Disaccharides and Polysaccharides: Structures, Functions, and Enzymes in Carbohydrate Chemistry
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What reaction forms disaccharides?
A condensation reaction of two monosaccharides.
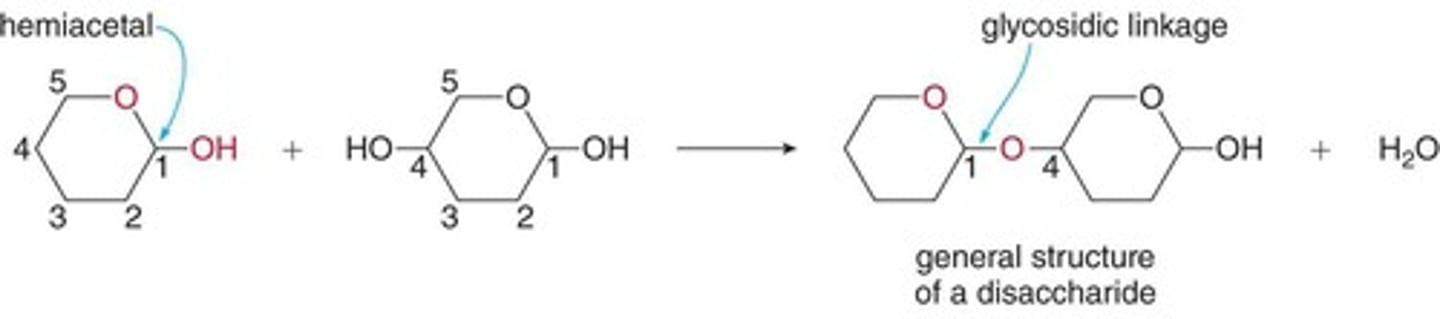
What is the glycosidic bond?
A bond formed between an anomeric carbon and a hydroxyl carbon of two sugar molecules.
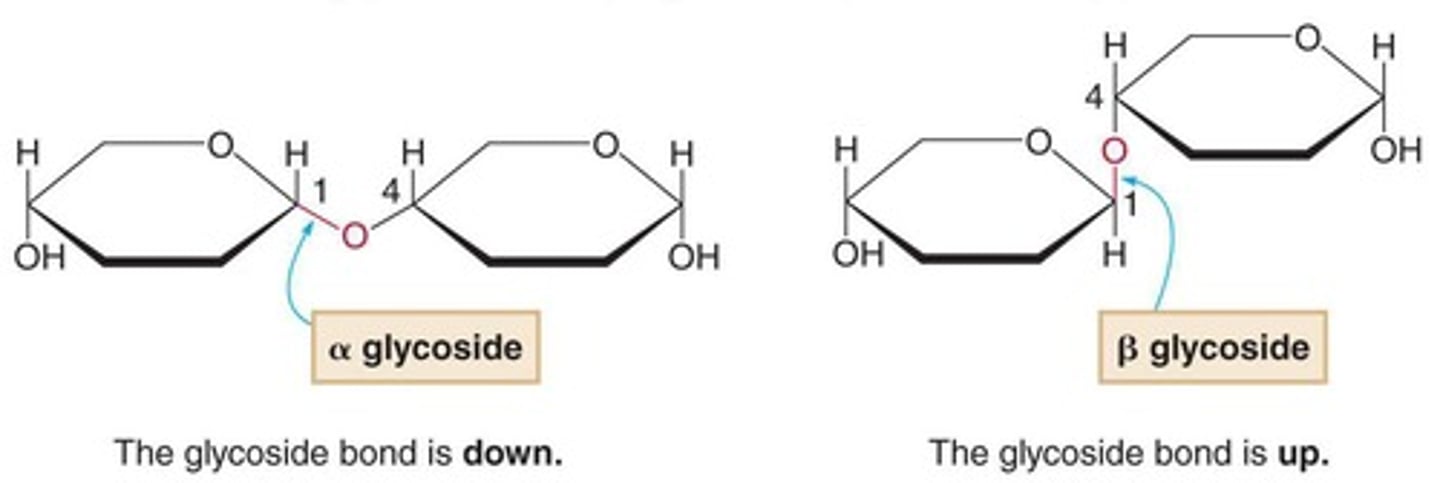
What types of glycosidic bonds exist?
