Disaster Risk Reduction and Management
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Hydrometeorology
It is studying natural phenomenon with atmospheric, hydrological, or oceanographic origin
It is the study of transfer of water of water and energy between the eart’s surface and lower atmosphere
What are the hydro meteorological hazards
Typhoons
Storm-surge
Thunderstorm
Flooding
Enso Cycle
Typhoon
It is a severe weather disturbance characterized by strong winds and heavy rains which revolve around central low pressure area. It the most powerful type of tropical clcone that forms in the northwestern Pacific Ocean
Tai Fung
TROPICAL CYCLONE / HURRICANE
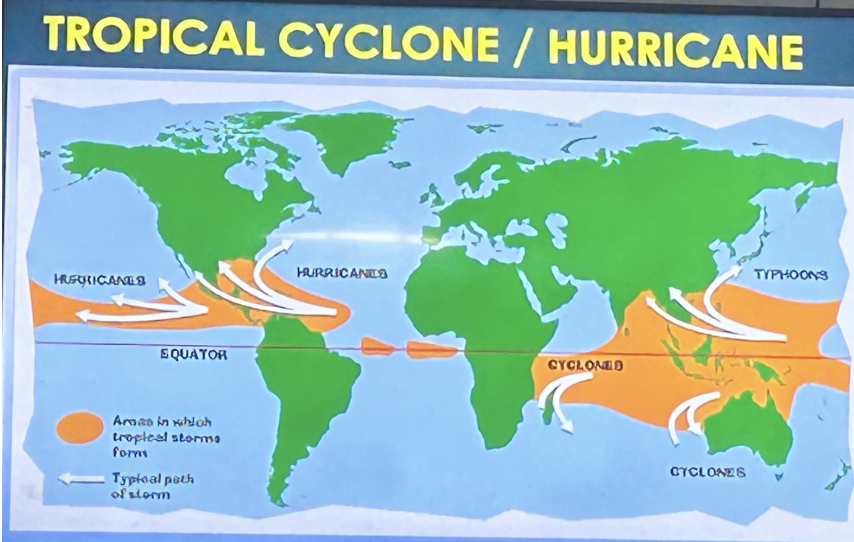
Coriolis effect
Refers to the deflection of an object's motion due to the earth’s rotation about its axis.
Northern Hemisphere air deflects to the right
Southern Hemisphere air deflects to the left

Eye
It is the area of the lowest atmospheric pressure in the structure of a tropical cyclone.
20-65 km wide
Weak winds
Warm temperature
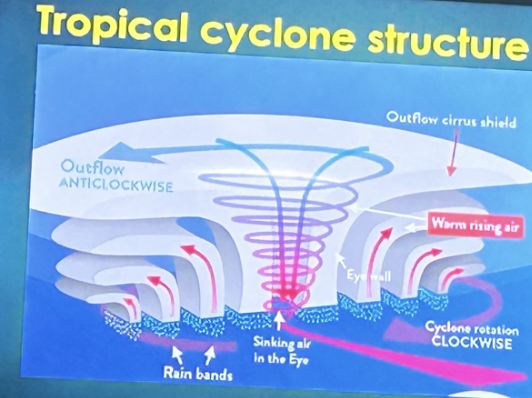
Eye wall
it is the region surrounding the tropical cyclone’s enter
15 kms ASL
Strong winds
Heavy rains
Rain bands
It is the spiraling strips of clouds in the tropical cyclones which are associated with rainfall
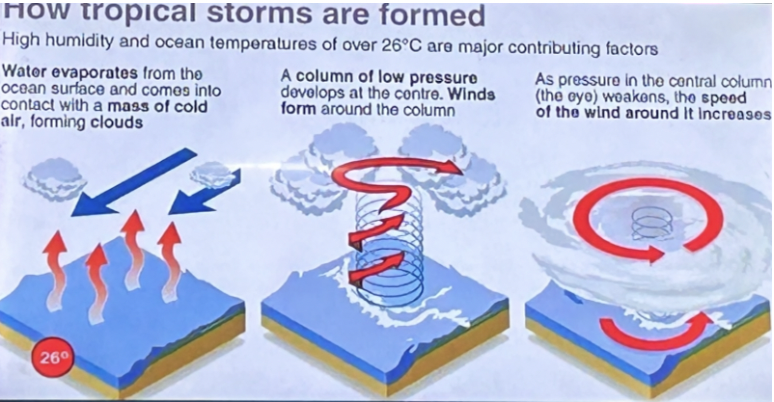
Conditions
Temperature over 26 degrees celsius
Low atmospheric pressure
Formative stage
formation where the hot and cold air meet
Immature stage
forms and creates the strong winds to it’s maximum
Mature stage
3 to 5 days
Decaying stage
happens very fast, 1 to 2 days
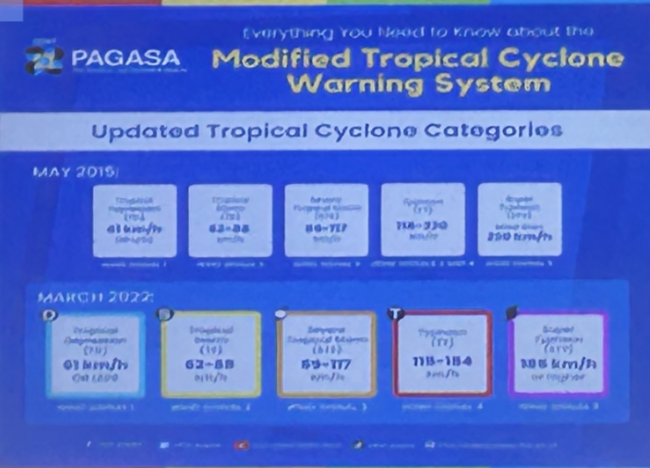
Tropical Cyclones Category
Tropical Depression
Tropical Storm - 62 to 88 kph
Severe Tropical Storm - 89 to 117 kph
Typhoon (hurricane) - 118 to 184 kph
Super Typhoon - 185 kph+
Why do TC’s form?
Natural tendency to maintain equilibrium by redistributing heat through wind from the equatorial regions to the polar regions.
Effects of Tropical Cyclones
Strong winds
Storm Surge
Heavy rains
Ways to Mitigate the Effects
Determining area prone to typhoon-related disasters
Implementing legislation involving land use planning, zoning, and building standards
Weather forecasting and monitoring
Effective public typhoon warning systems
Effects of Tropical Cyclones (Secondary)
1. Food shortage
2. Flooding
3. Infrastructure damage
4. Economic Disruption
5. Job loss
6. Death
7. Disease Outbreak
Ways to Mitigate the Effects
1. Determining area prone to typhoon-related disasters
2. Implementing legislation involving land use planning, zoning, and building standards
3. Weather forecasting and monitoring
4. Effective public typhoon warning systems