PT 805: lecture three manual therapy intro
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What two concepts of PT have the most scientific back up?
- Manual therapy
- Exercise
Musculoskeletal aberrations in normal motion can be from...
- Too much movement (hypermobile)
- Too little movement (hypomobile)
What two things are most used in PT exams and treatment
- Passive movement and palpitation
Types of manual techniques in this class
- Pain provocation or symptoms change test.
- Muscle length test
- Stability test
- Passive physiologic movements
- Passive accessory movements
Pain provocation or symptoms change test.
- Passive movement intended to load or unload structures to determine if they are mechanically sensitive.
o May not be informative of the cause of the problem.
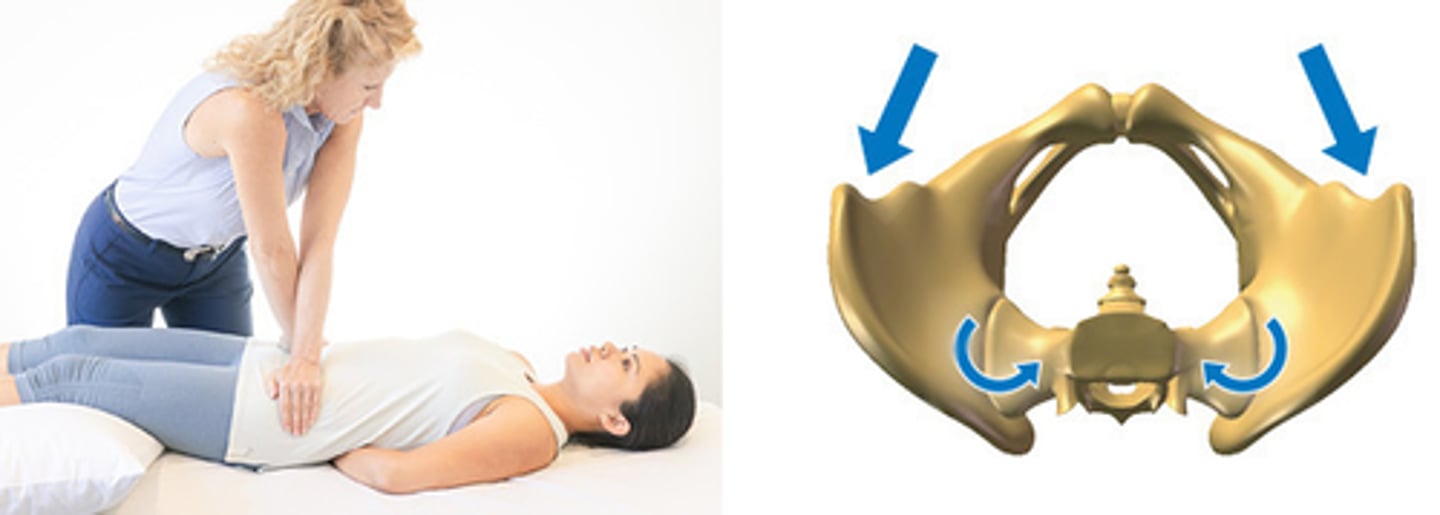
Muscle length test
- Determine length of muscle tendon units
- Complementary testing: not a basis for diagnosis
o Often just classified as normal or abnormal
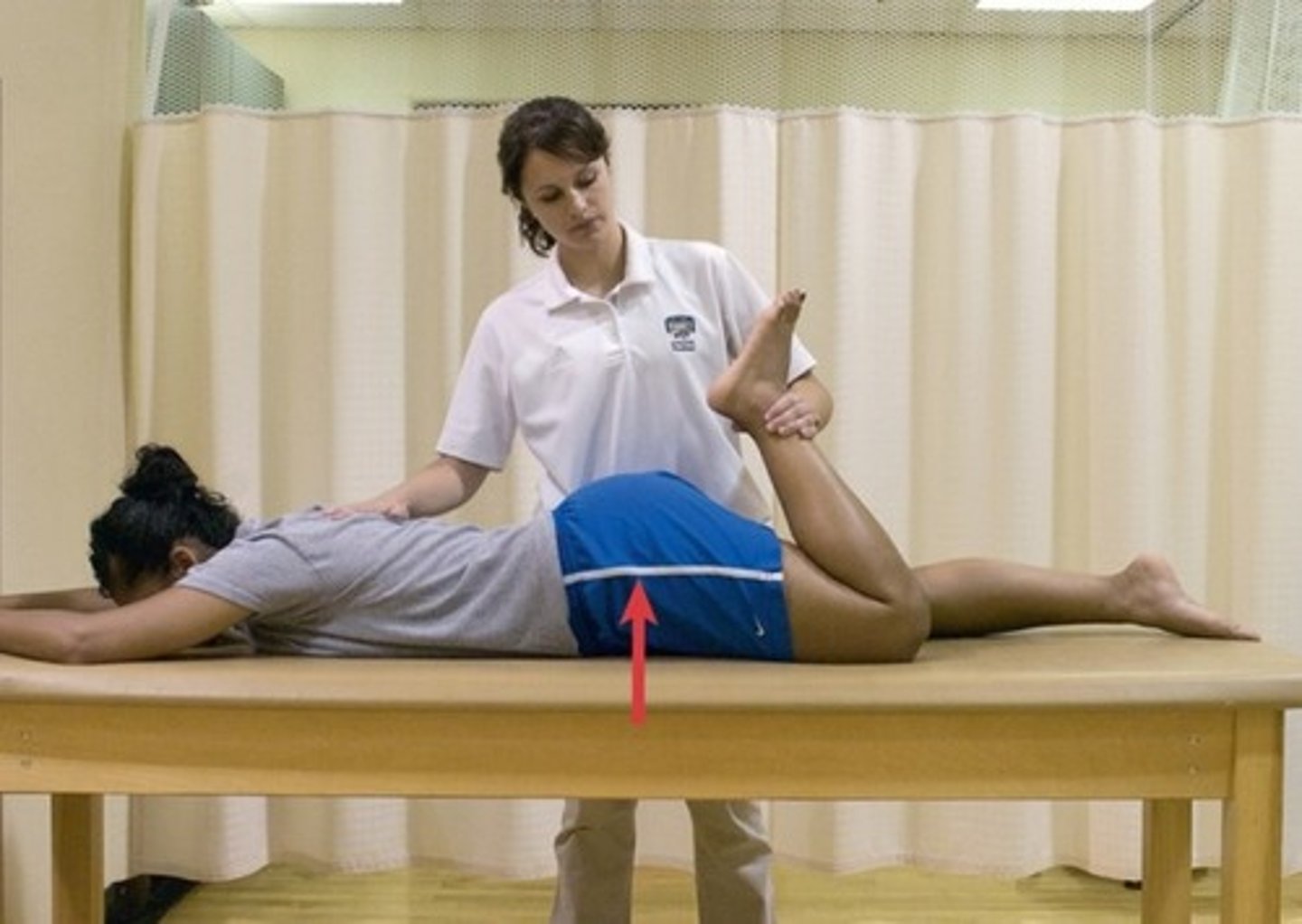
Stability test
- Passive movement to stress joint stabilizing structures.
- Test for magnitude of motion and quality of barrier
- Directionally specific
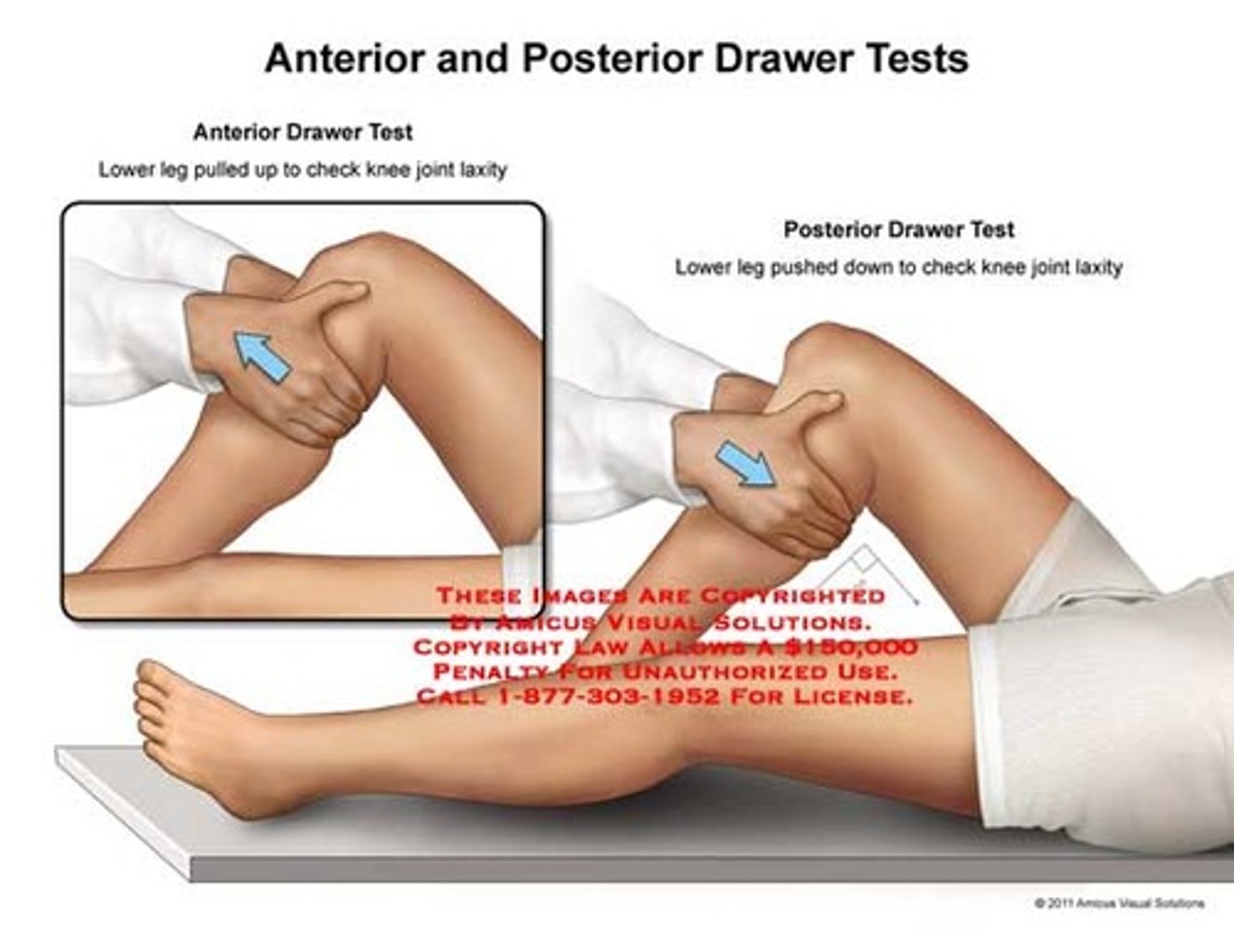
