BLOOD BANK 262-382
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
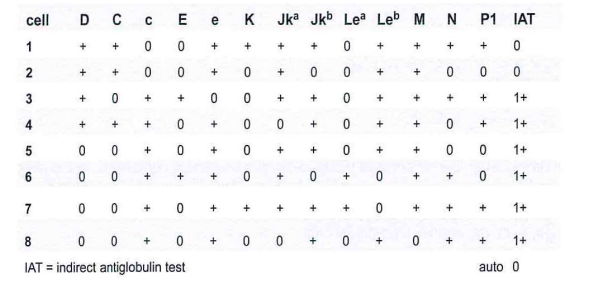
A 25-year-old Caucasian woman, gravida 3, para 2, requires 2 units of Red Blood Cells. The antibody screen is positive and the results of the antibody panel are shown in this table:
B- anti-c and anti-E
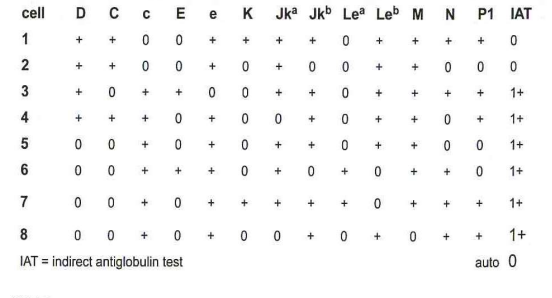
263. The sample from a 45-year-old Asian woman, gravida 2, para 2 demonstrates a positive antibody screen. The results of the antibody panel are shown in the panel:
d- anti-E

264-A 5-year-old with chronic upper respiratory infections arrives in the Emergency Room with chronic anemia. The antibody screen and antibody identification panel are all strongly reactive when tested by solid phase automation. The direct antiglobulin test (DAT) is negative, and the patient's phenotype is shown in the panel. With these initial findings, what is suspected?
b McLeod syndrome
265-A 16 -year-old female is admitted to the emergency room with a gunshot wound. A massive transfusion protocol has been activated before a blood type can be completed. In the patient's record, the patient has a history of being group A, D-negative. The technologist should:
b- release group O, D-negative Red Blood Cells
266-Transfusion of Ch+ (Chido positive) red cells to a patient with anti-Ch has been reported to cause:
a -no clinically significant red cell destruction
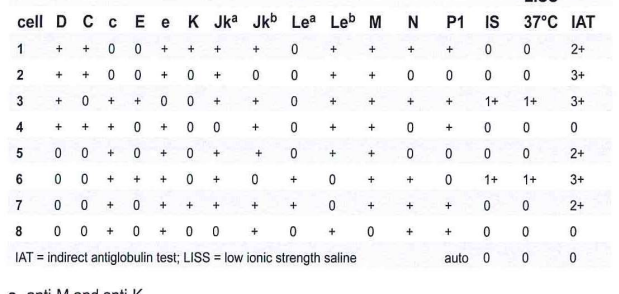
267-Based on the results of the panel, the most likely antibodies are:
B- anti-E, anti-Jk(a) and anti-K
268-Which characteristics are true of all 3 of the following antibodies: anti-Fy(a), anti-Jk(a), and anti-K?
a- detected at IAT phase and may cause hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) and transfusion reactions
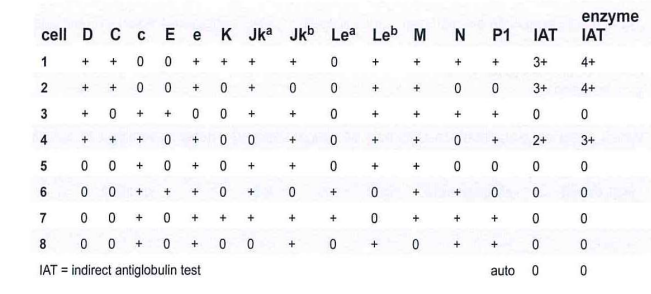
269-Based on the results in the panel, which of the following antibodies is most likely present?
A- anti-C
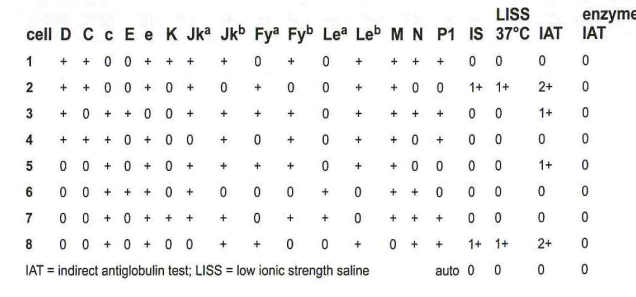
270. A pregnant woman has a positive antibody detection test and the antibody identification results by are given in this panel:
B- may cause HDFN
271. Which of the following tests is most commonly used to detect antibodies attached to a patient's red blood cells in vivo?
a- direct antiglobulin
272. Anti-lin cold agglutinin disease may cause a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) because of:
b- C3d bound to the red cells

