
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
To prepare a sample in a capillary tube for a melting point determination, gently tap the tube into the sample with the
________ end of the tube down. Continue tapping until the sample
__________.
Then, with the
________ end of the tube down, tap the sample down slowly or
________ move the sample down faster.
Finally, make sure that you can see ________ in the magnifier when placed in the melting point apparatus before turning on the heat.
open; is a couple millimeters high
closed; drop the tube into a longer tube
some or all the solid
When performing a melting point determination, how should you report your findings?
As a range from the temperature when melting starts to end, temperature when it ends
What is the recommended order of measurements to report the most accurate melting point possible?
First Step: Use quick heating to estimate the melting point
Second Step: Use slow heating to carefully observe melting
Third Step: Use slow heating to confirm the careful measurement.
The Diels-Alder mechanism between a diene and a dienophile is _________, which means that bond breaking happens _______ bond forming.
To help the mechanism succeed, the diene should have an
________ group and the dienophile should have an
_________ group.
concerted; at the same time as; electron releasing; electron withdrawing
Consider the Diels-Alder reaction of anthracene and maleic anhydride.
What is the role of each of the reactants?
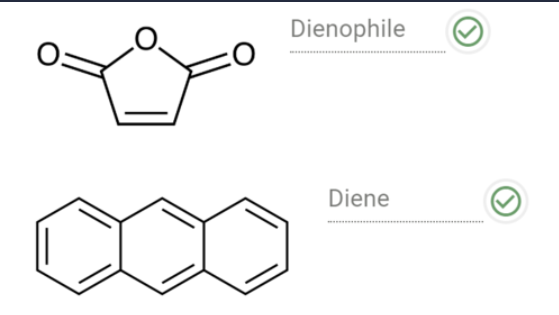
When maleic anhydride reacts with anthracene, it adds to the _______ of anthracene. The product of this addition has
________, which is more stable than the other possibilities, because there are ________ aromatic π electrons.
middle ring; two separate aromatic rings; more
Consider the given structure of the product of a Diels-Alder reaction.
What reactants are necessary to make the product?

Why does the reaction of anthracene with maleic anhydride needs to be kept away from water?
Maleic anhydride can react with water, opening its ring.
In the Diels-Alder lab procedure, a wet paper towel is used.
What is the purpose of the wet paper towel?
To encourage condensation during the reflux
Xylene is an ideal solvent for Diels-Alder reactions, like that of maleic anhydride and anthracene.
What properties of xylene are beneficial to the Diels-Alder reaction?
- High boiling point
- Low freezing point
- Better solvent for reactants than product
Complete each statement on safety precautions when using round bottom flasks.
- Before using the flask, inspect it for _________.
- Use ______ for stability when suspending the flask on a ring stand.
- Never heat a flask that is ________.
- cracks or imperfections
- a clamp
- closed
In order to heat a round bottom flask in a heating mantle, plug the heating mantle into _______. Turn the heat up ______, and do not exceed ________ of the maximum output of the device.
a variac or powermite; gradually; 50-60%
What is meant by the term bumping?
Sudden and uncontrolled boiling of liquid
What is the best technique for removing a round bottom flask from an oil bath?
Wearing heat-resistant gloves, raise the clamp to lift the flask out of the oil bath. Allow the flask to cool for a while, then use a paper towel to wipe any oil from the bottom of the flask.
Identify items that can be used to control the boiling when heating liquid in a round bottom flask.
- Boiling chips or stones
- A stir bar and stir plate
According to Markovnikov's rule of the electrophilic addition to an alkene, the electrophile, usually a proton, is more likely to add to the ________ in a double bond. This arrangement places the intermediate carbocation on the ________, which stabilizes it with the presence of ________. In the major product of a reaction following Markovnikov's rule, the ________ will then end up on the more-substituted carbon in a double bond.
less-substituted carbon; more-substituted carbon; more substituents; nucleophile
Determine whether each alcohol could be a major product of the acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene.

Determine the order of steps in the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydration of propene.