Alpha (α) and beta (β) glycosidic bonds.
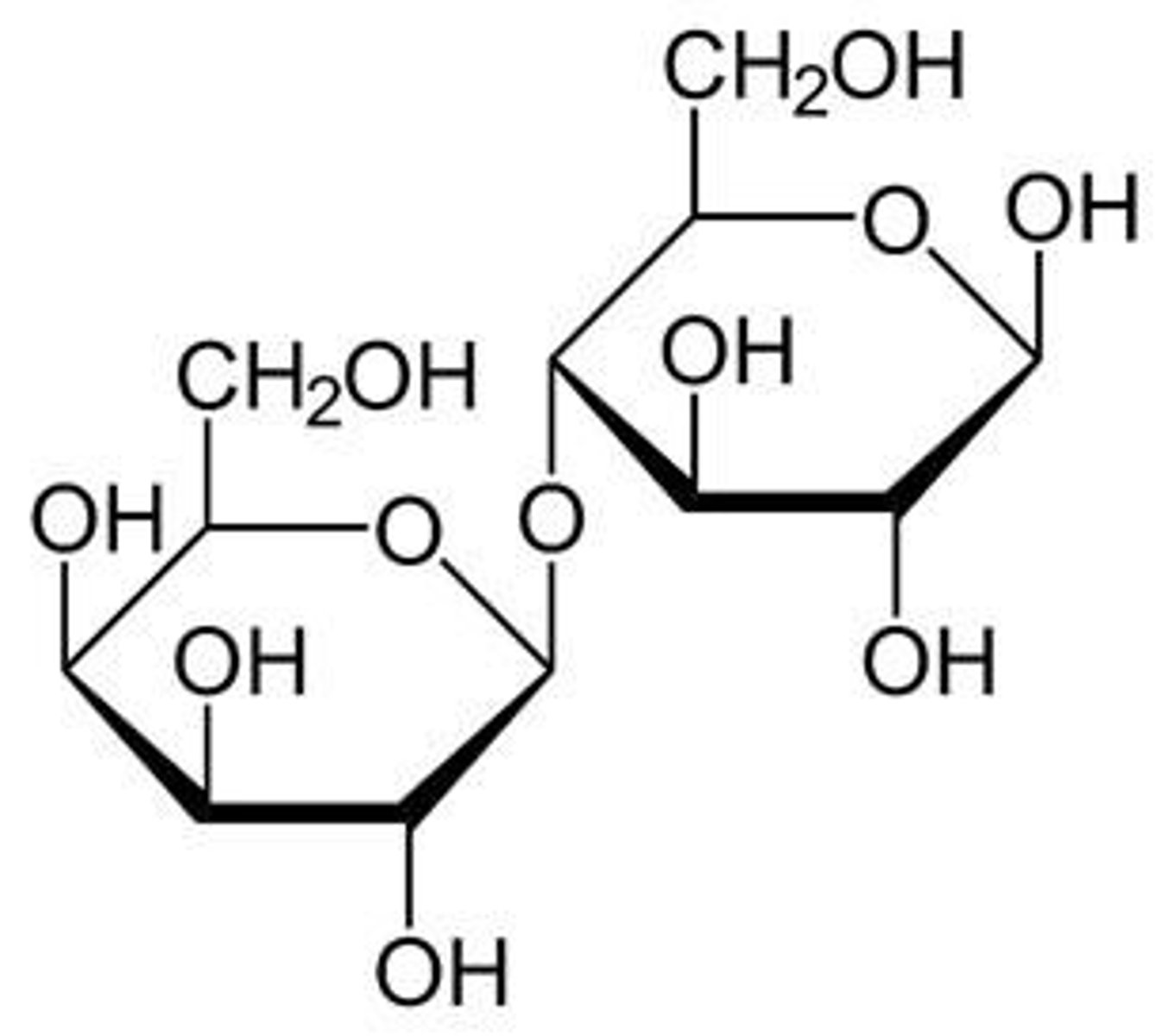
What is maltose composed of?
Two glucose molecules linked by an α-1,4 glycosidic bond.
What enzyme hydrolyzes maltose in the body?
Maltase.
What is lactose composed of?
Galactose and glucose linked by a β-1,4 glycosidic bond.
