ASVAB - General Science
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Kingdom
First and largest category used to classify organisms
Phylum
Second largest category. Divided by general characteristics
Class
Group of similar orders
Order
Group of similar families
Family
Group of genera that share many characteristics
Genus
A group of similar species
Species
Most specific category, similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring
Animals
Many-celled organisms that don't have cell walls, chlorophyll, or capacity to photosynthesize.
Plants
Organisms that can't move, don't have nervous or sensory systems, and possess cell walls made of cellulose.
Fungi
Don't photosynthesize, but do have cell walls made of a carbohydrate called chitlin.
Protists
One-celled organisms that do have a nucleus (protozoan).
Eubacteria
Single-celled organisms that don't have distinct nuclei or organelles.
Central nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Responds to physical stimuli.
Circulatory system (Cardiovascular system)
Heart, blood, and blood vessels. Delivers blood from the heart to the
rest of the body and returns to heart.
Digestive system
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, and anus. Breaks down food into smaller substances that the body can absorb and process into energy and eliminates the resulting waste
Muscular system
Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles. Allows organs to contract and allows body movement.
Skeletal system
Bones, joints, tendons, and cartilage. Supports body's muscles and organs. Allows bones and joints to move.
Respiratory system
Nose, nasal cavity, trachea, lungs, and blood. Brings oxygen into the body. Gets rid of carbon dioxide.
Nucleus
Brains behind the cell, and it holds the cell's genetic material, such as DNA.
Cytoplasm
Contains many chemicals that carry out the life processes in the cell.
Cell membrane
Thin barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
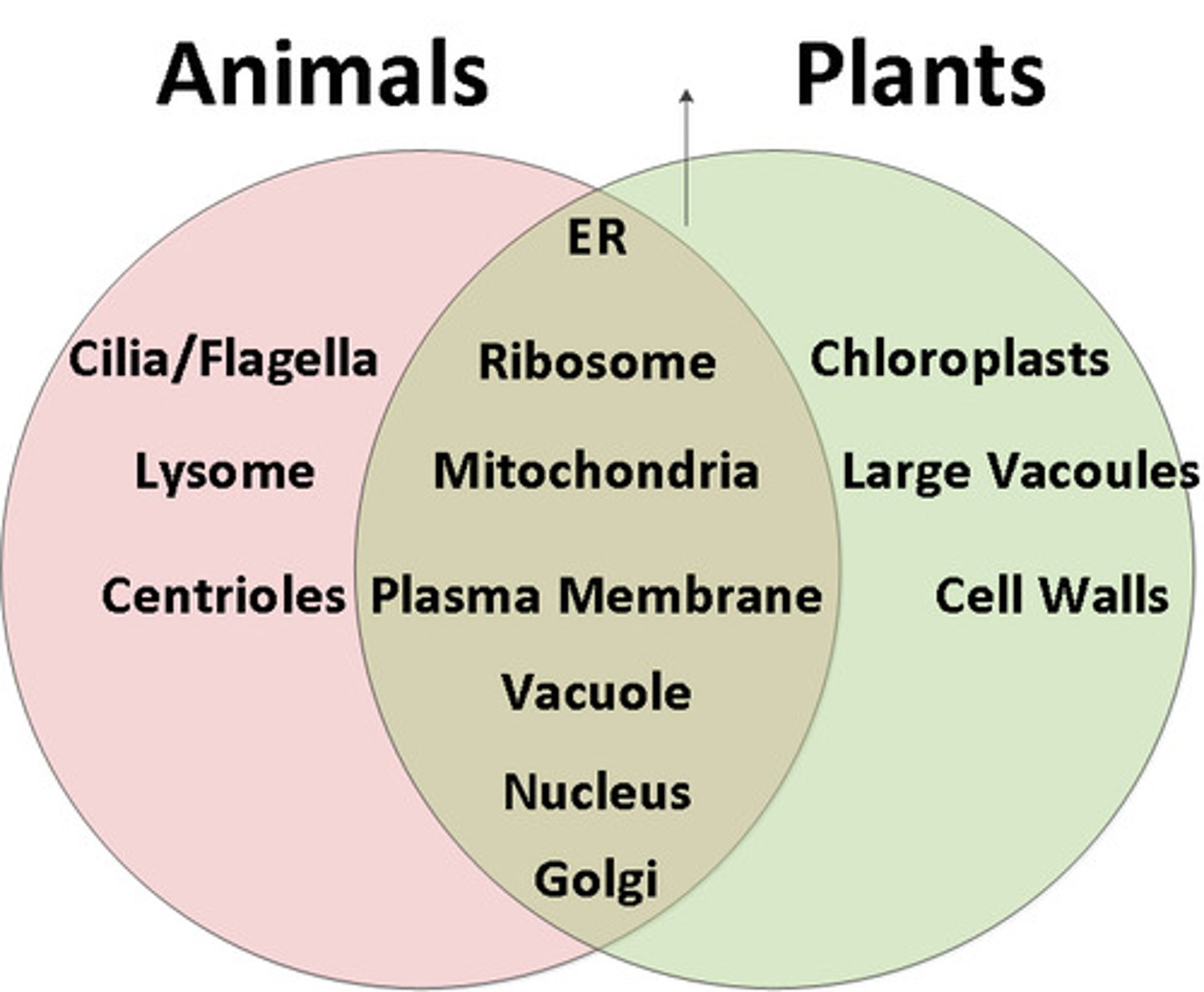
Plant cells vs Animal cells
Plant cells have a cell wall, animal cells do not. Plant cells have larger vacuoles, animal cells' are smaller. Plant cells contain chloroplasts, animal cells do not. Plant cells do not have centrioles and lysosomes.
Atom
Smallest part of an element that still retains the characteristics of that element
Atom nucleus
Contains protons and neutrons
Atomic number
Number of protons
Mercury moons
0
Venus moons
0
Earth moons
1
Mars moons
2
Jupiter moons
63
Saturn moons
61
Uranus moons
27
Neptune moons
13
Troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere.
0 to 5-9 miles.
Stratosphere
2nd layer of atmosphere; extends from 9 to 31 miles up; location of ozone layer; absorbs 95% of Ultraviolet radiation; temperature increases with altitude increase.
Mesosphere
31 to 53 miles. Most meteors burn up here.
Thermosphere
The uppermost layer of the atmosphere. 53 to 373 miles. ISS has a stable orbit here.
Exosphere
373 to 6,200 miles. Merges with outer space.
Scientific name
genus + species
Scientific method
1. Observe
2. Ask question
3. Develop hypothesis
4. Make prediction
5. Experiment
6. Use results to create new hypothesis
Endocrine system
Communicates through hormones
Lymphatic and immune system
Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and lymph. Rids the body of waste and fights infections
Exocrine system
Skin, hair, nails, and glands. Protects body from damage.
Reproductive system
Production of offspring
Carbs
Main source of energy
Fats
Secondary energy source when carbs are limited or when needing long-term energy
Fiber
Get rid of waste
Minerals
Iron for red blood cells, calcium to keep bones strong, and potassium to regulate electrical activity.
Protein
Needed by the body for growth and repair
Vitamins
Regulates blood clotting, processing food, and regulating hormones
Water
Universal solvent for cells