What is an example of a stability test?
Manual therapy to test for ACL tear
Passive physiologic movements test
- Passive movement at a joint or multiple joints (PROM)
- Includes osteokinematics and arthrokinematics.
o Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, and external rotation
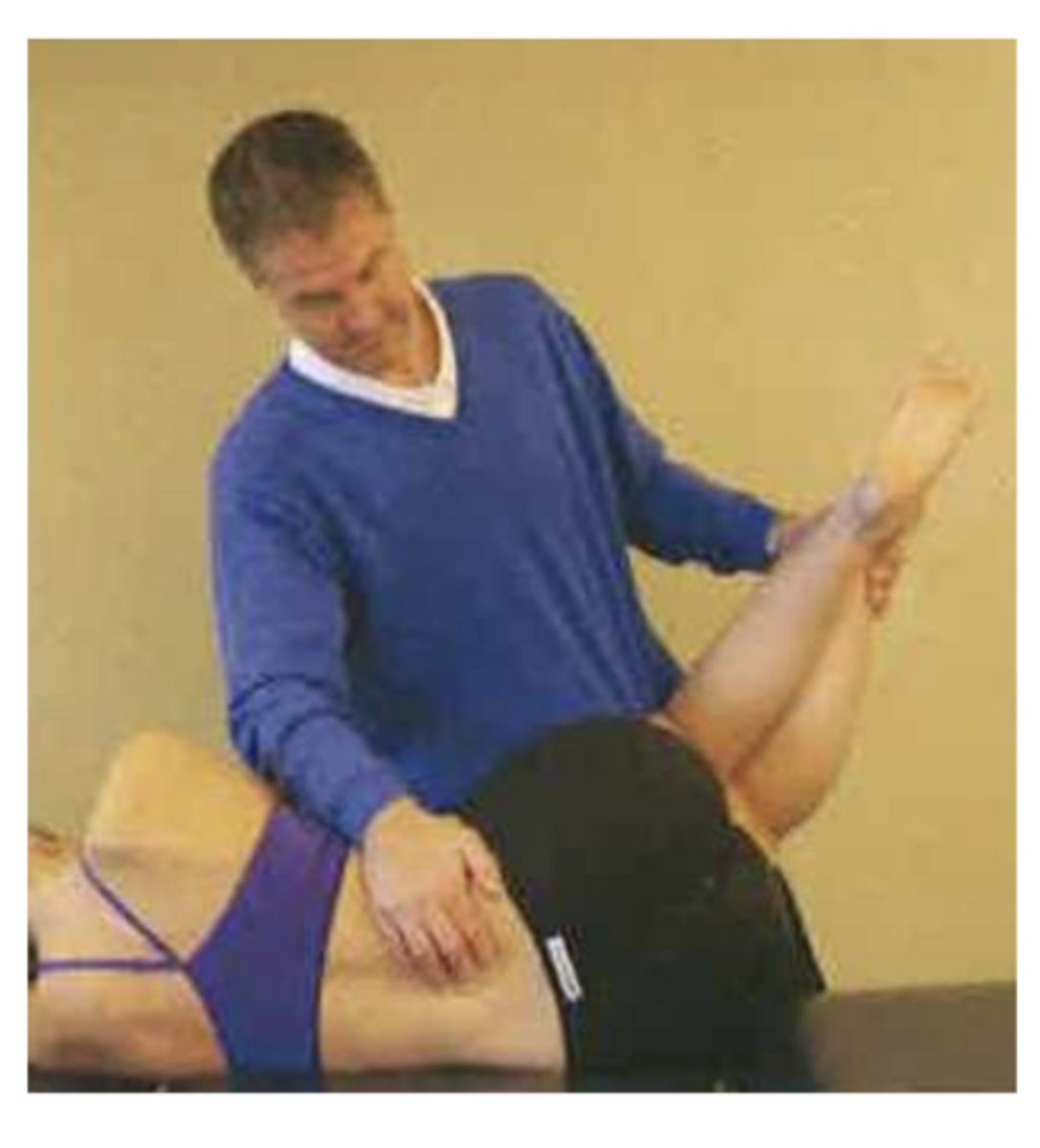
What two things can limit passive physiologic movements
- Musculotendinous units
- Articular and peri articular structures (joints)
Passive accessory movements test
- Passive movement at a joint that includes SPECIFIC arthrokinematics and NONSPECIFIC accessory motions.
