PLASTICS
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
PLASTICS
a product of synthetic origin which is capable of being shaped at some stage of its manufacture, but is not rubber, wood, leather or metal.
monomers
It is made from a number of common substances such as coal, salt, natural gas, cotton, wood and water, from which relatively simple chemicals known as
polymers
monomers are built up into chainlike molecules of high molecular weight
condensation polymerization, vinyl polymerization.
Polymers have low extensibility, can be molded, extruded, cut or worked into a variety of shapes and objects, rigid or non-rigid, relatively light, which are formed by _________________ and _____________________
hot water
Plastics can be hard, soft, clear, opaque, light, heavy, heat resistant or easily softened
Cellulose, Synthetic resin, from proteins and natural resins
three (3) types of Plastics
Thermoplastics, Thermosetting plastics
Synthetic resin plastics are subdivided into two (2) classes:
Thermoplastics
- soften when heated and harden when cooled (reversible and repeated)
-
linear or threadlike
Thermoplastics have a molecular structure which is essentially __________ or _____________ in form
Thermosetting plastics
- set into shape permanently when heat and pressure are applied during the forming stage
- They have a molecular structure in a 3-dimensional arrangement
thermocuring plastics
Thermosetting plastics, sometimes called
polyethyline (PE)
polystyrene
polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
polycarbonates
polypropylene
cellulosics
acrylic
nylons
fluoroplastics
acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
EXAMPLES OF THERMOPLASTICS (10; PPPPPCANFA)
ACRYLIC
- Popular brands are "LUCITE" and "PLEXIGLASS"
- transparency of glass (but not scratchproof quality) with shatterproof quality
- Used principally for skylights, skydomes, paints, safety adhesives, finish hardware, & lighting fixtures

CELLULOSICS
- primarily cellulose acetate or butyrate
- used principally for paints and lacquers, and transparent sheeting
Ziegler PE, ICI PE
examples of POLYETHYLINE (PE)
Ziegler PE
a hard, strong, tough and rigid thermoplastic fo household and industrial applications.
ICI PE
- developed by Imperial Chemical Industries of Britain
- a high-pressure, low-density PE that is flexible, tough and slightly resilient thermoplastic used in construction as pond or lagoon lining, and watervapor barriers and dampproofing.
POLYSTYRENE
- sensitive to solvent action
- one of most important thermoplastics because of its excellent transparency and rigidity and its easy moldability.
- non- water absorbent, found in colorful, but brittle wall tiles.
- one of several plastics used in lighting fixture diffusers.
- In foam form, it has become an important thermal insulator. Also found in paint for concrete.

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- is a largely amorphous, rigid, tough, solvent-resistant, flameresistant thermoplastic.
- Used for resilient floor tile, films, pipes, and for paint lacquers, adhesives and safety glass.

POLYCARBONATES
- a family of linear polyesters
- a white, substantially amorphous, very tough and strong material
- with good heat resistance up to 150 deg C and excellent dimensional stability.
- It is injection-molded to produce plates, rods, gears, and other shaped parts that advantageously replace die-cast metal parts.
- Used for skylights.

POLYPROPYLENE
tough plastic with good resistance to heat and chemical action.

nylon
exceptionally strong, elastic, abrasion resistant, easy to wash, resistant to damage from oil and many chemicals, can be precolored or dyed in wide range of colors, and resilient

linear polyamides
The term nylon refers to a family of polymers called __________ ________
FLUOROPLASTICS
- are a class of paraffinic polymers that have some or all of the hydrogen replaced by fluorine.
- characterized by excellent chemical resistance, heat resistance, good electrical properties, and group is excellent excellent wear resistance.
- However, despite these attributes, perhaps the most desired characteristic of this group of plastics is their ability to resist abrasion
paraffinic polymers
FLUOROPLASTICS are a class of __________ _____________ that have some or all of the hydrogen replaced by fluorine.
ACRYLONITRILE BUTADIENE STYRENE (ABS)
- is a styrenic resin with improved toughness and heat resistance.
- ABS exhibits high gloss, low shrinkage, and good dimensional stability, is widely used in injection molding of appliances, furniture, and automotive parts.
- has high melt strength suitable for the production of extruded sheet, some of considerable size and thickness.
- Applications include panels for large appliances and thermoformed items such as hot tubs and recreational vehicle parts

styrenic resin
ABS is a __________ ___________ with improved toughness and heat resistance.
Melamine and Urea, Epoxy, Alkyds, Phenolics, Polyester, Urethanes, Silicones
EXAMPLES OF THERMOSETTING PLASTICS (6; MEAPUS)
Melamine and Urea
hard, durable and dimensionally stable, these similar plastics are resistant to chemicals, electric potential, and heat
Melamine
is well known for its use in molded dishes,

Urea
is useful for incandescent light diffusion and for baked enamels

EPOXY
- used in buildings for its remarkable adhesive qualities.
- It may also be used for special paints that are chemically resistant and for special caulking compounds

ALKYDS
appear chiefly as molded electrical parts, and as the vehicle in paints, lacquers, and enamels .
PHENOLICS
used for paints, baked enamels, adhesives, impregnating resins for paper and wood, and finish hardware

POLYESTER
- the plastic most used in large commonly glass-fiber reinforced translucent panels that are strong, rigid, and impact-resistant.
- Also used for impregnating paper and wood, as laminating material, and for contact adhesive

URETHANES
used in paint coatings, and as foams, are self-adhesive

SILICONE
used for clear, water repellant paint for surfaces and masonry above grade.

