Human Anatomy Quiz 10: Muscle Tissue - Macroscopic
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
muscles
Movement of the skeletal system would not be possible without:
2
New cards
no
Is it possible for a single muscle to act alone to produce a movement?
3
New cards
yes
Should muscles be coordinated to produce movement?
4
New cards
two bones, a joint
What do muscles usually connect? What do muscles usually cross?
5
New cards
shorten
What does a contracted muscle do?
6
New cards
a muscle pulls on one bone while the other bone is stationary
What occurs when a contracted muscle shortens?
7
New cards
origin, insertion
What do you need to know about a muscle in order to determine its function?
8
New cards
opposing pairs
How do most muscles work in?
9
New cards
flexor, extensor
What is an example of an opposing pair?
10
New cards
40-50%
How much of an adult's body weight do muscles compose?
11
New cards
mechanical energy
What do the muscles convert chemical energy into?
12
New cards
move, stabilize, regulate organ volume, generate heat, propel and store fluids and solids through several body systems
Muscles transform chemical energy into mechanical energy to... (5 reasons)
13
New cards
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
What are the three types of muscle found in the body?
14
New cards
move bones of skeleton
What do skeletal muscles do?
15
New cards
striated
How do skeletal muscles appear under a microscope?
16
New cards
striped
What is another word for striated?
17
New cards
voluntary, somatic division of the nervous system
Are *most* of the skeletal muscles under voluntary or involuntary control? What are they in control by?
18
New cards
diaphragm, muscles of posture
Which skeletal muscles are under involuntary control?
19
New cards
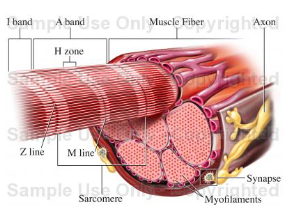
skeletal
What kind of muscle is pictured here?
20
New cards
walls of heart
Where is the cardiac muscle only found in?
21
New cards
involuntary
Are the cardiac muscles under voluntary or involuntary control?
22
New cards
actin, myosin
What do the cardiac muscles have the same arrangement as?
23
New cards
mitochondria
What do cardiac muscles have more and larger of?
24
New cards
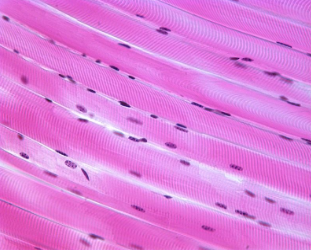
cardiac
What kind of muscle is pictured here?
25
New cards
involuntary
Are the smooth muscles under voluntary or involuntary control?
26
New cards
organs, vessels
Where are smooth muscles found *in*?
27
New cards
slow, last long
Describe the contractions of the smooth muscle:
28
New cards
a state of continued partial contraction
What is smooth muscle tone?
29
New cards
GI tract, walls must maintain steady pressure on the contents
What is smooth muscle tone important in? Why?
30
New cards
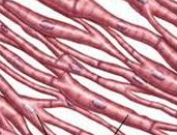
smooth
What kind of muscle is pictured here?
31
New cards
electrical excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
What do all muscle tissue have (4 properties of muscle tissue)?
32
New cards
produce action potentials
What does electrical excitability do?
33
New cards
when muscle shortens and pulls on attachment points
What is contractility?
34
New cards
muscle to stretch without being damaged
What does extensibility allow for?
35
New cards
muscle to return to its original length after stretch or contraction
What does elasticity allow for?
36
New cards
organ
What is each skeletal muscle?
37
New cards
composed of many tissues
Why is a skeletal muscle an organ? (think definition of organ)
38
New cards
muscle cells (muscle fibers)
What is each skeletal muscle composed of thousands of?
39
New cards
fibers
What are muscle cells also known as?
40
New cards
a group of muscle fibers
What is a fascicle?
41
New cards
fascicles
What makes up a muscle (component-wise)?
42
New cards
protect, strengthen
What do the three layers of connective tissue do for the skeletal muscle? (2 things)
43
New cards
epimysium, perimysium, endomysium
What are the three layers of connective tissue of the skeletal muscles?
44
New cards
outermost layer, encircling around entire muscle
Where is the epimysium located in a skeletal muscle?
45
New cards
fascicle
What does the perimysium surround in a skeletal muscle?
46
New cards
fascicles
What give meat its "grain" appearance?
47
New cards
separate each muscle fiber (muscle cell) from each other
What does endomysium do in a skeletal muscle?
48
New cards
tendon
Where do the three layers of connective tissue of the skeletal muscles extend beyond the muscle to form?
49
New cards
attaches a muscle to a bone
What does a tendon do?
50
New cards
one artery, two veins, one somatic nerve
What is each skeletal muscle supplied with? (give #s for each)
51
New cards
within the skeletal muscle
Where are capillary beds located?
52
New cards
supply nutrients and take away waste
What do the capillary beds in the skeletal muscles do?
53
New cards
collection of many neurons
What is a somatic nerve?
54
New cards
branch many times to contact many muscle fibers (cells)
What does each axon of the skeletal muscle do?