marketing: survey and analysing qualitative data
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
why is it marketing research important?
it helps understand who buys your products, why, when and under which circumstances
understanding consumer insights, motivations, barriers and explicit or latent desires/needs
to pre or post test concepts, products and campaigns
what are the steps of market research?
survey design
direct or indirect? quantitative or qualitative or experimental?procedure
questionnaire? guide? sample?analysis
how results are analysed
quantitative vs qualitative vs experimental
quantitative studies
describing trends, attitudes, behaviors
potential problem: representativeness
methods: online platforms and tools (Typeform, SurveyMonkey)
qualitative studies
understanding beliefs, cultures, implicit feelings
potential problem: biases
methods: focus groups, individual meetings, ethnography (observation), netnography (online)
experimental studies
understanding causal links, explaining phenomena
potential problems: enviroment and stimuli need to be controlled
methods: field experiments and lab experiments
results can be qualitative or quantitative
info about quantitative methods
aim to describe, quantify, predict
results are based on larger sample sizes → representative, macro view
data in form of numbers and statistics, charts, tables etc
as tools, quantitative questionnaires are usually used (closed questions)
which method should be chosen? (quantitative/quali/experimental)
ex: plus size fashion brand wants to identify characteristics of clothes to appeal to customers → mixed methods
- qualitative insights: understanding of customer needs, what drives behavior of consumers
- quantitative data: prevalence of characteristics on broader base to ensure product strategy is data-driven & representative
ex: study to understand path taken by Louvre visitors
→ observational research (ethnographic, qualitative)
using trained researchers to observe or heat mapping
identifying common patterns in visitor flow
ex: find purchase drivers of Birkin bag → mixed methods
- qualitative research, exploratory phase
interviews, ethnographic research, focus groups
Birkin bags are not just luxury but also status symbols so perception is important
- quantitative research, confirmatory phase
surveys can quantify importance of different purchase drivers after deep insights gained from qualitative phase
indirect methods
website reviews, social networking, forums
observation
usage, inferred data (quali/quanti)
from shopping assistants: virtual assistant, recommendations systems
from social media and chatbots
from behavioural data: purchase history, loyalty cards, cookies, delivery apps
user generated content: reviews etc
projective methods
builds meaning indirectly
construction techniques (movie in which the Orangina brand is the hero)
association techniques (first words that come to mind when I tell you Monoprix)