Passive accessory movements are limited by ________ only.
- Articular or peri articular structures
What manual therapy technique is used often for PT evaluation and treatment?
- Passive accessory movement
Active vs passive movement skills analysis (during evaluation)
- Active: composite movement and joint physiologic (AROM)
- Passive: osteokinematic and arthrokinematics
What is the BIG different between physiologic motion and arthrokinematics motion
- PHYSIOLOGIC MOTION CAN BE MEASURED
ARTHOKINEMATIC MOTION CAN ONLY BE EVALUATED USING MANUAL THERAPY
Components of osteokinematic motion
- Bone on bone movement
- Usually, angular motion
- Can control voluntarily.
Components of accessory motions
- Accompany osteokinematic motions.
- Movement of one surface onto another (arthrokinematics)
- Not under voluntary control (passive movement)
Relationship between osteokinematics and arthrokinematics (not normal motion)
- If motion is reduced, can be cause by the loss of osteokinematic motion with or without loss of arthrokinematics motion.
Roll (arthrokinematics)
- Multiple points on one surface hit multiple points on another.
- Usually in same direction as movement
Spin (arthrokinematics)
A single point on one surface rotates on a single point of another surface.
Examples of spins that occur within the body.
- Hip flexion and extension.
- Radial head on capitulum during pronation
glide (arthrokinematics)
A single point on one surface contacts multiple on another surface
Why are rolls and glides usually combined?
- To prevent one joint surface from gliding off the other
________ motion + _______ motion = physiologic motion
Arthrokinematic + osteokinematic
Joint compression (description)
- Decreases the space and volume between to joints.
- Adds stability (less glide in joint)
- Can occur due to muscle contraction or external force.
Joint distraction (distraction)
- Increase the space and volume between joints.
- Joint capsule and accessory ligaments are tensioned.
- Only occur from external forces
End feel of a passive movement.
- Quality of resistance during and at the end of a motion
- Provides information about the extensibility, irritability, and presence of inflammation.
Relationship between pain and end- feel
- Pain before end feel: high mechanical sensitivity
- End feel before pain: low mechanical sensitivity.
