Microbio UNIT 3
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
chemical reactions
making or breaking of bonds between atoms
a change in chemical energy occurs during a chemical reaction
endergonic reaction
absorb energy
exergonic reaction
release energy
synthesis reactions
atoms, ions, or molecules combine to form new, larger molecules
A + B —> AB
anabolism
synthesis of molecules in a cell
decomposition reactions
a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions, or atoms
AB —> A + B
Catabolism
decomposition reactions in a cell
Exchange Reactions
are part synthesis and part decomposition
NaOH + HCl —> NaCl + H2O
Reversible Reactions
can readily go in either direction
each direction may need special conditions
A + B ←- AB
—>
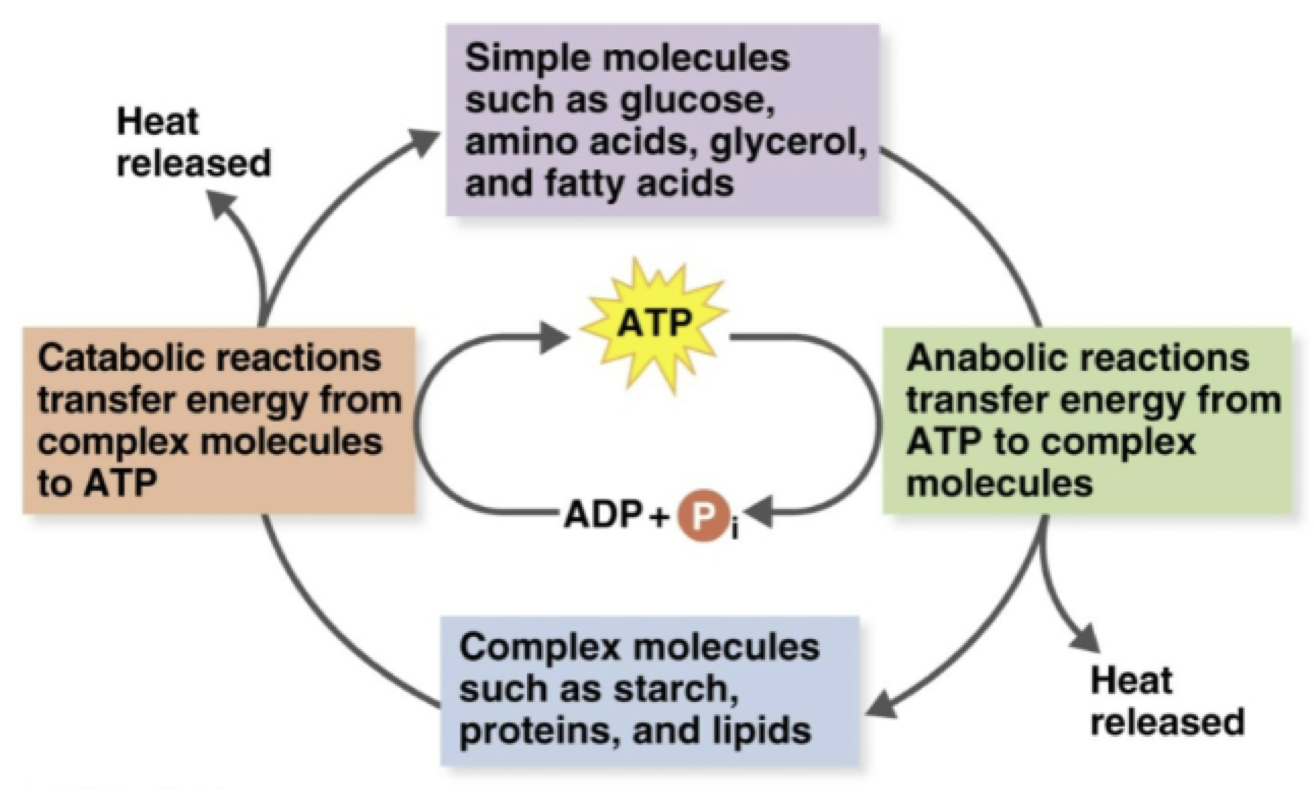
Metabolism
the sum of the chemical reactions in an organism
Catabolism
provides energy and building blocks for anabolism
Anabolism
uses energy and building blocks to build large molecules
Role of ATP in Coupling Reactions
Metabolic Pathway
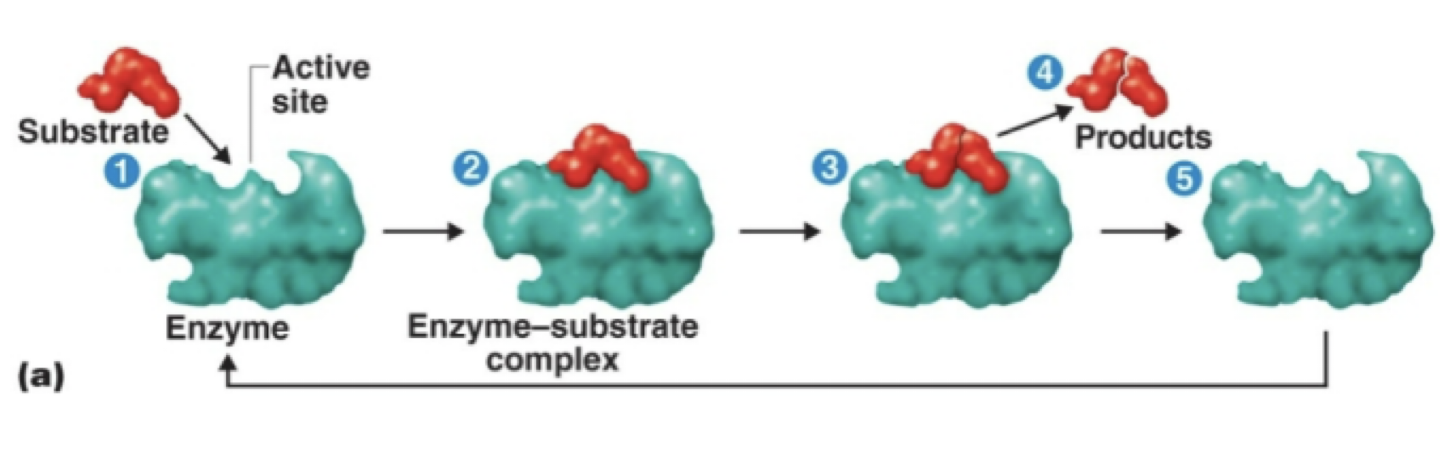
sequence of enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell
determined by enzymes
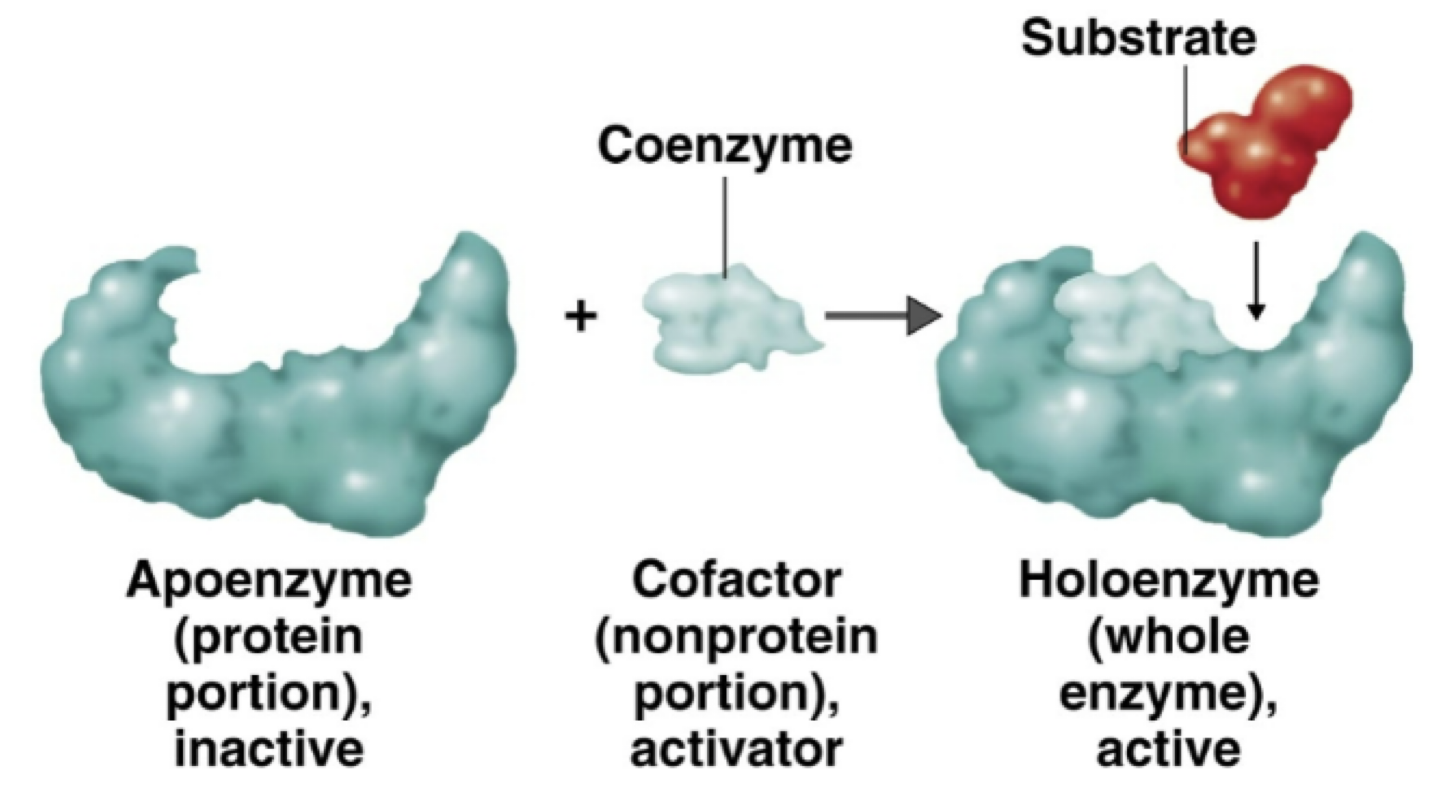
Enzyme components
biological catalysts
apoenzyme
cofactor
holoenzyme
biological catalysts
specific for a chemical reaction, not used up in that reaction
apoenzyme
protein
cofactor
nonprotein component
