CH 302 Electrochemistry
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts related to electrochemistry from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
This element can assume many oxidation states (-3 to +5)
Nitrogen
This element is found in explosives, fertilizers, as an oxide in laughing gas, viagra, smog, and peservatives
Nitrogen
this element is found in man common materials including soaps, toothpaste, fertilizer, and pesticides. It is extracted from Ca3(PO4)2 rock.
phosphorus
_________ is the backbone in nucleic acids like DNA. _________ cause algae bloom and increasingly their use is discouraged for environmental reasons.
phosphates
H2SO4
Sulfuric Acid
________ is the chemical manufactured in the largest quantities; it is made by a two-step process, Claus and contact.
H2SO4
This element has many uses as a strong acid, oxidizing agent, and dehydrating agent, including extraction of phosphate from rock, production of paper, and as a reactant in production of many other important chemicals
H2SO4
_______ have small radii, high ionization energy, high electronegativity, and form -1 anions. Their oxides and hydrides are acidic.
Halides
_________ inserts instead of OH– in tooth enamel to protect from decay
Fluoride (F-)
________ is manufactured as ___2, a strong oxidizing agent. It is used in
disinfection and sanitation. It is also used to make PVC tubing.
Chlorine, CL2
_____ gases are inert with 2 or 8 electrons in filled shells. Specialty uses
include as cryogens (He), inert gases (Ar), and lights (Ne)
Noble
_________ and _______ processes combine to produce ________ through a series of oxidation and acid/base reactions.
Claus, Contact, H2SO4
Claus process
A two-step oxidation produces elemental sulfur from H2S,
which is a contaminant in natural gas, methane.
Contact Process
A four-step oxidation process produces H2SO4 from
elemental sulfur, S
Rule #1 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Free elements have an oxidation # of 0.
examples:
Mg has 0
Cl2 has 0
Rule #2 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Individual ions are their charge, and alkali metals (Group I) have +1.
examples:
• Mn2+ has +2, Al3+ has +3
• In NaCl, Na has +1
• In Li2O, Li has +1
Rule #3 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Rule #4 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Rule #5 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Oxidation numbers are typically assigned by group on the periodic table:
Group I: +1, Group II: +2, Group III: +3 or -5, Group IV: +4 or -4,
Group V: -3 or +5, Group VI: -2, Group VII: -1
Examples
CH4, H has +1, so C has -4
NO3–, O has -,2 so N has +5
Rule #6 in assigning Oxidation Numbers
Sum of individual charges must equal overall charge on molecule.
The ________ agent is the species that causes oxidation of other
species. This is the species that is being ________.
oxidizing, reduced
The ________ agent is the species that causes reduction of other
species. This is the species that is being ________.
reducing, oxidized
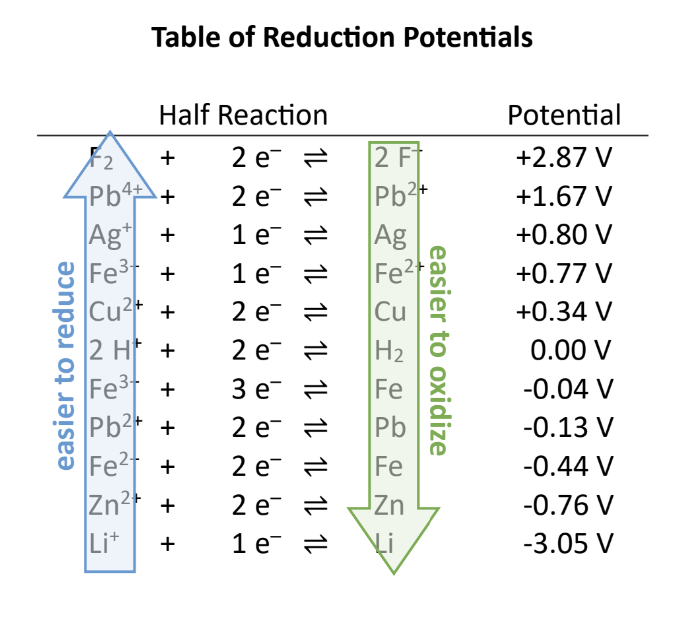
As you move ______ the table of reduction potentials, the species on the left are easier to ________ (stronger oxidizing agents). These are the parts of the half-cell with the largest ________ reduction potential.