273-Which direct antiglobulin test results may be associated with a delayed serologic transfusion reaction in a recently transfused patient?
a- result A
274-A patient's antibody identification panel demonstrates anti-M. The antibody is most reactive with homozygous M+ cells compared to heterozygous M+ cells. Which of the following cells would demonstrate the strongest reaction?
c- M+N-S-s+
275-In the direct antiglobulin test, the antiglobulin reagent is used to:
d- detect preexisting antibodies on erythrocytes
276-The mechanism that best explains hemolytic anemia due to penicillin is:
a-drug-dependent antibodies reacting with drug-coated RBCs
277-Use of EDTA plasma prevents activation of the classical complement pathway by:
d- preventing chemotaxis
278-The drug cephalosporin can cause a positive direct antiglobulin test due to modification of the RBC membrane by the drug, which is independent of antibody production. This mechanism related to the drug cephalosporin is best described as:
d nonimmunologic protein adsorption
279-During prenatal studies, a woman is noted to have a positive antibody screen and anti-Kp? is identified. What percentage of units will be compatible for this patient if transfusion is necessary?
d >98%
280-The purpose of testing with anti-A,B is to detect:
c- subgroups of A
281-A group O, Rh-negative pregnant female has anti-Vel in her serum. If needed, how might blood be provided for her infant?
a-maternal donation

282-In a prenatal workup, the results shown in the table are obtained:
This ABO discrepancy is thought to be due to an antibody directed against a component of the ABO typing sera. Which test would resolve this discrepancy?
b-saline wash patient's cells and repeat forward typing
283-While performing an antibody screen, a test reaction is suspected to be rouleaux. A saline replacement test is performed and the reaction remains. What is the best interpretation?
C-original reaction was due to true agglutination