coenzyme: organic cofactor
holoenzyme
apoenzyme plus cofactor
components of a holoenzyme
Important coenzymes
NAD+
NADP+
FAD
Coenzyme A
Mechanism of enzymatic action
Oxidoreductase
oxidation-reduction reactions
transferase
transfer functional groups
hydrolase
hydrolysis
lyase
removal of atoms without hydrolysis
isomerase
rearrangement of atoms
ligase
joining of molecules, uses ATP
Factors Influencing enzyme activity
temperature (37) and denature proteins (unfolded proteins)
pH (5)
substrate concentration
inhibitors
competitive inhibtor
temporary
competitive inhibitor has a similar shape to the normal substrate and the molecules compete for the active site
noncompetive inhibitors
permanent
product binds to regulatory site and permanently changes the shape of the active site
oxidation
removal of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
redox reaction
an oxidation reactions paired with a reduction reaction
How is ATP generated?
by the phosphorylation of ADP
ADP + energy + P —> ATP
substrate level phosphorlyation
energy from the transfer of a high energy PO4- to ADP generates ATP
C-C-C + P + ADP —> C-C-C + ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation
energy released from transfer of electrons (oxidation) of one compound to another (reduction) is sued to generate ATP in the electron transport chain
Carbohydrate Catabolism
3 steps
1) Glycolysis
2) Krebs cycle
3) Oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis
the oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid produces ATP and NADH
2 ATP are used
glucose is split to form 2 glucose-3-phosphate
Energy Conserving stage of glycolysis
2 glucose-3-phosphate oxidized to 2 pyruvic acid
4 ATP produced
2 NADH produced
Glucose + 2 ATP + 2 ADP + 2 PO4- + 2 NAD + —>
2 pyruvic acid + 4 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+
Pentose phosphate pathway (alternatives to glycolysis)
uses pentose and NADPH
operates with glycolysis
B. subtitles, E. coli
Net gain of 1 molecule of ATP / glucose molecule
Entner-Doudoroff pathway (alternatives to glycolysis)
produces NADPH and ATP
does not involved glycolysis
Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Agrobacterium
Net gain of 1 ATP / glucose molecule
Intermediate step
pyretic acid (from glycolysis) is oxidized and decarboxylated
Krebs cycle (TCA or Citric Acid Cycle)
oxidation of acetyl CoA produces NADH and FADH2
electron transport chain
series of carrier molecules oxidized and reduced as electrons pass down the chain
chemiosmosis
energy released used to produce ATP
aerobic respiration
the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen (O2)
anaerobic respiration
the final electron acceptor int he electron transport chan is not O2. Yields less energy than aerobic respiration because only part of the Krebs cycle operates under anaerobic conditions.