Normal capsule or ligament barrier (end-feel)
- Firm with small elastic yield
Shorted capsule or ligament barrier (end-feel)
- Very firm with little to no elastic yield
o After a cast
lengthened capsule or ligament barrier (end-feel)
- Soft and less resilient with greater elastic yield
o Torn ligament or capsule
Soft tissue interposition barrier (end-feel)
- Soft and visible barrier
Bone to bone (end- feel)
Hard
Edema and effusion (end-feel)
- Soft (boggy)
Pain (end-feel)
- NONE
o Huge problem
Relationship between mobility and end feel
- Increased mobility = soft end-feel
- Decreased mobility = hard end feel
Force displacement curve of passive accessory motion
- Relationship between force and displacement regarding end-feel and capsule length
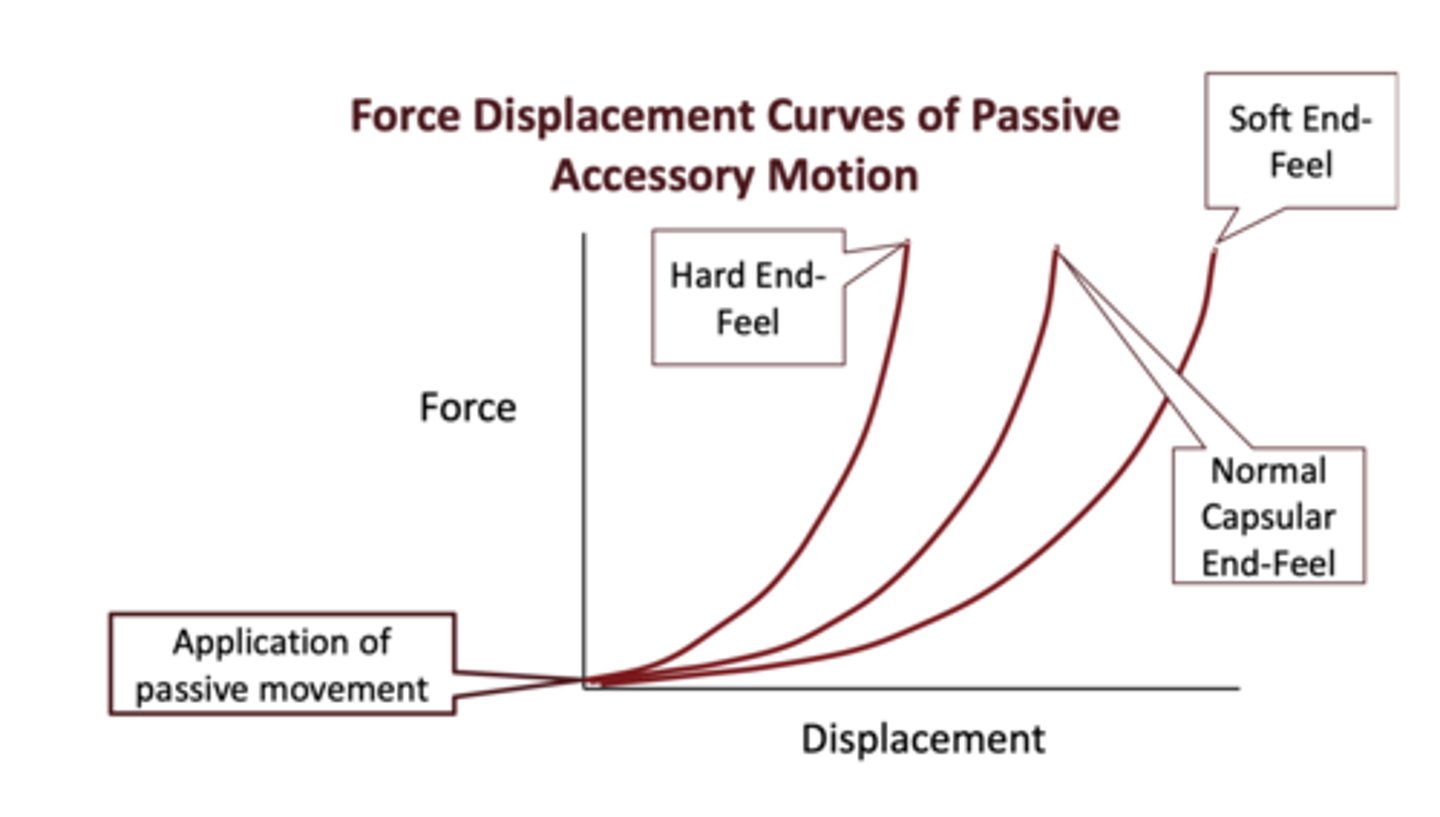
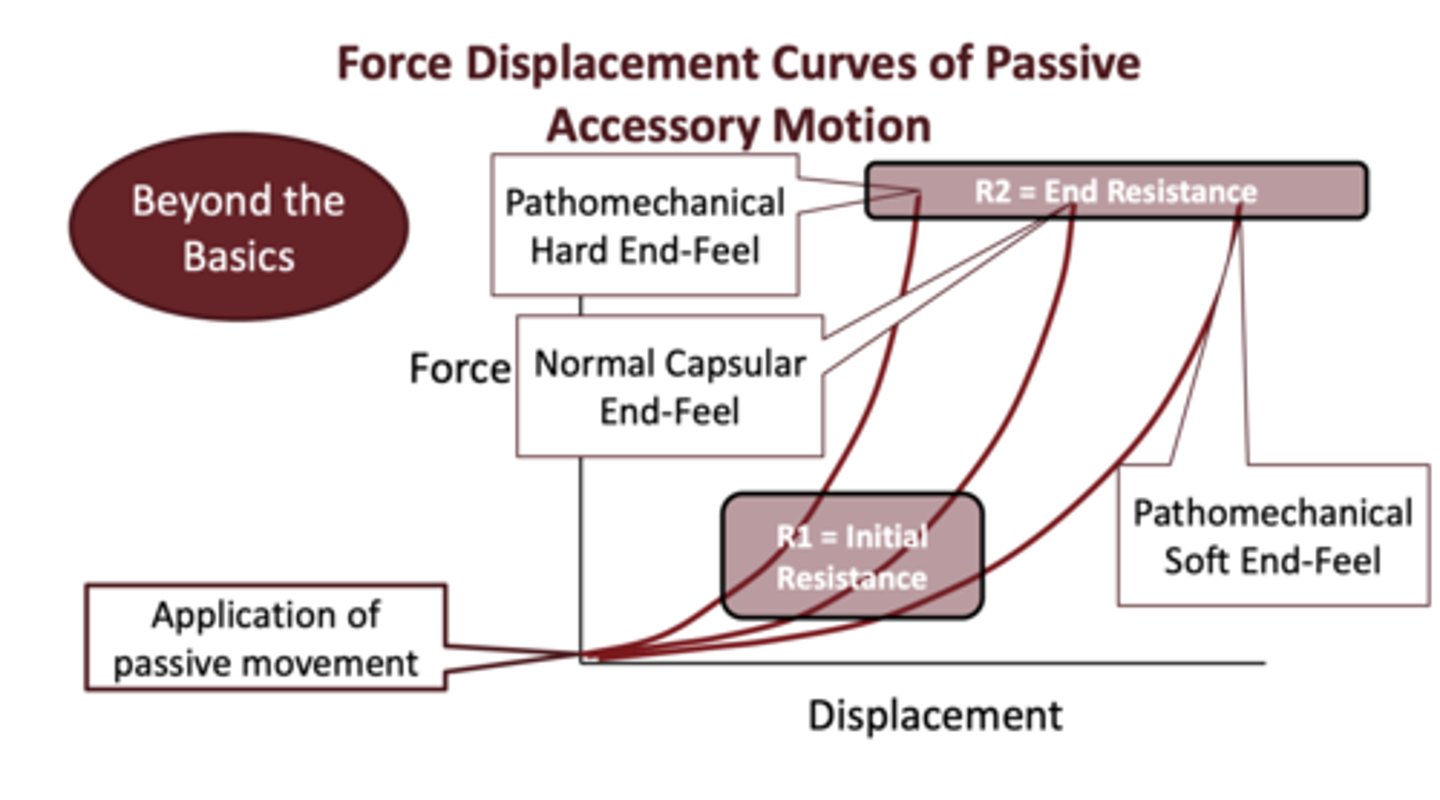
R1 vs R2 (Force displacement curve of passive accessory motion)