284-A 10-year-old girl is hospitalized because her urine has a distinct red color. The patient has recently recovered from an upper respiratory infection and appears very pale and lethargic. Tests are performed with the results show in this table:
a- paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
285-A transfusion request must show 2 recipient identifiers, the specific type and amount of blood component with any special processing requirements, and what additional information?
b- name of ordering physician or authorized health professional
286-A 15-year-old bone marrow transplant recipient with a historical blood type of group A, D-positive has a transfusion request for 1 unit of Apheresis Platelets. The transfusion request received in the transfusion service shows that the patient's name and medical record number are cut off and are illegible, although the patient's date of birth is legible. What action should the blood bank technologist do to provide platelets for this patient?
c-reject the request due to the incomplete and illegible order
287-When completing recipient pretransfusion ABO testing, the sample must be tested with which of the following reagents?
C- anti-A; anti-B; A, cells; B cells
288-pretransfusion blood typing and antibody detection test is completed on Tuesday at 4:00pm from a patient with an unknown transfusion history. This sample is valid to use for crossmatching for transfusion until what day and time?
C- Friday at 11:599m
289-What is the purpose of the immediate spin (IS) crossmatch?
b-detect ABO incompatibility between donor and recipient
290-Use of the computer to detect ABO incompatibility (computer crossmatch) can only be used when:
C- the patient fails to demonstrate clinically significant alloantibodies
291-A unit of Red Blood Cells, Leukocytes Reduced is released from the transfusion service for a patient in ICU. After release, the patient's clinical course changes, and the blood transfusion is no longer needed. The unit is returned to the transfusion service within the hour. The temperature of the unit at the time it is returned is 12°C. The unit has not been entered, is visually acceptable, and multiple segments are still attached to the unit. What action should the transfusion service take?
B-discard the unit as appropriate temperature has not been maintained
292-What are the two tasks a phlebotomist must complete when collecting a pretransfusion blood sample?
C- identify the patient before phlebotomy and label the tube immediately after phlebotomy
293-The tie-tag or label attached to each blood component issued for transfusion must include which of the following?
a- recipient's 2 independent identifiers
294-Mixed field agglutination encountered in ABO forward typing with no history of transfusion would most likely be due to:
C- A3 red cells
295-A patient demonstrates 4+ reactivity with all red cells tested and the autocontrol is nonreactive. This high incidence antibody is suspected to be related to the P1PK blood group system as the patient is the rare p phenotype. What antibody specificity should be suspected?
C- anti-PP1Pk
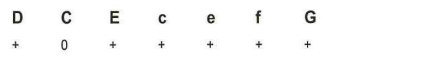
296-Using the antigen typing results in this table, what is the patient's likely phenotype?
c R2r
297-A patient receives 2 units of Red Blood Cells and has a delayed transfusion reaction. Pretransfusion antibody screening records indicate no agglutination except after the addition of IgG-sensitized cells. Repeat testing of the pretransfusion specimen detects an antibody at the antiglobulin phase. What is the most likely explanation for the original results?
C- patients serum is omitted from the original testing
298-Results of a serum sample tested against a panel of reagent red cells gives presumptive evidence of an alloantibody directed against a high incidence antigen. Further investigation to confirm the specificity should include which of the following?
b-serum testing against red cells known to lack high incidence antigens
299-Polyspecific reagents used in the direct antiglobulin test should have specificity for:
B- IgG and C3d
300-A 56-year-old female with cold agglutinin disease has a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). When the DAT is repeated using monospecific antiglobulin sera, which of the following is most likely to be detected?
c-C3d
301-Inheritance of the rare M(k) gene results in the deletion af both GYPA and GYPB. Which of the following blood group antigens is not expressed on red cells in the presence of a M(k) gene?
B- En®
302-Which of the following might cause a false-negative indirect antiglobulin test (IAT)?
d-too heavy a cell suspension
301-A patient's serum sample is reactive with all cells except the autocontrol when tested by polyethylene glycol-antihuman globulin (PEG-AHG). The patient's phenotype is confirmed as C-E+c+e+; K-k+, Kp(a-b+), Js(a—b+); Fy(a-b+); Jk(a-b—); M+N+S+s+. Phenotypically similar cells are tested and found to be nonreactive. In what population of donors are we most likely to find a compatible donor for this patient?
b En®
302-Which of the following might cause a false-negative indirect antiglobulin test (IAT)?
d-too heavy a cell suspension
303-A patient's serum sample is reactive with all cells except the autocontrol when tested by polyethylene glycol-antihuman globulin (PEG-AHG). The patient's phenotype is confirmed as C-E+c+e+; K-k+, Kp(a-b+), Js(a—b+); Fy(a-b+); Jk(a-b—); M+N+S+s+. Phenotypically similar cells are tested and found to be nonreactive. In what population of donors are we most likely to find a compatible donor for this patient?
d-Polynesian
304-Reagent antibody screening cells may not detect all antibodies. Which of the following antibodies is most likely to go undetected?
C- anti-CW
305-A 25-year-old pregnant female demonstrated anti-K in her serum. At delivery, the baby's cord blood sample demonstrate a 3+ direct antiglobulin test (DAT) with IgG antibody. What serologic testing should be done to verify that the positive DAT is related to the maternal anti-K?
b- perform and test acid elution from cord blood
306-A 32-year-old male types as group O, D-negative with a positive antibody detection test. Antibody identification studies demonstrate anti-D, anti-Jk2, and anti-K. Patient records confirm that he received 12-units of group O, D-positive Red Blood Cells 2 months earlier following a motor vehicle accident. What testing should be performed to verify the patient's red cell phenotype?
C-microhematocrit cell separation and testing of autologous reticulocytes with monoclonal antisera
307-In a Group O individual with Le and Se genes, what ABH and LE antigens are present in their secretions?
b- Le(a) Le(b), H
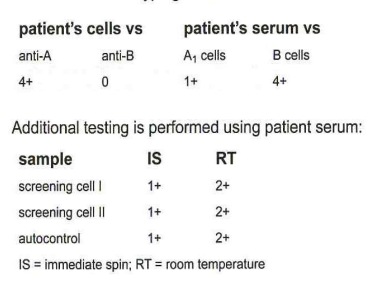
308-Consider the ABO typing results shown in this table:
What method may be used to resolve the patient's ABO serum typing?
C- cold autoantibody
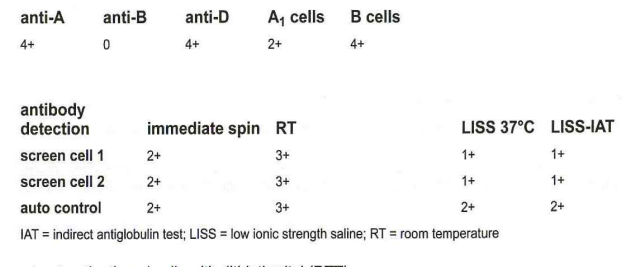
309-What method may be used to resolve the patient's ABO serum typing?
d-cold-autoadsorption