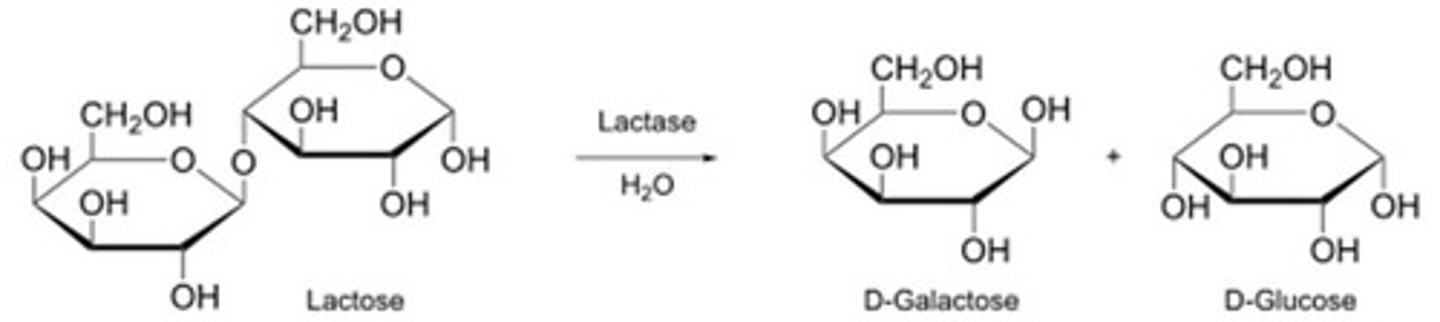
What enzyme is responsible for hydrolyzing lactose?
Lactase.
What condition results from a lack of lactase enzyme?
Lactose intolerance.
What is sucrose composed of?
Glucose and fructose linked by an α-1,2 glycosidic bond.
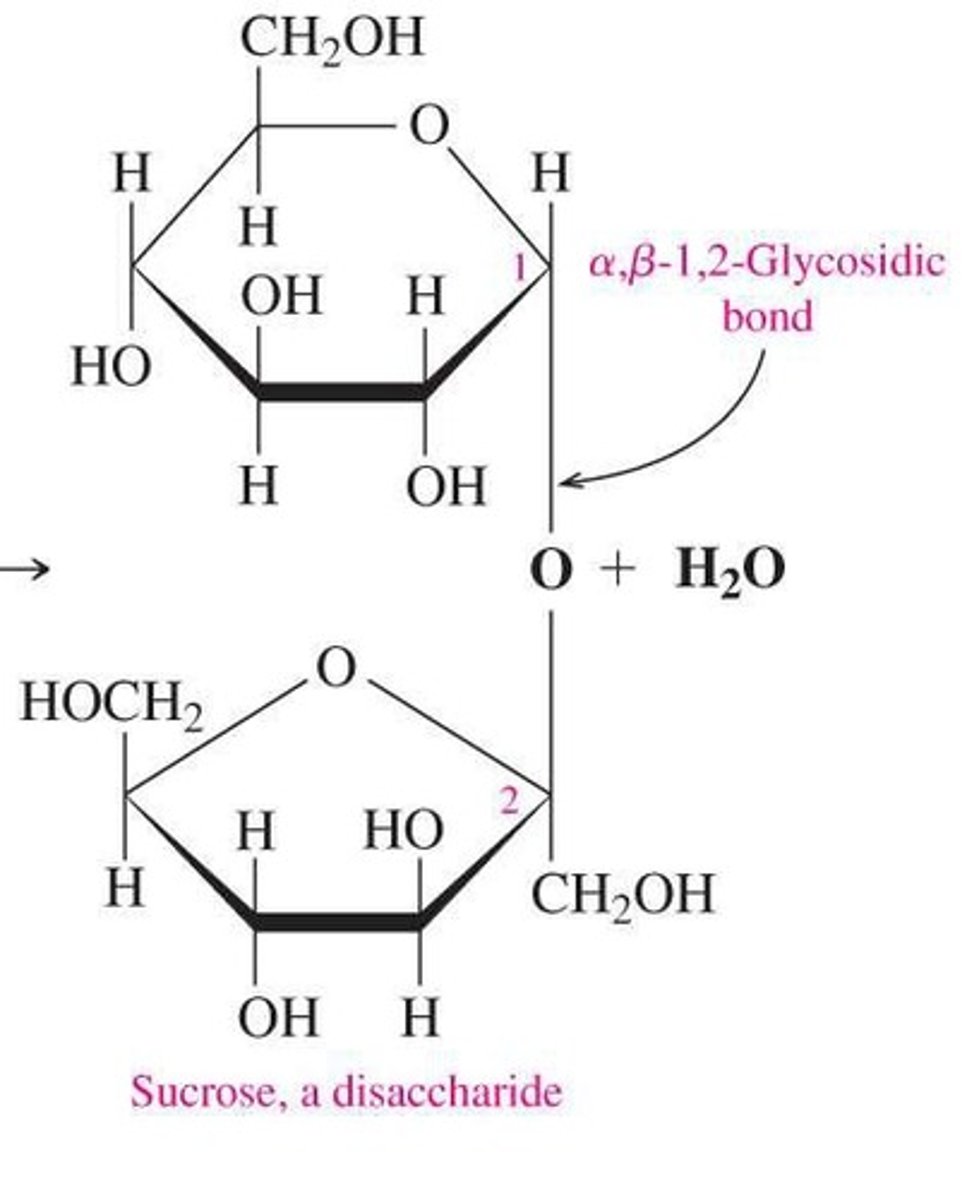
