BIO230 UofT Final Exam
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
What domains are polar in multicellular organisims
Apical domain
basolateral domain
Polarized cells can...
have different functions at different cell regions
define inside v outside
transmit signals from one end to the other
Exocytosis
directly to the target domain
-out
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
in
Trafficking routes
polarized
proteins are organized at sorting station
balanced by retrieval pathways
ER-> Golgi-> plasma membrane
some trafficking routes are polarized
Transmembrane ->Golgi network
proteins are organized at sorting stations
ER retrieval from Golgi
different routes are balanced by retrieval pathways
Most cargo moves through
Constitutive sectretion
What is not required for constitutive secretion
specific signals
returns membrane back to the golgi
clathrin-coated vesicles
Clathrin-coated vesicles
shrink vesicle
makes cargo more concentrated
Regualted secretion
releases material in response to a signal
do not fuse with the plasma membrane until signal is received
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Plasma membrane repair
fixes a wound in the cell by exocytosis
Plasma membrane - early endosome- lysosome
polarized
endosomes
sorting stations
re-secretion to plasma membrane
retrieval pathways
3 options for endocytosed proteins
recyclying, transcytosis, degradation
Vesicle trafficking types
donor membrane into cytoplasm
vesicle fusion
donor membrane away from the cytoplasm
what does LDL bind to?
LDL receptors coated with clathrin triskelion
COPII
ER to cis-Golgi
COPI
Golgi to ER
Clathrin
Trans Golgi-->Lysosomes; Plasma membrane-->Endosomes
Retromer
multiprotein coat that forms on an endosomal vesicle only
SNARE proteins
help mediate vesicle fusion
t-SNARES and v-SNARES required
-must be on opposite membranes
ESCRT proteins
can form vesicles away from the cytoplasm
into lumen or extracellular space
vesicle formation machinery in cytoplasm
ESCRT-0
binds PI(3)P and collects mono-ubiquitinated cargo proteins, provides binding site for ESCRT-I
- initiation and cluster cargo selection step
ESCRT-1, 2, and 3
help push vesicle away from cytosol
How many of the following are examples of vesicle formation into the cytoplasm?
COPII-mediated secretory vesicle formation at the ER
ESCRT-Mediated vesicle formation
clathrin-mediated endocytic vesicle formation
any process mediated by SNARE proteins
2
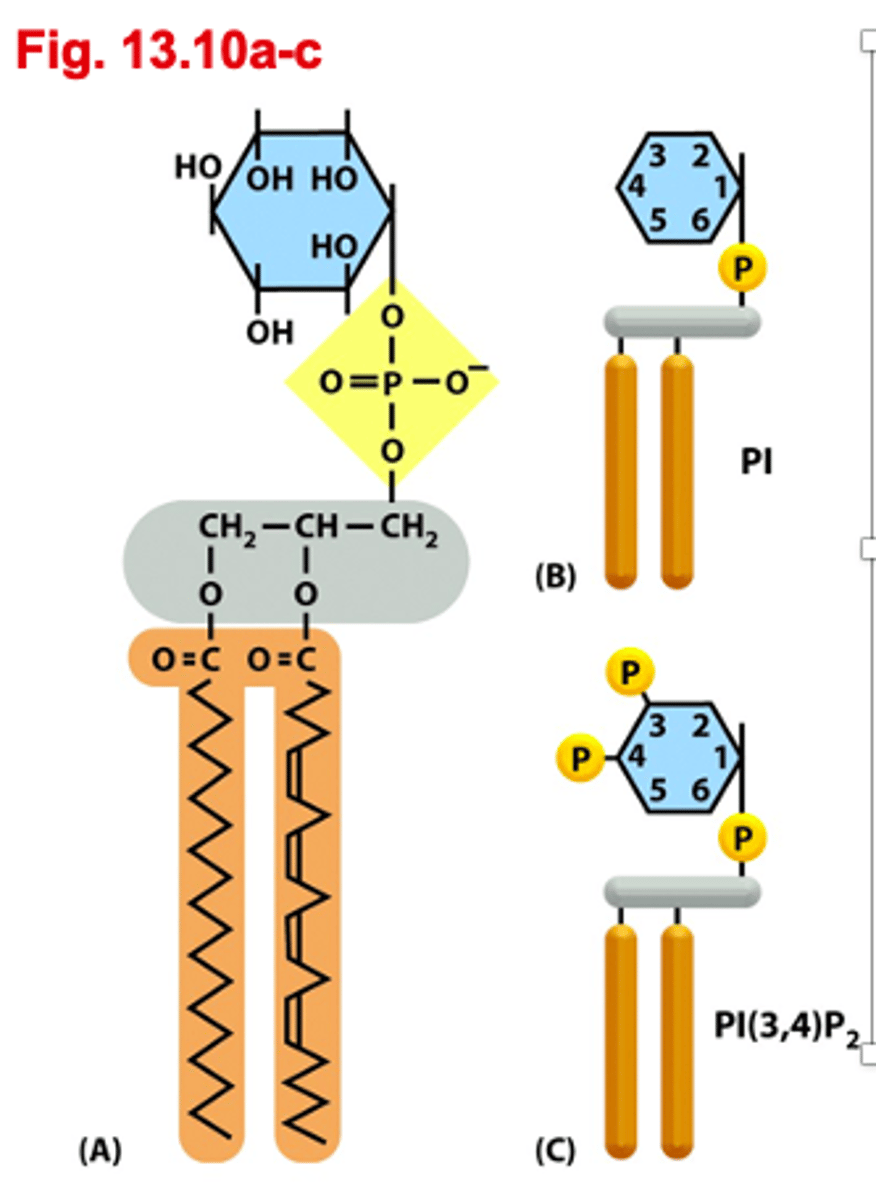
Phosphoinositides
label different membrane domains
diff membrane domains and compartments contain diff lipids
diff PIPS are found at diff subcellular locations
Phosphorylation site positions are numbers in brackets
total number of phosphorylation sites subscript number
PI(3)P
phagocytosis
-endosomes
-can phosphorylate PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,5)P2
-can dephosphorylate PI
PI(4)P
endocytosis
-golgi
-can dephosphorylate PI
-can phosphorylate PI(3,4)P2 and PI(4,5)P2
PI(4,5)P2
Golgi and PLasma membrane
can dephosphorylate Pi(5)P and PI(4)P
can phosphorylate PI(3,4,5)P3
bind to adaptor proteins for clathrin mediated enodocytosis
PI(3,5)P2
Endocytosis
-late endosomes
-can dephosphorylate PI(5)P
PI(3,4,5)P3