Respiration
Glycolysis + NAD+ —> ATP + NADH
Glycolysis location in Eukaryotes
cytoplasm
Glycolysis location in Prokaryote
cytoplasm
Intermediate step location in Eukaryotes
mitochondria
Intermediate step location in Prokaryotes
cytoplasm
Krebs cycle location in Eukaryotes
mitocondrial matrix
Krebs cycle location in Prokaryotes
cytoplasm
ETC in Eukaryotes
Mitochondrial inner membrane
ETC in Prokaryotes
plasma membrane
Carbohydrate Catabolism
ATP produced from compete oxidation of one glucose using aerobic respiration
Fermentation
any spoilage of food by microorganism (general use)
any process that produces alcoholic beverages of acidic dairy products (general use)
a large scale microbial process occurring with or without air (commonly used in industry)
Fermentation requirements
does not require oxygen
does not use the Krebs cycle or ETC
uses an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor
Alcohol fermentation
produces ethanol + CO2
lactic acid fermentation
produces lactic acid
Homolactic fermentation
produces lactic acid only
Heterolactic fermentation
produces lactic acid and other compounds
Microbial Growth
increase in number of cells, not cell size
-populations
-colonies
Physical requirements of microbial growth
temperature (minimum, optimum, and maximum growth temperature)
pH
osmotic pressure
Chemical requirements of microbial growth
carbon
Nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus
trace elements
oxygen
organic growth factor
Psychrotophs
grow between 0 C and 20-30 C
cause food spoilage
pH
most bacteria grow between pH 6.5 and 7.5
molds and years grow between pH 5 and 6
acidophilus grow in acidic environments
hypertonic envrionemts
or an increase in salt or sugar, cause plasmolysis
Extreme or obligate halophiles
require high osmotic pressure
Facultative halophiles
tolerate high osmotic pressure
barophiles
can survive under extreme pressure and will rupture if expoed to normal atmospheric pressure
Plasmolysis
water leaves the cell due to a high NaCl concentration on the outside of the cell
Oxygen requirements
most cells have developed enzymes that neutralize these chemicals
superoxide dismutase, catalase
if a microbe is not capable of dealing with toxic oxygen, it is forced to live in oxygen free habitats
as oxygen is utilized it is transformed into several toxic products
singlet oxygen (O2)
superoxide ion (O2-)
peroxide (H2O2)
hydroxyl radicals (OH-)
biofilm
microbial communties
form slime or hydrogels
bacteria attracted by chemicals via quorum sensing
share nutrients
sheltered from harmful factors
Obligate aerobes
an organism that cannot grow without oxygen and needs oxygen at atmospheric levels
facultative anaerobes
can grow with or without oxygen
can switch between aerobic and anaerobic respiration to grow
Obligate anaerobes
do not use oxygen for cellular respiration and cannot grow in the presence of oxygen
Aerotolerant anaerobes
do not use oxygen for respiration, but can grow if oxygen is present
Microaerophlies
an organism that uses oxygen for cellular respiration, but at a concentration lower than in the atmosphere
require oxygen in small amounts
Organic Growth Factors
vitamins
amino acids
purines
pyrimidines
biofilms
microbial communities
form slime or hydrogels
bacteria attracted by chemicals via quorum sensing
share nutrients
sheltered from harmful factors
Biosafety levels
1) no special precautions
2) lab coat, gloves, eye protection
3) biosafety cabinets to prevent airborne transmission
4) sealed, negative pressure
exhaust air is filtered twice
Reproduction in Prokaryotes
binary fission
budding
conidiophores (actinomycetes)
fragmentation of filaments
Lag phase
cells are visibly active by are not mature enough to divide
very few cells
exponential growth/ log phase
cells are live and reproducing rapidly
stationary phase
the amount of live cells = the number of dead cells
death phase
a limiting factors intensify cells die exponentially
direct method of measuring microbial growth
plate counts
filtration
direct microscopic count
indirect method of measuring microbial growth
turbidity
the pour plate method
1) inoculate empty plate
2) add melted nutrient agar
3) swirl to mix
4) colonies grow on and ion solidified medium
the spread plate method
1) inoculate plate containing solid medium
2) spread inoculum over surface evenly
3) clones grow only on surface of medium
direct microscopic count
hemacytometer: has channels, small amount of liquid
enumeration of bacteria:
viable colony count
direct cell count: count all cells present, automated or manual
Turbidometry
most simple
degree of cloudiness, turbidity, reflects the relative population size