Ch 4 Part 4: modifications of mendelian ratios (SEPT 22nd)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What do genes express in response to
Genes are expressed in response to both the genetic environment and physical environment of the organism
Define Penetrance
what is the expression like
Frequency that identical genotypes are expressed
-expression is binary: it’s either expressed or not expressed
Define Expressivity
what is the expression like
Degree to which genes are expressed for known identical genotypes
-expression by degree
Define incomplete penetrance
Individuals that carry a specific disease-causing mutation will not always develop symptoms of disease
What is an example of incomplete penetrance…
how many show the trait and what type of allele is it?
what causes low penetrance
Brachydactyly in humans.
-50%-80% of people with dominant allele show trait
-genes that give susceptibility for cancer have low penetrance
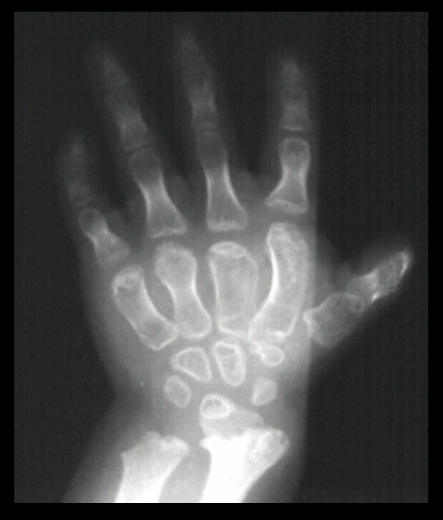
What is an example of expressivity…
what is the penetrance, what type of allele is it in?
symptom
how is it manifested
Osteogenesis imperfecta
-autosomal dominant. has 100% penetrance
-failure to make functional collagen
-manifested in differing degrees
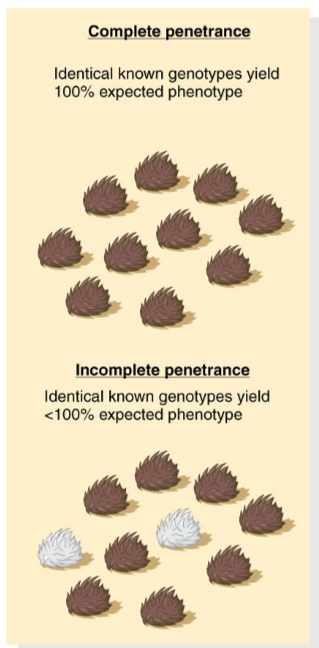
Compare complete and incomplete penetrance
Complete penetrance: Identical known genotypes yield 100% expected phenotype
Incomplete penetrance: Identical known genotypes yield less than 100% expected phenotype
Compare constant expressivity and variable expressivity
Constant: Identical known genotypes with no expressivity effect yield 100% expected phenotype
Variable: Idenitcal known genotypes with an expressivity effect yield a range of phenotypes

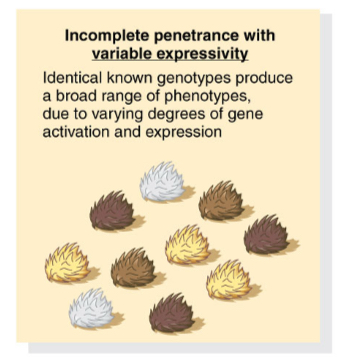
Describe incomplete penetrance with variable expressivity
Identical known genotypes produce a broad range of phenotypes. due to varying degrees of gene activation and expression
Define sex limitation
Autosomal genes may be expressed in one sex only
Examples of sex limitation and which sex
-Females dont get testicular cancer
-Males dont get uterine cancer
-milk production in mammals
-horn production in sheep
-distribution of facial and bodily hair in humans
Define sex influence
Differences in expressivity or penetrance between sexes
What is an example of sex influence
male pattern baldness
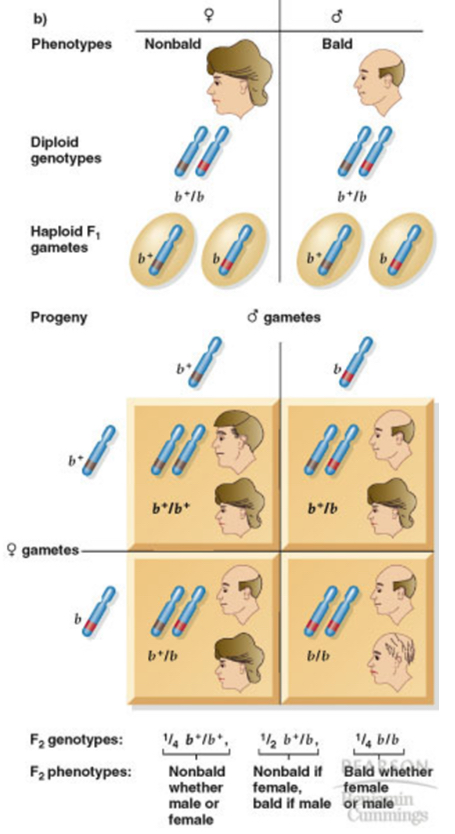
What occurs with baldness in humans…
what type of chromosome is it
what differs between men and women
what happens in men
what happens in women
-It is Autosomal
-Relationship between genotype and phenotype differs between men and women
-males: b allele is dominant, resulting in male pattern baldness
-females: b allele is recessive, pattern of baldness is disorganized
What does hair loss further vary in
penetrance and expressivity
Describe how temperature is an environmental effect
Temperature: Mutations may result in temperature sensitivity of ensymes
How does temperature affect siamese cats
In siamese cats, expression of black pigmentation in fur is temperature dependent
-a tyrosinase mutation causes failure to function at high temperature, inability to produce melanin
-tyrosinase will function at cooler extremities