phagocytosis
-plasma membrane
-can dephosphorylate PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4)P2
Structure of Phosphoinositides
inositol sugar-blue
phosphate group-yellow
glycerol-grey
lipids-orange
Rab GTPase
molecular switches that can direct vesicles
off when bound to GDP
on when bound GTP
GEF turns on this exchange from GDP to GTP
Rabs and PIPS combination in early endosome
Rab5-GTP recruits PI 3-Kinase
PI(3)P can recruit Rab5-GEF
More Rab5-GEF makes more active Rab5-GDP
Rabs and SNARES
work together in vesicle targeting & fusion
interact with tethering protein
Polar cytoskeleton organization
Microtubules
actin
intermediate filaments
Microtubules
transport vesicles and proteins to diff ends of the cell
actin
defines cell shape and behaviour
Intermediate filaments
contribute to cell polarity
Interphase crawling/ migrating cell
microtubules radiate from cell centre
actin enriched at cell cortex
Mitosis
microtubules form the mitotic spindle
actin at cell cortex dissembles
cytokinesis
microtubules keep cell components separate
actin forms the contractile ring
Polar tublin dimers for polar microtubules
monomeric proteins
-alpha tubulin
-beta tubulin
-both form dimers
tubulins bind and hydrolyze GTP
tubulin heterodimers assemble head-to-tail to make polarized protofilaments
alpha tubulin
found at minus end
d-form heterodimer
-less stable
-GDP-bound
-is hydrolized t-form subunits
-if found at tip of microtubule will fall (depolymerization)
Beta tubulin
found at plus end
t-form heterodimer adds to plus end
-stable associations
-GTP-bound
Dynamic instability
The rapid switching between growth and shrinkage shown by microtubules.

gamma tubulin
interacts w/ alpha tubulin at minus end
nucleates or stabilized the (-)end
protects microtubules from depolymerization at (-) end
(+) end grows away from nucleation site
in animals, found near centrioles
in plants, found on other microtubules
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
a class of proteins that participate in the regulation of microtubule assembly and function
some kinesis can "walk" towards (+) end
some dyneins can move towards (-) end
hold onto vesicles or organelles w/ other domain
both use ATP hydrolysis for energy
Transported along microtubules
vesicles and organelles
Which of these statements about microtubules is true?
a) when a centrosome is present each microtubule contains a variable number of protofilaments
b)long, growing microtubules will contain GTP and GDP
c) A cell with many microtubules will not have any actin filaments
d) gamma-tubulin stabilizes microtubules minus ends by anchoring them onto a cylindrical centriole core
B
Actin Monomers
asymmetric
polar
bind and hydrolize ATP
assemble polarized actin filaments
Actin Filaments
t form (ATP bound)-more stable
D form (ADP bound)-less stable
T form polymerize and then hydrolyze into a d form in the (-) end... T form more likely in (+) end
treadmilling
Hydrolysis will catch up with the (-) end because it is slow
Hydrolysis lags behind the (+) end
pushes cell leading edge forward
-(+) end grows towards edge
-allows cells to crawl
-must be anchored tho
ARP2/3 complex
A protein complex that binds actin filaments and initiates the formation of branches.