310-The patient’s results are listed in this table. What is the most likely specificity based on the reaction pattern?
B- autoantibody

311-Based on these reactions, what is the patient's ABO type?
a- A1
312-A patient has a variable reacting anti-P1 pattern in antibody identification studies. What test can be used to verify the specificity of anti-P1 and rule out other common alloantibodies?
a- P1 neutralization
313-A patient serum reacts with 2 of the 3 antibody screening cells at the AHG phase, and 8 of the 10 units crossmatched are incompatible at the AHG phase. All reactions are markedly enhanced by enzymes. These results are most consistent with:
c-anti-c
314-A patient's serum reacted weakly positive (1+*) with 16 of 16 group O panel cells at the AHG test phase. The autocontrol is negative. Tests with ficin-treated panel cells demonstrated no reactivity at the AHG phase. Which antibody is most likely responsible for these results?
a-anti-Ch
315-A male patients sample demonstrates a pattern most consistent with anti-D. The patient is Rh-negative, and was transfused with Rh-positive blood emergently after a motor vehicle accident 2 years previously. The anti-D shows variable reactivity when tested with D-positive cells. What test would be appropriate to enhance the anti-D reactivity and verify specificity?
a- ficin-AHG
316-Which of the following genes on chromosome 1 encodes for the 4 common antigen combinations ce, cE, Ce and CE.
b- RHCE
317-Which of the following blood bank chemicals produce Ko red cells (Kell null cells)?
a- dithiothreitol (DTT)
318-Which of the following antigens gives enhanced reactions with its corresponding antibody following treatment of the red cells with proteolytic enzymes?
b- E
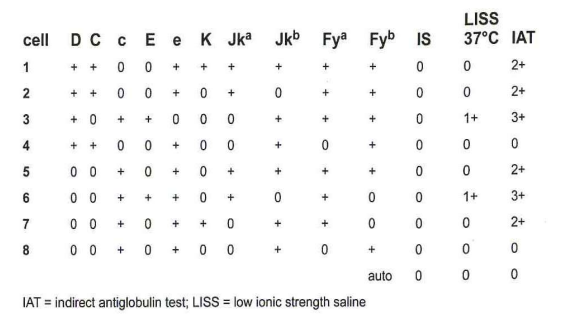
319-Based on the results of the panel, which technique would be most helpful in determining antibody specificity?
a- proteolytic enzyme treatment

320-To confirm a serum antibody specificity identified as anti-P1, a neutralization study is performed and the results obtained are shown in this table:
What conclusion can be made from these results?
d-anti-P1 cannot be confirmed due to the results of the saline control

321-Plasma neutralization is best used to verify which of the following antibodies?
c- anti-Ch/Rg

322-To confirm the specificity of anti-Le®, an inhibition study using LE substance is performed with the results shown in this table:
b- anti-Le b is confirmed because the tubes with LE substance are negative
323-Which is the correct interpretation of this saliva neutralization testing?
d- group O secretor
324-Antibody identification results performed using solid phase technology resulted in undetermined results as all common alloantibodies are excluded. What additional testing could determine if a cold reactive antibody is responsible for the questionable results?
B- testat1S, room temperature (RT) and 37°C with manual tube testing
325-An antibody screen performed using solid phase technology revealed a diffuse layer of red blood cells across the entire well. These results indicate:
a- a positive reaction
326-Which of the following genes on chromosome 1 is made up of 2 exons, leading to the expression of the FY glycoprotein and its antigens?
d- ACKR1
327-Which of the following is useful for removing IgG from red blood cells with a positive direct aniglobuluin test (DAT) to perform a phenotype?
b- chloroquine
328-A patient's serum contains a mixture of antibodies. One of the antibodies is identified as anti-D. Anti-Jk2, anti-Fy? and possibly another antibody are present. What technique(s) may be helpful to identify the other antibody(ies)?
a- enzyme panel; select cell panel