In general, what are the possible products of an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene?
- Primary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
Consider the mechanism of forming phenacetin from p-acetaminophenol, bromoethane, and methoxide. Identify the species that performs each listed role in the reaction.
- Base
- Nucleophile
- Acid
- Leaving group
- Methoxide
- p-Acetamidophenolate
- p-Acetamidophenol
- Bromide
In a Williamson ether synthesis, you start by adding a base like methoxide to deprotonate a phenol so the deprotonated phenolate can act as a nucleophile.
The moles of base should be ________the moles of the phenol.
Less base might result in the phenol ________. More base might result in the base ________.
- equal to
- not reacting completely
- acting as the nucleophile
The SN2 mechanism occurs in________ with the nucleophile attacking _______ leaving group leaves. Therefore, unsubstituted electrophiles react _______ than substituted electrophiles due to the __________.
- one step
- at the same time
- faster
- decreased crowding
Phenacetin can be prepared from p-acetamidophenol, which has a molar mass of 151.16 g/mol, and bromoethane, which has a molar mass of 108.97 g/mol. The density of bromoethane is 1.47 g/mL.
What is the yield in grams of phenacetin, which has a molar mass of 179.22 g/mol, possible when reacting 0.151 g of p-acetamidophenol with 0.12 mL of bromoethane?
0.179g
During a recrystallization, the goal is to form purified crystals of a solid out of solution. However, you might form an oil instead. How should you respond if an oil forms during your recrystallization?
Add more of the recrystallization solvent to form a solution before cooling again.
What characteristics should a good sample for melting point determination have?
- Thoroughly dry
- Solid phase
- Small particles
Consider the structure of benzil and its reduction.
- The functional group reduced in benzil is _________
- An appropriate reducing agent for this reaction is __________
- a ketone
- sodium borohydride
Describe each pictured molecule based on whether it is chiral and how many stereocenters are present.

There are two common ion versions of hydrogen, the proton (H+H+) and the hydride ion (H−H−).
Determine whether each statement describes a proton or a hydride ion.
- Can act as an oxidizing agent
- Can act as a reducing agent
- Is often the ending point of an arrow in a mechanism
- Can act as a nucleophile
- Is often the starting point of an arrow in a mechanism
- Can act as an electrophile
- Proton
- Hydride
- Proton
- Hydride
- Hydride
- Proton
Suppose you notice a solid impurity in a small liquid sample with a volume less than 10 mL.
What technique can you use to remove the solid impurity?
Filter the sample through a Pasteur pipet with glass wool in it.
How many reducing equivalents are present in each unit of sodium borohydride, NaBH4NaBH4?
4
What statements about the possible hazards of sodium borohydride are correct?
- Sodium borohydride can have a violent reaction with acids.
- Sodium borohydride is flammable.
- Sodium borohydride is corrosive.
n nucleophilic aromatic substitution, the _______ aromatic ring ________ an added _________. The resulting intermediate has a _______ charge and the replaced substituent usually leaves as _______
- Electrophilic
- Is attacked by
- Nucleophile
- Negative
- An anion
Consider the properties of a good nucleophile. When comparing ethanol, CH3CH2OH, and sodium ethoxide, NaOCH2CH3, _______________ is the better nucleophile because it ____________.When comparing sodium methoxide, NaOCH3, and sodium t-butoxide, NaOC(CH3)3, _____________________ is the better nucleophile because it _______________.
-Sodium ethoxide
-Has a negative charge
-Sodium methoxide
-Is smaller
Consider the structure of 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene.A nucleophile added to this reaction will most likely start by attacking carbon _____ because that carbon has ___________ and is __________ to the nitro group.
-4
-a leaving group
-para
Determine whether each description applies to electrophilic aromatic substitution or nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
- The aromatic ring is the electrophile and the added group is the nucleophile.
- The aromatic ring is the nucleophile and the added group is the electrophile.
- Electron donating groups on the aromatic group increase reactivity.
- Electron withdrawing groups on the aromatic group increase reactivity.
- The position of the added group is mostly determined by the location of a leaving group.
- The position of the added group is mostly determined by electronics.
- Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution
- Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
- Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Which reactant will be the best reactant for a nucleophilic aromatic substitution?

Consider the structure of the product of a nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
What reactants were required to form the product?

Determine whether each melting point observation corresponds to a pure sample of a single compound or to an impure sample with multiple compounds.
- Experimental melting point is close to literature value.
- Wide melting point range
- Narrow melting point range
- Experimental melting point is below literature value
- Pure sample of a single compound
- Impure sample of multiple compounds
- Pure sample of a single compound
- Impure sample of multiple compounds
What is the visual indicator that enough of a drying agent, such as anhydrous MgSO4 or CaCl2, has been added to properly dry an organic solution?
The drying agent will move freely like a powder around the solution.
Identify the best practices when storing and using drying agents in the lab.
- Wrap the lid of the drying agent container with tape for storage.
- Close the drying agent container whenever it is not in active use.