nucleates the (-) end and protects them from depolymerization
(+) end grows away from complex
nucleate actin filaments on pre-existing filaments
whole network can go through treadmilling
proteins sever (-) end to release complex
-will depolymerize
-capped
proteins cap the (+) ends
-will stop additional subunits
-will go towards edge of cell
Integrins
anchor actin filaments to the extracellular matrix
directly bind extracellular matrix proteins
indirectly acts w/ actin filaments
prove adhesion necessary for cell migration
Mysosin
motor domains use ATP hydrolysis for energy
hold onto vesicles or organelles w/ their other domain
can help cells contract
"walk" towards (+) end
actin and myosin work together to generate force
A graduate student adds actin monomers and ATP into a test tube with a buffer that resembles the cell cytosol. What else must be added to the tube to produce ADP?
a) severing protein cofilin
b) nucleating protein ARP2/3
c) cofilin and ARP2/3
d) nothing
D
RHO family GTPases
influence actin organization (Rho, Rac, and Cdc42)
molecular switches
affects cell shape, cell polarity and cell behaviour
on when bound to GTP
off when bound to GDP
activation of Rho family GTPases
can have a dramatic effect on the organization of actin filaments in fibroblasts
Rac-- thick wall
Rho-- lines across one end to the other (a lot)
Cdc42-- lines spreading away from the wall
Rac-GTP activation
dominates the leading tip to explore and to push the cell forward
Rho-GTP activation
dominates at the back to pull the back of the cell
Cytoskeletal organization
defines cell polarity
symmetry breaking
cytockeleton polarization is triggered
symmetry breaking
anterior v posterior
Which of the following would most directly increase the amount of constitutive protein secretion?
a) a chemical that increases the formation of COPI-coated vesicles
b) a chemical that increases the formation of COPII-coated vesicles
c) a chemical that increases the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles
d) a chemical that increases the formation of ESCRT-0
B
epithelial tissue
cells directly connected to each other with minimal extracellular matrix
polarized
connective tissue
cells dispersed through extracellular matrix
basal lamina
separates the connective tissue and the epithelial tissue
epithelial cells
skin, disgestive tract, surrounding organs
polar
different functions
inside v outside
basal domain adheres to basal lamina
lateral domain adheres to each other
apical domain is exposed
tight junction
seals gap between epithelial cells
apical domain
basal domain
basolateral domain
domains are defined and maintained
formed by occludins & claudins
limit diffusion into extracellular space
limit diffusion of membrane proteins
regulates what enters organism
adherens junctions
connects actin filament bundle in one cell with that in the next cell
form first
provide polarity cues to define apical from basolateral domains
desmosome
connects intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell
gap junction
allows the passage of small water-soluble molecules from cell to cell
Cadherins
cell-cell junctions
transmembrane proteins expressed by both cells
interact homophilic interactions of their extracellular domains
require Ca2+
directly link adjacent cells
indirectly interact w/ actin filaments
indirectly link the actin cytoskeleton btwn adjacent cells in epithelial tissues
interact in patches to form a strong adhesion belt
integrins
cell-extracellular matrix junctions
heterodimers directly bind to extracellular matrix(EXCM) proteins
transmembrane domain
indirectly interact w/ actin filaments
alpha and beta subunit act together to bind to an EXCM protein
Homophilic interactions
btwn E-cadherins
btwn N-cadherins
none btwn E and N cadherins
sort into 2 seperate groups
Adhesion belts
mediate morphogenisis
-pulls cells to form a tube
-diff cadherins establish new interactions and ensure neural tube closure
Which of the following most closely resembles adherins junctions mutation in the outer epithelium of Drosophila embryos?
a) Hemidesmosome mutation in the outer epithelium
b) calcium removal at the outer epithelium
c) intermediate filament depolymerization in the outer epithelium
d) occludin mutation in the outer epithelium
B
Basal domain
faces the inside of the body
apical domain
faces the surface, cavity or organ
basolateral domain
basal & lateral domains often grouped
Occludins & Claudins
form homophilic interactions
directly link adjacent cells
many rows of them will form tight junction
Active transporters
move glucose into the epithelial cell on the apical domain
passive carriers
basolateral domain allow glucose to diffuse out of the epithelial cell into the connective tissue/blood
Cell polarity
the cell has a "front" and "back"
extracellular or internal signals can polarize cell behaviour
initial polarity signal is external
Intracellular trafficking + cytoskeleton organization + cell adhesion = functional epithelium
An occludin mutation in ________ cells will directly affect _____.
