Mitosis, Chromatin Structure, and Cancer: Cell Cycle and Apoptosis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the basic structural components of a eukaryotic chromosome?
Chromatid, centromere, sister chromatid, and daughter chromosomes.
How is DNA packed into a mitotic chromosome?
DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which further compact into chromatin, aided by condensins and cohesins.
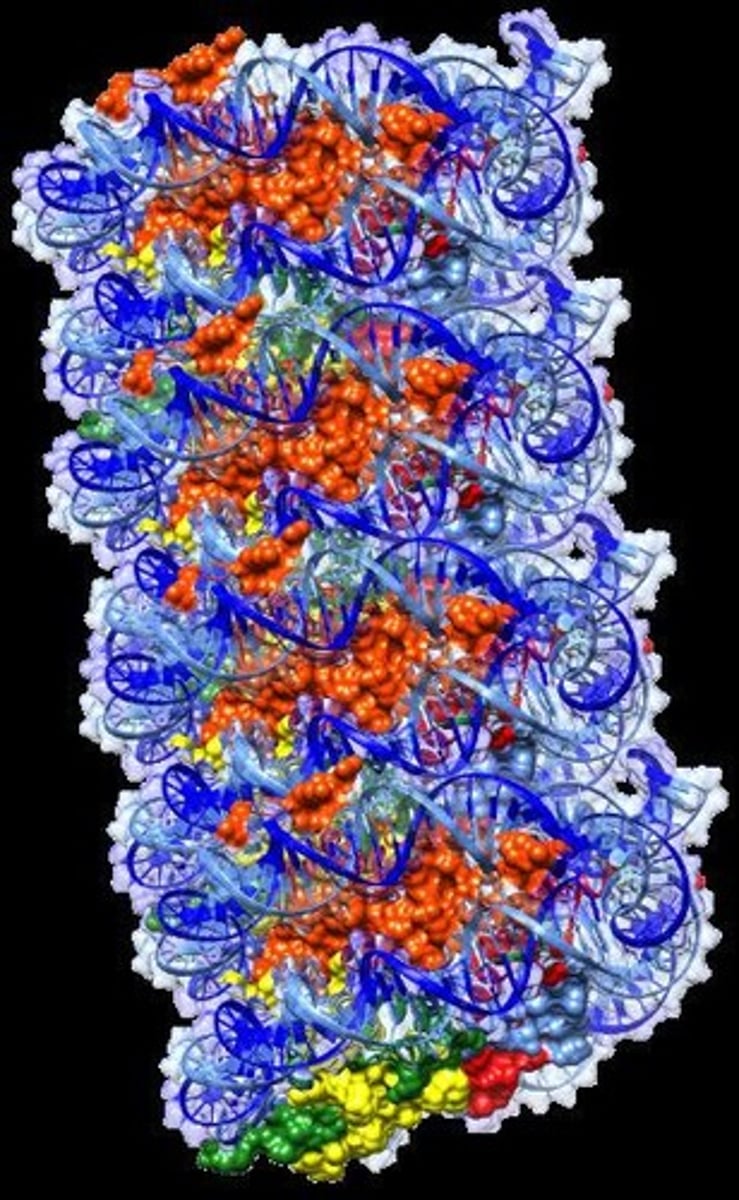
What is the difference between chromosomes in G1 and G2 phases?
In G1, chromosomes consist of a single chromatid; in G2, they consist of two sister chromatids attached at the centromere.
What types of interactions facilitate histone-DNA association in a nucleosome?
Hydrogen bonds, nonpolar interactions, ionic bonds, and structural grooves in DNA and histones.
What are the phases of mitosis?
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What is the function of the spindle apparatus during mitosis?
To move sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell.