Describe how position is an environmental effect…
what does this mean with heterochromatin
Position: Location of a gene in the chromosome may influence the level of expression
-heterochromatin (tightly packed, no gene expression): DNA with high repeat content, low levels of expression
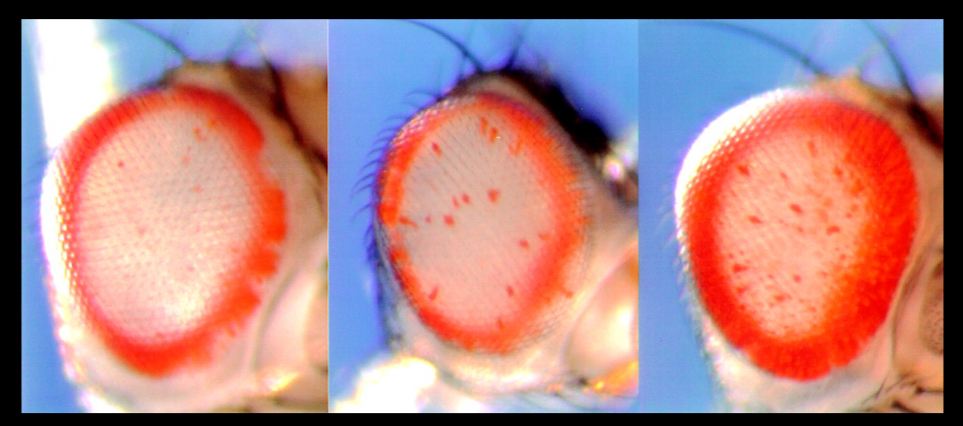
How does position affect fruit fly eye pigmentation
inserting repeats near genes that code for red pigment mutations, will result in varied expression of red pigment

Describe how age is an environmental effect
Aging results in changes in internal environment
-little is known regarding the mechanism by which aging induces changes in expression
What are some examples connected to age being an environmental effect
at what age is it present in
-male pattern baldness (20-30 years)
-Duchenne muscular dystrophy (5-6 years)
(a fatal disorder in which muscles begin to weaken in early childhood)
Define Genetic anticipation
Age of onset increases/changes over generations, not an environmental effect
Define myotonic dystrophy, an example of genetic anticipation
mutations in one of two genes that promote communication between muscle cells and neurons
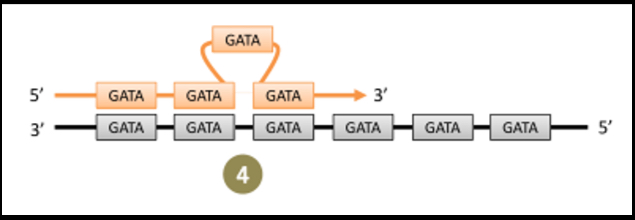
- slip-strand mutations produce repeats that elongate the coding sequence in serial
-increased repeats increase the probability of further slip-strand error
-when DNA is repeated serially, replicate DNA can “loop out” and still avoid error repair function of polymerases
How does myotonic dystrophy affect later generations due to genetic anticipation
-where the condition becomes more severe and appears at an earlier age in successive generations.
-Anticipation is due to the DMPK gene having an unstable CTG trinucleotide repeat that expands in length during meiosis.
-The increased repeat count in offspring results in more severe symptoms.
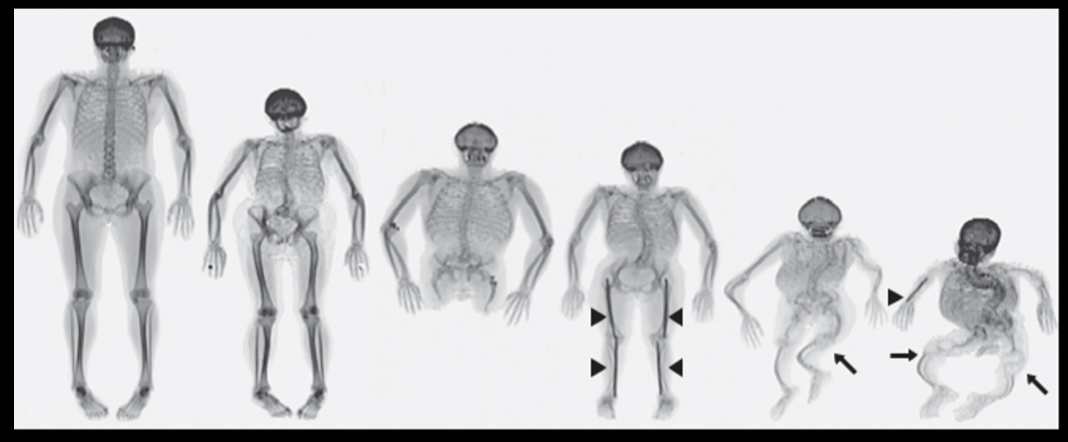
Myotonic dystrophy generational example, include generation number, repeat number and phenotypic effects
Gen 1: few repeat number, cataracts late in life
Gen 2: more repeat number, muscle weakness in adults
Gen 3: even more repeat number, cognitive disability in children
Gen 4: many repeat number, developmental failure in embryogenesis