a) intesitnal epithelial; glucose transport
b) drosophila embryonic; movement of the outer epithelium
c) drosophila embryonic; segmentation of the outer epithelium
epithelial; adherens junction formation
A
Multicellular development
ongoing process that occurs in adults from stem cells
Embryogenesis
fertilized egg --cleavage--> blastula--gastrulation--> grastula
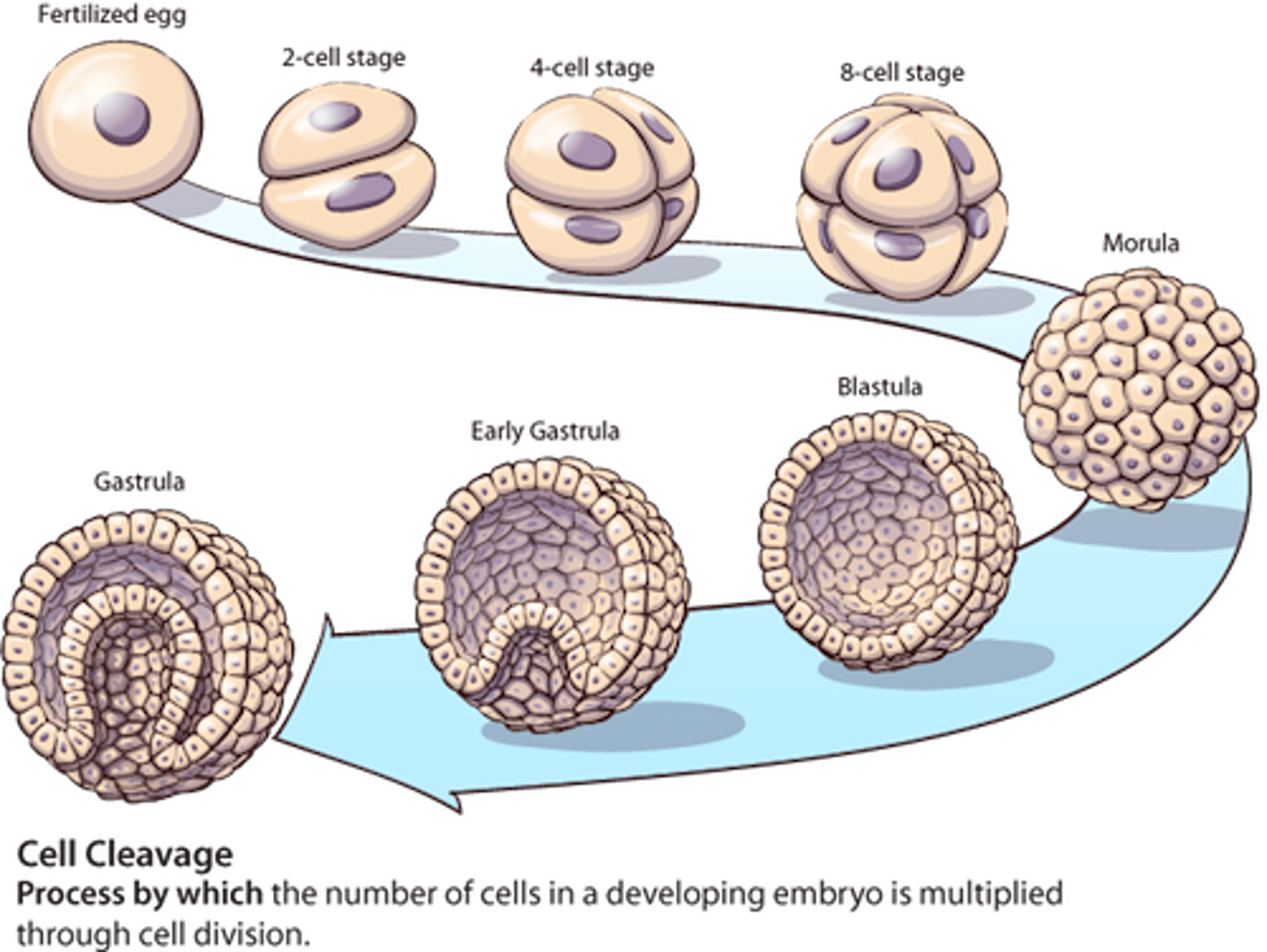
Cleavage
cell proliferation
Gastrulation
cell differentiation
cell morphogenisis
change from ball of cells to an embryo with a guy & 3 germ layer
Grastula
Ectoderm- outer layer
Mesoderm- hanging around in the middle
Endoderm- middle but still slightly connected
ectoderm
epidermis and nervous system
Mesoderm
muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, circulatory system
Endoderm
gut, liver, lungs
Morphogenesis
generation of shape
1. cell internalization
2. elongation
3. fine repositioning of cells