completion techniques (the people who watch at Arte are…)
expressive techniques (what if Ford was an animal/country/character?)
direct methods
text/SMS surveys
direct phone calls
surveys
direct vs indirect
direct: straightforward, conscious responses
indirect: digging deeper, unconscious opinions
limitations in research
limited cognitive abilities (verbalisation)
social desirability bias ‘
wanted to appear better, responding according to hypothesis
can be avoided with single blind design: subject doesn’t know purpose of experiment until after
the procedure for market analysis
qualitative methods: for interview guides follow logical order for the questions
quantitative methods: different scales to use, scales give you reliable data because it‘s all collected in the same way
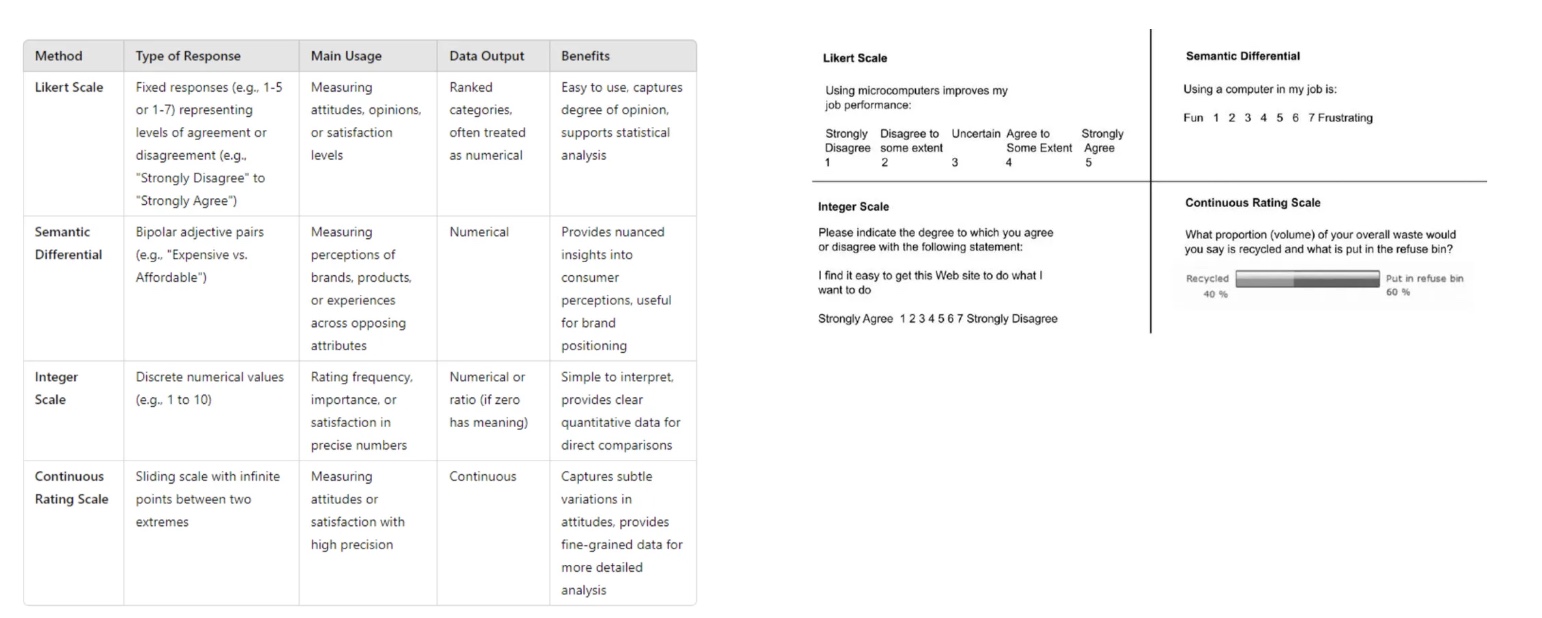
different scales for quantitative methods
Likert Scale
1-5 with different levels of agreement, easy, statistical analysis
Semantic Differential
scale with adjectives (fun - frustrating), nuanced insights, brand positioning
Integer Scale
discrete numerical values like 1-10, precise, simple to read
Continuous Rating Scale
sliding scale, fine-grained data, detailed analysis
what to pay attention to in questionnaires
response options
shouldn’t be only agree, neither, disagree
clear questions
no vague statements
statements shouldn’t address two topics, only one at a time
open ended feedback
where respondents can elaborate for richer insights
what is a sample
a specific group chosen out of the general population to be studied
can a quantitative study be valid with a non-representative sample?
yes
when study wants to understand individual causes
when it compares groups under different conditions
in exploratory studies when goals is to get insights even if the findings might not apply to general populaion
can a quantitative study be invalid even with a representative sample?
yes
if it only focuses on having a large sample but ignores other factors
direct methods (survey etc) have limitations like leading questions or bias
if study doesn’t account for biases than can affect results and make findings unreliable
which sampling methods exist?
probability sampling
everyone has equal chance of being selected
random, stratified, systematic sampling
statistically representative results → findings can be generalisednon probability sampling
selection is based on convenience or judgment
convenience, quota, snowball sampling
quick insights
for limited resources
if generalization is not required
what is selection bias?
when the group chosen for a study doesn’t represent the whole population
makes results unreliable because the sample isn’t diverse enough to reflect broader audience
how to do qualitative data analysis
organise collected data
transcribe, translate, label
identify framework
the plan to structure, label and define data
sorting data into framework
descriptive analysis based on framework
second order analysis
identifying recurrent themes/patterns in data