- R1: initial resistance still moves.
- R2: end resistance: no movement
Causes of hypomobility
- Shorted muscle and tendon units
o Loss of ostetokinematics only
- Loss of articular and periarticular tissue length
o Loss of osteokinematics and arthrokinematics
Causes of hypermobility
- Excessive osteokinematic motion only due to ligament tear or rupture
Causes of instability
Excessive arthrokinematics motion due to ligament tear or rupture
Concave surface on convex surface
- Roll and glide in the same direction as physiologic movement.
Convex surface on concave surface
- Roll and glide in opposite directions.
- Glide is opposite direction of physiologic movement.
Loose packed joint position
- Position of least tension of capsule and periarticular tissue
- Allows for maximal joint volume.
- Greatest availability for glide
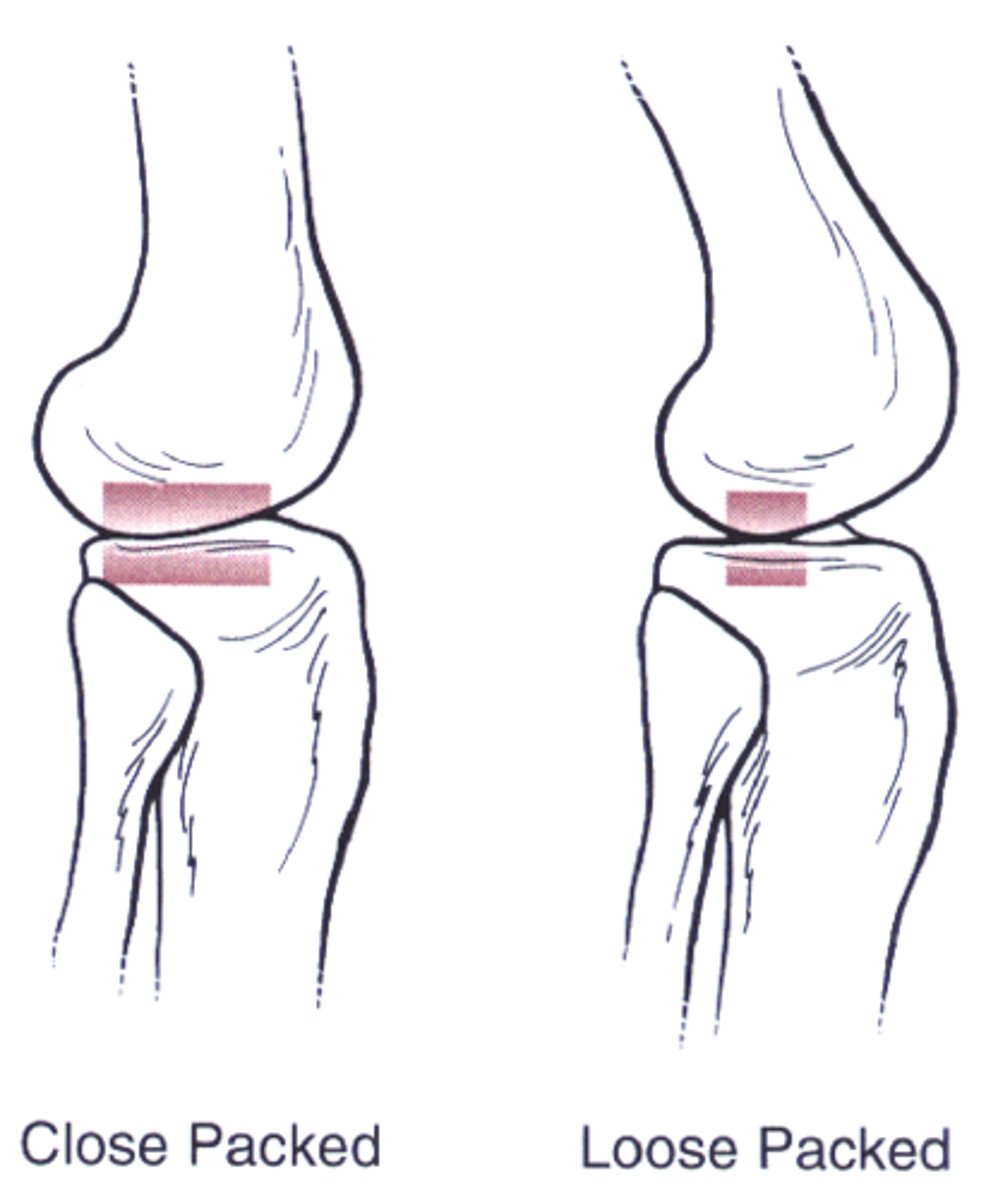
Closed pack joint position
- Maximal joint congruency and stability
- Maximal tightening of ligaments and capsule
- Least available for traction and glide

Capsule pattern
- Pattern of movement loss of a joint
- Shortening of joint capsule
Capsule pattern example
FOZEN SHOULDER patients loose external rotation first then other motions
Contractile tissues and how they are tested for tension.
- Muscle, tendon, TMJ, bursa, and bone
- Isometric contraction
Why are contractile tissues tested via isometric contractions?
- TO NOT MOVE THE JOINT
noncontractile tissues and how they are tested for tension.
- Ligaments, capsule, bone, synovium, bursa, fascia
- Passive motion (stress and stretch test)
Mobilization or a non- thrust manipulation
- In the available motion or to the barrier
o Oscillations and stretches.
Manipulation or thrust manipulation.
- High velocity and small amplitude thrust through the barrier.
