Psychology - Motivation and Wellbeing
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Sources of motivation
Physiological, Cognitions, Emotions, Social
However these can overlap, e.g PhysiologicL Needs can trigger emotions
Physiological
The basic biological requirements for survival, such as hunger, and thirst.
Drive us to take action to satisfy them.
e.g when you’re hungry, your body signals you to seek food.
Cognitions
Our thoughts, beliefs, and mental processes significantly influence motivation.
Include our goals, expectations, and, self-perceptions.
When we set goals or anticipate rewards, our cognitive processes influence our behaviour.
Emotions
Powerful motivators. energise and direct our actions
Social Factors
Norms, expectations, relationships, desire for social approval. Can inspire us to cooperate and contribute to collective goals
Self-Determination Theory (Deci & Ryan 1985)
Amotivation, Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivation
A theory of human motivation and personality that concerns people's innate growth tendencies and innate psychological needs. It pertains to the motivation behind people's choices
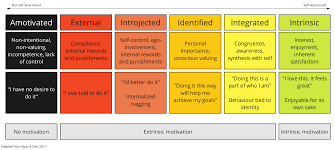
Amotivation
lack of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. People who don’t attempt a behaviour at all, or if they are in a situation that requires a behavior, they do so without any personal intent.
Extrinsic
Stems from external rewards.
Respect of other people, social recogitiom
Intrinsic
Stems from an inner desire for self satisfaction, arising from a specific goal.
e.g reading a book because you like it vs if you were told to read it
External Regulation
Compliance, based on external rewards and punishment
Introjected Regulation
taking in a regulation but not fully accepting it as one’s own
e.g when people are motivated to demonstrate ability
Identified Regulation
a more autonomous, or self-determined, form of extrinsic motivation. conscious valuing of a behavioural goal or regulation, accepted or owned as personally important
Integrated Regulation
when action or goal have been evaluated and brought into congruence with one’s other values and needs
Intrinsic Regulation
Internal drives that inspire us to behave in certain ways, including our core values, interests and our personal sense of morality
Self Determination by Ryan
Autonomy, Competence and Relatedness
Autonomy
The need for people to feel in control of their actions
Improves wellbeing and increased motivation
Competence
The desire to feel capable of mastering new skills and experiencing a sense of achievement
Increases the likelihood someone will feel satisfaction from overcoming obstacles and engaging in their pursuits
Relatedness
People have a desire to form social connections and be a part of positive relationships with others
Contributes to wellbeing
Strengths of Theory (Deci & Ryan)
Applicable to many cultures
Used in many domains
Widely considered an excellent model to explain motivation
Limitations of the Theory
Does not account for social and cultural factors that may influence motivation and behavior
A complex theory to apply'
The emphasis on autonomy minimises the influence of external rewards
Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow 1954, 1970)
The theory believes that each person is motivated by the need to fulfil unmet needs. Lower level needs must be met for higher needs to be fulfilled.
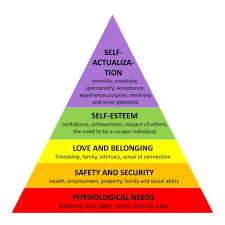
Physiological Needs
biological requirements for human survival. If these needs are not satisfied the human body cannot function optimally
e.g air, food, shelter, sex
Safety Needs
Protection from elements, security, order, law, freedom from fear
Physical - stability, order, limits
Emotional - free from chaos, threats, fear
Love and Belongingness Needs
Social; and feelings of belongingness.
Receiving love - deeming oneself worthy of being loved accepted and having a place within a group
Giving love - having love and affection towards others
e.g friendships, intimacy, trust
Esteem Needs
Self-esteem - the desire for achievement, confidence when challenged, experiences of freedom and independence.
Respect from others - receiving recognition, attention, and appreciation from other people including reputation.
Self Actualisation
Realizing personal potential, self-fulfilment, seeking personal growth and peak experience.
Deficiency Needs
Are concerned with basic survival including physiological needs and safety needs. Motivation to fulfil such needs will get stronger the longer they are denied
Growth Needs
Psychological and are associated with realising an individuals full potential and needing to self-actualize
Cognitive Needs
Mental process of gaining knowledge and understanding through the senses, personal experiences and mental activity.
Gain knowledge, curiosity
Aesthetic Needs
Aesthetic beauty as well as the appreciation of anything beautiful
Transcendence
Experience of going beyond the limitation of a physical human experience,
Strengths of Maslow
Focused on the positive aspects of human nature
Simple and understandable
Universal relevance - to understand and motivate people
Limitations of Maslow
Need to complete them in order
No proof a person has met Transcendence
Sample bias
Subjective Data Set
Subjective Well-being (Diener 1984)
people’s cognitive and affective evaluations of their lives
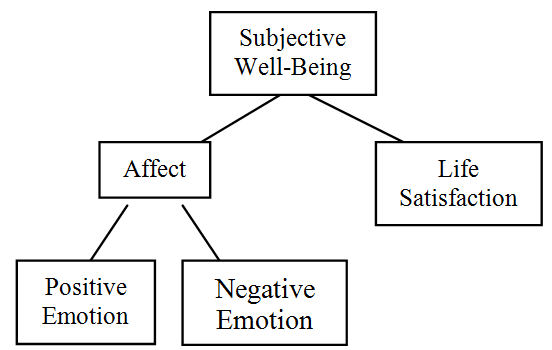
Life Satisfaction
Overall assessment a person makes of their life and their life experiences, these global judgements of one’s life makes up the cognitive measure of wellbeing
Affective balance
the experience and outward expression of emotion of emotion.
POSITIVE affect - pleasant emotions such as happiness, excitement, joy and contentment
NEGATIVE affect - distressing emotions such as anger and sadness
Limitations of Diener
Mainly focuses on emotion and personal experiences of the individual, while external factors also affect wellbeing they are not considered in this model
Wellbeing
How people feel and function both on a personal and social level, and how they evaluate their lives
Six Factor Model of Wellbeing - Ryff (1989)
Autonomy, Environmental Mastery, Personal Growth, Positive Relations with Others, Purpose in Life, Self-Acceptance
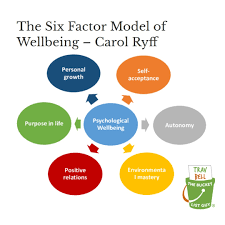
Autonomy Ryff
Having a sense of independence and self-determination, ability to make decisons that align with our values and desires, resist social pressures
Environmental Mastery
Ability to adapt to and effectively manage the external world. Setting and achieving goals
Personal Growth
Importance of embracing new experiences seeking knowledge and pursuing personal development
Positive Relations with Others
Healthy social connections play a vital role in our well-being, emphasis is on the importance of having meaningful relationships
Purpose in Life
Setting meaningful goals, finding a sense of meaning and significance in our actions
Self-Acceptance
Having a positive attitude towards oneself, embracing both strengths and weaknesses.
Healthy self image.