PSL 310- PNS afferent -incomplete
1/193
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PSL 310 MSU exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
afferent information
information that goes into the brain/ spinal cord
efferent information
information that is released from the brain/ spinal cord
afferent infomation is known as
sensory information
efferent information is known as
motor information
3 sensory receptors
exteroceptors, interoceptors, proprioceptors
exteroceptors function
sense external information
exteroceptor 2 types
somatic and external
somatic exteroceptor information
skin and special senses like eyes, nose, ears, mouth
external exteroceptors information
from the environment to the body
interoceptors function
sense internal enviroment
interoceptors example
sense stomach pain via pain receptors in the stomach, sense blood pressure via the carotid barocepters
proprioceptors function
knowing position of body in space
proprioceptors example
nerve fibers in muscles, tendons, and ligaments
exteroceptors send information to different lobes of the brain examples
parietal lobe, and occipital lobe
where is afferent information integrated
the parietal cortex
what are the commands generated form the afferent information
efferent information
what are the two types of efferent neurons
somatic and autonomic
somatic nervous system function
controls skeletal muscle
autonomic nervous system functions
controls everything you can’t manually control;
autonomic nervous system divisions
sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric
parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system controls
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, exocrine glands, B cells, adipose tissue
enteric nervous system function
nerve fibers in the GI tract that sense the internal environment of the GI tract sending the information to the brain to release enzymes and acids to help digest food
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
how many pairs of cranial nerves are there
12
olfactory nerve function
sense of smell
optic nerve function
vision
vestibular and cochlear nerve function
sense of balance and equilibrium
vagus nerve function
regulate involuntary functions
are cranial nerve motor or sensory
they can be both
how many pairs of spinal nerves are there
31
how many vertebrae are there in the spine
30
how many vetebrae are cervical
7
how many vertebrae are thoracic
12
how many vertebrae are lumbar
5
how many vertebrae are sacral
5
what does one verterbra on top of another form
intervertebral foramen
intervertebral foreman function
allow spinal nerves to come out between discs
what are discs made out of
fibracartilage, GAGs, and proteoglycans
GAGs
glycosaminoglycans
disc function
separate vertebrae, help form the intervertebral; foramen
bulging disc
dehydration of disc causing stress of outer layer and buldging, can press on nerves
herniated disc
(slipped disc) disc leaks out towards the foramen
thin disc
discs loose water and what makes them up
spinal stenosis
osmotic potential increases over time due to not as many GAGs and proteoglycans being produced, disc will thin
osteophyte fermation
“bone spurs”spikes that face the intervertebral foramen, can pinch nerves
grey matter
H shape in spinal cord, contains cell bodies, glial cells, and glial cells
white matter
axons
ventral roots are made up of
bundle of motor (efferent) axons
where do ventral roots come out of the spinal cord
the front ventral ramus
dorsal roots are made up of
bundles of sensory axons
where do dorsal rootlets come out of the spinal cord
the back dorsal ramus
dorsal root and ventral root fuse to become
the spinal nerve
sympathetic chain ganglia
autonomic nerve fibers hang to regulate fight or flight
dorsal root ganglion contains what two types of neurons
unipolar and bipolar (sensory)
spinal reflex arc steps
arrival of stimulus/ activation or receptor
activation of a sensory neuron
relay in brain via an interneuron
activation of a motor neuron
sensory processing by brain
response by effectors
does a spinal reflex require the brain
no the AP will be integrated in the spinal cord by an interneuron and an AP will be fired from a motor neuron to the skeletal muscle to contract
what glial cells are found in the spinal arc
satellite cells
mechanoreceptors types
tactile, nociceptors, baroceptosr, proprioceptors, auditory, equilibrioceptors
tactile receptors
touch
baroceptosr
pressure
proprioceptors
pressure
auditory receptors
hearing
equilibrioceptors
equilibrium and balance
what 3 receptor types contain nociceptor
mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoceptors
chemoreceptor types
olfactory, gustatory, nociceptors
olfactory receptors
smell
gustatory receptors
taste
thermoreceptor types
thermal, nociceptors
thermal receptors
cold and hot
osmoreceptors
osmolarity of ISF
Photoreceptor
vison
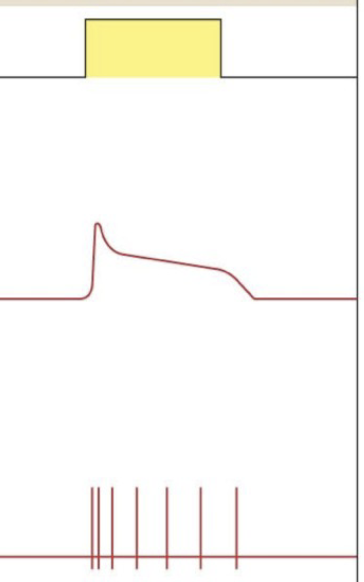
tonic vs phasic receptor
tonic- slowly adapting receptor that respond for duration of a stimulus.
phasic- rapidly adapt to a constant stimulus and turn off
how long does a graded potential last for tonic receptors
as long as the stimulus
what is the AP frequency for tonic receptors
high AP frequency/ slowly adapting and constant APs
how long does a phasic receptor graded potential last
it will be quick at the beginning of the stimulus
what is the AP frequency for phasic receptors
the APs will rapidly adapt and APs will disappear quickly
phasic receptor image
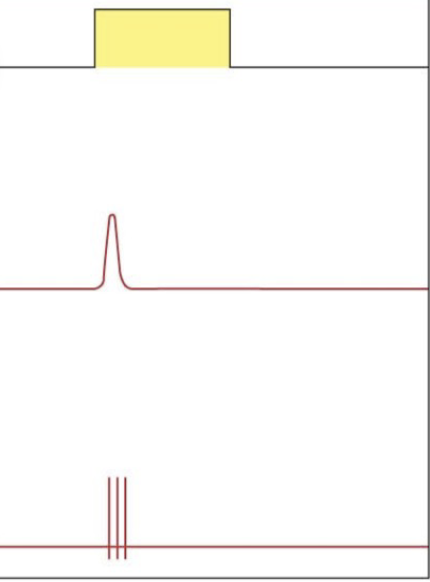
tonic receptor image
tonic stimulus example
burn
phasic stimulus example
clothing toughing skin, SMELL
somatic general senses
touch, vibration, pressure, stretch, pain, temperature
what are the 3 layers of skin parietal to deep
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
what do free nerve endings detect
pain, temperature
what layer of skin are free nerve endings located in
epidermis
what do merkle discs detect
light touch
where are Merkel discs located
dermis
what do meissners corpuscle detect
light touch
where are meissners corpuscle located
dermis
how do hair follicles detect touch
they are innervated with nerve fibers
what do Ruffini corpuscles detect
stretch
where are Ruffini cospuscles located
hypodermis
what do pacinian (lamellate) corpuscles detect
vibration and pressure
where are pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles located
hypodermis
what is the temperature range for no sense touch
86-98 F
what is body temperature
~98.6 F
what is the only somatic sense not phasic
Ruffini corpuscles
what are the somatic general senses mechano receptors
piezo
what is the temperature range for TRPV to be activated
95F - 122 F
what perceptions do TRPV receive
perception of warmth and hot