Up, Reduce, Positive
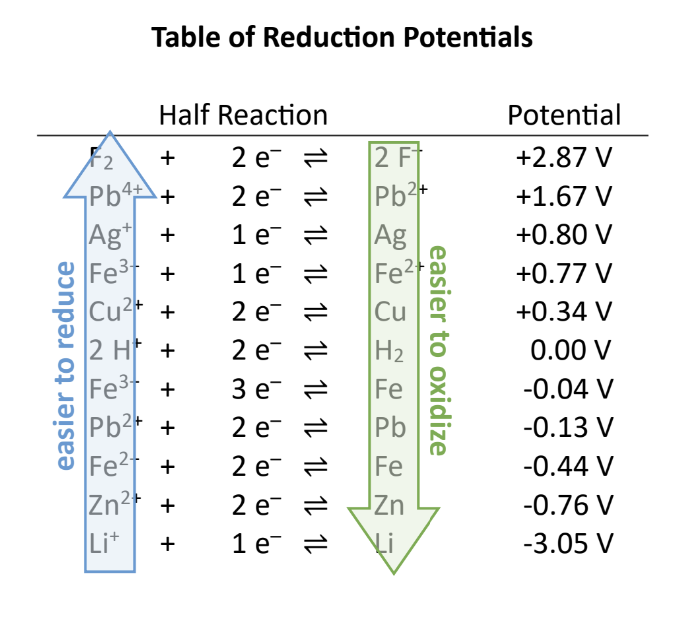
As you move ______ the table of reduction potentials, the species on the right are easier to ________ (stronger reducing agents). These are the parts of the half-cell with the largest ________ reduction potential.
Down, Oxidize, Negative
For a Battery(Voltaic, Galvanic) cell type, ΔG is (positive/negative), K is (<1,>1), E is (positive/negative), the cathode is (positive/negative), and the anode is (positive/negative).
negative, k >1, E is positive, cathode is positive, anode is negative
For a Electrolytic cell type ΔG is (positive/negative), K is (<1,>1), E is (positive/negative), the cathode is (positive/negative), and the anode is (positive/negative).
positive, k <1, E is negative, cathode is negative, anode is positive
electrons from (anode/cathode) to (anode/cathode)
anode to cathode
what are the standard conditions?
1M and 1 atm, 298K
how are reduction and oxidation potential found?
by measuring the potential difference between a half-cell of a substance and a standard hydrogen electrode
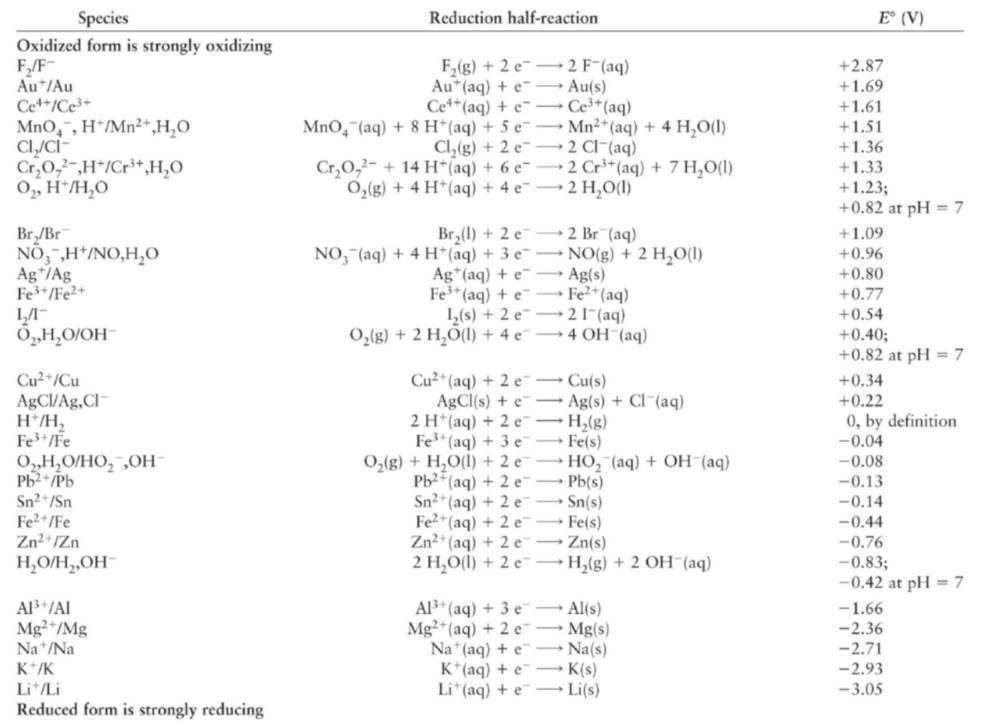
Where the strong oxidizing and reducing agents are found?
top of the table for oxidizing agent, bottom of tabled for reducing agent.

