nausea / vomiting
•Light-headedness / sudden
weakness
No previous diagnosis of heart disease
•Resolves with rest with no other
symptoms
•Unable to exclude that its heart related
•Unable to determine if MSK
Dyspnea (shortness of breath) at rest, with mild exertion or usual activities
An abnormally uncomfortable awareness of breathing
factors to consider with dyspnea
Typically occurs with moderate to strenuous exertion health trained/untrained adults, Abnormal when it occurs at levels of exertion not expected to evoke this symptom
When to send someone to the hospital for Dyspnea
• Sudden on set
• Doesn’t improve with rest
• Accompanied by
• Chest pain
• Weakness / Feeling Faint
• Nauseous
• Fast Irregular Heart Rate
• Confusion / Drowsiness
• Blue or ashen in colour
Unusual fatigue with usual activities
May be benign and caused by deconditioning
May signal of change in cardiovascular or metabolic disease
Factors to consider with unusual fatigue
•Often accompanied by dyspnea
•Activity level
•Sleep
•What’s normal for them?
•How many flights of stairs can you do?
•How many blocks can walk without stopping?
•Is it accompanied by other cardiovascular symptoms?
Dizziness or Syncope (loss of consciousness) can be cause by
• A blunted or reduced cardiac output
• Results in reduced perfusion to the brain
Light headed
typically associated with poor blood pressure, or not enough oxygen in the brain
Dizziness
something that is more closely related to the vestibular complex in the ear
provoking factors of dizziness or syncope during exercise
may be cardiac disorder
provoking factors of dizziness or syncope after exercise
may be due to blood pooling in extremities
factors to consider with dizziness or syncope
•Hydration
•Medications (related to the heart)
•Blood pressure
•Heart Rate
•Level of exertion
Edema
Swelling cause by too much fluid trapped in the body’s tissues
characteristics of edema
generally occurs in the abdominal area and limbs, leading to a noticeable increase in size and discomfort.
factors to consider with edema
•Sudden change in weight > 2kg in 1-3
days
•Decrease in exercise tolerance
When to send someone to the hospital for edema
When it as accompanied by
•Dyspnea
•Irregular heartbeat
•Chest pain
•Fatigue
•Severe pain in affected leg(s) affecting ability to walk
Orthopnea
Dyspnea occurring at rest when laying
down, Relieved by sitting upright or standing
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
•Dyspnea beginning 2-5 hrs after sleep
•Relieved by sitting upright or standing
factors to consider for both orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Sudden change in weight > 2kg in 1-3
days
May be accompanied by fatigue
How many pillows do they sleep with
at night
Intermittent claudication
Pain in the lower extremities brought on with exercise
Characteristics of intermittent claudication
Brought on with exercise (i.e., stairs, hills)
•Disappears within 1-2 minutes of rest
•Doesn’t occur with sitting or standing
•Described as cramping
•Reproducible from day to day
•Doesn’t relieve with stretching
When to send an individual to a family doctor for intermittent claudication
•New symptom and not previously
diagnosed
•Unable to determine if its muscular
When to send an individual to the hospital for intermittent claudication
•Unable to determine if its muscular
•Pain doesn’t go away with rest and
affects ability to walk
Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)
A problem with the rate or rhythm
palpations
unpleasant awareness of forceful rapid heartbeat
tachycardia
Fast heart rate > 100 bpm
bradycardia
Slow heart rate < 60 bpm
factors to consider when suspecting arrythmias
•What’s their normal resting heart rate ?
•What is their training status?
•Do they have a pre-existing heart condition?
•Medications (for the heart)
•May be induced by
various cardiac rhythms
anxiety
anemia
fever
when do you send someone to hospital for Arrhythmias
•Resting HR > 120 bpm
•Resting HR < 40 bpm
Accompanied by;
•Chest Pain
•Dyspnea
•Irregular heartbeat
•Syncope / Presyncope
•Fatigue / Weakness
•Edema
•Confusion / Drowsiness
Know Heart Murmur
May be indication of valvular disease or cardiovascular disease
what part of exercise prescription can ACSM’s Pre-participation Screening help prescribe
desired exercise intensity
categorizing exercise intensity
Light, moderate, vigorous
Light intensity
• 30 to 40% HRR or V02R
• 2 to < 3 METs
• RPE 9-11
• An intensity that causes slight ↑ in
HR and breathing
Moderate intensity
• 40 to < 60% HRR or VO2R
• 3 to < 6 METs
• RPE 12-13
• an intensity that causes noticeable
↑ in HR and breathing
Vigorous- Intensity
• > 60% HRR or VO2R
• > 6 METs
• RPE > 14
• An intensity that causes
substantial ↑ in HR and
breathing
ACSM CVD Risk Stratification
A guideline that categorizes individuals into different risk levels for cardiovascular disease based on health history, current health status, and lifestyle factors. This stratification helps determine appropriate exercise recommendations and pre-screening procedures.
non modifiable risk stratification factors
age and family history
Age as a risk stratification
• Men > 45 years; Women > 55 years
Family history as a risk stratification
• Myocardial Infarction, coronary revascularization,
or sudden death.
• 1st degree relative; male < 55 year; female < 65
years
modifiable risk stratification factors
Physical inactivity, BMI, BP, lipids, Blood glucose, cigarette smoke
Smoking cigarettes as a risk stratification
Current, quite within 6 months or exposed to
environmental smoke
Physical inactivity as a risk stratification
Not meeting > 150 min/week of mod-
vig intensity physical activity
BMI as a risk stratification
BMI > 30 or waist girth > 102 cm (40
in) men, >88cm (35 in) women
BP as a risk stratification
> 130 mmHg systolic, > 80 mmHg
diastolic based on average of 2
readings on 2 separate occasions, or
on antihypertensive medication
Lipids as a risk stratification
LDL > 3.37 mmol•L-1;
HDL < 1.04 mmol•L-1 in men;
HDL < 1.30 mmol•L-1 in women;
on lipid lowering medication
blood glucose as risk stratification
HbA1C > 5.7%;
or on medication
What is the one negative risk factor
having high HDL cholesterol > 1.55 mmol •L-1
What is considered low risk
Asymptomatic and who have < 2 (i.e., 1 or 0) CVD risk factors
What is considered moderate risk
Asymptomatic and who have > 2 risk factors
what is considered high risk
Individuals with one or more signs/symptoms or know
cardiovascular, pulmonary, or metabolic disease