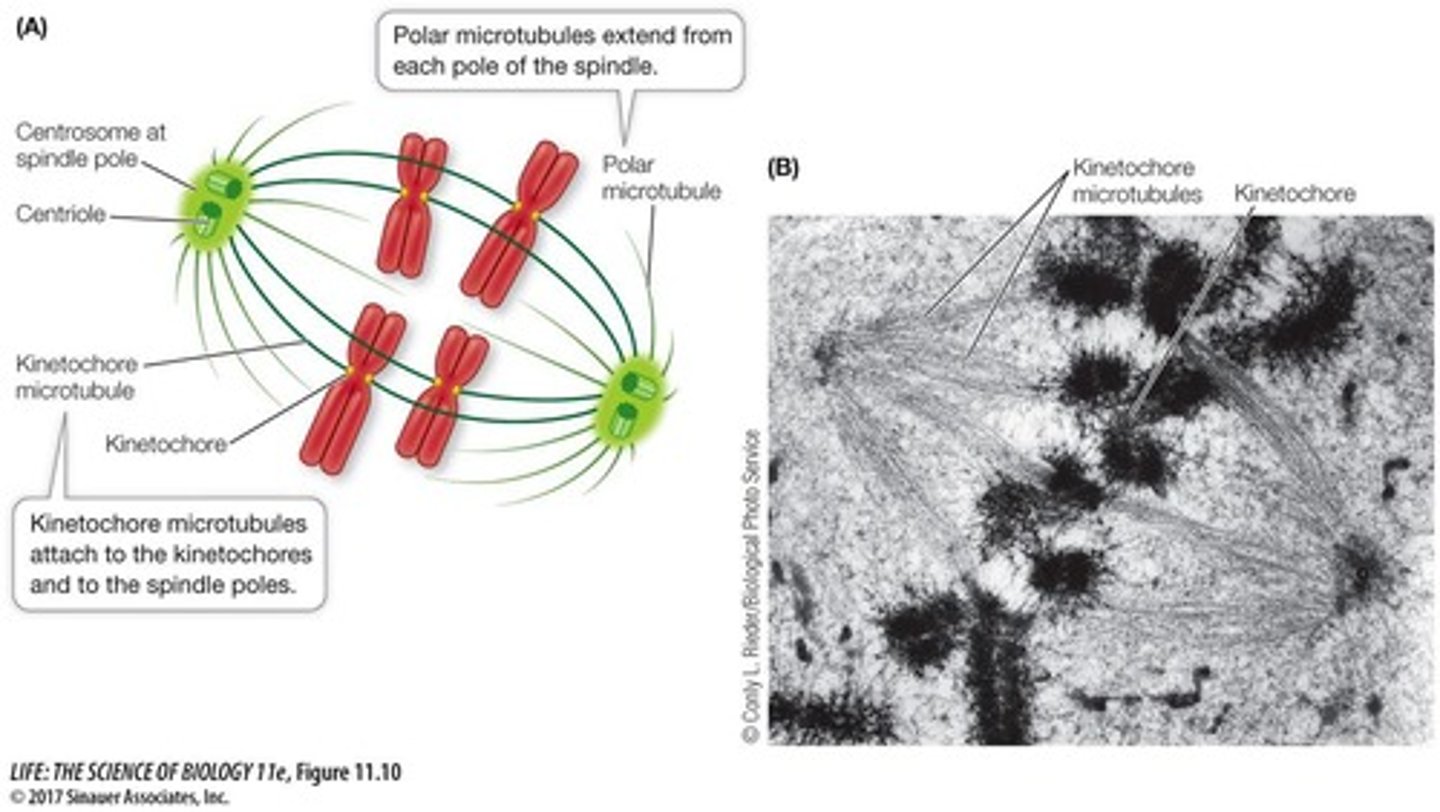
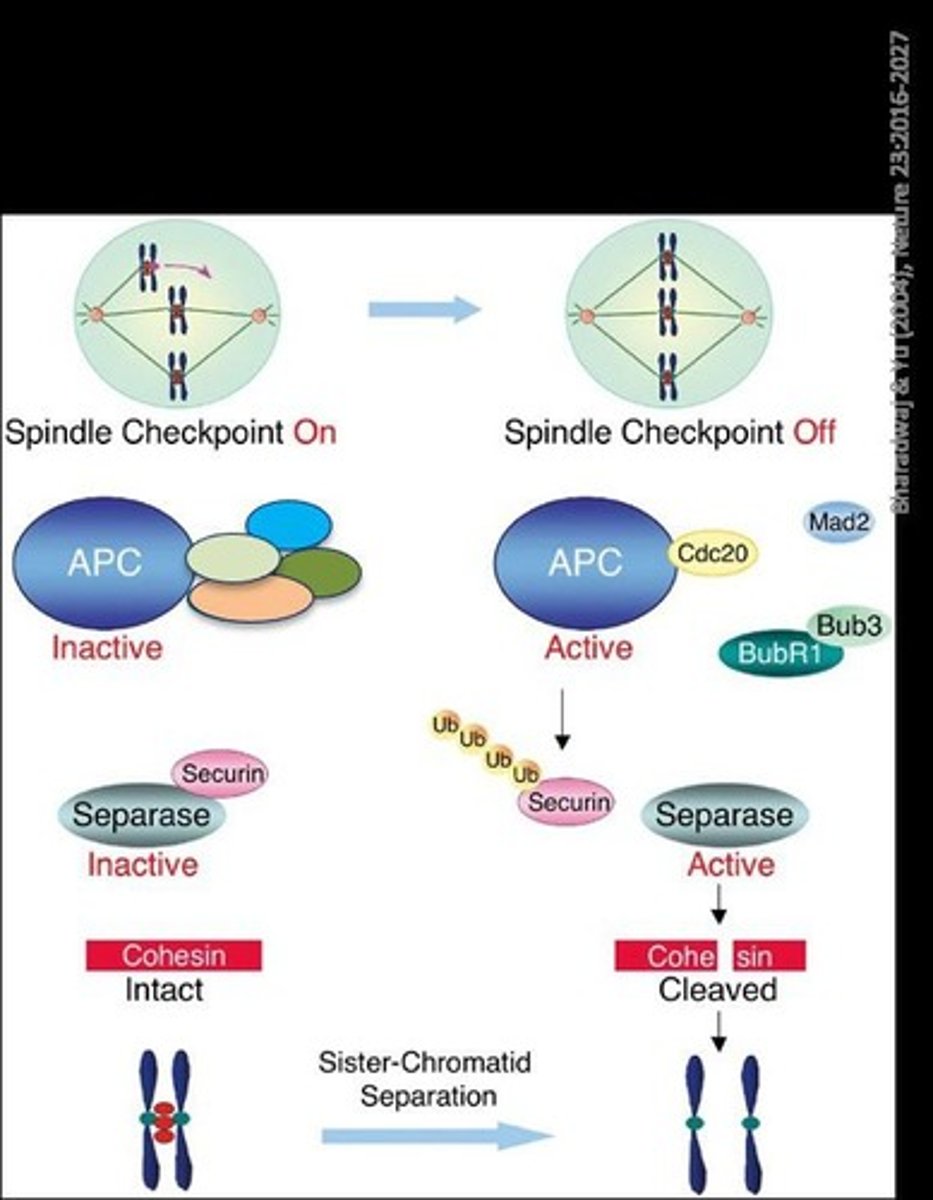
What role do cohesins play in mitosis?