What enzyme hydrolyzes sucrose in the body?
Sucrase.
What is the sweetness of sucralose compared to sucrose?
Sucralose has a sweetness of 60,000, while sucrose has a sweetness of 100.
Which disaccharides are considered reducing sugars?
Maltose and lactose.
What are polysaccharides?
Polymers of many monosaccharides.
What is starch primarily used for?
Energy storage in plants.
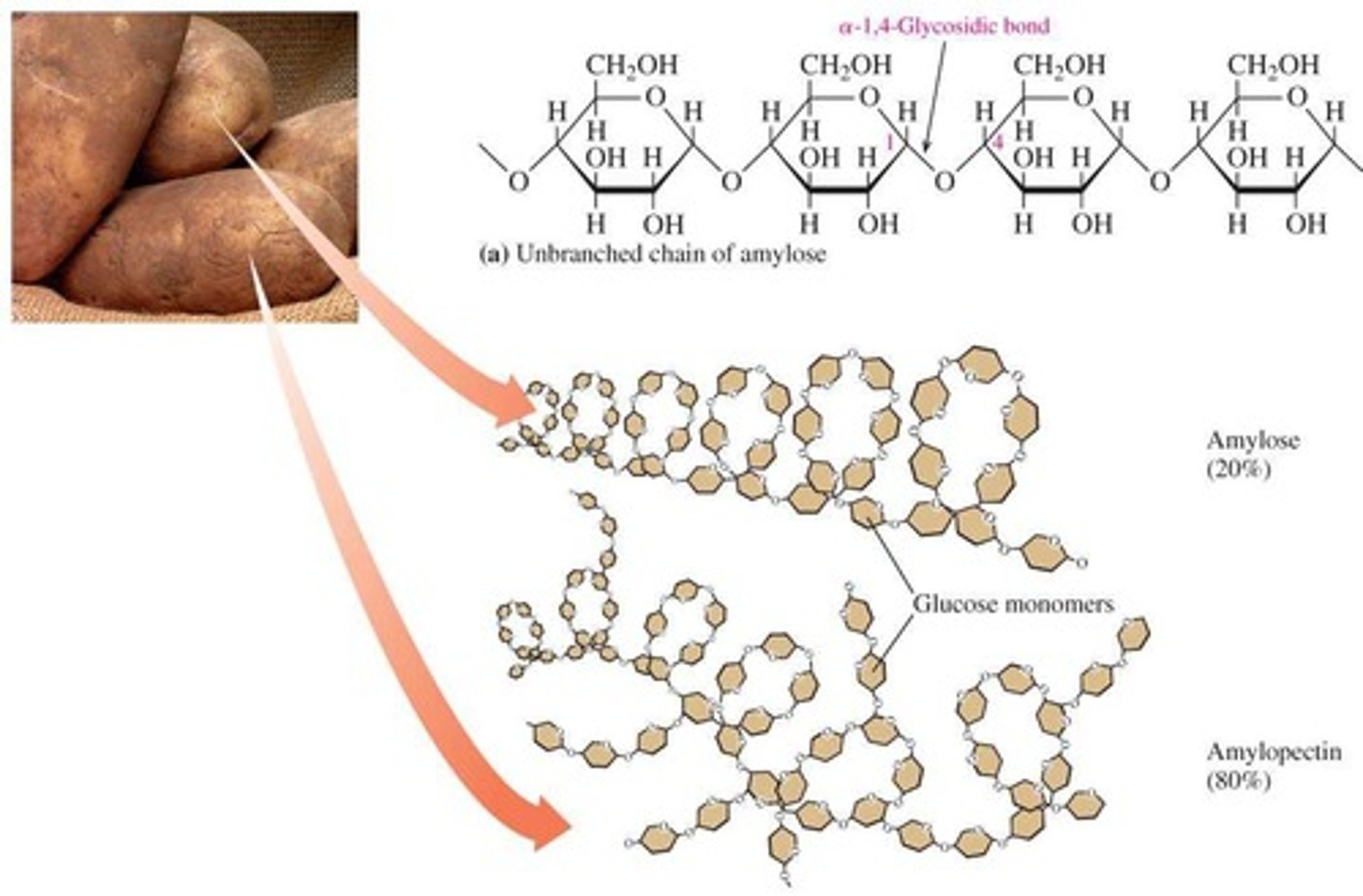
What are the two components of starch?
Amylose and amylopectin.
What type of bonds link glucose residues in amylose?
α-1,4 glycosidic bonds.
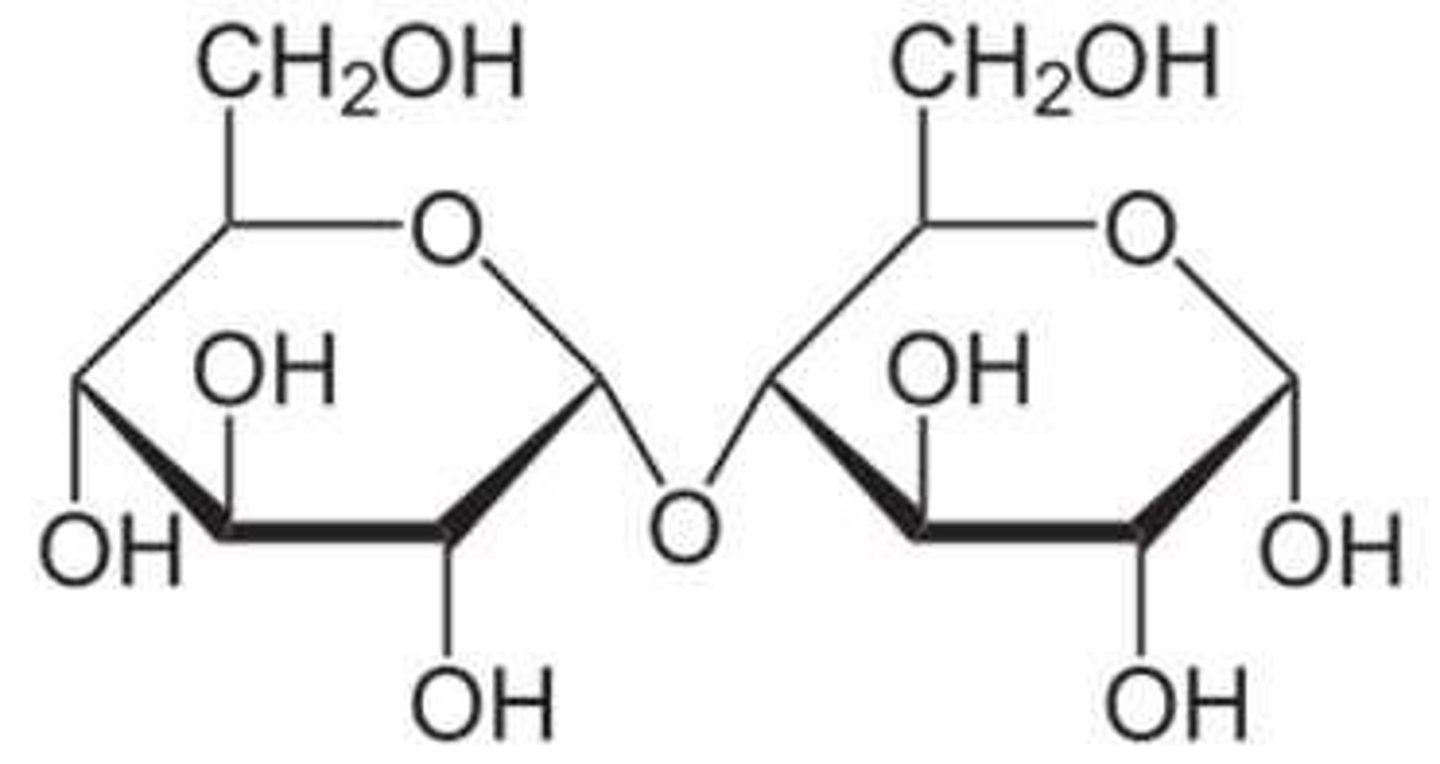
What distinguishes amylopectin from amylose?