329-A sample gives the results shown in this table:
Which lectin should be used first to resolve this discrepancy?
C-Dolichos biflorus
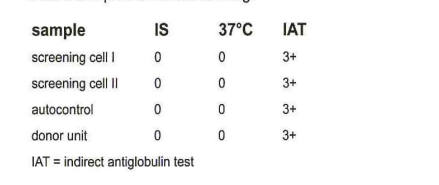
330-A 26-year-old female is admitted with anemia of undetermined origin. Blood samples are received with a crossmatch request for 1 unit of Red Blood Cells. The patient is group A, Rh-negative and has no history of transfusion or pregnancy. The results shown in the table are obtained in pretransfusion testing:
The next step to continue this investigation would be:
d- perform a warm autoadsorption
331-A patient's serum is reactive 2+ in the antiglobulin phase of testing with all cells on a routine panel including their own. There had been 2 units of Red Blood Cells transfused 6-months previously. The optimal adsorption method to remove the autoantibody is:
a- autoadsorption using the patient's dithiothreitol and cysteine-activated papain (ZZAP)-treated red cells
332-In a cold autoadsorption procedure, pretreatment of the patient's red cells with which of the following reagents is helpful?
a- ficin
333-The process of separation of antibody from its antigen is known as:
d-elution
334-Which of the following is most helpful to confirm a weak ABO subgroup?
a- adsorption-elution
335-Preparation of a two-fold serial dilution of an antibody may be used to characterize the relative amount of antibody present and also determine:
b- relative antigen expression on the red cells
336-Which of the following methods may be useful in determining an accurate phenotype in a transfused patient?
C- density separation
337-Which of the following genes is analyzed with molecular assays to distinguish weak D from partial D?
a- RHD
338-In which of the following clinical situations would DNA-based testing be useful?
d- evaluation of a patient with warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia and a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT)
339-In solid phase red cell adherence assays (SPRCA) to detect platelet specific antibodies, the wells of the microtiter plates are coated with immobilized:
C-platelets
340-Testing blood donors for the presence of antibodies to human neutrophil antigens (HNAs) can help prevent which of the following adverse events associated with transfusion?
B- transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)
341-The complement-dependent cytotoxicity test combines Iymphocytes, patient serum and complement and has been used to detect HLA antibodies. After incubation, visualization of damaged or undamaged cells is completed microscopically after addition of what stain or dye?
b-fluorescent vital
342-Anti-E is identified in a panel at the antiglobulin phase. When check cells are added to the nonreactive tubes and spun, no agglutination is seen. The most appropriate course of action would be to:
A-A quality control the AHG reagent and check cells and repeat the panel

343-A serological calibration is completed for a new centrifuge received in the blood bank.
Given the data, the centrifuge time for saline tests for this machine should be:
B-20 seconds
344-Which of the following represents an acceptably identified patient for sample collection and transfusion?
A- handwritten band with patient's name and hospital identification number is affixed to the patient's leg
345-AHG control cells (Check Cells):
C- are coated only with IgG antibody
346-Crossmatch results at the antiglobulin phase are negative. When 1 drop of check cells is added, no agglutination is seen. The most likely explanation is that the:
347-A pretransfusion sample is received in the transfusion service. When comparing the label on the blood sample with the transfusion request, the following is noted. The transfusion request documents Smith, Sam L. MR 7070111, DOB 5.22.70 but the blood sample is labeled Smith, Sam J. MR 7070111, DOB 6.23.71. What, if any, action should be taken?
a- a new blood sample and new transfusion request should be obtained
348-A new lot of anti-B needs quality control (QC) testing. When testing is completed, it is noted that the reagent fails to react with red cells known to be positive for the B antigen and red cells known to be negative for the B antigen. What action should be taken?
b- mark the lot as “not for use” and investigate and resolve the results
349-When preparing an eluate, what is the desired quality control result when testing the last wash?
b- nonreactive with all cells tested
350-A sterile connection device requires quality control of the weld at what frequency?
a- with each weld
351-A blood bank serologic centrifuge lid and wiring had to be repaired and replaced. What must be completed before the centrifuge is placed back into service?
C-recalibrate for speed and functionality
352- Deglycerolized Red Blood Cells are used to transfuse patients with:
a-an antibody to a high-incidence red cell antigen
353-The primary indication for granulocyte transfusion is:
d- severe neutropenia with an infection that is nonresponsive to antibiotic therapy
354-A 42-year-old male of average body mass has a history of chronic anemia requiring transfusion support. Two units of Red Blood Cells are transfused. If the pretransfusion hemoglobin is 7.0 g/dL (70 g/L), the expected posttransfusion hemoglobin concentration should be:
b-9.0 g/dL (90 g/L)
355-How many units of Red Blood Cells are required to raise the hematocrit of a 70 kg nonbleeding man from 24% to 30%?
B-2

356-For which of the following transfusion candidates would CMV-safe blood be most likely indicated?
C- bone marrow and hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
357-Washed Red Blood Cells are indicated in which of the following situations?
A-an IgA-deficient patient with a history of transfusion-associated anaphylaxis
358-What minimum increment of platelets is expected from each unit of Platelets (Whole Blood-derived) when transfused to a non-HLA-sensitized recipient weighing approximately 70 Kg?
b-5,000/uL
359-Platelet transfusions are of value in treating:
C- functional platelet abnormalities