Cohesins hold sister chromatids together until anaphase.
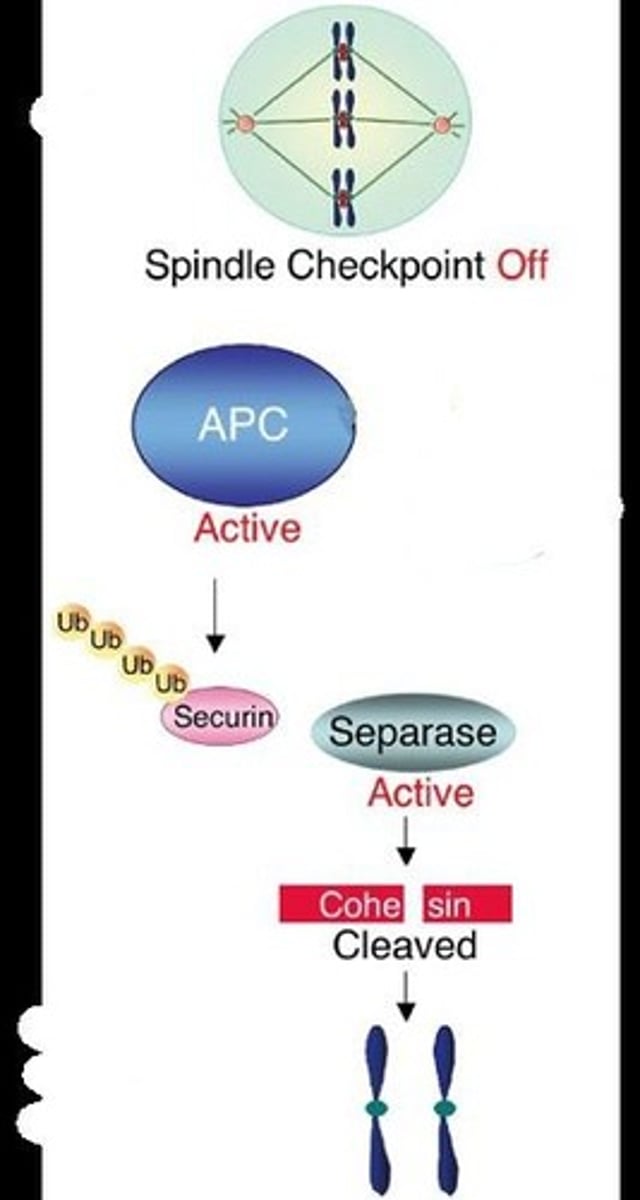
What is the function of the anaphase promoting complex (APC)?