Where famous coinage metals are found?
copper, silver, gold, and platinum
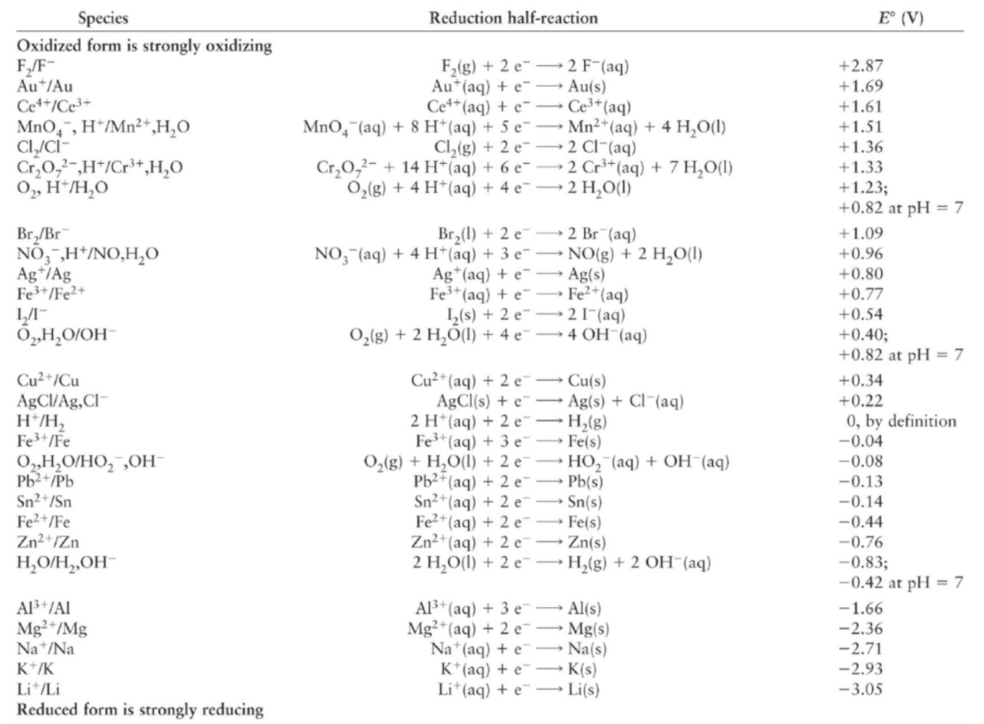
Where the elements that prevent rust are found?
Elements that prevent rust (corrosion of iron) typically have a more positive standard reduction potential than iron
When E > E°, there are more reactants than products then Q will be _____ than 1
less
When E = E°, there are equal products and reactants, Q will be _____ to 1.
equal
When E < E°, there are more products than reactants, Q will be _____ than 1.
Greater
When E = 0, the system is at equilibrium (dead battery) Q will be ______ to K
equal
a battery is dead when it has _____ cell potential, which happens when:
0, the cell reaches equilibrium.
groups ___ and ___ react in cold water
1 and 2
groups ___ and ___ react in steam/acid
3 and 4
groups ___ and ___ don’t react
5 and 6
what element is the strongest reducing agent
lithium
what is the weakest reducing agent?
Au
what are secondary batteries are built with consideration given to?
minimizing liquid or gas production
Modern batteries fun facts
Modern batteries are made with solids and pastes rather than
liquids and gases to avoid losses of material.
secondary batteries fun facts
Rechargeable = secondary
batteries are environmentally superior and convenient
why are inefficient batteries bad?
• Inefficient batteries produce heat, not work. Controlling heat
dissipation is important practically and for safety
light wheight batteries use:
use less dense, higher charge density materials like lithium.
famous examples of primary batteries
Common alkaline battery (think Duracell)
The inexpensive Zn-C
Smaller specialty batteries like Zn-air battery used in hearing aids (although some Zn-air are now rechargeable)
Secondary Batteries
Built with consideration given to minimizing liquid or gas production so that the contents of the reaction are better contained in the battery casing for recharging.
famous secondary batteries
lithium-ion batteries in electronics
Lead-acid batteries found in cars that are recharged by an alternator when the engine is running
NiMH batteries that have replaced NiCd batteries as the common household rechargeable battery
How is rust made?
by oxidation of iron in the presence of water and air for a long period of time:
Fe + H2O + O2 → Fe(OH)2 + Fe(OH)3
how can rust be prevented?
by adding in metals which are easier to oxidize than iron through specific processes:
Galvanization with Zn
Sacrificial electrodes with Mg, Al
Stainless steel with Cr and V added to Fe
Waxes and coating
Atom economy formula:
equation: ((molecular weight of product atoms utilized)/(molecular weight of all reactant’s) )(100%)