1.6 Chemical equilibria, Le Chatelier’s principle, and Kc
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AS Papers 1 and 2 A Level Papers 1, 2, and 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What two things happen in a reversible reaction at equilibrium?
In a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions proceed at equal rates.
The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant.
What does Le Chatelier’s Principle state?
Le Chatelier’s Principle states that if a reaction at equilibrium is subjected to a change in concentration, pressure, or temperature, the position of equilibrium will move to counteract the change.
What can Le Chatelier’s Principle be used for?
Le Chatelier's principle can be used to predict the effects of changes in temperature, pressure and concentration on the position of equilibrium in homogeneous reactions.
Explain the effect of an increase in temperature on the position of equilibrium.
An increase in temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift in the endothermic direction to absorb the heat.
Explain the effect of a decrease in temperature on the position of equilibrium.
A decrease in temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift in the exothermic direction to release more heat.
Explain the effect of an increase in pressure on the position of equilibrium.
An increase in pressure will cause the equilibrium to shift to the side with fewer gas molecules to reduce the pressure.
Explain the effect of a decrease in pressure on the position of equilibrium.
A decrease in pressure will cause the equilibrium to shift to the side with more gas molecules to raise the pressure.
Explain the effect of an increase in the concentration of a reactant on the position of equilibrium.
An increase in the concentration of a reactant will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right to produce more product.
This will decrease the concentration of the reactant.
Explain the effect of a decrease in the concentration of a reactant on the position of equilibrium.
A decrease in the concentration of a reactant will cause the equilibrium to shift to the left to produce less product.
This will increase the concentration of the reactant.
Explain the effect of an increase in the concentration of a product on the position of equilibrium.
An increase in the concentration of a product will cause the equilibrium to shift to the left to produce more reactants.
This will decrease the concentration of the product.
Explain the effect of a decrease in the concentration of a product on the position of equilibrium.
A decrease in the concentration of a product will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right to produce fewer reactants.
This will increase the concentration of the product.
True or False. Explain why.
A catalyst does not affect the position of equilibrium.
True.
A catalyst does not affect the position of equilibrium.
This is because they speed up the reaction in both directions by the same amount.
Explain why lower temperatures may not be used, even if they increase the yield.
Lower temperatures may not be used because they give a slower rate of reaction.
Explain why high pressures may not be used, even if they increase the yield.
High pressures may not be used because they are expensive to produce and strong pipes and containers are needed.
What is the equilibrium constant deduced from?
The equilibrium constant Kc is deduced from the equation for a reversible reaction.
In the expression for Kc, how is the concentration, in mol dm-3, of species X involved represented?
In the expression for Kc the concentration, in mol dm-3, of a species X involved is represented by [X].
Consider a homogeneous system in equilibrium:
aA + bB ⇌ dD + eE
Construct an expression for Kc.
An expression for Kc is
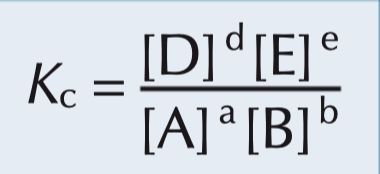
Which two factors do not affect the value of the equilibrium constant?
Two factors which do not affect the value of the equilibrium constant are changes in concentration or the addition of a catalyst.
True or False.
The temperature does not affect the value of the equilibrium constant.
False.
The temperature does affect the value of the equilibrium constant.
A reversible reaction has an exothermic forward reaction.
How will an increase in temperature affect the value of the equilibrium constant?
An increase in temperature will decrease the value of the equilibrium constant.