APC activates separase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of cohesins, allowing sister chromatids to separate.
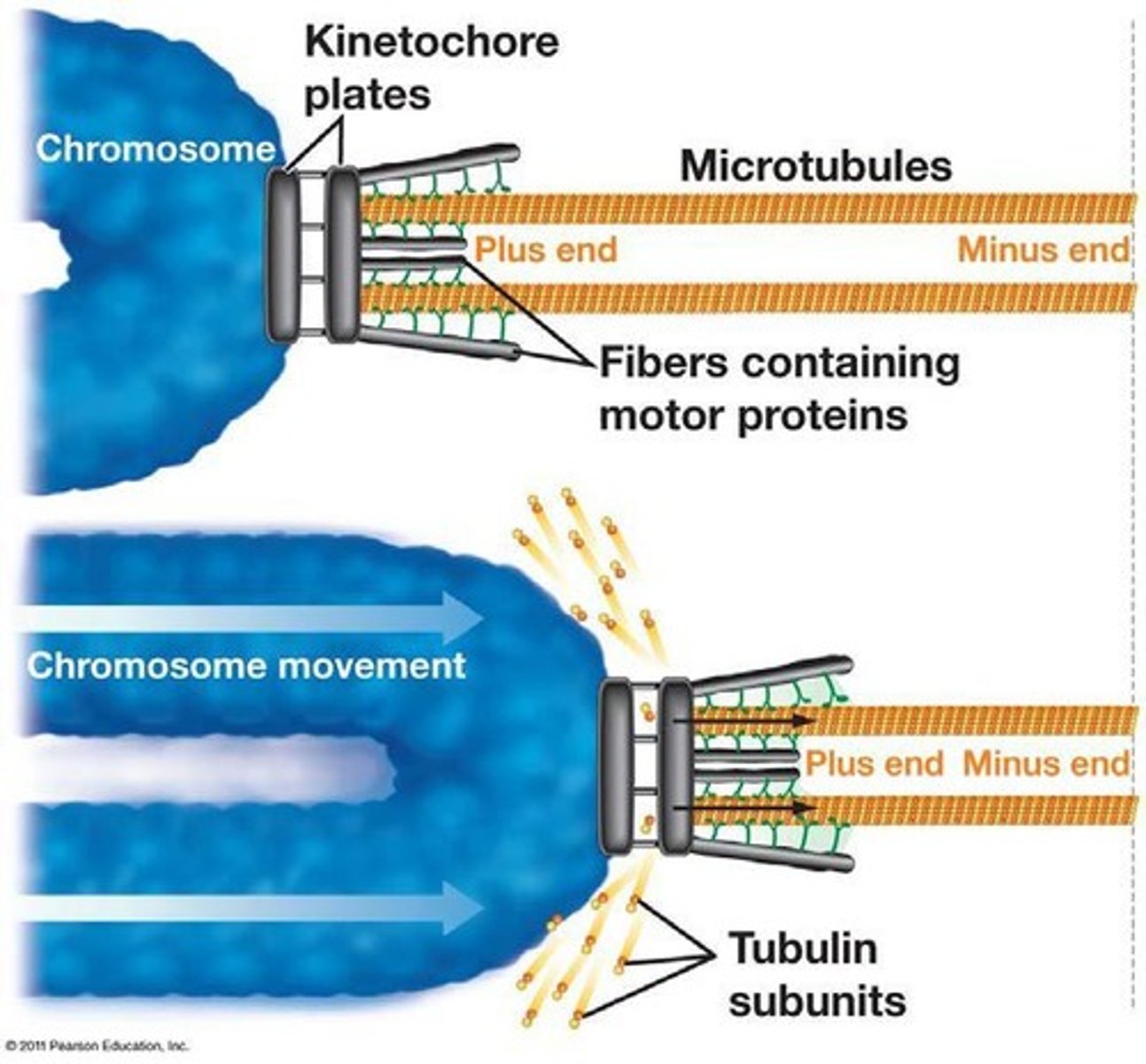
What are the three mechanisms of chromosomal movement during anaphase?
Motor proteins move chromosomes along microtubules, kinetochore microtubules shorten, and centrosomes move apart.
What is the difference between necrosis and apoptosis?
Necrosis is uncontrolled cell death due to damage, while apoptosis is programmed cell death that is a normal part of development.