SHEETS
Usually made of acrylate, polyester, or polystyrene plastics, either plain or reinforced with glass-fiber, are available in flat or corrugated sheets and various deformed shapes
1.5mm to 2.38mm
Sheets thicknesses vary from ___________ to _________
Plastic sheets
can be used to replace glass in any type of windows or doors, skylights, shower enclosures, or in any area where a translucent, transparent or opaque material in a wide variety of colors are needed in the interior
corrugated sheet
As ____________ _________, plastics make good roofing material and other similar uses as sheet plastic
FILM SHEETS
As water barrier or dampproofing material, it is generally made of polyethylene and polyvinyl and come in thicknesses ranging from 1 to 10 mils

2, 4, 6
For building construction, ___, ____, & ______ mils are most commonly used
4 mil
Over tamped earth or sand fill, use ___ __________
6 mil
Over gravel and stone, use _____ ________
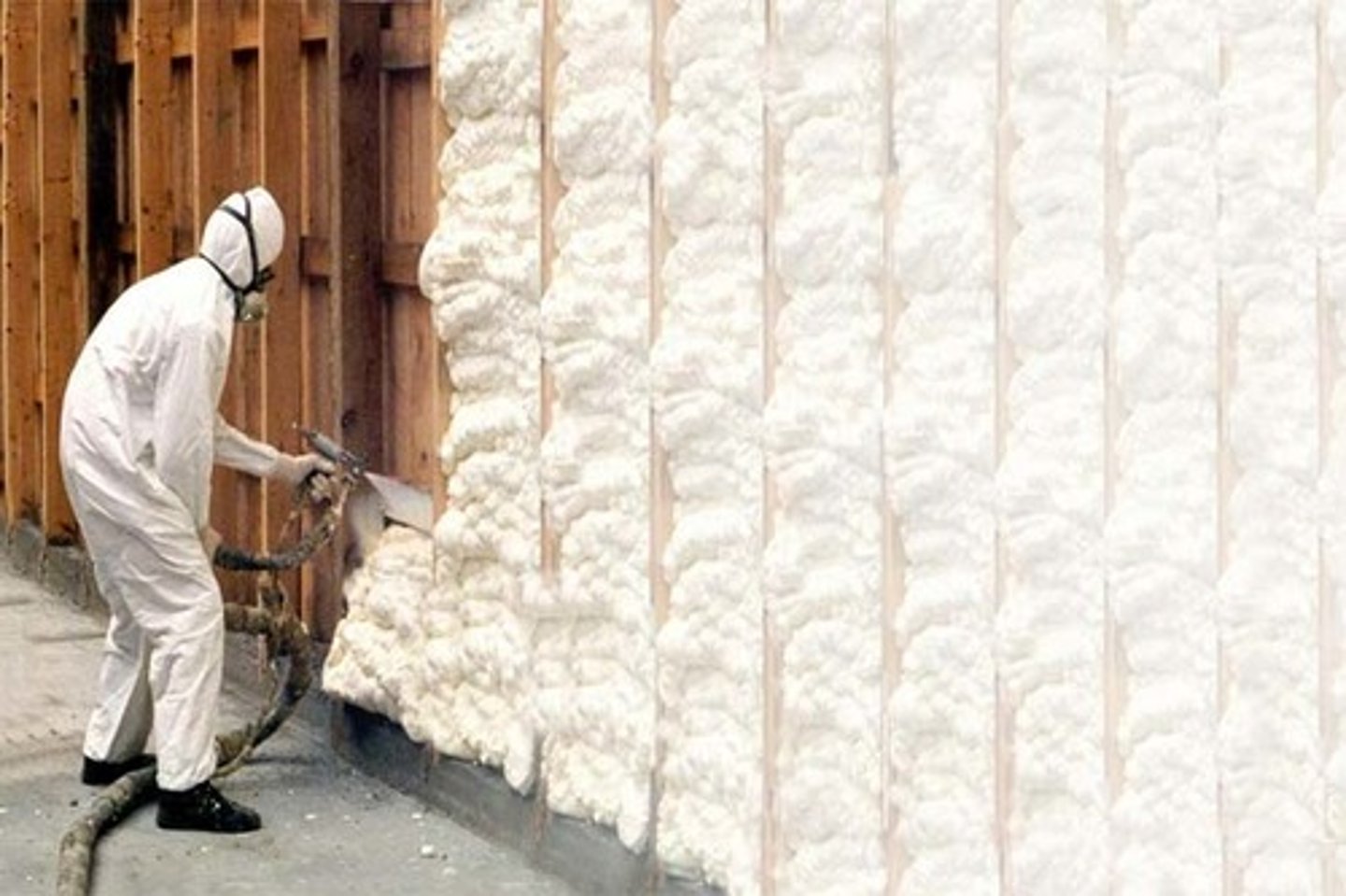
Foams
Used as flotation material, thermal insulators, and shock-resistant mountings. Offers possibilities for lightweight materials of high strength .
Lamination
is the process applied to paper or fabric impregnated with thermosetting resins.
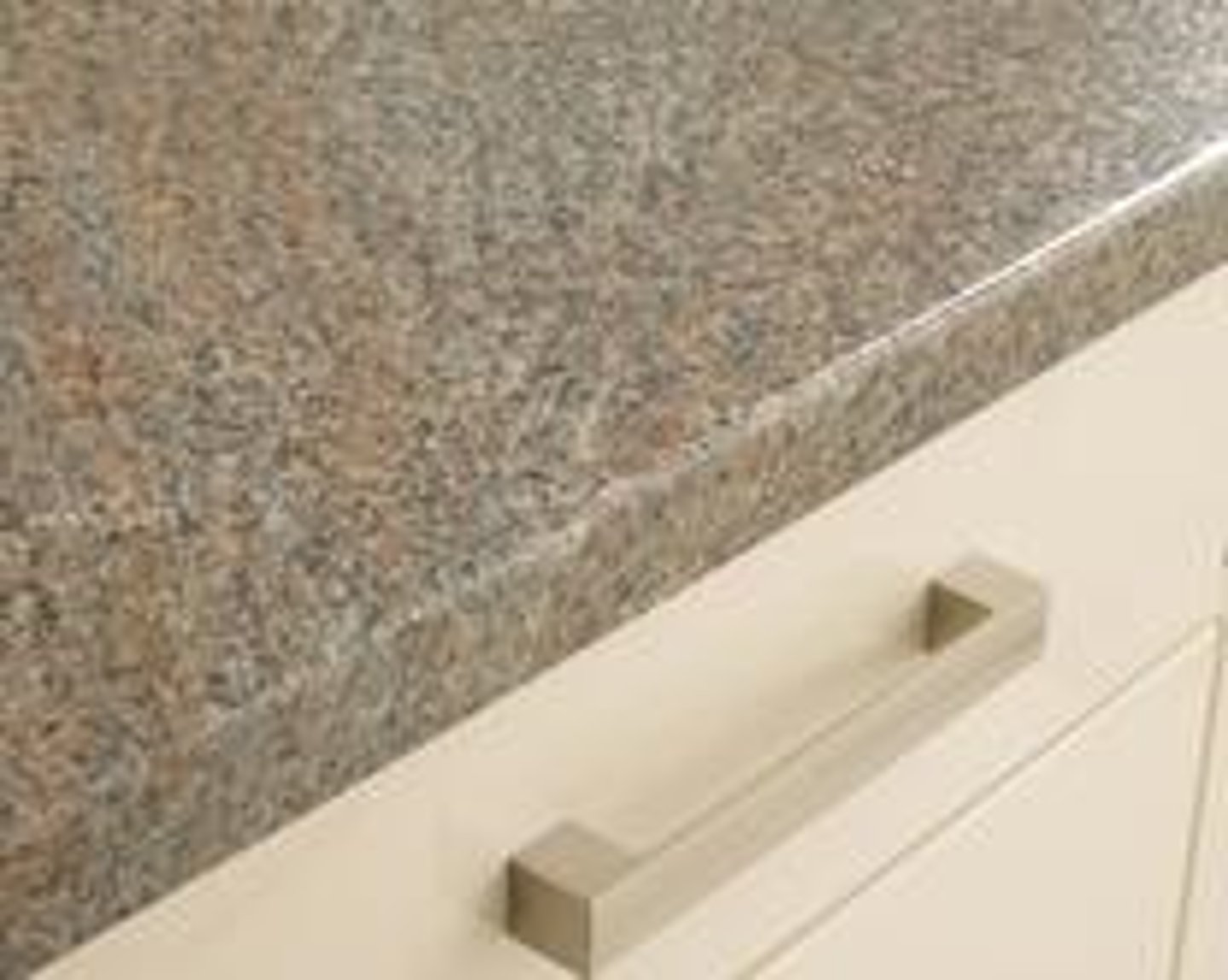
LAMINATES
- Cotton cloth and paper are used as filler materials, usually in sheet forms, that are bonded together by heat and pressure to form an integral body
- The thickness is determined by the number of sheets placed between the two steel pans or platens of the press used in the process.
- extensively used for tabletops and wall facings