o Grades 1-5
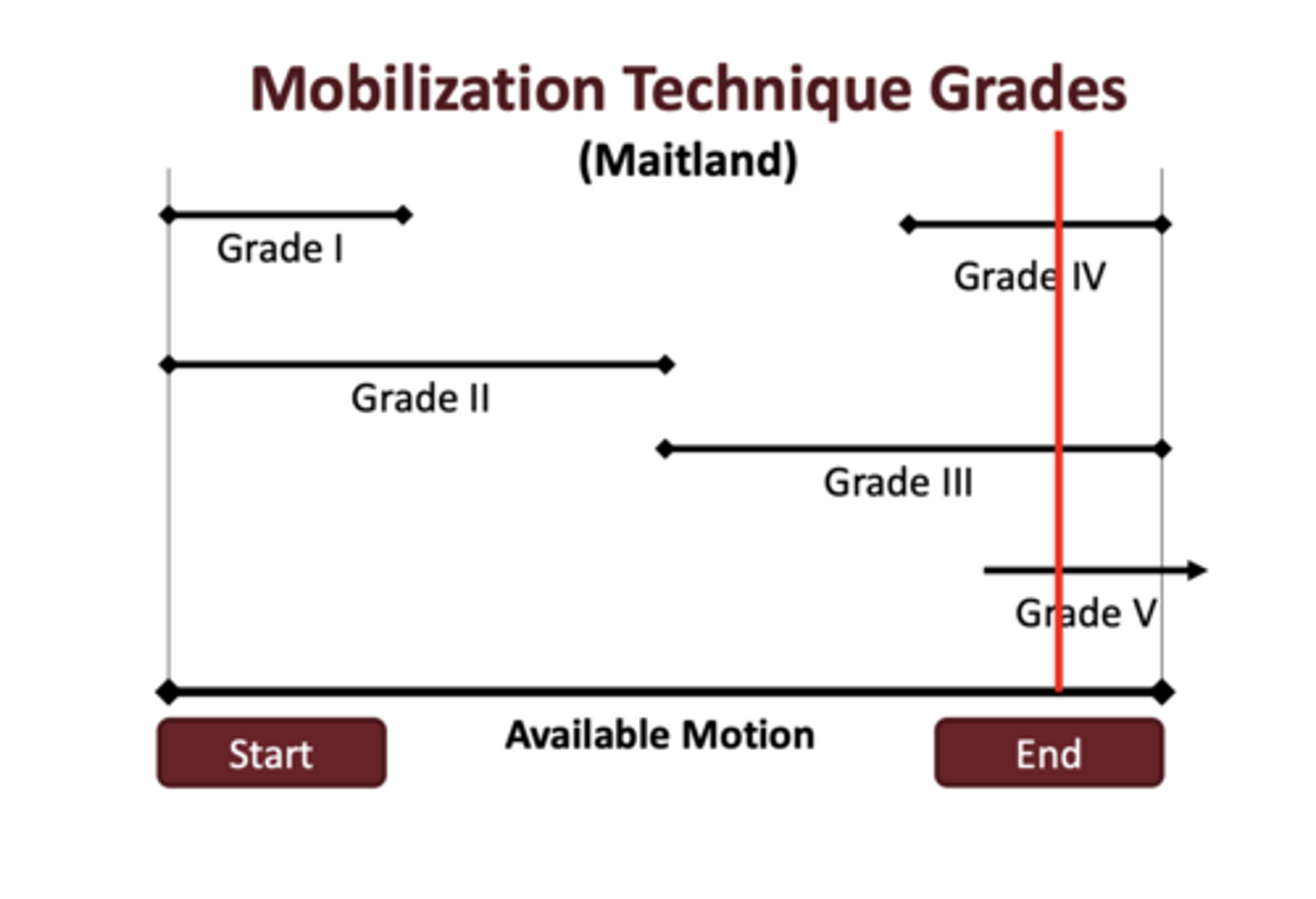
Mobilization technique grades
- Grade 1: small amp at the begging of a motion
- Grade 2: large amp at the begging and middle of a motion
- Grade 3: large amp at the middle and end of a motion
- Grade 4: small amp and end
- Grade 5: manipulative thrust
Cavitation vs tribonucleation (cracking noises)
- Cavitation: collapse of gas bubbles or voids in liquid (popping fingers)
- Tribonucleation: creation of small gas bubbles by breaking contact between solid surfaces emerged in liquid.
Three effects of manual therapy
- Biomechanical
- Neurophysiologic
- Psychological
Biomechanical effects of manual therapy
- Realignment
- Breaking adhesions
- Reduction of hypomobility (increased motion)
- Increased fluid exchange
Neurophysiologic effects of manual therapy
- Change in central pain processing.
- Change in muscle recruitment.
- Reduced temporal summation (chronic pain)
- Biochemical changes
Psychological effects of manual therapy
- Placebo effect of POP noise
- Perception of benefits
Which of the three effects of manual therapy is greatest in magnitude
- Neurophysiologic effects
Pain definition (KNOW)
- An unpleasant sensory and EMOTIONAL experience associated with or resembling an association with actual or potential tissue damage.
Are pain and nociception the same phenomena?
- NO
o Pain involves perception, and nociception are pain signals in the body.
Three types of pain
- Peripheral nociceptive pain
- Neuropathic pain
- Nociplastic pain (central sensitization)
Peripheral nociceptive pain and example
- Input to the brain from a peripheral structure which may be interpreted as pain.
o Sprained ankle
Neuropathic pain and example
- Nerve root and peripheral nerve injury
o Carpal tunnel
Nociplastic pain/ central sensitization pain and example
- Predominantly central mechanisms
o Brain interoperates input signals as pain.
Pain dominate patients.
- Patients with joint limitations and pain that that is easily provoked and elevated.
- Pain is disproportional.
Stiffness dominate patients.
- Patients with joint limitation and pin that is rapid but returns to baseline.
Indications vs. contradictions vs. precautions
- Indications: probability of benefit
- Contradictions: probability of negative result or harm
- Precautions: may or may not contribute to positive and negative outcome and require clinical reasoning