What is the significance of cell blebbing in apoptosis?
Cell blebbing is a characteristic feature of apoptosis, indicating the breakdown of the cell membrane and cellular components.
What are oncogenes and how do they relate to cancer?
Oncogenes are mutated positive regulators that promote uncontrolled cell division in cancer cells.
What is the role of tumor suppressor genes in cancer?
Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cell division; mutations in these genes can lead to cancer.
What distinguishes benign tumors from malignant tumors?
Benign tumors resemble normal tissue and grow slowly, while malignant tumors are morphologically distinct and can metastasize.
What is metastasis?
The spread of malignant cells to other locations in the body via the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
What are the current cancer treatments and how do they differ?
Chemotherapy uses drugs to target cellular processes, while radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to induce DNA damage leading to apoptosis.
What is the role of caspases in apoptosis?
Caspases hydrolyze nuclear proteins, nucleosomes, and cytoskeletal components, leading to the morphological changes associated with apoptosis.
What is the significance of the spindle assembly checkpoint?
It ensures that all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle apparatus before anaphase begins.
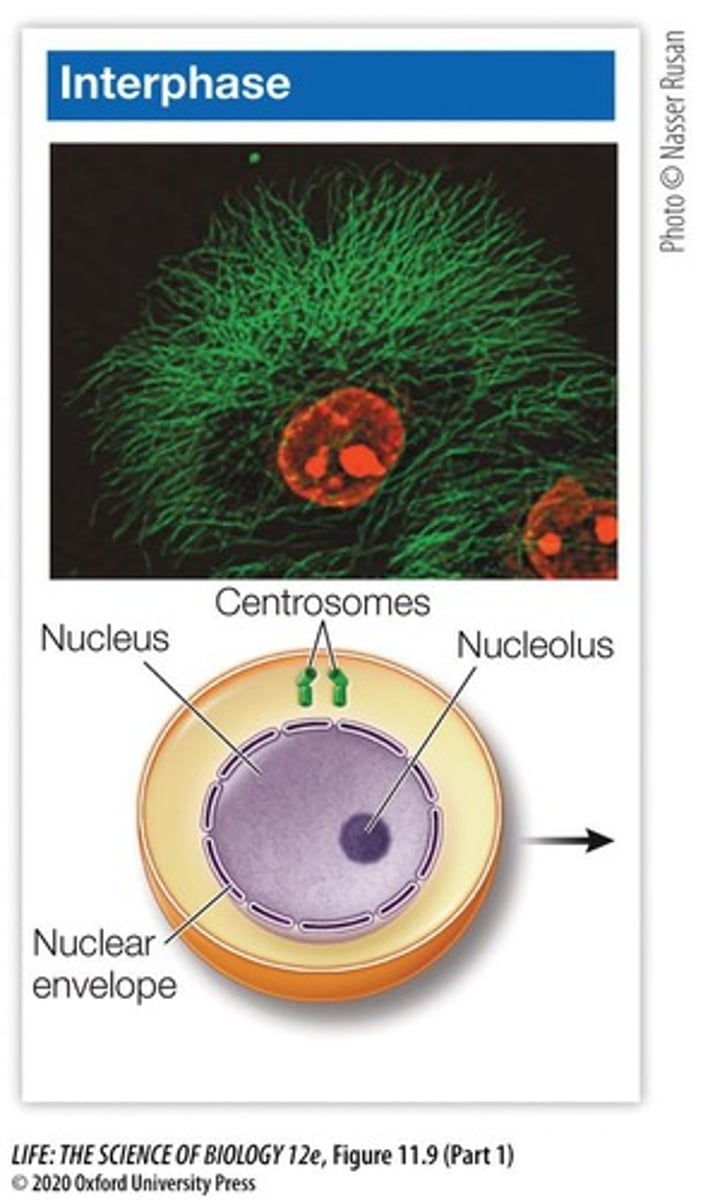
What happens to the nuclear envelope during mitosis?
The nuclear envelope breaks down during prophase and re-forms during telophase.
How does chromatin change during the cell cycle?
Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes during mitosis and is dispersed throughout the nucleus during interphase.
What is the function of motor proteins in chromosomal movement?
Motor proteins (kinesins and dyneins) facilitate the movement of chromosomes along microtubules during mitosis.
What is the role of centrosomes in mitosis?
Centrosomes organize microtubules and help position the spindle apparatus during cell division.
What occurs during telophase?
Daughter chromosomes reach the poles, the spindle disintegrates, and the nuclear envelope reforms.