Amylopectin is branched, while amylose is unbranched.
What enzyme digests starch into maltose?
Amylase.
What is glycogen and its primary function?
A branched homopolysaccharide of α-D-glucose, functioning as energy storage in animals.
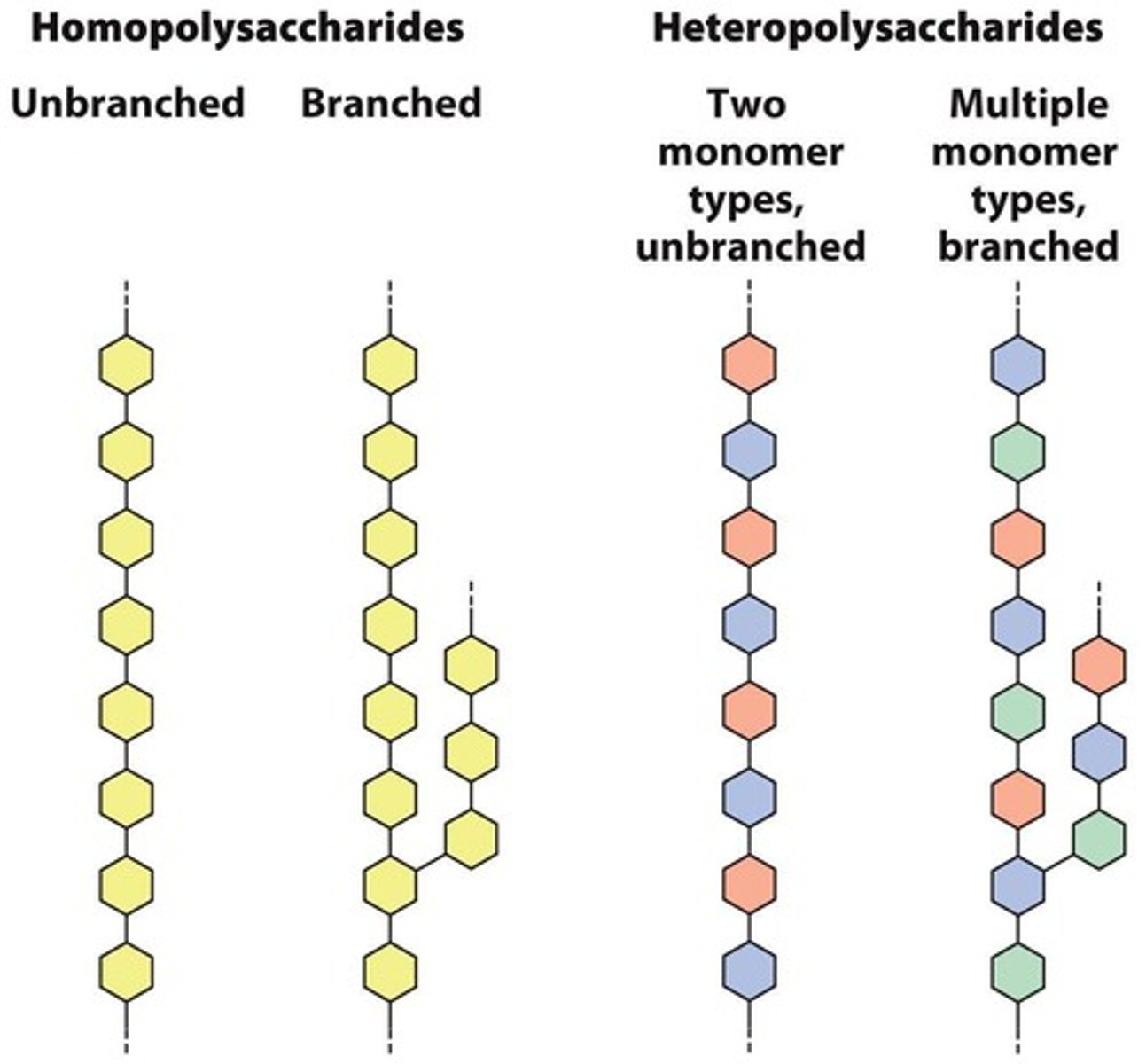
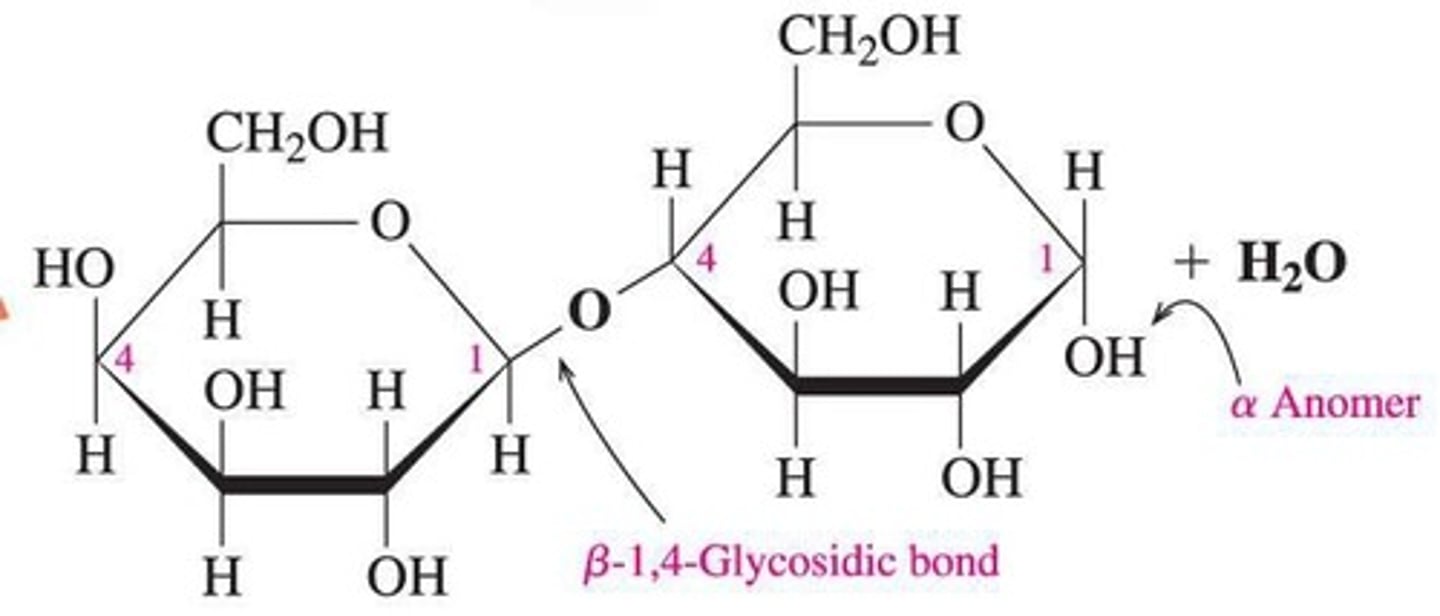
What is cellulose and why can't humans digest it?
A linear unbranched homopolysaccharide of glucose; humans lack cellulase to break β-1,4 glycosidic bonds.
What is chitin and where is it found?
A linear homopolysaccharide of N-acetylglucosamine found in cell walls of mushrooms and exoskeletons of arthropods.
What are oligosaccharides?
Short chains of different monosaccharide residues that can be attached to proteins or lipids on cell surfaces.
How do oligosaccharides function in vertebrates?
They determine blood groups by their carbohydrate composition.